APP1 - Biological Bases of Behaviour, Part B: The Brain & Sleep
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Phrenology
A pseudoscience in the 19th century that proposed the shape of a person's skull, including bumps and indentations, indicated their personality, mental faculties, and character.
Biological Psychology
The scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychology logical processes
Neuroplasticity
The brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
Lesion
Tissue destructions. Brain lesions may occur naturally (from disease/trauma), during surgery or experimentally (using electrodes to destroy brain cells)
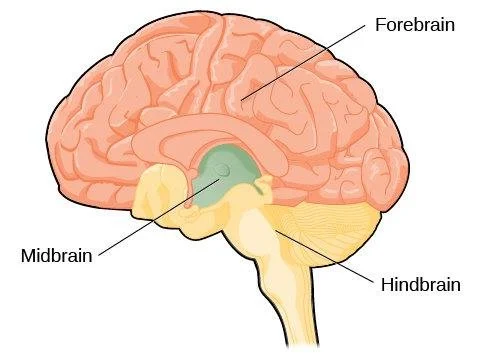
Hindbrain
Consists of the ,medula, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions, such as breathing, sleeping and wakefulness as well as coordination
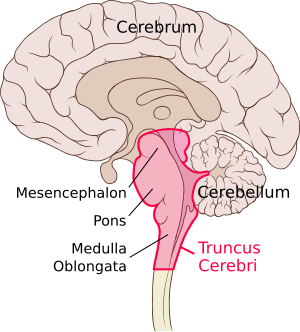
Midbrain
Found a top the brain stem; connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movement and transmits its auditory and visual information
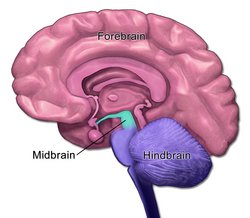
Forebrain
Consists of the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions and voluntary motor activities
Brainstem
The central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
Which structures make up the brainstem?
Medulla: The hindbrain structure that is the brainstems base; controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons: Helps coordinate movement and control sleep
Thalamus
The forebrains sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum
Reticular Formation/Reticular Activating System (RAS)
A nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; it filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal
Cerebellum
The hind-brains “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning/memory
Limbic System
Neural system located mostly in the forebrains and processes drives, smells and various emotional responses
Limbic system’s structures
Amygdala: Two lima-bean sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
Hypothalamus: A limbic system neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several
Hippocampus: A neural center in the limbic system that helps process explicit (conscious) memories —of facts and events — for storage
Cerebral Cortex/Cerebrum
Ultimate control and information processing
What four lobes make up the Cerebral Cortex?
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Frontal Lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead. They enable linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher-order thinking and executive functioning
Parietal Lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; it receives sensory input for touch and body position
Occipital Lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; it includes areas that receive information from the visual fields
Temporal Lobes
Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; it includes the auditory areas, each of which receives information primarily from the opposite ears.
Motor Cortex
A cerebral cortex area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
Somatosensory Cortex
A cerebral cortex area at the front of the partial lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
Neurogenesis
The process of forming new neurons
Lateralization
The specialization of functions in different hemispheres of the brain. It describes the tendency for certain cognitive processes and abilities to be more dominant in one hemisphere than the other.
Corpus Callosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two Brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
Split Brain
A condition resulting from surgery that separates the brains two hemispheres by cutting the fibers connecting them
Consciousness
The states of being aware of and able to perceive one’s thoughts, feelings, sensations and surroundings
States of consciousness
Daydreaming, sleeping, drug-induced hallucinating, meditating and hypnosis
Cognitive Neuroscience
The interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating)
Dual processing
The principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
High Road: A conscious deliberate
Low Road: An unconscious automatic
Blindsight
A condition which as person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing
Parallel processing
Processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
Sequential Processing
Processing one aspect of a stimulus or problem at a time; generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems