DSA12 - Pathology of the Endocrine Pancreas
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Increase rate of glucose transport into certain cells (decrease Serum Glucose)
What is the main function of Insulin?
GLUT2; GLUT4
(GLUT2/GLUT4) is an Insulin INDEPENDENT Glucose transport; (GLUT2/GLUT4) is an Insulin DEPENDENT Glucose transporter
GPCR (activates AC --> more cAMP)
The Glucagon receptor is what kind of receptor?
Universal inhibitor (Inhibits insulin/glucagon secretion, enzymes & Bile + Stops Motility)
What is the function of Somatostatin?
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
Define Condition:
AUTOIMMUNE Metabolic disease involving inappropriately increasing blood glucose - Issue with INSULIN HORMONE LEVELS
-Hx:
> Unknown Etiology
> Genetic Susceptibility w/ Environmental Trigger (ex: Viral Infex via Coxsackievirus)
> Low genetic predisposition
> A/w HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4
> Onset = Child/Teens --> Adults
-Path: Type IV Hypersensitivity = Failure of T cell self-tolerance -> destruction of beta cells by T cells -> absolute insulin deficiency
-Dx:
Labs
INSULIN LOW
> Autoantibodies =
>> Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (Anti GAD-65)
>> Anti-islet cell Autoantibodies
>> Insulin Autoantibodies
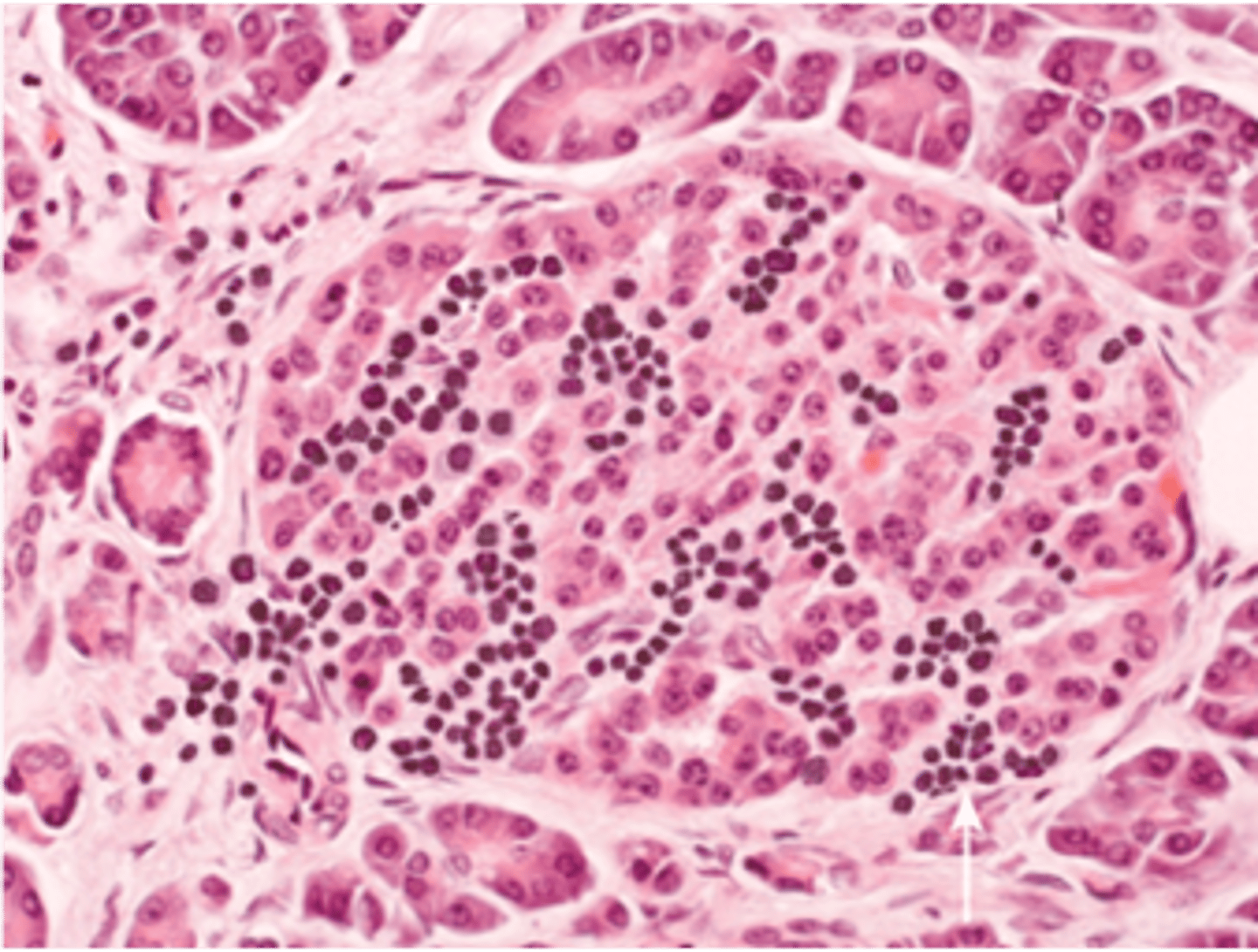
Histo
> Autoimmune "Insulitis" - inflammatory (LYMPHOCYTIC) infiltrate in islets
> Late = Beta-cell depletion, islet atrophy, fibrosis
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
Define Condition:
End-organ INSULIN RESISTANCE leading to Associated Beta-cell dysfunction leading to Metabolic disease involving inappropriately increasing blood glucose - Issue with INSULIN RECEPTOR
-Hx:
> MC Type (90%)
> A/w...
>> OBESITY
>> GENETIC PREDISPOSITION
> Onset = Adulthood (but more incidence in childhood/teens)
-Path:
> Insulin made, but skeletal muscle/fat and liver don't respond --> Hyperglycemia
> Central Obesity (Abd/Visceral Fat) = More LIPOLYTIC (more adipokines & FFAs --> inflammation --> INSULIN RESISTANCE & BETA CELL DYSFUNCTION)
-Dx:
Labs = INSULIN starts high, then drops with advanced disease
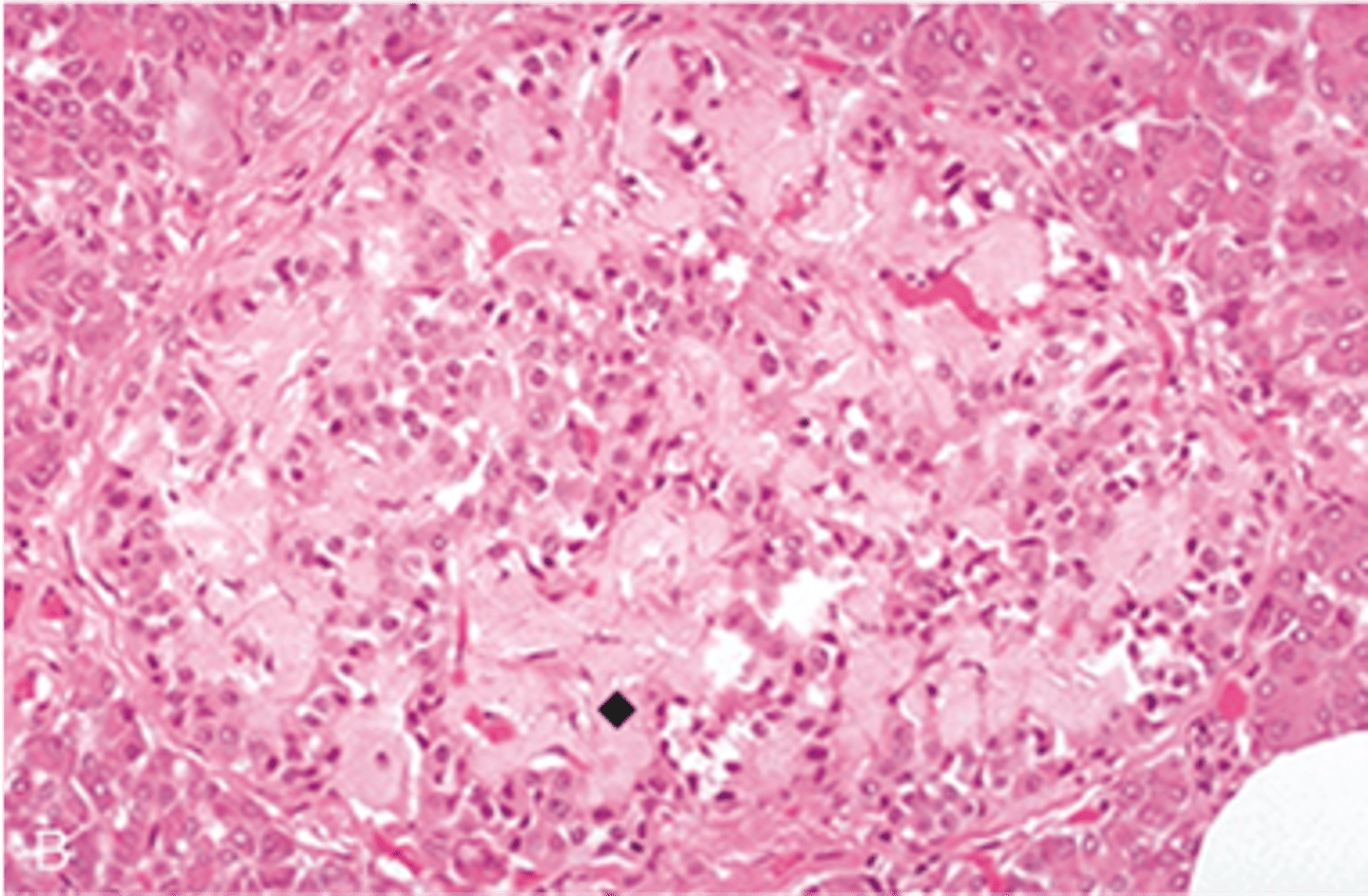
Histo
> Beta-cell hyperplasia & hypertrophy (overcompensation by insulin resistance) --> Less Beta cells --> Less Insulin ==> Hyperglycemia
> Amyloid in islets = Beta-cells also secrete amyloid polypeptide (amylin) --> More insulin = More Amylin accumulation
Gestational Diabetes
Define Condition:
Hyperglycemia that develops during pregnancy
-Path: Pregnancy hormones (ex: human placental lactogen) increases insulin resistance to supply fetus w/ glucose & Amino acids
-Dx:
Histo (in Mother & Fetus)
> Islet Hyperplasia
> Islet Hypertrophy
Hyperglycemia --> Formation of Advanced Glycation End (AGEs) products ==> Damage cells & Promote Atherosclerosis
Describe how Non-enzymatic Glycation occurs and what it can cause
HbA1c (measures avg blood sugar over 3 months)
How is glycated Hb measured?
Coronary Artery Disease; d/t Diabetic Macrovascualr disease as AGEs cause accelerated atherosclerosis
What is the most common cause of death in pts w/ DM?
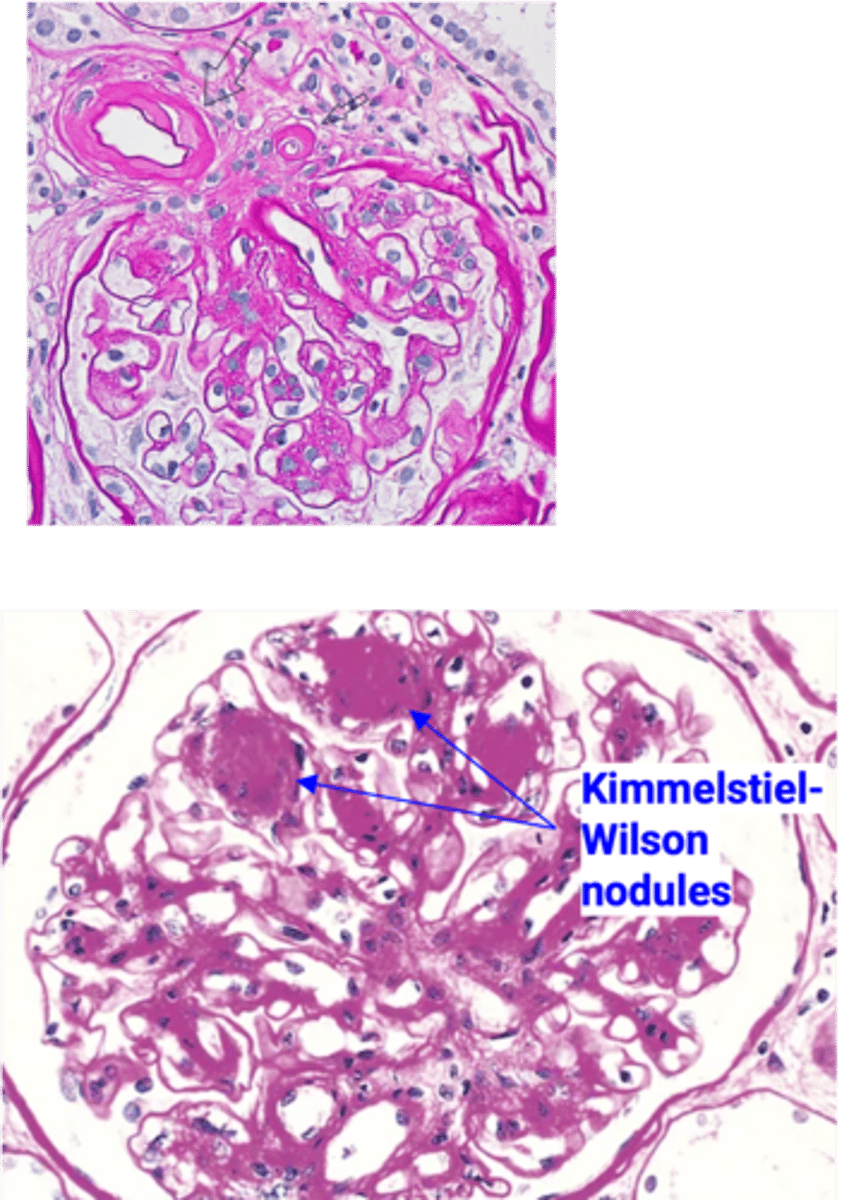
Diabetic Nephropathy
Define Condition:
MCC of ESRD in U.S.
-Path: AGEs crosslink w/ Collagen IV in Basement Membrane --> DIFFUSE THICKENING, esp of VASCULAR VM ==> HYALINE ARTERIOSCLEROSIS (more of EFFERENT Arteriole) --> More pressure in Glomerulus --> Increased GFR --> Hyperfiltration of Glucose (Pulls water) ==> Polyuria --> Eventually, renal failure & Decrease in GFR
