IB DP Biology SL 2025 - Unity and diversity: Molecules & Cells
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Polar Covalent
Unequal sharing of electrons
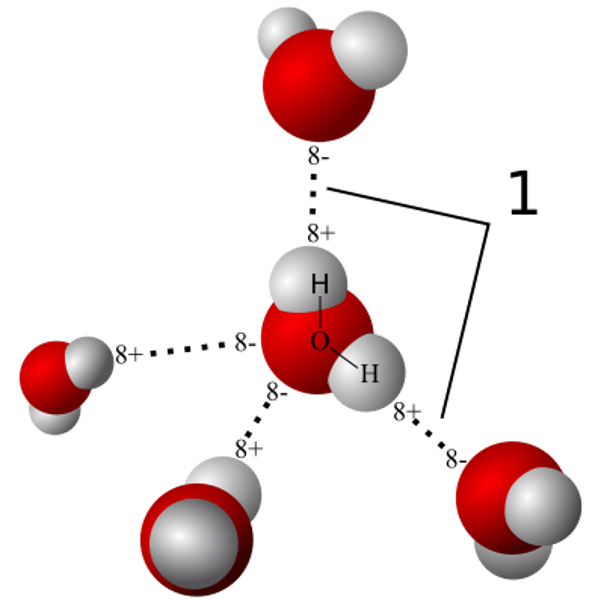
Hydrogen bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
Hydrophobic
Water hating, non-polar
Buoyancy
The ability or tendency to float in water or air or some other fluid.
Viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing
Thermal conductivity
The ability of an object to transfer heat
Specific heat capacity
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of substance by one degree celsius
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances

DNA
Material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information.
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
Double stranded
Structure of DNA
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
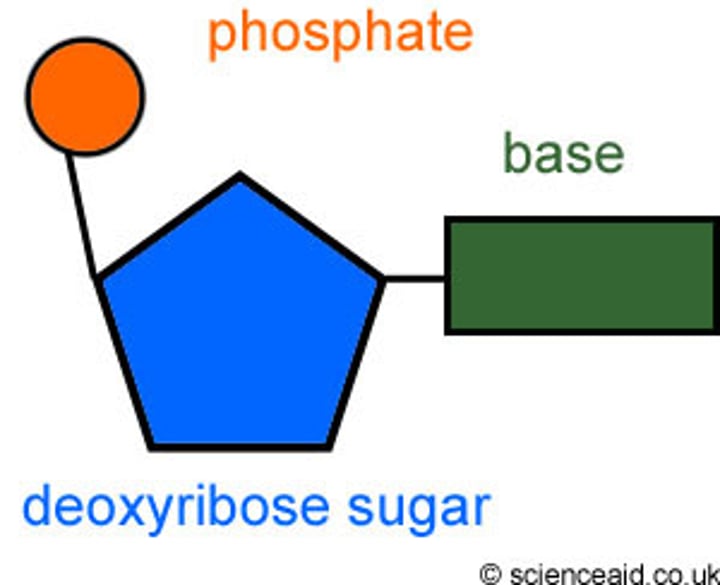
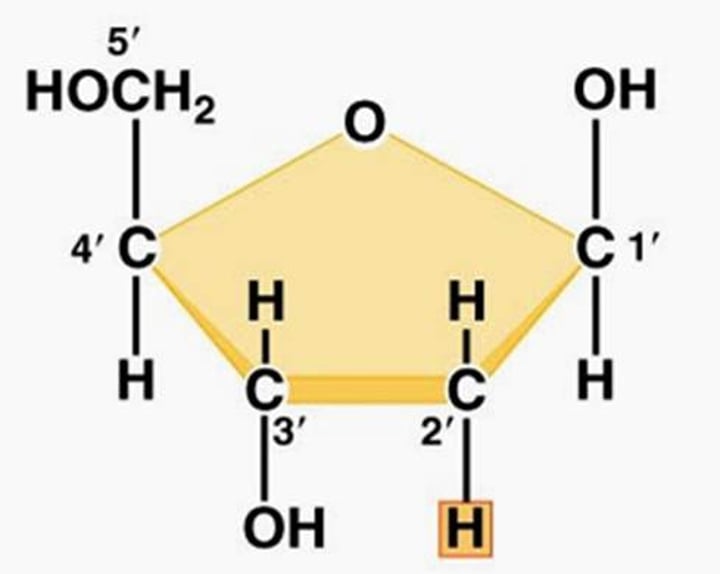
Pentose sugar
A five-carbon sugar molecule found in nucleic acids
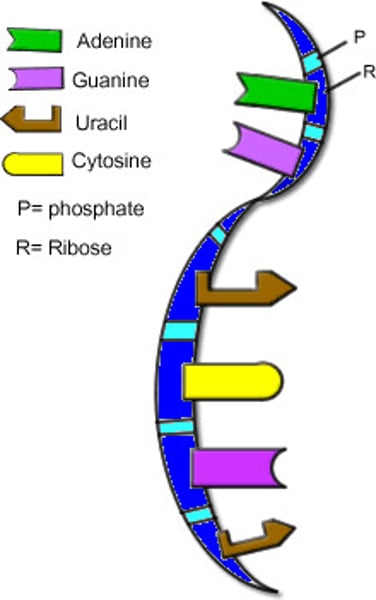
Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracail
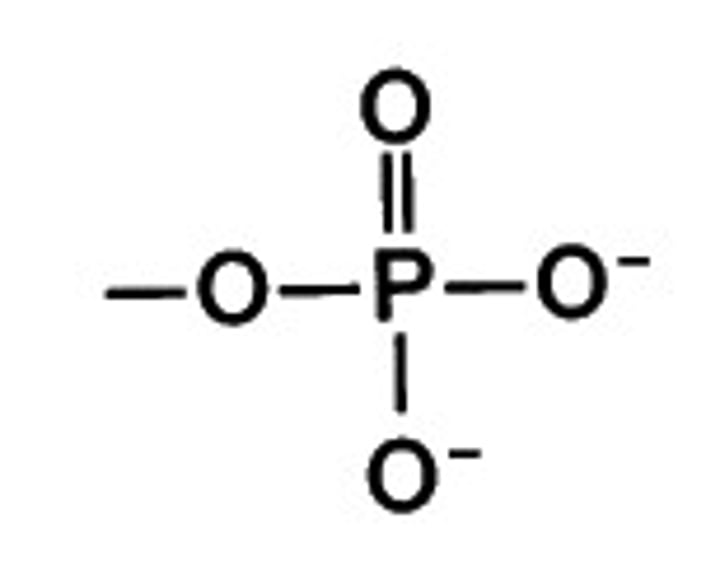
Phosphate group
A chemical group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms; important in energy transfer.
Gene expression
Process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
Adenine and guanine
Nitrogenous bases in DNA
Cytosine and thymine
Nitrogenous bases in DNA
Uracil and cytosine
Nitrogenous bases in RNA
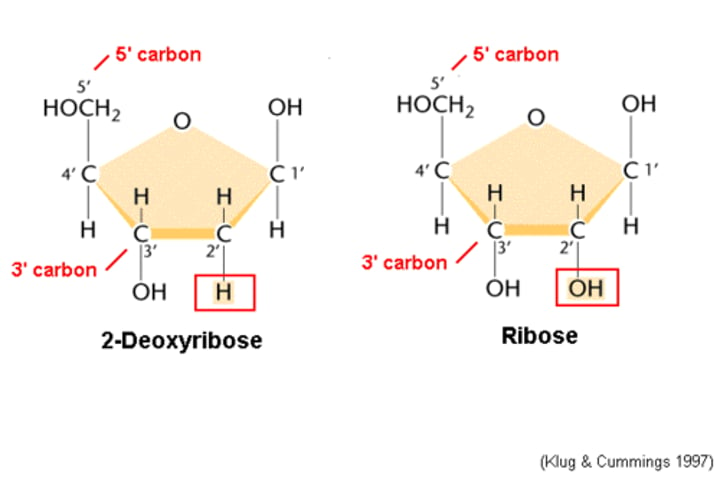
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
Base paring
Nitrogen bases only line up with certain nitrogen bases
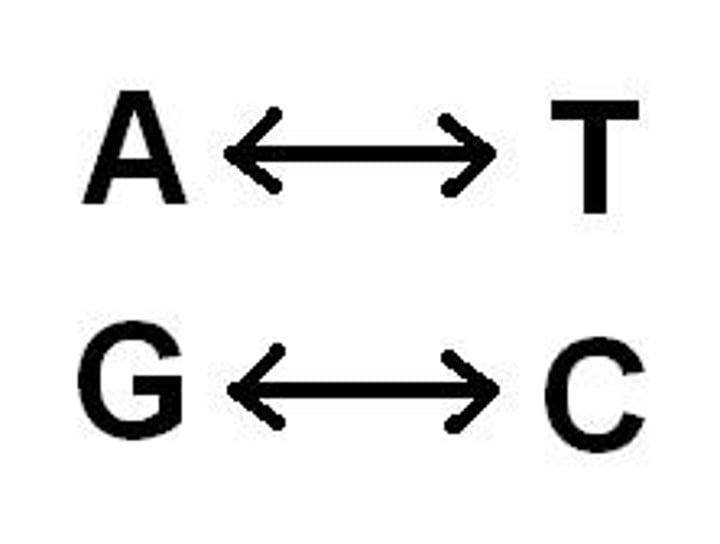
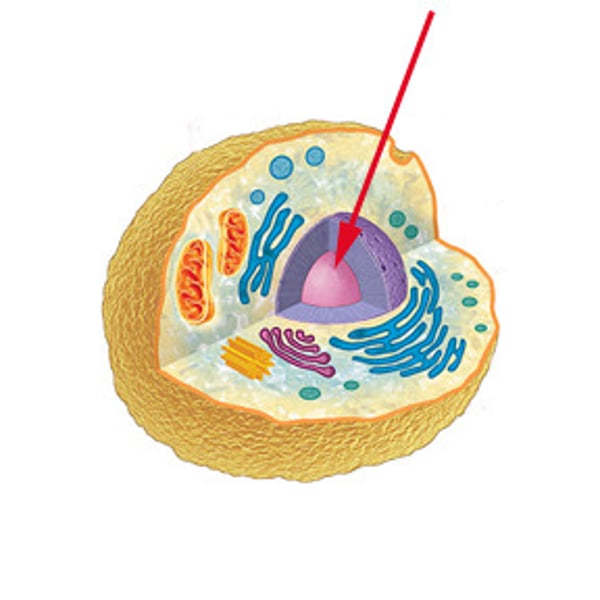
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
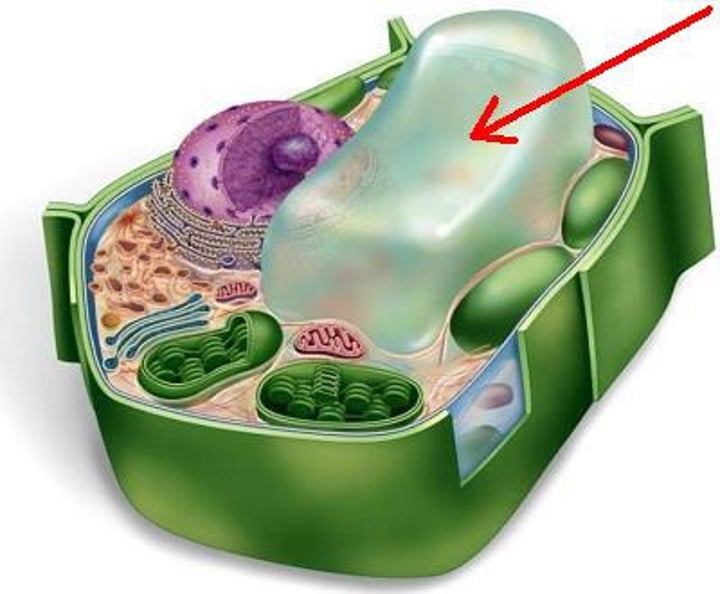
Vacoule
An organelle that stores water, food or other substances; plant cells have a large central vacoule
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
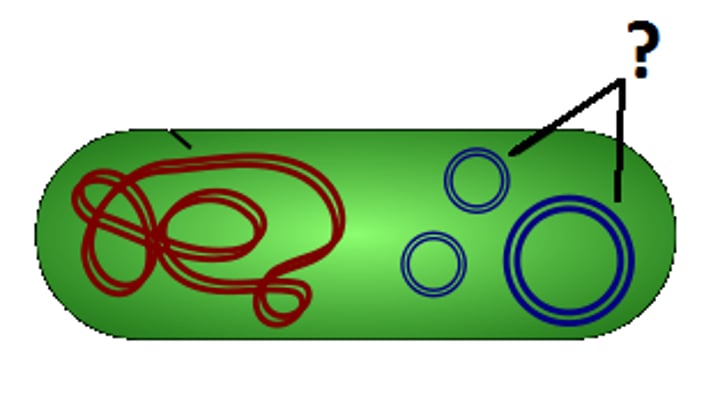
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
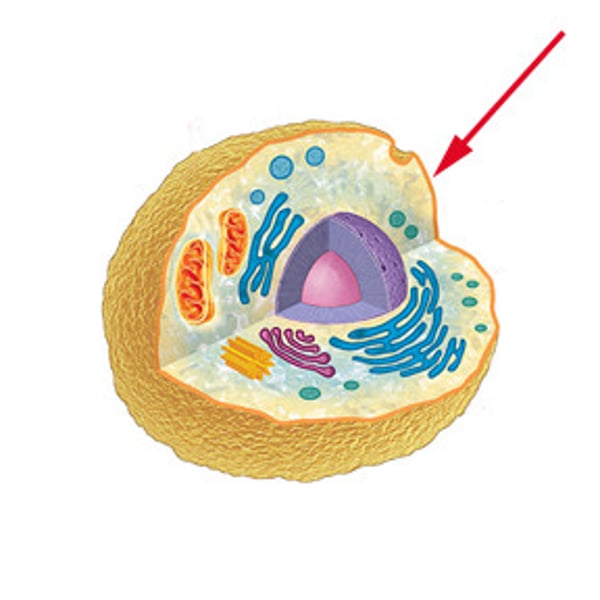
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
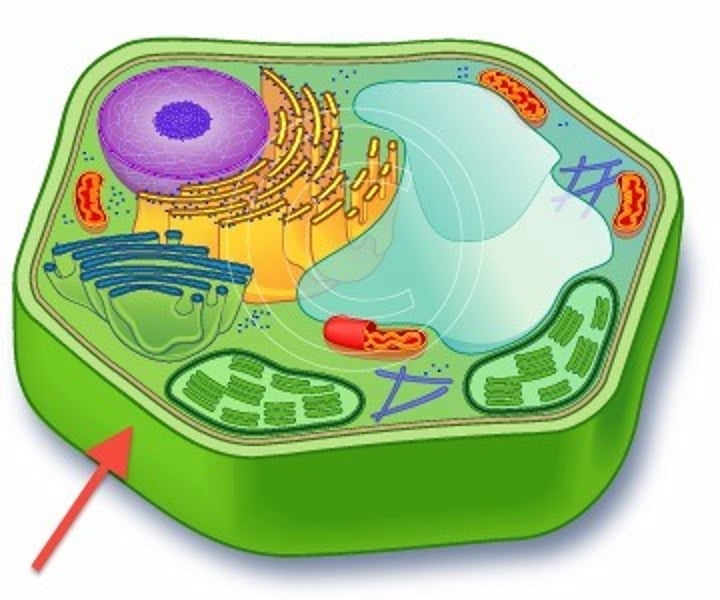
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
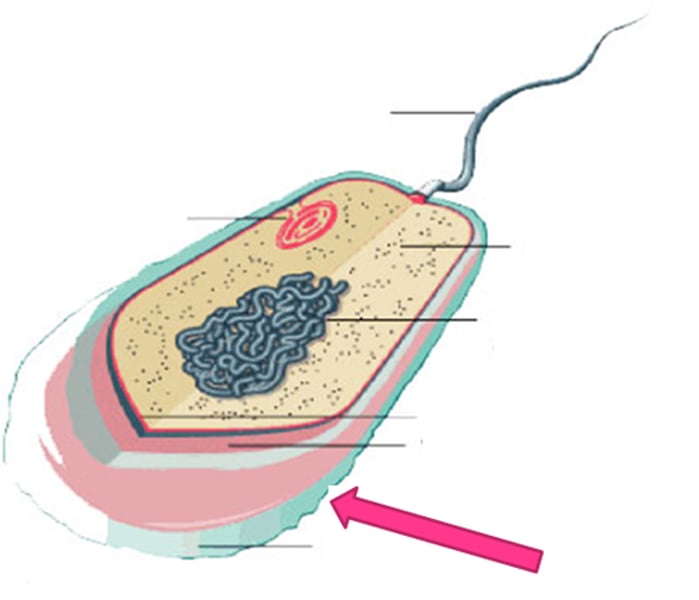
Flagella
Whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
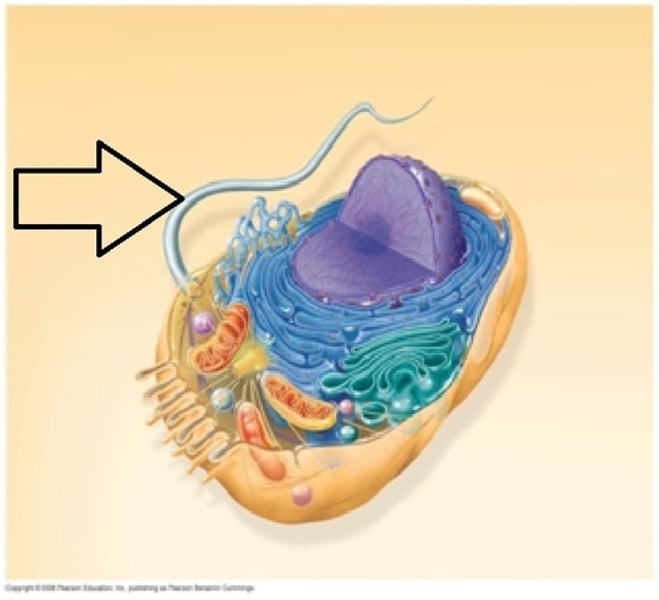
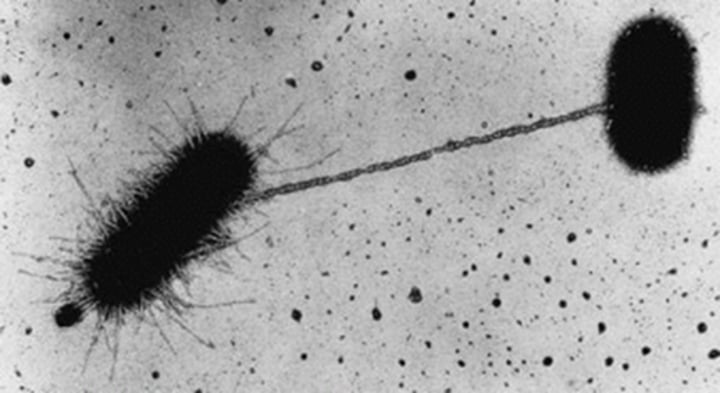
Pili
Short, hairlike protein structures on the surface of some bacteria
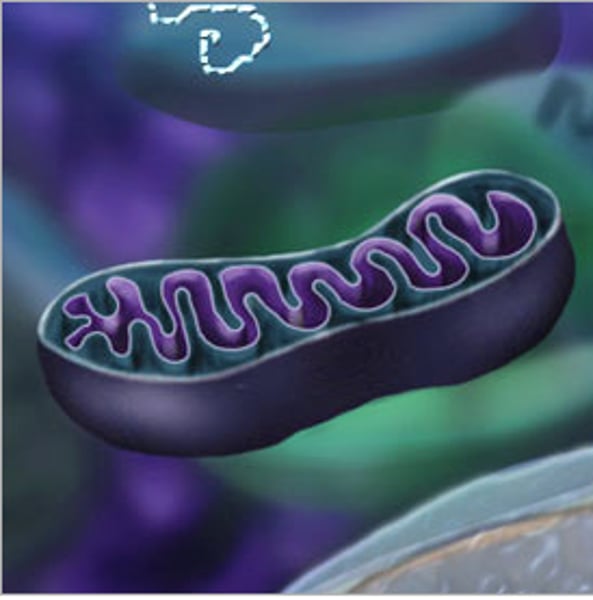
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Cell theory
Idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
light microscope
Microscope that uses a beam of light passing through one or more lenses to magnify an object

electron microscope
Microscope that forms an image by focusing beams of electrons onto a specimen

Advantages of light microscope
Able to view living organisms, relatively inexpensive
Disadvantages of light microscope
Limited magnification and resolution
Advantages of electron microscope
High resolution, good magnification, different computer viewing capabilities (3D, interior etc)
