Medical Procedures with Lab 103 ECG
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What is the first impulse?
p wave
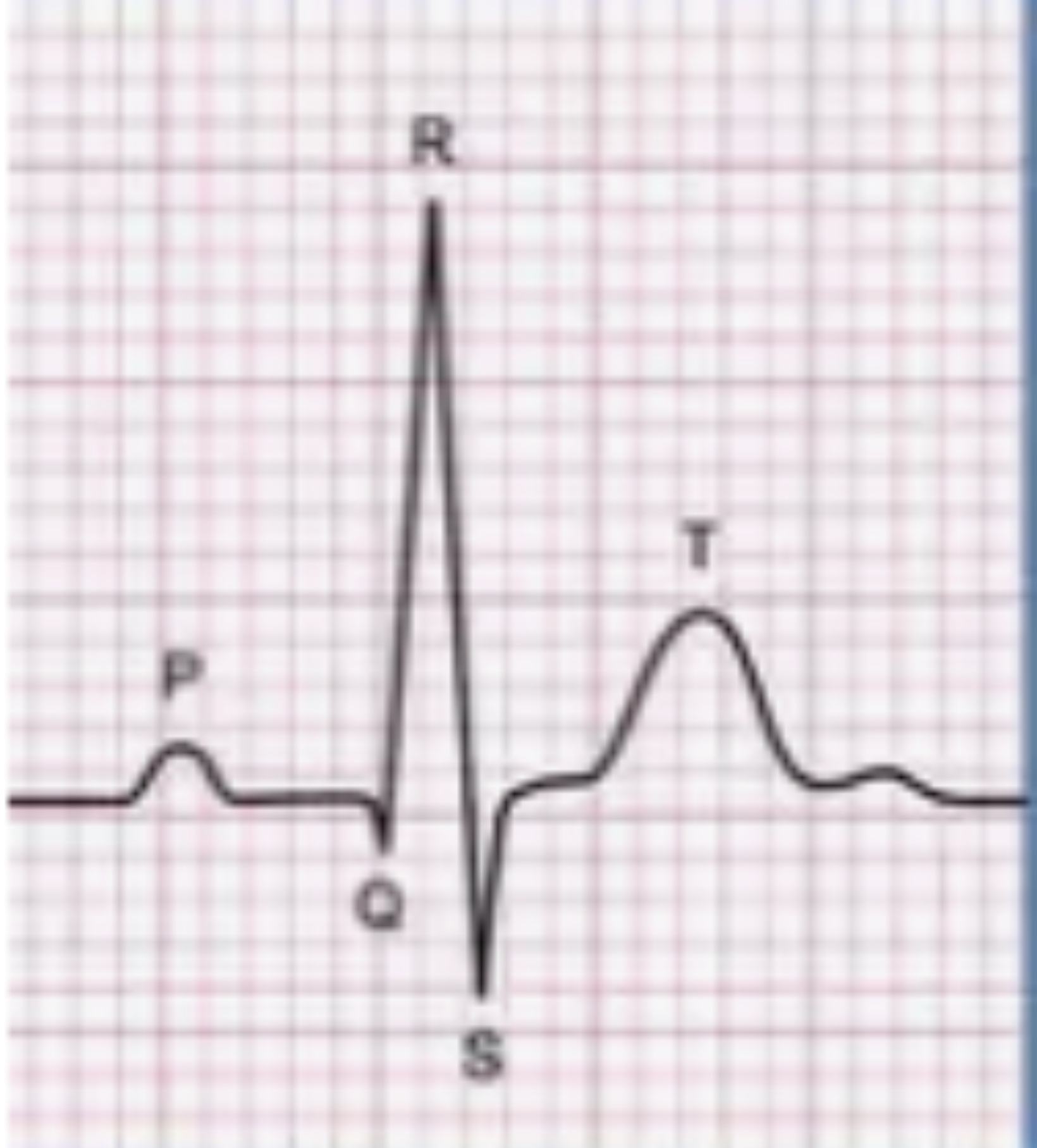
What is this?
The ECG waveform is a crucial component of an electrocardiogram (ECG) that represents the heart's electrical activity during a single heartbeat.
ECG
A graphic representation of the hearts activity. Does not provide information about the mechanical (contractile) condition of the myocardium
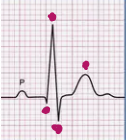
What is for p stand for?
Atrial depolarization
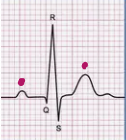
What does QRS stand for?
QRS Complex Ventricular depolarization.
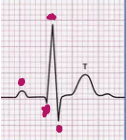
What T stand for?
Ventricular Repolarization
PR interval
The time it takes the impulse to travel from the SA node to the AV node
Where the P wave begins until the beginning of the QRS Complex

How many seconds is the PR Interval and how many small boxes does it take up?
0.12-0.20 seconds and takes up 3-5 small boxes
QT interval
The amount of time between the beginning of ventricular contraction and the completion of ventricular recovery
where the QRS complex begins to the end of the T wave
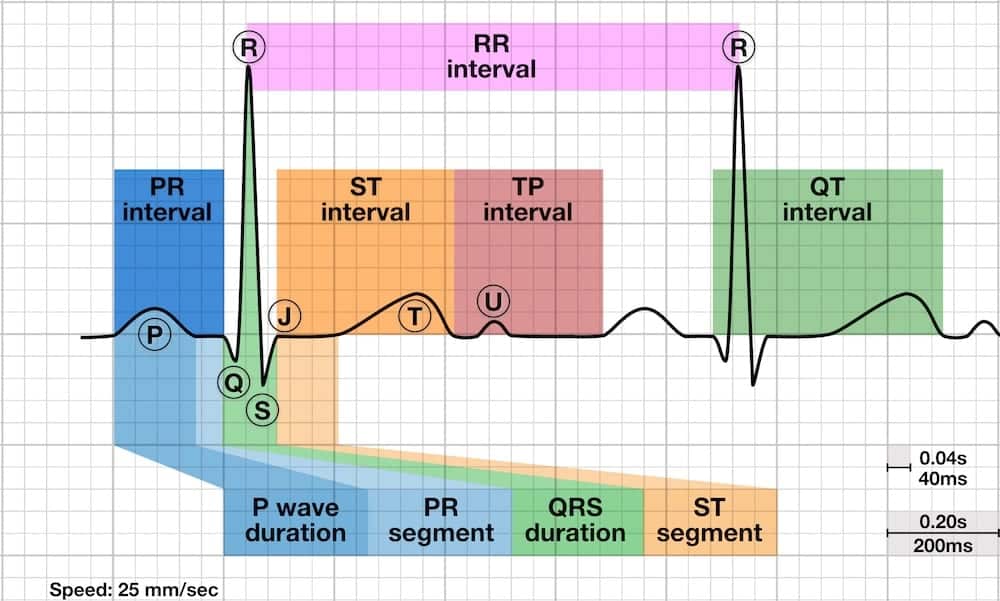
How many seconds is the QT interval and how many small boxes does it take up?
0.36-0.44 seconds and it takes up 9-11 small boxes, but this will vary with patient, gender, age, and heart rate.
ST segment
Transition period between depolarization and repolarization
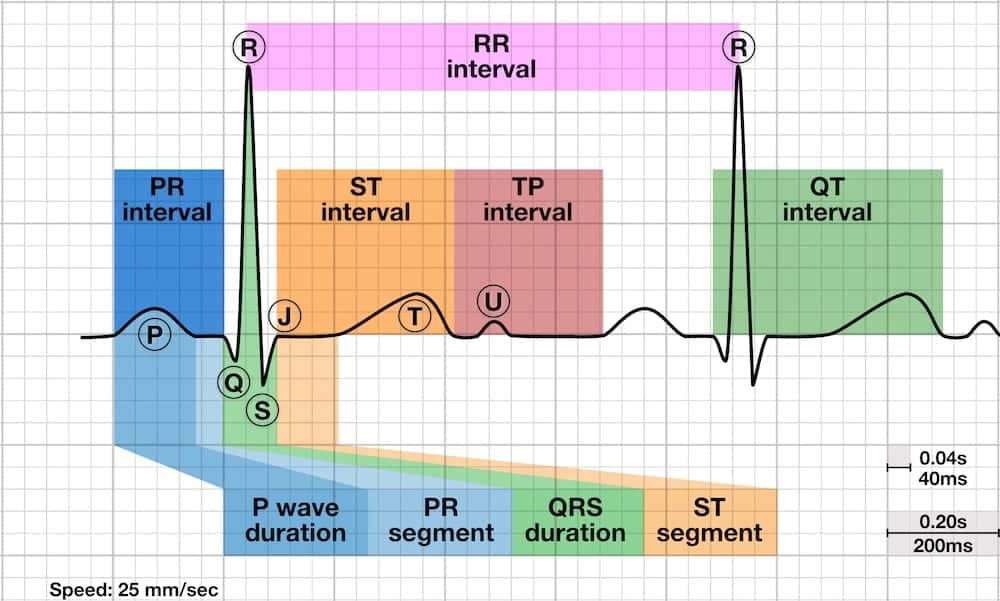
What is the speed of the ekg?
25mm/sec
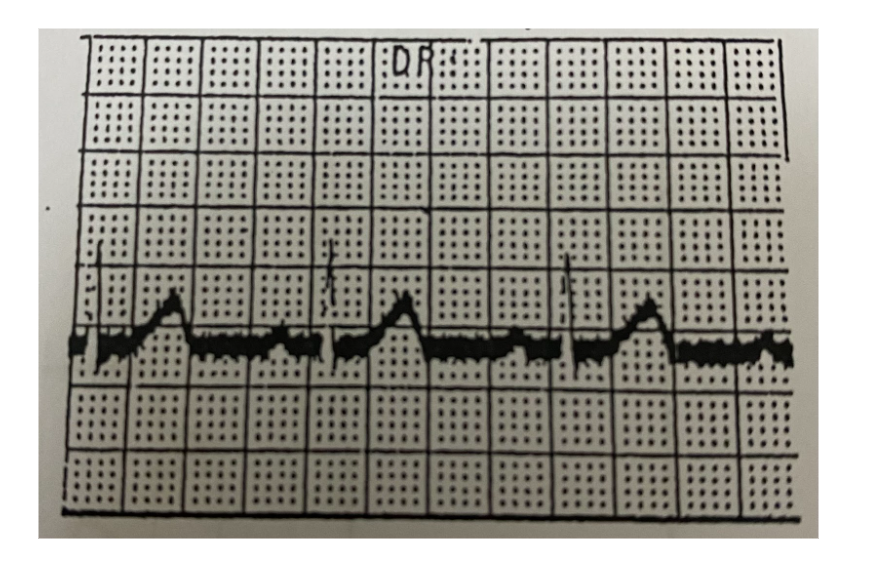
What does this mean?
Severe Alternating current (AC) Interference
interference has regular vibrations with constant amplitude.
is electrical noise that appears on an ECG from nearby power sources, causing thick or wavy lines on the tracing.

What does this mean?
Light Alternating Current (AC) Interference.
means when two or more light waves overlap and mix, they can add up or cancel out each other - just like waves in water.
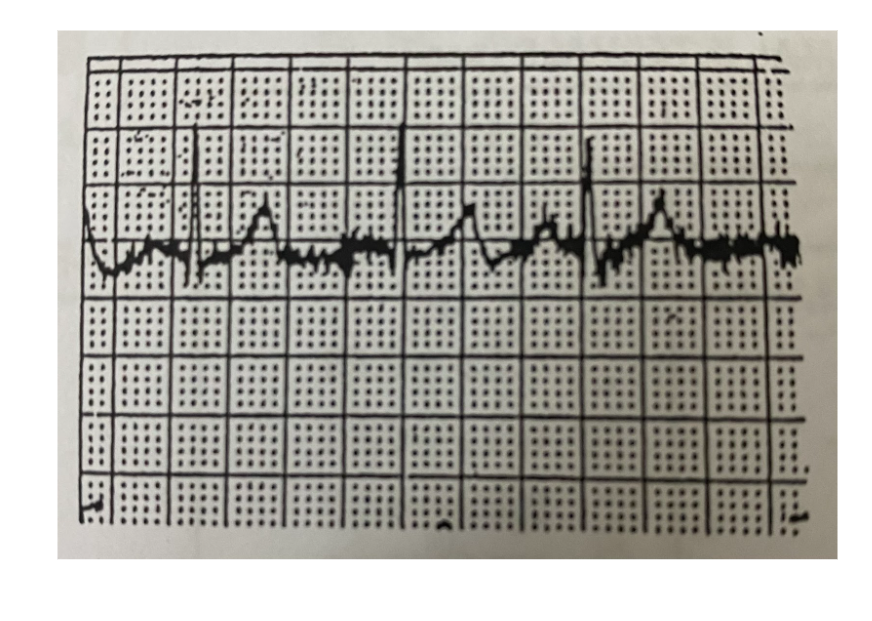
What does this mean?
Muscle Voltage Interference
Interference has random rate of vibration; amplitude fluctuates, indicates muscle movement usually caused by apprehensive or uncomfortable patient.
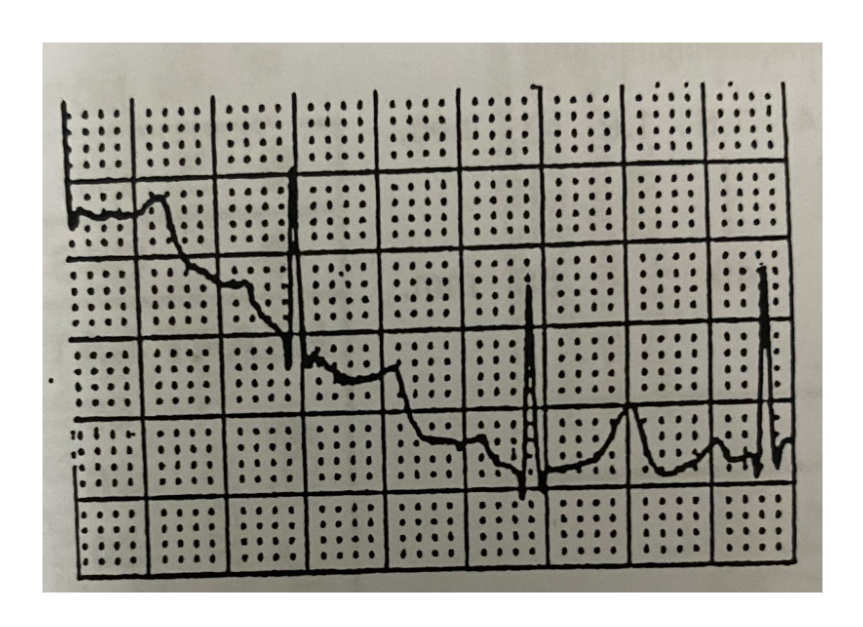
What does this mean?
Baseline Wandering
Baseline drifts during lead, or shifts when switching leads.
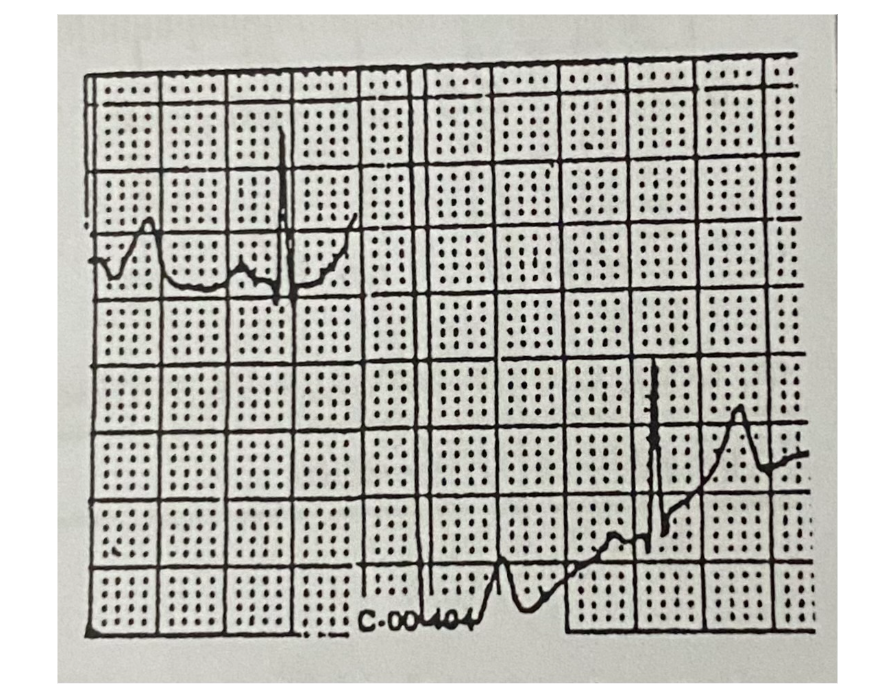
What does this mean?
Baseline Interruption
Broken electrical connection, usually because of loose wires or poor connections.
is when the normal steady line (baseline) on a recording, like an ECG, is temporarily broken or unstable, usually because of loose wires, poor connections, or movement.
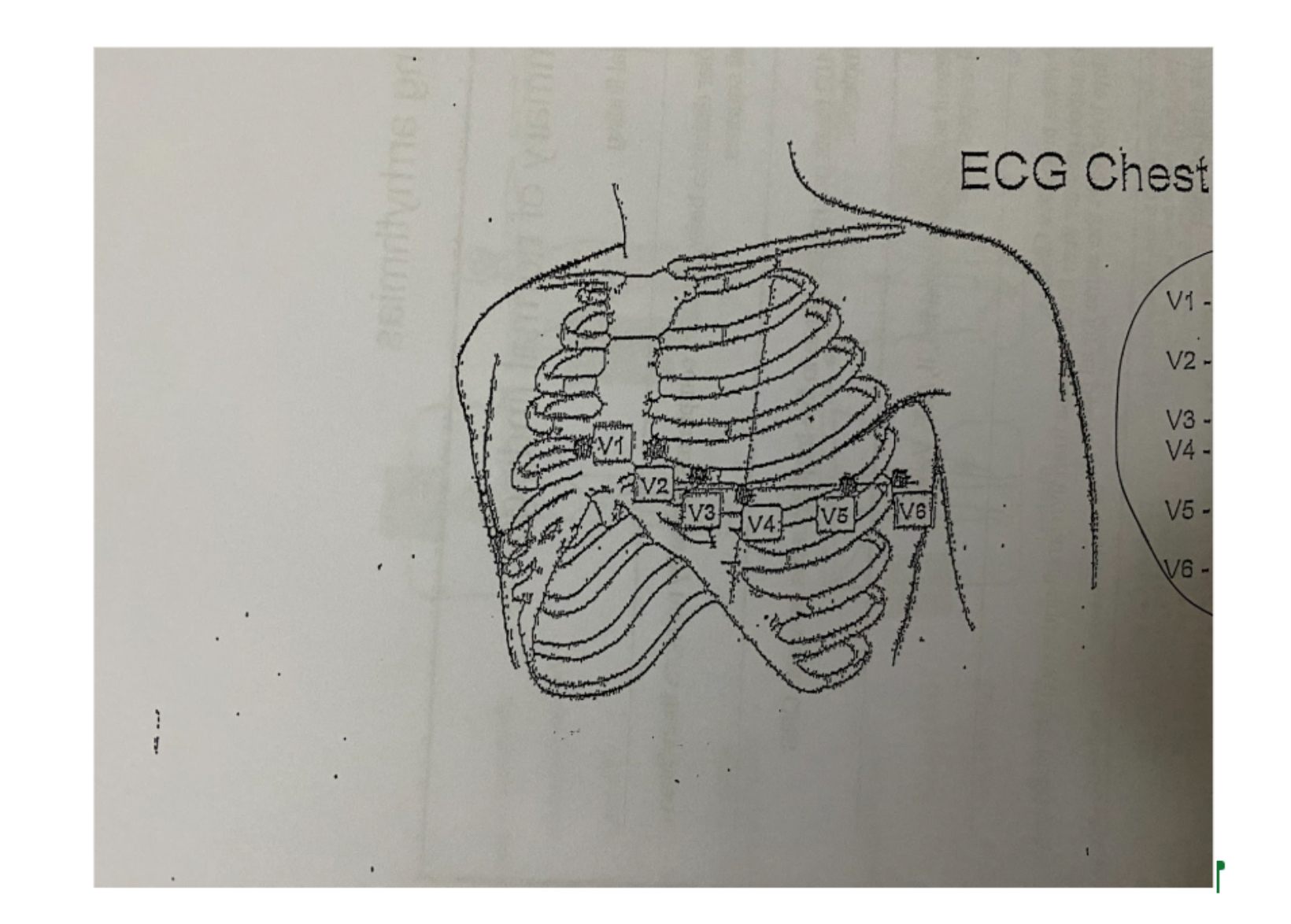
What is this?
ECG chest lead placement
What is being shown here?
V1
4th intercostal space along the right margin of the sternum.
ex. V1 ICS R side of sternum
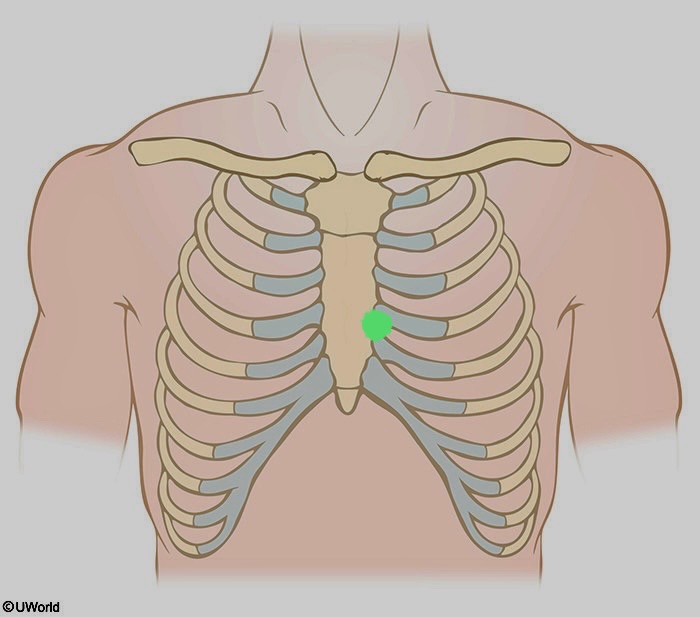
What is being shown here?
V2
4th intercostal space along the left margin of the sternum
ex. V2 ICS L side sternum
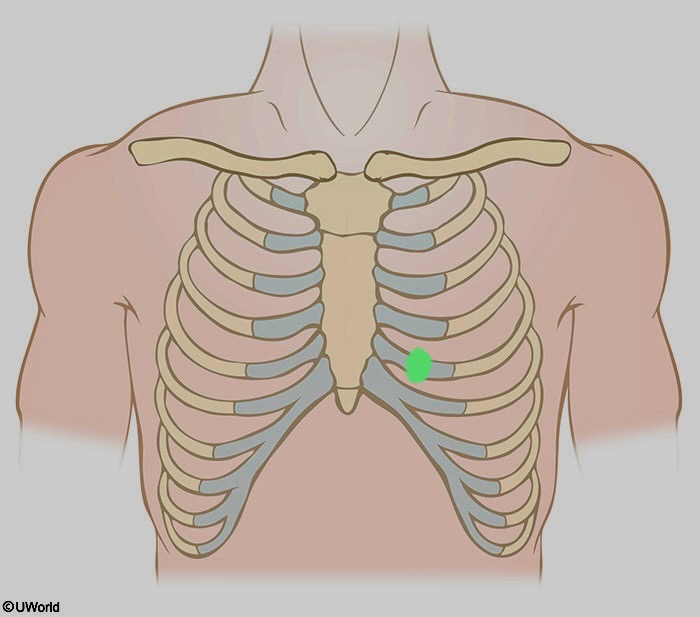
What is being shown here?
V3
Located between V2 and V4
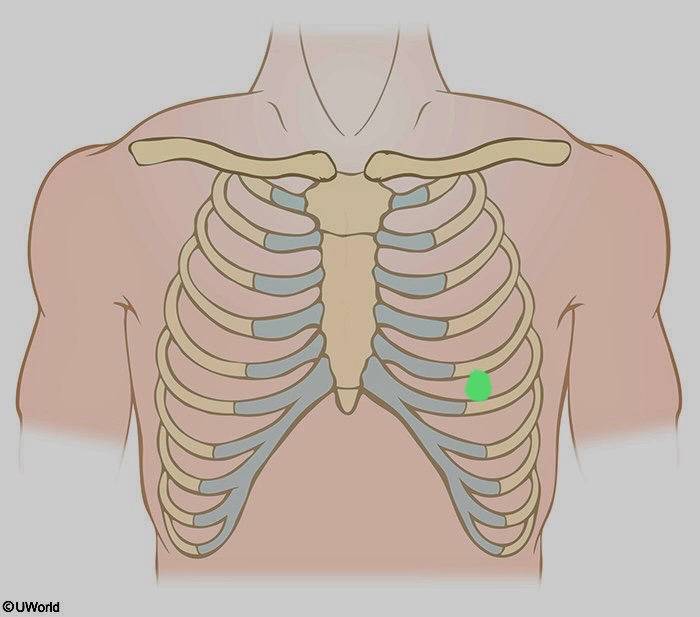
What is being shown here?
V4
5th intercostal space at the left mid-clavicular junction
mid clavicular junction: mid point of clavicle
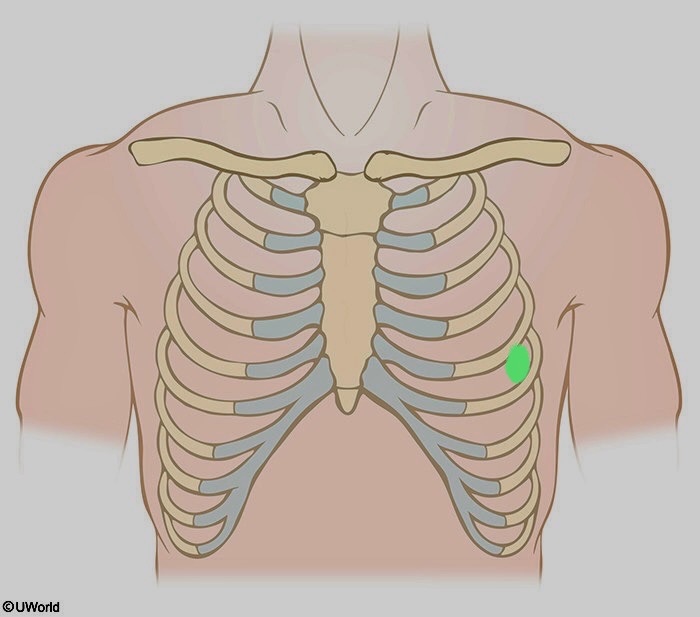
What is being shown here
V5
Horizontal to lead V4 at the left anterior axillary line.
left anterior axillary line: imaginary vertical line on the left side of body that starts at the anterior (toward the front of body) axillary fold (front of armpit where chest meets arms)
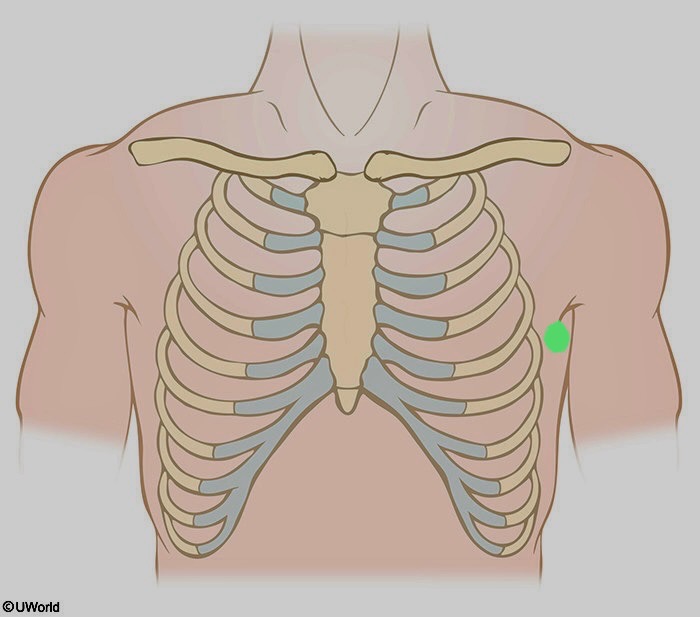
What is being shown here?
V6
Horizontal to lead V4 at the left mid axillary line.
mid axillary line: imaginary vertical line on side of torso that runs from mid point of armpit (axilla) downwards.
