BIOL 4431 Exam 3 Part 2: Cardiovascular Functions
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Blood components
Plasma is made with: Blood minus cell, ~50% of whole blood;
has water which is 90% of plasma and >100 diff. solutes;
has proteins mostly from liver and ~8% of plasma weight;
has albumins which is ~60% of plasma proteins, shuttle non-polar mols, maintain blood vol. (osmotic pressure), and act as buffer (bind & release H+)
has other proteins like antibodies & clotting factors
has other substances like nutrients, gasses, wastes, & ions
Serum
Plasma - plasma proteins;
Clotted-spun blood
Platelets
Involved in clotting,
Contact damaged surface & rupture,
Release contents,
Causes additional platelet sticking,
Platelet plug formed
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Biconcave shape (optimizes diffusion),
Contain hemoglobin (O2 carrier)
Leukocytes (WBC): Granulocytes
Inherited immunity (non-specific),
Lobed nuclei,
Neutrophils – stain little,
Eosinophils – stain pink,
Basophils – stain blue
Leukocytes (WBC): Agranulocytes
Acquired immunity (specific),
Less lobed nuclei
Formed element production
Same hematopoietic stem cell differentiates into all,
Different elements have different pathways
Antigen
CHO residue on RBC
Antibody
Recognizes antigen as self vs. non-self
O antigen
everyone has this
A antigen
“A” blood type
B antigen
“B” blood type
O
has A & B antibodies
A
has B antibodies
B
has A antibodies
AB
has no antibodies
Rh factor (D antigen)
are additxnal antigens and most people have it
Atria (atrium)
Receiving chambers from body (systemic) + lungs (pulmonary)
Right atrium blood source
Superior and inferior vena cava (from systemic)
Coronary sinuses (from myocardium)
Left atrium blood sources
Right & left pulmonary veins
Ventricles
Discharging chambers to body (systemic) + lungs (pulmonary)
Right ventricle
Thinner vs. left
Pumps to pulmonary trunk (artery)
Left ventricles
Thicker vs. right
Pumps to aorta (artery)
Pulmonary circuit
From right heart through lungs then returns to left heart
Low pressure (~15 mmHg)
Systemic circuit
From left heart through body then returns to right heart
Higher pressure (~100 mmHg)
Pericardium
Double-walled sac around heart
Within mediastinum (medial thoracic cavity)
Protects & anchors heart
Fibrous pericardium
Dense Connective Superficial tissue layer that helps prevent overfilling
Parietal
Below fibrous with serous (watery) secretions
Visceral
Against heart and serous
Pericardial cavity
B/w visceral & parietal that contains serous fluid, allowing smooth gliding of heart
Cardiac Muscle
Myocardium; Contractile layer of heart; Spiral & circular bundles
Joined by fibrous skeleton that works as one unit (interconnected cells)
Spontaneously depolarizes
Intrinsic rhythm
Intercalated disk
Depolarizes adjacent cells
Cardiac action potential
Plateau phase due to Ca++ entry
Long (250msec)
Endocardium
Smooth endothelial sheet (squamous)
On thin connective tissue layer
Lines chambers
Continuous w/ vessels
Valves
connective tissues reinforced endocardium that prevent backflow
Atrioventricular (AV) Right valve
Tricuspid
Atrioventricular (AV) Left valve
bicuspid (mitral)
Semilunar (SL) Valves
Aortic & pulmonary
Ventricular exits
Chordae tendineae
Anchor valve cusps (flaps) to papillary muscles
Papillary muscles
Small muscles located in the ventricle walls that help prevent the backflow of blood by keeping the atrioventricular valves closed during ventricular contraction.
Stenosis
Incomplete opening
Insufficiency
Incomplete closing
Prolapse
Valve bulges backward
Arteries
Branches from aorta and supply cardiac muscle
Veins
Roughly follow coronary artery paths, which join to form sinuses and empty into R. atrium
Systole
Ventricular contraction
AV valves close & SL valves open
Diastole
Ventricular relaxation
SL valves shut while AV valves open
“Lub”
Vents contract and AVvs close
“Dub”
Vents relax
SLvs close
Blood pressure measurement
Pressure in large arteries
Fluctuates w/ systole & diastole
Blood pressure measurement procedure
Occlude circulation w/ cuff then gradually release pressure
First sound
Systolic pressure (turbulent flow)
Last sound
Diastolic pressure
No sound
laminar flow
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Fastest intrinsic rhythm (pacemakers)
Conduction system
1. Sinoatrial (SA) node
2. Atrial depolarization
3. Atrioventricular (AV) node
4. AV bundle (of His)
5. Rt. & left bundle branches
6. Purkinje fibers
7. Cardiac muscle
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
Electrical picture of heart
Measured w/ skin electrodes
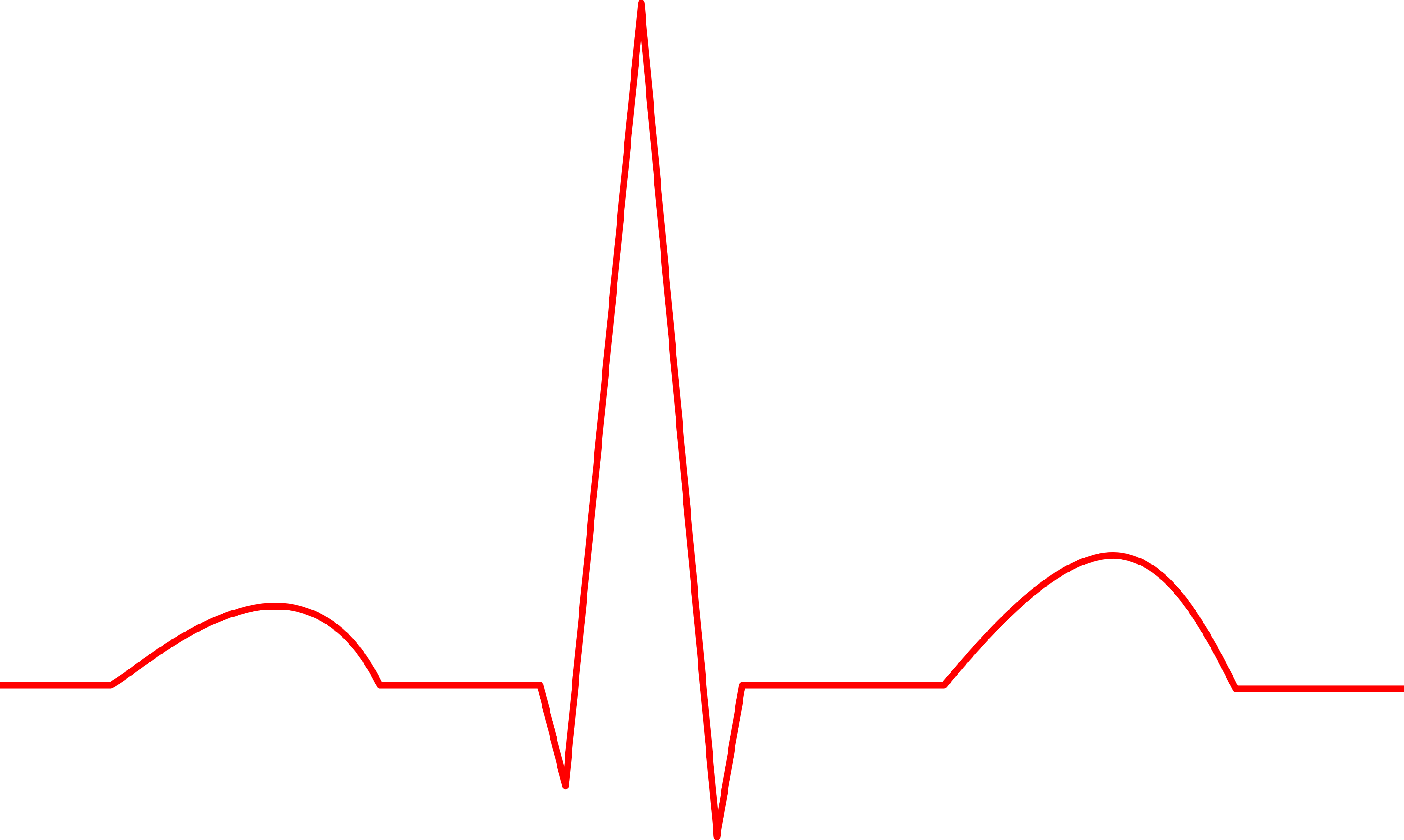
P wave
Atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
T wave
ventricular repolarization
Cardiac pressure cycle: Isovolumetric contraction
Pressure up and AVvs snap shut (lub)
Cardiac pressure cycle: Ventricular pressure exceeds aortic
SL valves open
Cardiac pressure cycle: Ventricles empty
Pressure go up then down; SLvs shut
Cardiac pressure cycle: Isovolumetric relaxation
All valves shut
Cardiac pressure cycle: Atrial exceeds
ventricular pressure
A-V valves open and ventricles fill
Cardiac pressure cycle: Atrial contraction
Ventricles topped off
Cardiac output (CO, ml/min) = Heart rate( HR, beats/min) * Stroke vol (SV, ml/beat)
Heart rate( HR, beats/min) * Stroke vol (SV, ml/beat)
Heart rate control
Rate of spontaneous depolarization and Chronotropic (timing) effect
Sympathetic do what?
inc. HR
inc contractility which inc Ca++ (ionotropic effect) and inc conduction speed through heart
Parasympathetics
dec. HR
End diastolic volume (EDV)
From venous return, preload, and if inc. then SV inc.
Peripheral resistance (PR)
Resistance of arterial vessels, afterload, if inc. then SV dec.