Disadvantages of electron microscopes
Cannot view living specimens, expensive
Specimen
Sample
Resolution of a microscope
The sharpness or clarity of an image.
Magnification
The ratio of an object's image size to its real size
Freeze fracture microscopy
Cells are frozen and then a knife is used to crack them open. The crack often passes through the interior of cell and internal membranes. The "bumps" that appear are usually large proteins or aggregates embedded in the interior of the membrane.
Cryogenic electron microscopy
A technique in which samples are frozen to cryogenic temperatures, then viewed using electron microscopy.
Immunofluorescence
Method of tagging antibodies with a luminating dye to detect antigen-antibody complexes
Fluorescent dyes
Staining technique using special microscopes that detect chemical fluorescence due to special stains
Prokaryotic
cells that do not have a nucleus
Eukaryotic
A cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can be unicellular (protists) or multicellular (fungi, plants and animals).
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Unicellular
Made of a single cell
Multicellular
Consisting of many cells
Naked DNA in loop
Not associated with histone proteins (as it is in eukaryotic cells)
Compartmentalisation
The formation of separate membrane-bound areas in a cell
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Produces and stores lipids, including steroids.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Has ribosomes attached to its surface which produce proteins that are usually destined for use outside the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
Processes and packages proteins, which are then released in Golgi vesicles.
Vesicle
Small sac that transports and releases substances produced within the cell by fusing with the cell membrane.
Cytoskeleton
A system of protein fibres called microtubules and microfilaments. The cytoskeleton helps to hold organelles in place and maintain the structure and shape of the cell.
Archea
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan