Comparative Cultures 12 - Greek Unit
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
The Acropolis
A fortified hill in Athens that served as a religious and ceremonial center.
Key buildings: Parthenon, Propylaea, Erechtheion, Temple of Athena Nike, and the Theatre of Dionysus.

Construction of the Parthenon
Built 447–438 BCE, commissioned by Pericles.
Made of marble, featured Doric columns and detailed sculpture.
Used subtle optical illusions for visual perfection (e.g., columns bulging in the middle, curved base).
Phidias
Lead sculptor responsible for decorative elements of the Parthenon.
Designed the massive chryselephantine (gold and ivory) statue of Athena.
History of the Parthenon
Originally a temple for Athena
Later became a church, mosque, and was damaged during warfare.
Much of its sculpture was removed (Elgin Marbles).
Statue of Athena
38 ft tall, depicted with shield, spear, helmet, and Nike in hand.
Represented military victory and was the centerpiece of the Parthenon.
Aspects of the Parthenon’s Construction
Harmony, balance, and proportion were key.
Inward-leaning columns, thicker corners, and strategic spacing all create optical illusions.
The Elgin Marbles
Sculptural decorations removed by Lord Elgin and sold to the British Museum.
Controversial due to modern debates about cultural repatriation.
Caryatids
Female statues used as architectural supports on the Erechtheion.
Rigid enough to bear weight but sculpted with grace.
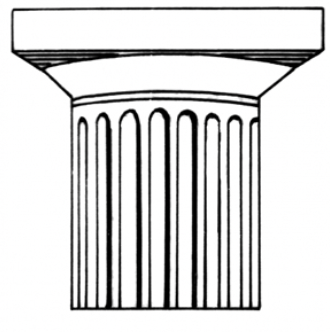
Doric Pillar
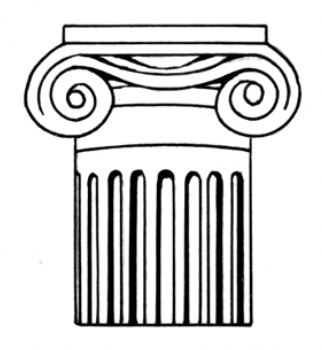
Ionic Pillar
Corinthian Pillar
Pottery Uses & Shapes
Used for storing oil, wine, water; also ceremonial and funerary purposes.
Durable, mass-produced — a major industry.
Red Figure
5th century BCE; red figures on black background.
Allowed for more realistic detail and expression.
Black Figure
6th century BCE; black figures on red/orange background.
Featured mythology, daily life, and occasionally erotic themes.
Exekias
Master potter and painter known for precision and storytelling (e.g., Dionysus cup).
Mediums & Themes
Bronze, marble, ivory-gold (chryselephantine).
Focus on realism, anatomy, movement, and idealized beauty.
Charioteer of Delphi
Bronze statue, slightly stiff but lifelike.
Subtle details: twisting torso, turned head, glass eyes.

Nike Adjusting her Sandal
Marble relief, elegant drapery showing feminine form.
Found in the Temple of Athena.

