ch15 - emotions: neural mechanisms of fear and motivation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
we’re now looking at the second aspect of emotion which is….
actions!
pavlovian classical conditioning
tone CS (condition stimulus) presentation prior to conditioning
conditioning (CS-US pairing)
CS presentation (after pairing)
fear conditioning requires the ____
amygdala
click to reveal the amygdala/fear diagram👀
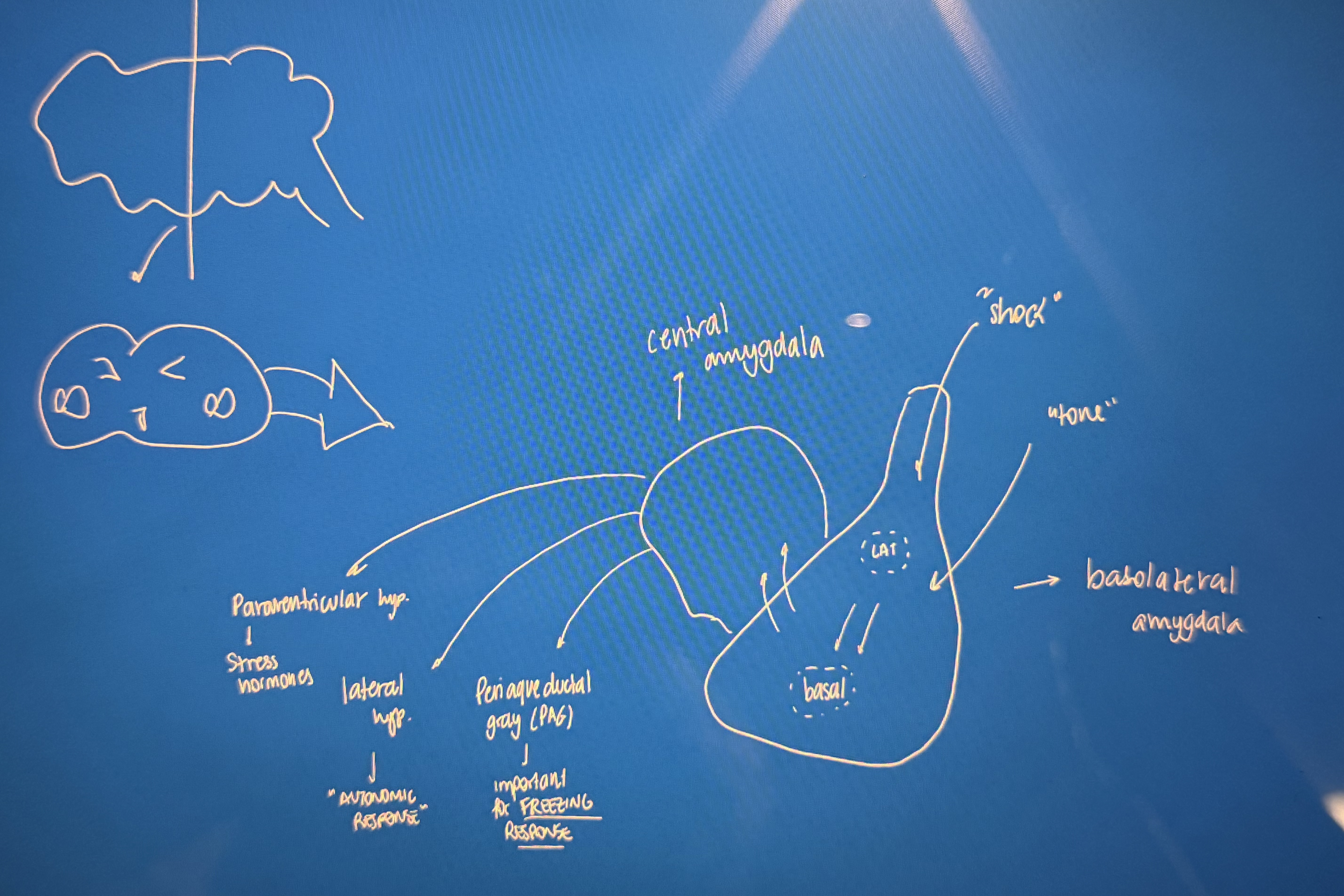
sensory info about threat is conveyed to ____ of amygdala
lateral nucleus
info flow of threat in amygdala
LN → CA (central amygdala) → PAG → LH → avBST and PVH
LN (lateral nucleus)
sensory info about threat
CA (central amygdala)
output to structures
PAG
petiaqueductal gray; defensive behavior (like freezing)
LH (lateral hypothalamus)
autonomic activation (involuntary functions)
avBST and PVH
bed nucleus/ paraventricular: release stress hormones
amygdala activated under these emotional contexts (5):
threatening faces
frightening situations
disturbing scenes
people of other races (hostility/fear)
anxiety-like conditions
what are the four aspects of emotion again!
physiological (autonomic)
actions
motivation (approach/avoidance)
feelings
is hypothalamus singularly important for emotional expression?
nope!
info relevant to _____ (like fear-related freezing) exists amygdala, may bypass _____ and project directly to the ___ and others to produce ___ responses.
emotional behavior/ hypothalamus/ PAG/ behavioral
third aspect of emotion
motivation!
amygdala actually has an important role in ____ emotional states
negative
olds and milner’s landmark finding
brain self-stimulation (targeted LH accidentally)
in order for a brain to self-stimulate, you activate the _____ pathway.
medial forebrain bundle
medial forebrain bundle (pathway)
contains dopamine neurons from the VTA that inner age nucleus accumbens
pleasurable experiences involve ____ activation
dopamine-nucleus accumbens pathway
VTA-DA neurons play a role in ______
reward prediction error (fire more AP when it’s higher than expected, vice versa)
key to relationship between experience and consequences
VTA-DA, reward prediction error and AP firing