-Sx/PE: Polyuria
-Dx:
Histo = Thickened GBM --> loss of size & charge of barrier
↑ sorbitol accumulation in lens -> osmotic damage -> fluid in lens -> cataract formation (clouding or opacification of the lens)
How does cataracts occur d/t Diabetes Mellitus?
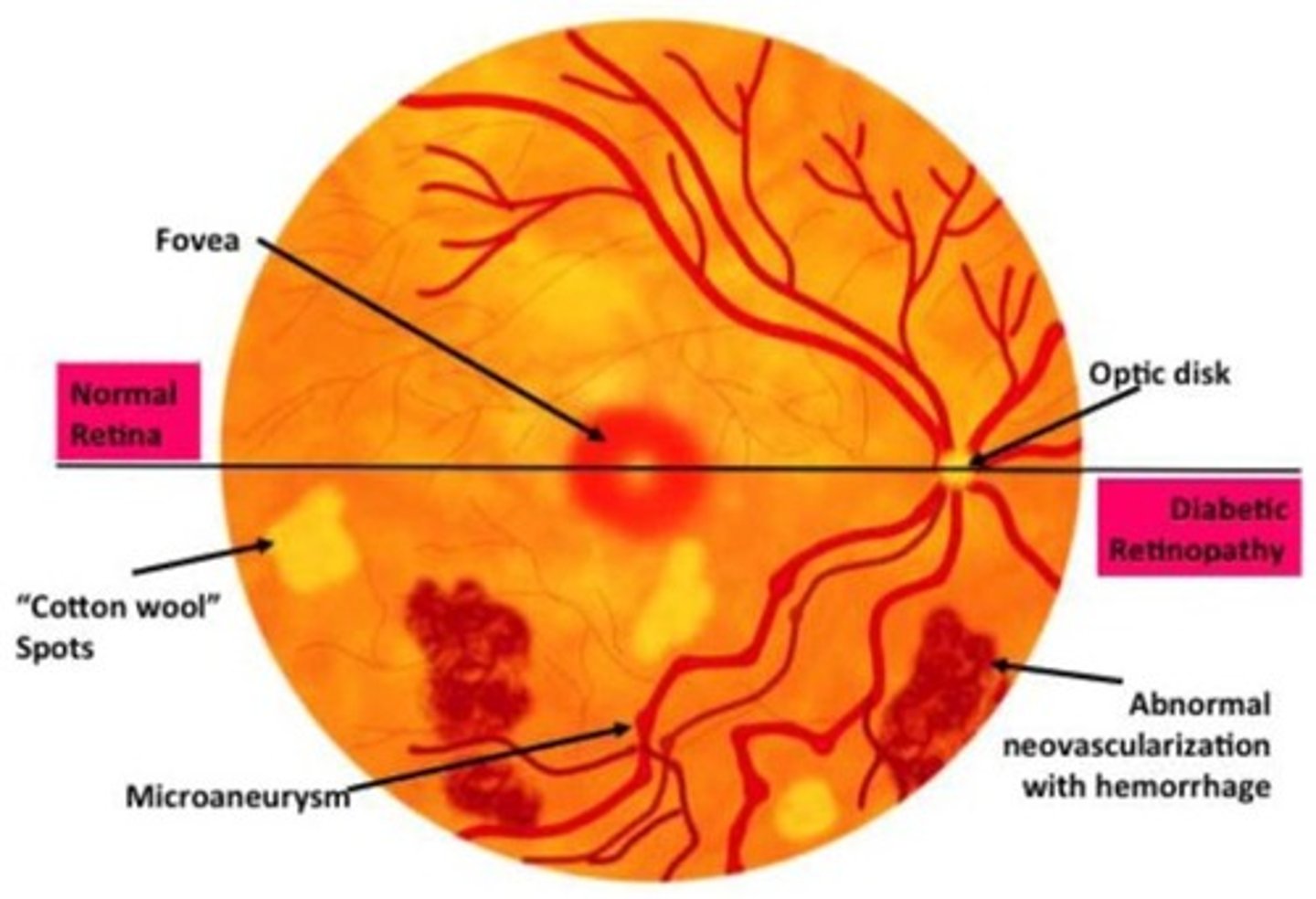
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
Define Condition:
-Path: AGEs, oxidative stress, sorbitol accumulation -> damage small blood vessels of the retina
-Dx: Fundoscopy
> Early = Non-Proliferative
>> Microaneurysms
>> Blot Hemorrhages (rupture of microaneurysms)
>> Hard exudates --> Capillary leakage --> lipid deposits
>> Cotton wool spots = areas of retinal ischemia
> Late = Proliferative
>> Neovascularization (attempt to compensate for poor blood supply)
Diabetic Neuropathy
Define Condition:
-Path: ↑ sorbitol accumulation in Schwann cells (myelinate peripheral nerves) -> osmotic damage
-Sx/PE:
> Affects Sensory axons more than motor
>> Paresthesias/Numbness
>> "Sock and Glove" Sensory Loss
> Autonomic Neuropathy
>> Bowel Issues
>> Bladder Issues
>> Issues w/ sexual function
Insulinoma
Define Condition:
Type of Islet Cell Tumor/PanNET
-Hx:
> Usually in ADULTS
> USUALLY BENIGN
-Path: Tumor of Beta cells --> overproduce insulin --> Hypoglycemia
> Functional Tumor
> May be part of MEN1 Syndrome
-Dx:
Labs
> Glucose = LOW
> Insulin = HIGH
> C-Peptide = HIGH
Histo = Cells arranged in NESTS (Monotonous cells demonstrating round nuclei w/ salt + pepper-like chromatin and abundant cytoplasm)
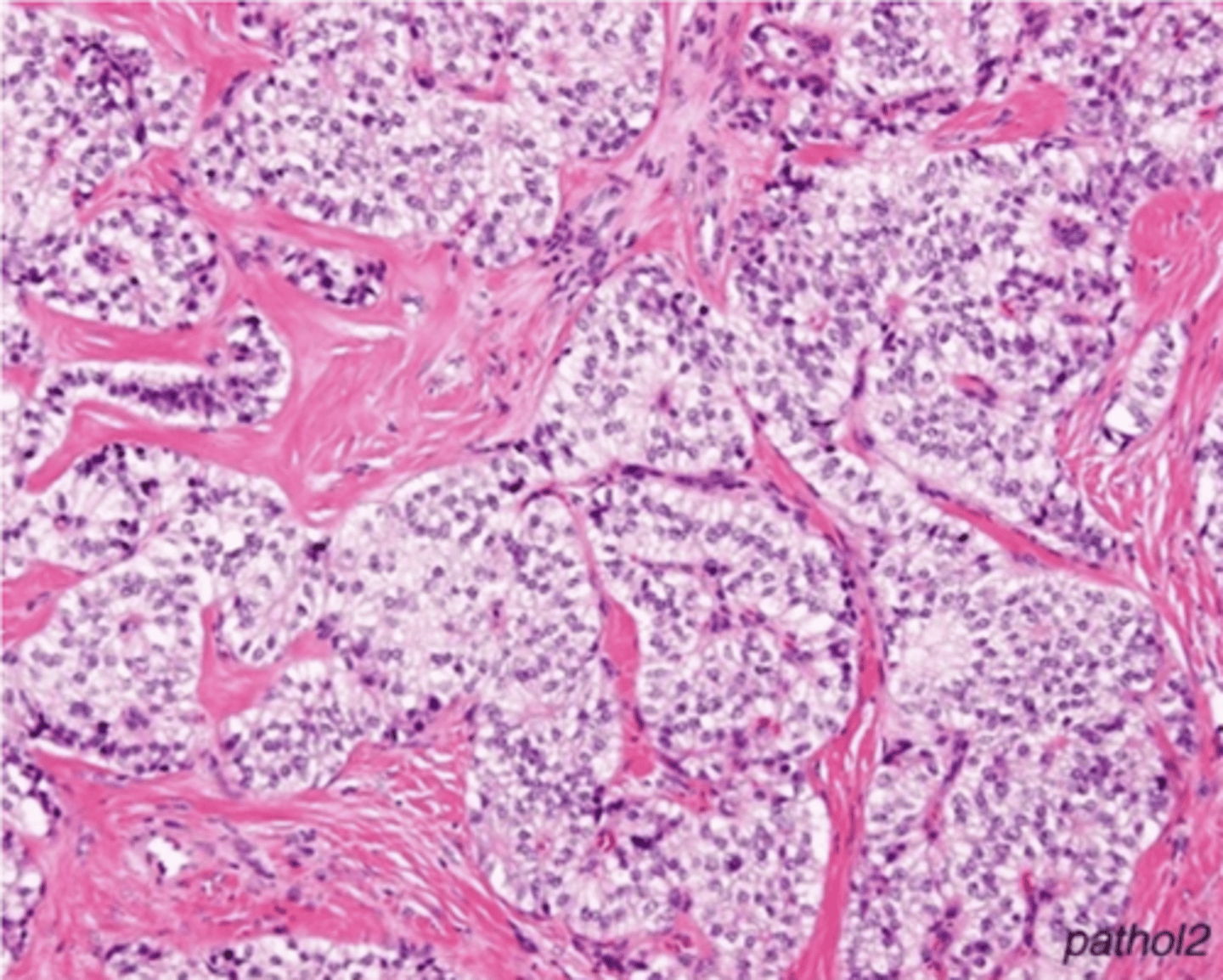
Glucagonoma
Define Condition:
Type of Islet Cell Tumor/PanNET
-Hx:
> Usually in ADULTS
