ECG Interpretation in Ischemic Heart Disease
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
myocardial ischemia v. infarction
-ischemia: occurs when the oxygen supplied by the coronary arteries does not meet the metabolic demands of the heart muscle, most commonly caused by a blockage of a coronary artery caused by atherosclerotic plaque; can also occur when there is an oxygen supply-demand mismatch that is not caused by obstructive plaque
-infarction: cell necrosis that occurs from prolonged/severe ischemia; can be subendocardial (limited to the innermost layers of the myocardium) or transmural (the entire thickness of the myocardium)
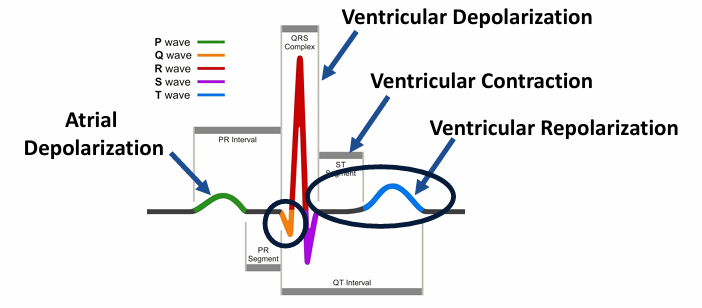
ECG wave form
