Bergsbaken: Chemotherapy-induced Nausea and Vomiting
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Name treatment and patient-related risk factors for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
Younger age
Female
Prior anticancer agents
History of little or no alcohol use
HIstory of morning sickness
History of prone to motion sickness
Anxiety
Name 5 chemotherapy drugs that are considered highly emetogenic at typical doses.
Carboplatin (AUC >24)
An Anthracycline + Cyclophosphamide
Cisplatin
Cyclophosphamide (>1500 mg/m2)
Doxorubicin (>60 mg/m2)
*he won't test on cut offs
In global terms, describe the emetogenic risk of most oral, targeted agents.
Define acute vs delayed N/V, anticipatory N/V, and breakthrough N/V
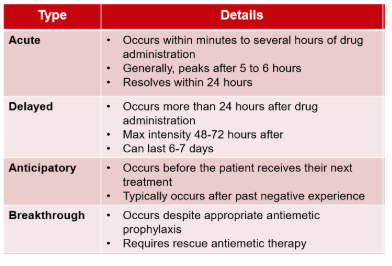
What is the difference between a regimen that is considered highly-emetogenic vs moderately emetogenic?
Go with whatever the highest risk drug is
What four drugs or drug classes are employed in current prophylaxis regimens for nausea & vomiting for high-emetic risk chemotherapy.
What is the maximum daily dose of ondansetron? How about the max single IV dose of ondansetron?
Max daily dose = 24 mg
Max single IV dose = 16 mg
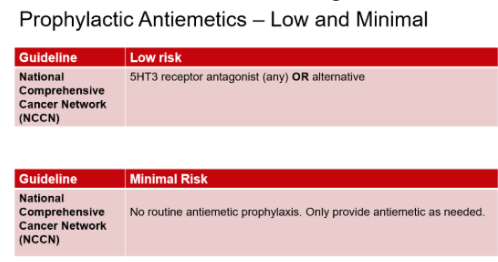
What antiemetic prophylaxis regimen is typical for patients receiving chemotherapy with Minimal risk for nausea & vomiting? Low risk for nausea & vomiting?
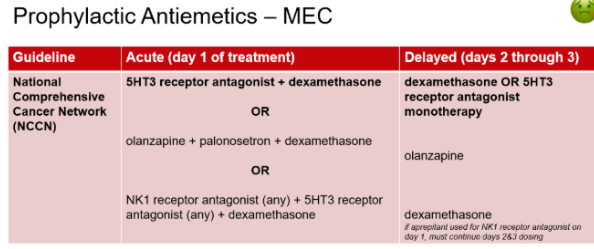
What antiemetic prophylaxis regimen is typical for patients receiving chemotherapy with Moderate risk for nausea & vomiting?
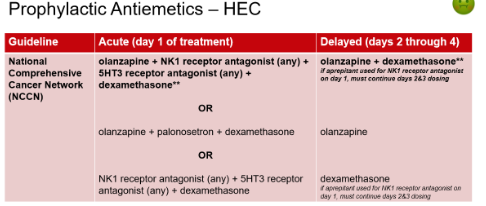
What antiemetic prophylaxis regimen is typical for patients receiving chemotherapy with High risk for nausea & vomiting?
4 drug regimen!!
acute (day 1)
Olanzapine
NK1 antagonists **
5HT3 R-antagonists
Dexamethasone
delayed (days 2-4)
olanzapine
dexamethasone
**If aprepitant PO is used in the acute stage, must continue days 2+3 dosing
How should patients experiencing breakthrough nausea & vomiting be treated?
Ondansetron or prochlorperazine
Add one drug in a different class and continue standard antiemtic regimen
Olanzapine
Dronabinol
halo/metclo/scopola
prochlorperazine/promethazine
5HT3 antag
Dexamethasone
Lorazepam(anticipatory only)
How long should CINV prophylaxis continue for patients receiving regimens that are:
Only listed the NCCN preferred options, there are other treatment options
Moderately emetogenic
3 days
Day 1 (2 drug regimen): 5HT3 RA + dexamethasone
Days 2-3: dexamethasone OR 5HT3 RA monotherapy
Highly emetogenic
4 days
Day 1 (4 drug regimen): Olanzapine + NK1 RA + 5-HT3 RA + Dexamethasone
Day 2-4:
Olanzapine + Dexamethasone +/- Aprepitant on days 2 & 3 IF NK1-RA used on day 1
What are the major differences in the pharmacology and routes of administration of the HT3R antagonists?
Ondansetron (1st generation)
Very effective for preventing acute CINV, but less for delayed CINV
PO,IV
Granisetron (1st generation)
Very effective for preventing acute CINV, but less for delayed CINV
PO, transdermal patch, IV, SQ
Palonosetron (2nd generation)
IV administration or PO in combination w/ netupitant
40 hour half-life
Effective for preventing acute and delayed CINV
Which one of the HT3R antagonists is least likely to cause prolongation of the QTc interval?
Palonosetron
What is the most common GI adverse effect of the HT3R antagonists?
Ondansetron
Common: Headache and constipation
Rare: QT prolongation & serotonin syndrome
Granisetron
Common: constipation & headache (less extend than ondansetron), Injection site reaction
Rare: serotonin syndrome & QT prolongation (not associated with patch or SQ inj)
Palonsetron
Side effects are uncommon
Rare: serotonin syndrome
How do the doses of ondansetron differ for prophylaxis of patients receiving minimal/low, moderate, vs highly-emetogenic chemotherapy regimens?
Minimal / low
No routine prophylaxis recommended for minimal risk
Ondansetron 8-16 mg PO once for low risk
Moderate
Ondansetron 16-24 mg PO once or 8-16 IV once
Highly-emetogenic
Ondansetron 16-24 mg PO once or 8-16 IV once
What are the different formulations of the NK-1R antagonists, and how do their adverse effects differ?
Aprepitant
PO (3 day course), IV emulsion (once)
Common SE: fatigue
Fosaprepitant
IV (once)
Common AE: injection site reaction
What drug interactions are expected with NK-1 R antagonists?
CYP3A4, CYP2C9
Fosaprepitant- infusion reactions
Design a prophylactic regimen for each CINV risk category (i.e., minimal, low, MEC, HEC).
Minimal
No routine prophylaxis
Low
Day 1: Dexamethasone OR metoclopramide OR prochlorperazine OR 5-HT3-RA
MEC
Day 1 (2 drug regimen): 5HT3 RA + dexamethasone
Days 2-3: dexamethasone OR 5HT3 RA monotherapy
HEC
Day 1 (4 drug regimen): Olanzapine + NK1 RA + 5-HT3 RA + Dexamethasone
Day 2-4:
Olanzapine + Dexamethasone +/- Aprepitant on days 2 & 3 IF NK1-RA used on day 1
How do the doses and frequency of dosing of olanzapine for CINV differ from its use as an atypical antipsychotic?
For CINV, olanzapine is typically given at 5–10 mg once daily for 3–4 days per chemotherapy cycle to prevent nausea and vomiting. In contrast, when used as an atypical antipsychotic, olanzapine is prescribed at 5–20 mg once daily for long-term treatment of conditions like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.