What is happening during a P wave
Atria are contracting
Pushing blood out
What is happening during a QRS wave
Ventricles contracting
What is happening during a T wave
Ventricles relaxing
Isoelectric line
The flat, horizontal baseline on an ECG that separates the various waves and represents when there are no currents in the cardiac cycle. Electrical activity is not detected.
Waveform
Movement away from the baseline in either a positive (upward) or negative (downward) direction.
Conduction disturbances
May occur because of trauma, drug toxicity, electrolyte disturbances, MI
conduction may be too rapid or too slow
The heart has four chambers divided by the…
Septum
Layers
Endocardium, Myocardium, Epicardium
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node)
Located in the upper posterior portion of the right atrium at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium. It is the site of ORIGIN of the electrical impulse. Pacemaker of the heart.
On an ECG, the SA node's activity is seen as the P wave, which shows the electrical signal spreading through the atria and causing them to contract.
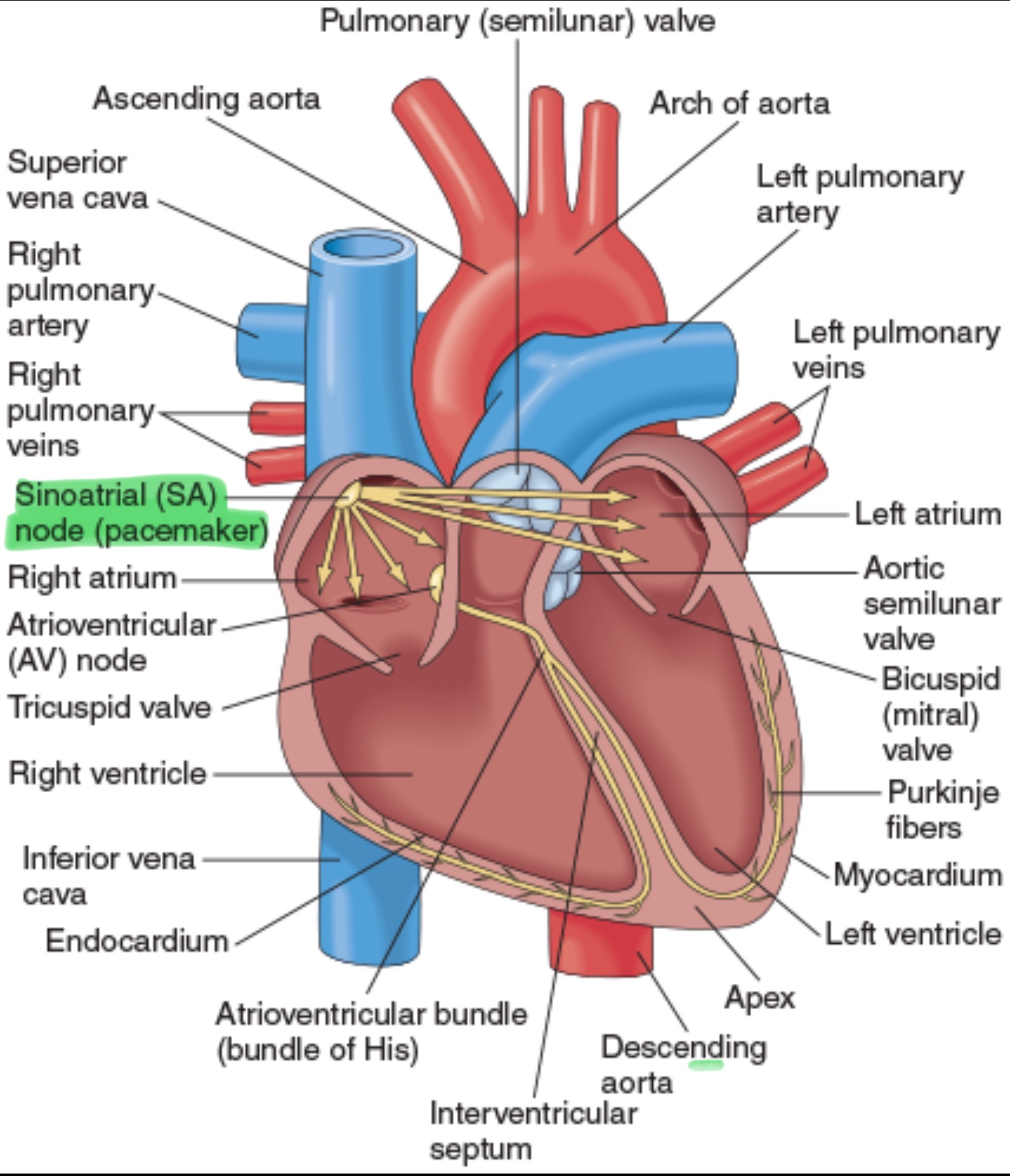
SA Node BPM
60-100 bpm
Atrioventricular Node (AV Node)
Located on the right side of the Interatrial Septum (IAS), immediately behind the tricuspid valve and near the opening of the coronary sinus.
IAS- a thin, muscular wall that separates the left and right atria
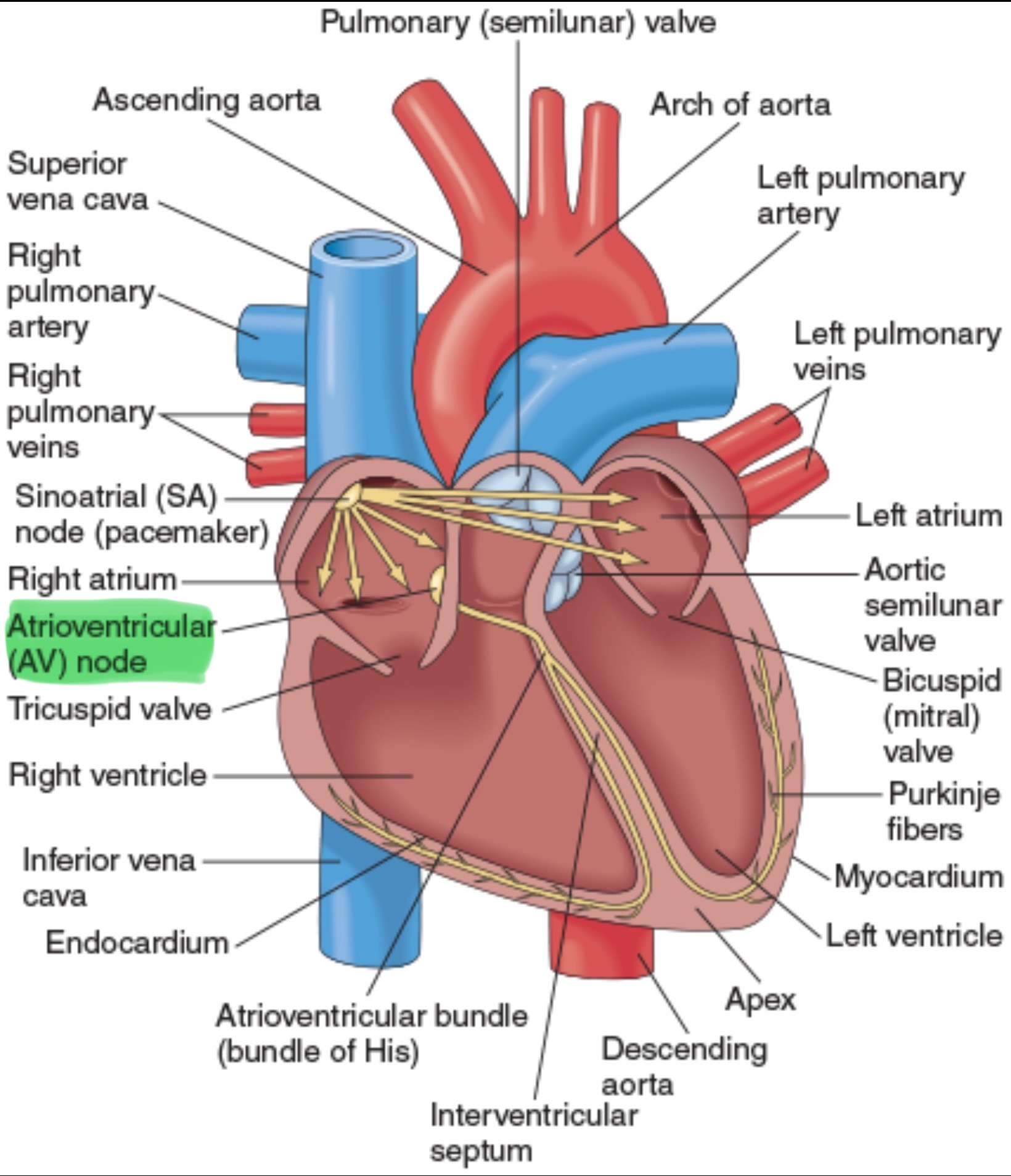
AV Node BPM
40-60 bpm
AV Junction
Electrical bridge between the atria and ventricles. Located at the base of the IAS and extends to the ventricular system
includes the AV node and Bundle of HIS
Bundle of His
The only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles. Bifurcates in the right and left Bundle Branches.
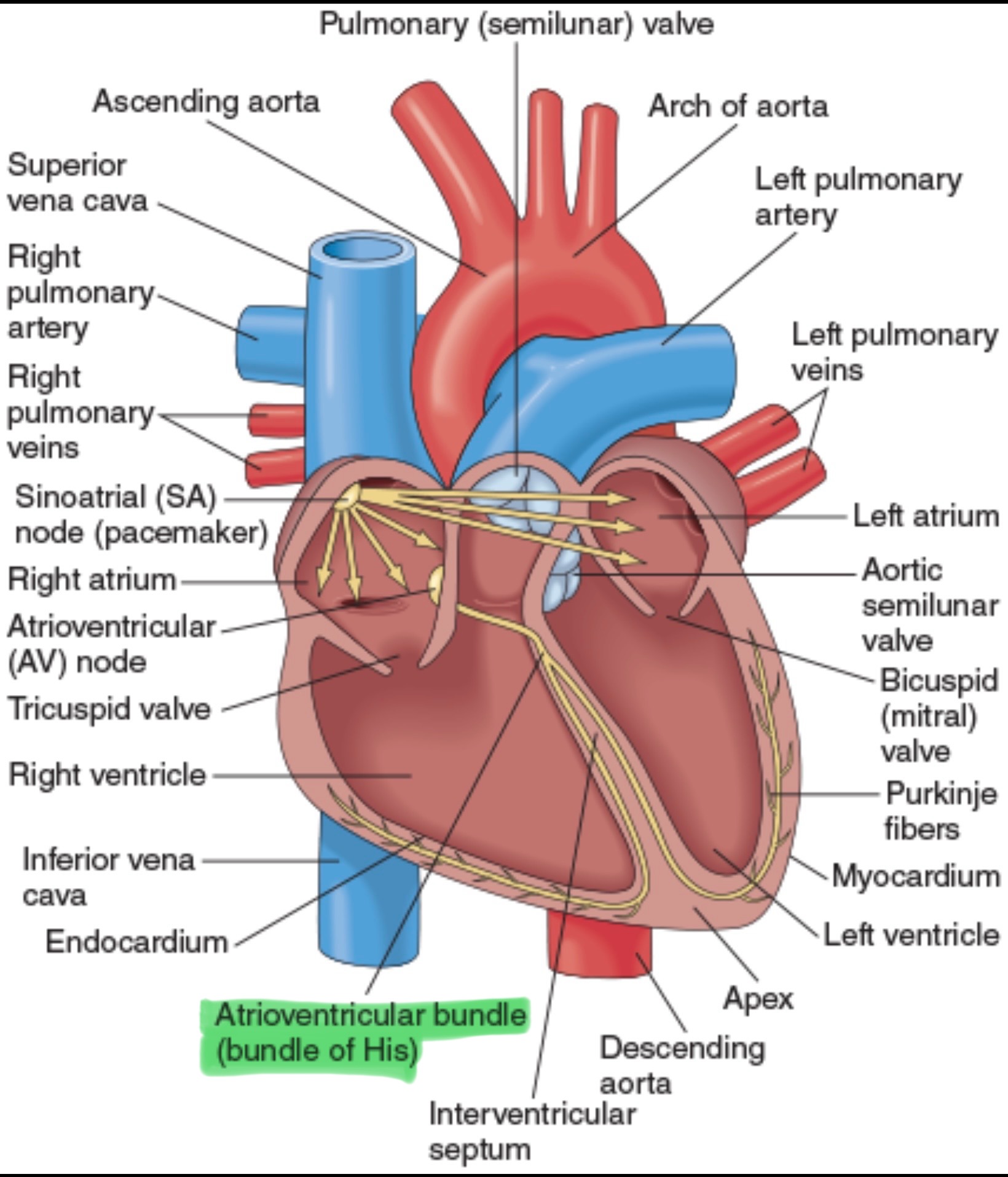
Right Bundle Branch
Supplies the electrical impulses to the right ventricle.
Left Bundle Branch
Supplies the electrical impulses to the left ventricle.
Purkinje Fibers
Because of the velocity (speed) of the conduction in the Purkinje Fibers, there is almost immediate spread of the impulses through the ventricle muscle.
Purkinje Fibers BPM
20-40 bpm
Depolarization
Discharge of electrical energy
Repolarization
Recovery of the heart as the cells recharge themselves
Polarization
Heart at rest
Impulses
Displayed on ECG paper
What type of instrument is an ECG?
A voltmeter
Why is gel used during an ECG?
Gel is used as a conductor — it helps transmit electrical signals between the skin and the electrodes for a clear ECG reading
The skin is a poor conductor of electricity
What does a normal ECG indicate?
A normal sinus rhythm — meaning the hearts electrical activity and rhythm are regular and originate from the sinoatrial (SA) node
How many placements are used to get a 12 lead ECG?
10 placements
What is recorded first on an ECG strip?
Bipolar leads
I, II, and III
What are the 3 types of ECG leads?
Standard limb leads, augmented limb leads, and precordial (chest) leads
Which leads are bipolar?
Leads I, II, and III (the standard limb leads)
Lead I
Views lateral wall of left ventricle
Lead II
Views inferior surface of left ventricle
Lead III
Views inferior surface of left ventricle
Which leads are unipolar limb leads?
aVR, aVL, and aVF
Lead aVR records electrical activity from…
Mid point of lead 3, towards RA
Lead aVL records electrical activity from…
Mid point of lead 2, towards LA
Lead aVF records electrical activity from…
Mid point of lead 1 towards foot
Which leads are chest leads?
V1 through V6
Horizontal Plane Leads
View of the heart as if the body were sliced in half horizontally
Directions: anterior, posterior, right, left
Six chest leads (precordial or “V”)
Frontal Plane Leads
Views the heart from the front of the body as if it were flat. 3 bipolar leads and 3 unipolar leads.
Standard Limb Leads
Leads I, II, and III
RA is always negative
LL is always positive
Lead I records the difference in electrical potential between left arm (+) and right arm (-) electrodes.
Augmented Limb Leads
Leads aVR, aVL, aVF
A= augmented, V= voltage, R/L= right/left arm, F= foot (usually left leg)
Einthoven’s Triangle
A triangle formed by 3 standard limb leads (RA, LA, LL) around the heart
Lead I: RA → LA
Lead II: RA → LL
Lead III: LA → LL
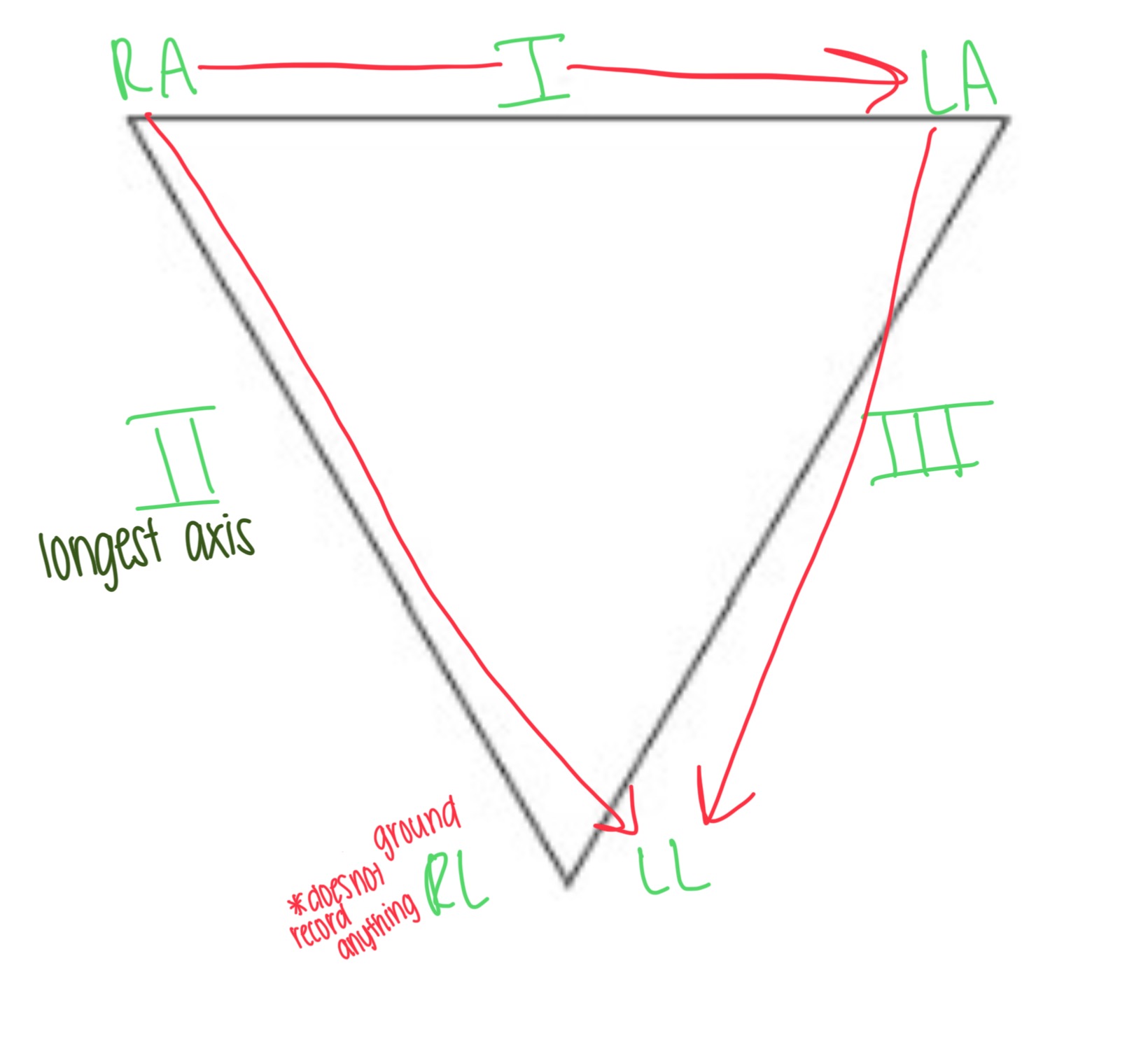
Which limb acts as the ground and doesn’t record anything?
The right leg (RL)
What is the order of ECG Leads?
I, II, III — aVR, aVL, aVF — V1, V2, V3 — V4, V5, V6
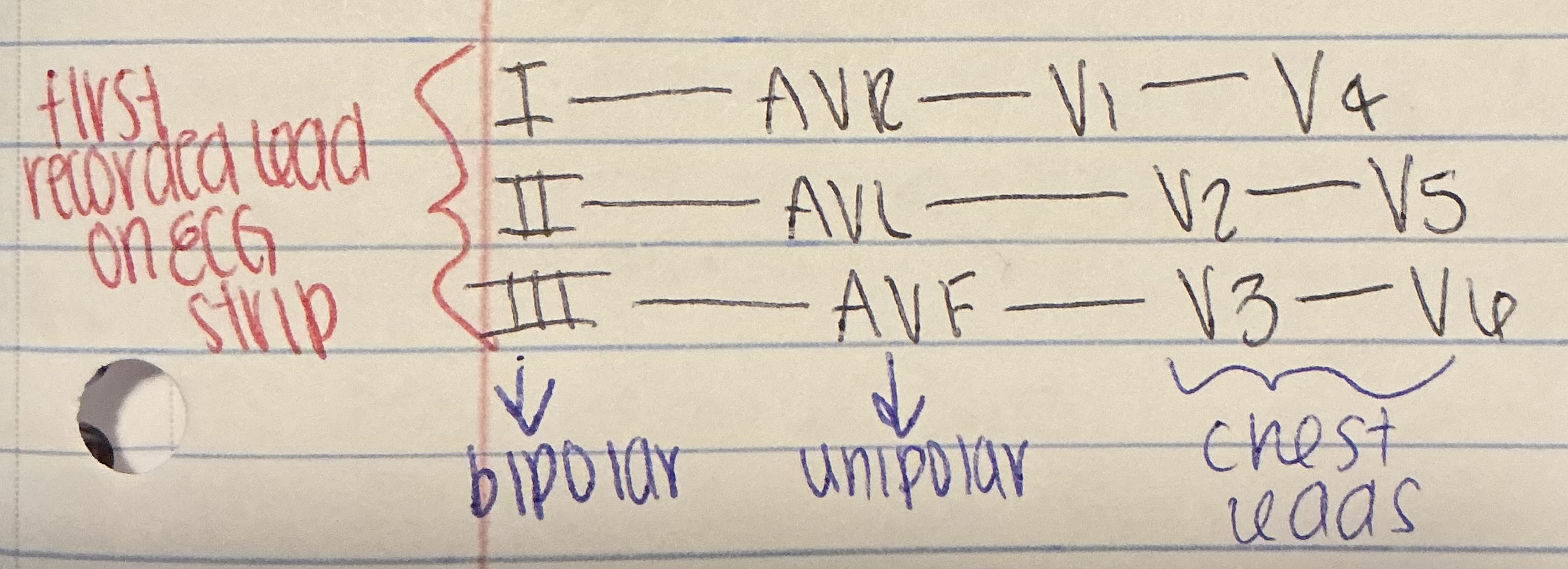
Are the bipolar leads recorded after or before augmented leads?