-ventricular repolarization is very sensitive to myocardial perfusion
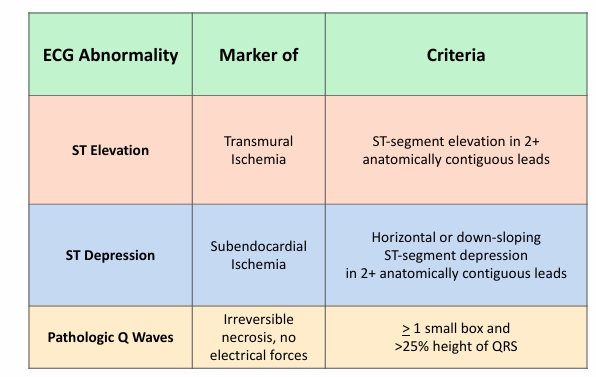
-ischemia and infarction can be detected by ST-segment and T wave changes, or in the case of irreversible myocardial necrosis, pathologic Q waves
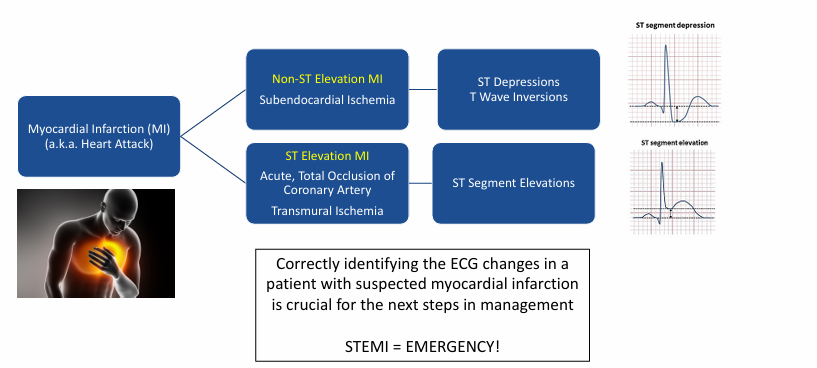
NSTEMI v STEMI
ST elevation, depression, and Q waves
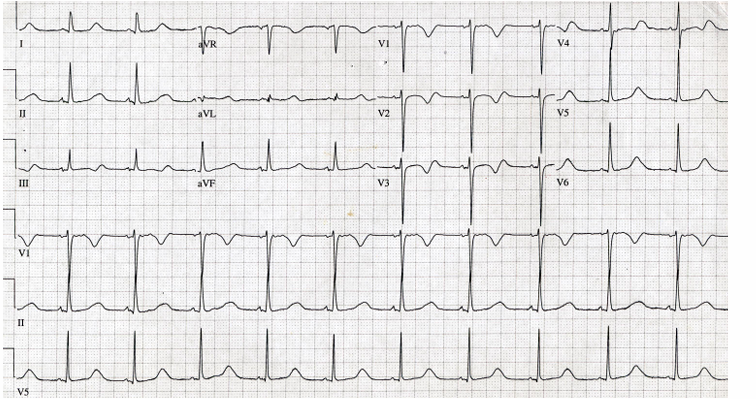
-non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
non-atherosclerotic causes of NSTEMI (type-2 NSTEMI)
-ischemia that is not related to an unstable coronary plaque
-arrhythmia/tachycardia
-hypoxia
-sepsis
-heart failure/cardiomyopathy
-pulmonary embolism
-post-operative
-anemia
-hypertension/hypotension