Contractility
Strength of contraction
Frank-Starling law?
if ventricle strength inc → contraction force → then SV inc (graph shifts left to resemble inc)
enhanced by Sympathetic
Ejection fraction
% EDV pumped out of heart (~ 60%)
Preload (EDV) factors
Venous smooth muscle constriction and Skeletal muscle pump
inc. intrathoracic pressure → inc. return
inc. blood volume → inc. return
Cardiac center is where?
In medulla
Cardioacceleratory center is what?
To SA & AV nodes
Sympathetic fibers projected (+ cardiac muscle)
Cardioinhibitory center is what?
Parasympathetic fibers projected
To SA & AV nodes
Arteries - Elastic (conducting)
Largest diameter
mainly elastic tissue
inc pressure fluctuations
“pressure reservoir”
Arteries - Muscular (distributing)
Smaller diameter
mainly smooth muscle
Large Arterioles
still muscular
Small Arterioles
begin losing musculature
Capillaries
Single cell layer (endothelial)
~1000 m2 surface area
Conts Capillaries
Muscle, lung, adipose, CNS
Fenestrated Capillaries
Pores in cell
Kidneys, endocrine glands, intestines
Disconts Capillaries
Gaps between cells
Bone marrow, liver, spleen
Precapillary sphincters
Control flow through capillary bed
Arterial end (O2 rich)
Hydrostatic > osmotic pressure
Net movement out (more)
Venous end (CO2 rich)
Osmotic > hydrostatic pressure
Net movement in (less, ~ 9/10)
Overall Capillary fluid exchange
Fluid movement out > movement in
Excess fluid removed by lymphatic system
Edema
Tissue fluid accumulation
Possibly caused by:
• High arterial pressure
• Venous obstruction (clot)
• Plasma protein leakage
• dec in plasma protein concentration (liver disease)
• Lymphatic obstruction (elephantiasis – parasitic)
Precapillary sphincter constriction
dec hydrostatic pressure
Same osmotic pressure
Possible flow reverse (… but more in)
Venules
Merger of capillaries
Veins (some smooth muscle)
Merger of venules
Volume reservoir (distensible)
Blood flow in veins
low pressure
skeletal & smooth muscle contractions aid
Flow direction in veins
Aided by one-way valves
Anastomoses
> 1 blood vessel supplies tissue
Alternate routes (collateral channels) for blood
Vasoconstriction & vasodilation
extremely important factors in controlling flowg flow