Dionysus
Depicted in pottery and statuary as god of wine, revelry, and transformation.
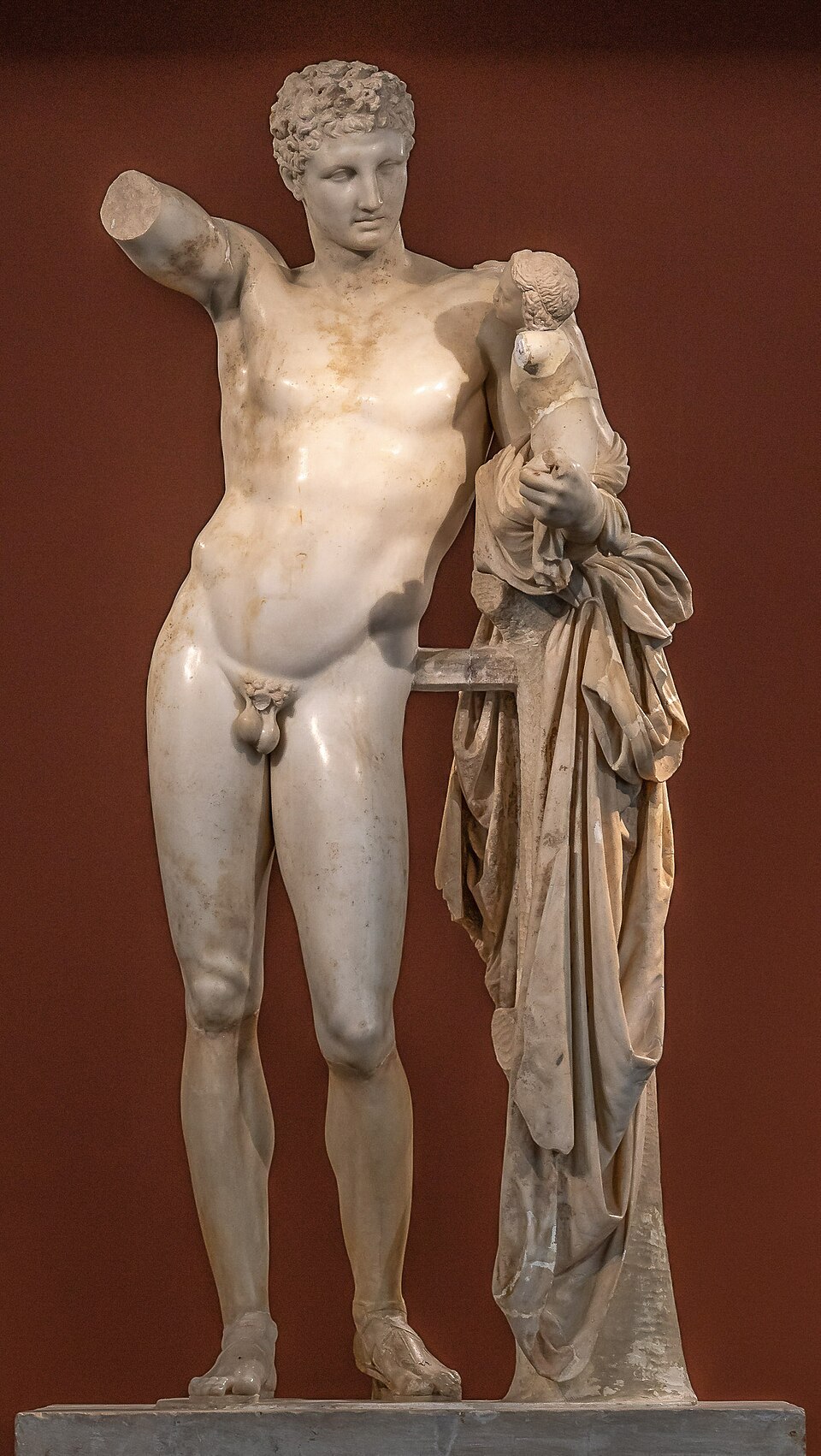
Hermes & Dionysus
Hermes holds baby Dionysus.
Delicate features and gentle human interaction
Missing grapes for infant Dionysus

Dying Gaul
Emotional realism; a mortally wounded Gaul.
Detailed features like mustache, neck band, and expression of pain.

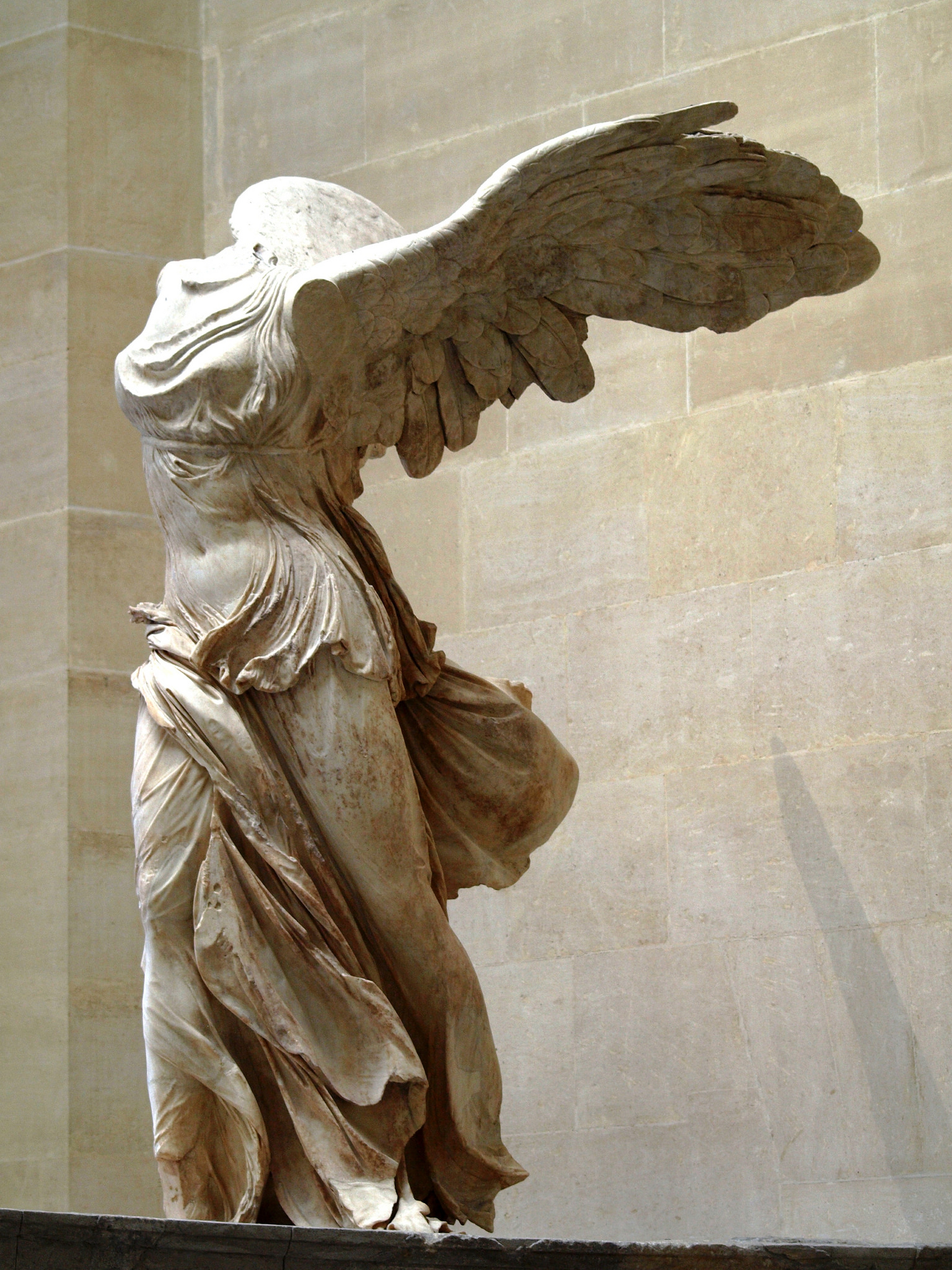
Nike of Samothrace
Victory goddess.
Wind-blown garments and wings suggest movement.
Set on a fountain base; now in the Louvre

Greek Pantheon of Gods
Lived on Mount Olympus.
12 main gods: Zeus, Hera, Poseidon, Hades, Athena, Apollo, Artemis, Aphrodite, Ares, Hermes, Dionysus, Hephaestus, and Hestia.
Aphrodite
Goddess of love, beauty, born from sea foam.
Apollo
God of sun, music, prophecy, medicine — promoted wisdom and moderation.
Zeus
King of the gods, sky/weather.
Poseidon
Sea, earthquakes.
Hades
Underworld, strict ruler of the dead.
Athena
Virgin goddess of wisdom, war strategy, crafts.
Born from Zeus’ head; protector of Athens.
Ares
God of war, destruction; disliked by other gods but lover of Aphrodite.
Greek Creation Myths
Chaos → Gaia & Uranus → Titans → Cronus → Zeus & Olympians
Titanomachy: War between Olympians and Titans.
Greek Morality Myths
Cautionary tales about hubris, fate, and the power of gods.
E.g., Persephone myth explains the seasons.
Physical Map of Greece
Mountainous (80%), many islands, divided by the Corinthian Gulf.
Geography led to development of independent city-states.
The Trojan War
Mythic war sparked by Paris abducting Helen.
Greeks used the "Trojan Horse" trick to win.
Important cultural and literary foundation (Homer's epics).
Ancient Athens
Small in size but rich in culture: democracy, theatre, philosophy, art.
Alexander the Great
Conquered Persia and beyond; spread Hellenism. Died in 323 BCE; empire divided among generals.
Hoplite Warfare
Citizen-soldiers in a phalanx formation.
Led to more democratic participation due to accessible weaponry.
Wars with Persia
Marathon (490 BCE): Greek victory.
Thermopylae (480 BCE): Heroic Spartan stand.
Salamis (480 BCE): Naval win for Greeks.
Plataea & Mycale (479 BCE): Final Persian defeats.
Wars between Greek City-States
Frequent conflicts despite shared culture.
Peloponnesian Wars
Sparta vs. Athens (431–404 BCE); ended Athenian power and Golden Age.
Wars with Rome
Macedonian and Punic wars led to Greek decline.
Rome became dominant Mediterranean power.