-Path: Tumor of pancreatic alpha cells --> Overproduce glucagon
> Functional Tumor
> May be part of MEN1 Syndrome
-Sx/PE: (6 Ds)
> Dermatitis (Necrolytic migratory erythema = red, blistering, itchy, painful rash; fluctuates in severity; usually seen in genitals, buttocks, groin, and extremities)
> Diabetes
> DVT
> Declining wt
> Depression
> Diarrhea
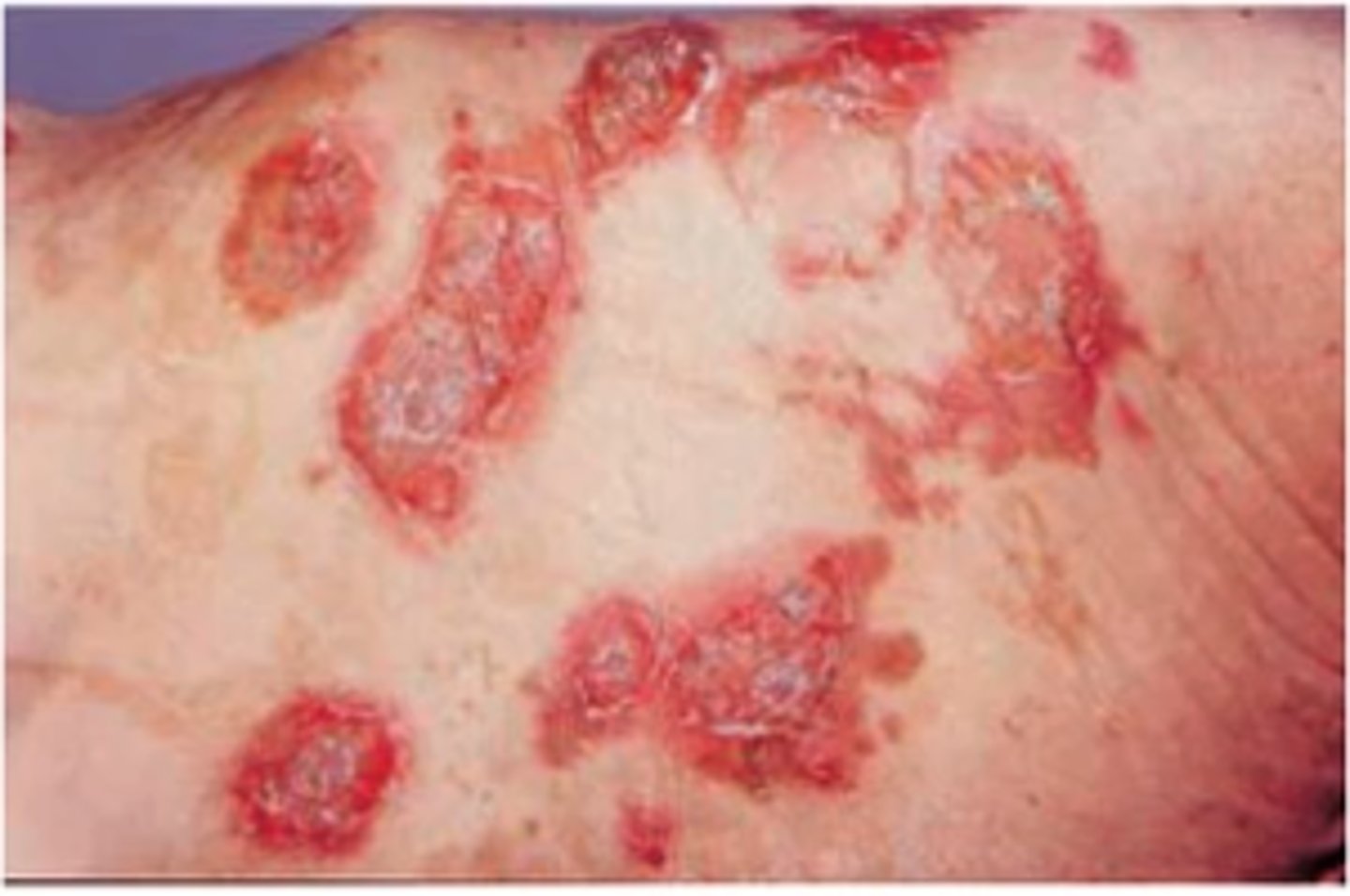
Somatostatinoma
Define Condition:
Type of Islet Cell Tumor/PanNET
-Hx:
> Usually in ADULTS
-Path: Tumor of pancreatic delta-cells -> overproduce somatostatin ==> Less glucagon/insulin & GI hormones (Secretin, CCK, Gastrin, GIP)
> Functional Tumor
> May be part of MEN1 Syndrome
-Sx/PE:
> Gallstones (Less CCK = bile stasis)
> Steatorrhea (Less GI enzymes & bile secretion)
-Dx:
Labs
> Diabetes/Glucose Intolerance (low Insulin)
> Achlorhydria (less gastrin --Less HCl in stomach)
-Prog: METASTASES