Before
What is the ECG’s function?
The 12 leads record the electrical activity from different directions, giving the physician a picture of the function of different areas of the heart
Leads
A record of electrical activity between two electrodes
Artifact
Distortion of an ECG tracing by electrical activity that is non cardiac in origin.
Can mimic various cardiac activity dysthymias, including ventricular fibrillation
Causes of artifacts
Loose electrodes, patient movement, broken ECG cables or broken wires, muscle tremor
What is the ECG paper?
Graph paper made up of small and larger heavy lined boxes
Smallest squares measurement
1mm wide & 1mm high
How many small squares are between the heavier black lines?
5 small squares
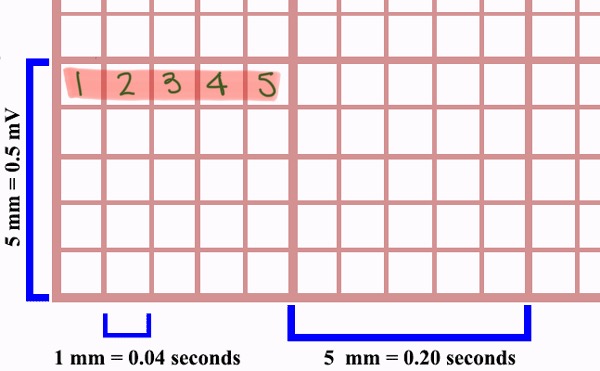
How many small squares within each large square?
25 small squares
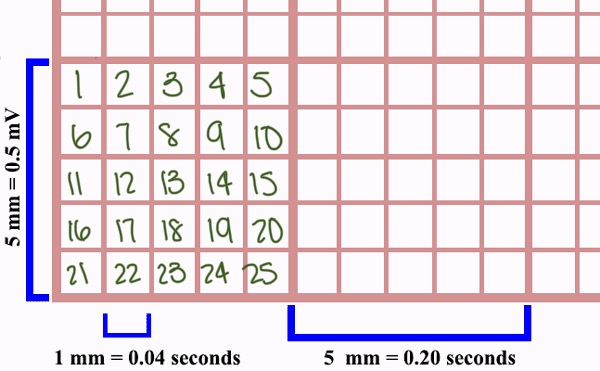
Time of the Cardiac Cycle (heartbeat & seconds)
1 heartbeat = 0.8sec
Axis orientation on ECG paper
Time on bottom, voltage on side
How many large boxes is a 3 second strip?
15 large boxes
How many large boxes is a 6 second strip?
30 large boxes
What is the standard calibration for an ECG?
1 millivolt (mV) = 10 millimeters (mm)
This means that 1mV signal produces a 10mm tall deflection on the ECG paper
Standardization Mark
Keeps machine running safe and properly
10mm high
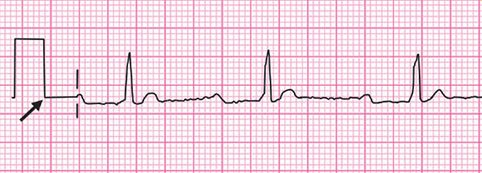
Galvanometer
Changes voltage into mechanical motion. Measures the electrical current
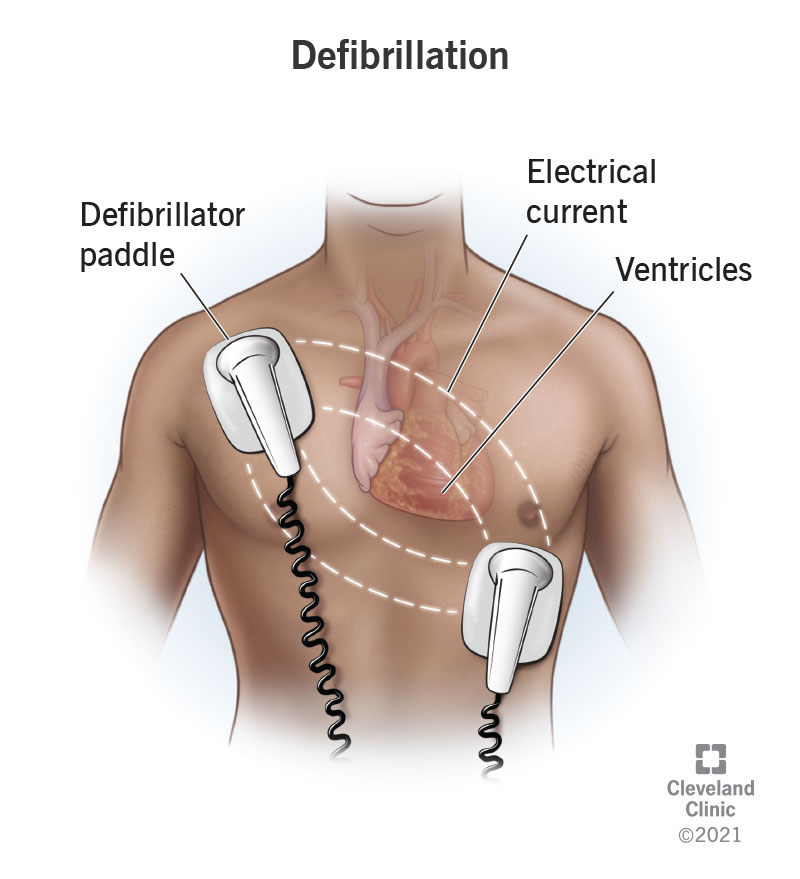
Defibrillator
Used to discharge a strong electrical current into the patients heart through electrode paddles held against the bare chest wall.
Amplifier
Device on an electrocardiograph that enlarges the ECG impulses
Stylus
Records motion (by heat)
How does deoxygenated blood enter the heart?
Through the RA — right atrium
Electrical Conduction System
A network of cells that generates and transmits electrical impulses
SA Node → AV Node → Bundle of His → R Bundle Branch → L Bundle Branch → Purkinje Fibers
What converts cardiac arrhythmia into a normal sinus rhythm?
Cardioversion
cardio- = heart
-version = turning
How to reduce artifacts:
Quiet, warm exam room. Away from electrical equipment.
Why are electrodes applied to the fleshy part of a limb?
To minimize artifacts
What is the step after removing the electrodes from the patient?
Assist the patient — help them get up and dressed (if needed)
Thallium Stress Test
Requires injecting the patient with a radioactive substance
Ventricular Fibrillation
Exam question: What is a true statement about Ventricular Fibrillation?
Life threatening
Holter Monitor
Patients have to keep a diary
Small device that records the hearts activity to detect irregular heart rhythms
Exam Question: What is not true about holter monitor electrodes?
❎ There are only 6-7 electrodes used
What is an example of an artifact caused by an electrical interference?
AC Interefence
What artifact can be caused by poor quality electrolyte gel?
Wandering Baseline
Why would the MA place the power cord pointing away from the patient and not allow it to go underneath the table?
Helps reduce AC Interference