-severe aortic stenosis
-stroke/neurologic
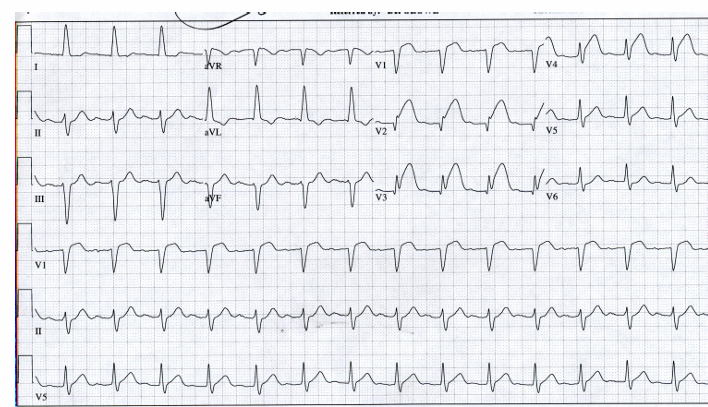
-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
non-atherosclerotic causes of STEMI
-spontaneous coronary artery dissection (tear of the coronary artery)
-coronary vasospasm (sudden constriction of the artery)
-embolism to the coronary artery (blood clot ejected and lodges in coronary artery)
-takotsubo cardiomyopathy (stress cardiomyopathy- heart failure caused by sudden/extreme stress)
-vasculitis (takayasu arteritis or Kawasaki disease)
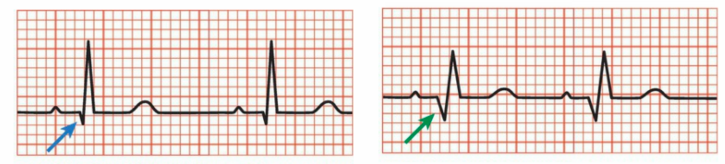
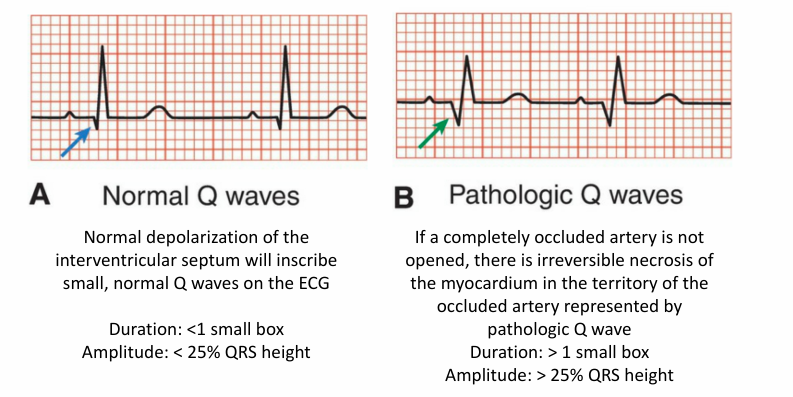
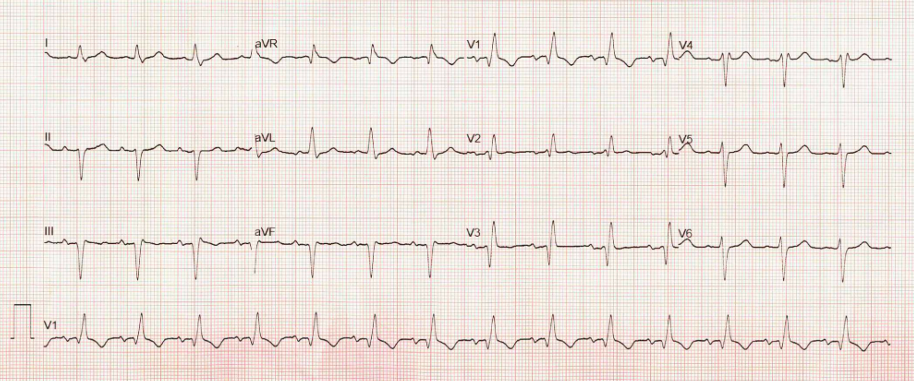
-old myocardial infarction with pathologic Q waves
evolution of STEMI
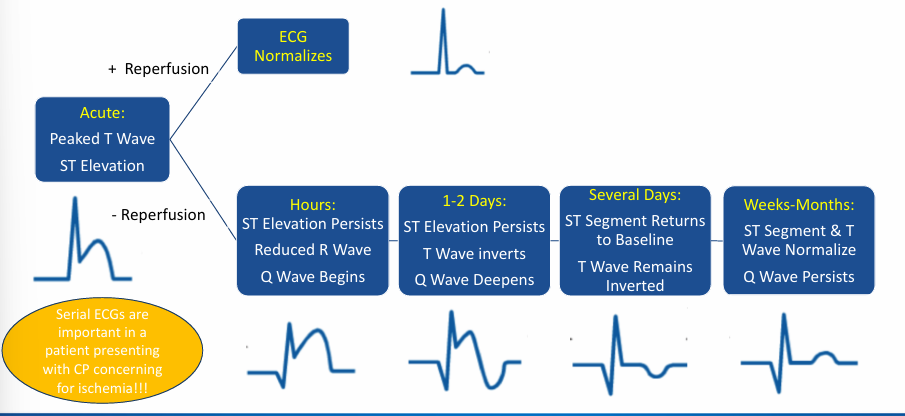
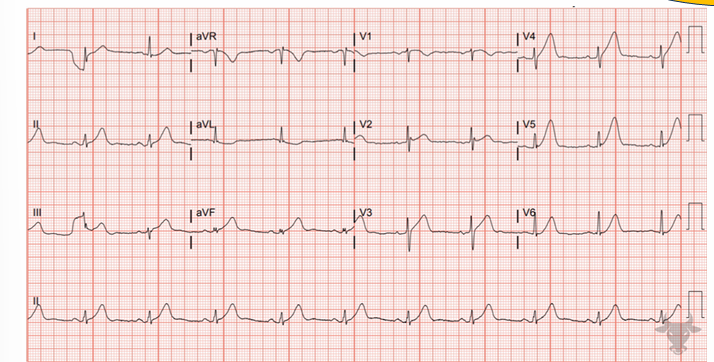
-hyperacute T waves
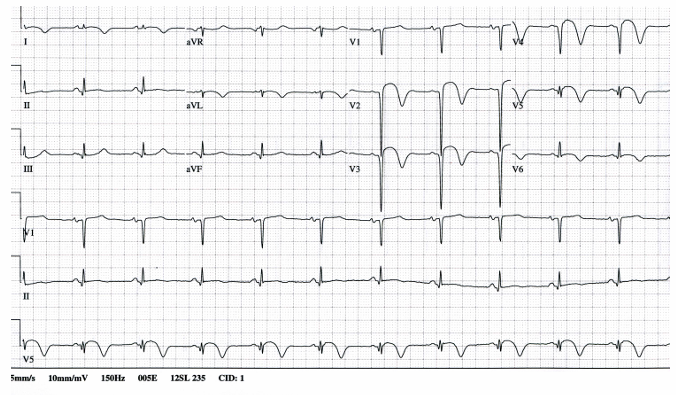
-evolving STEMI
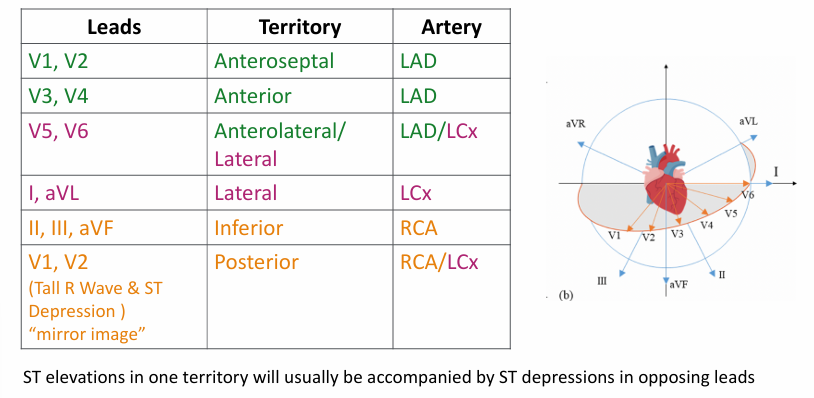
coronary artery distribution
-right coronary artery: perfuses the inferior wall of the left ventricle
-left anterior descending artery: perfuses anterior wall of the left ventricle
-left circumflex artery: perfuses lateral wall of the left ventricle
localization of STEMI- leads, territory, artery
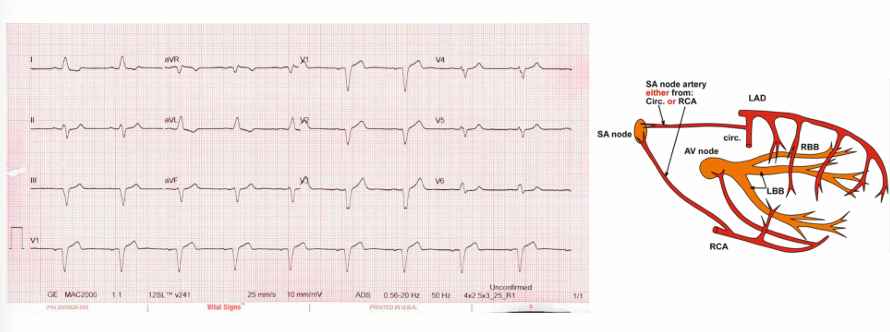
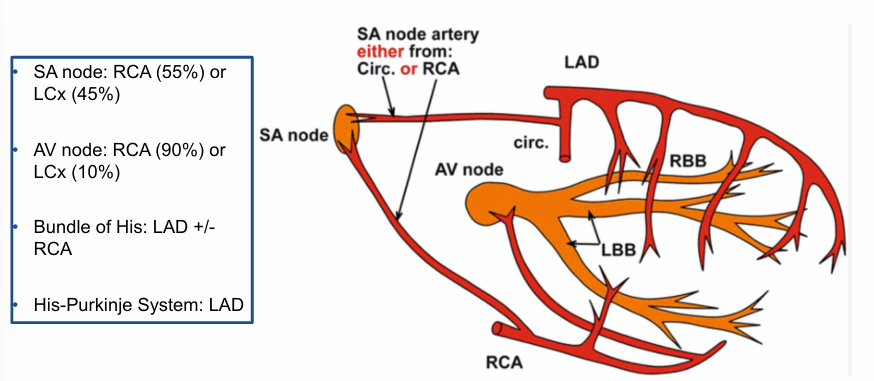
coronary blood supply of the cardiac conduction system
new LBBB + CP
-think STEMI equivalent