Sigma AP Score - AP HUG
1/387
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All Definitions Units 1-5 & 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
388 Terms
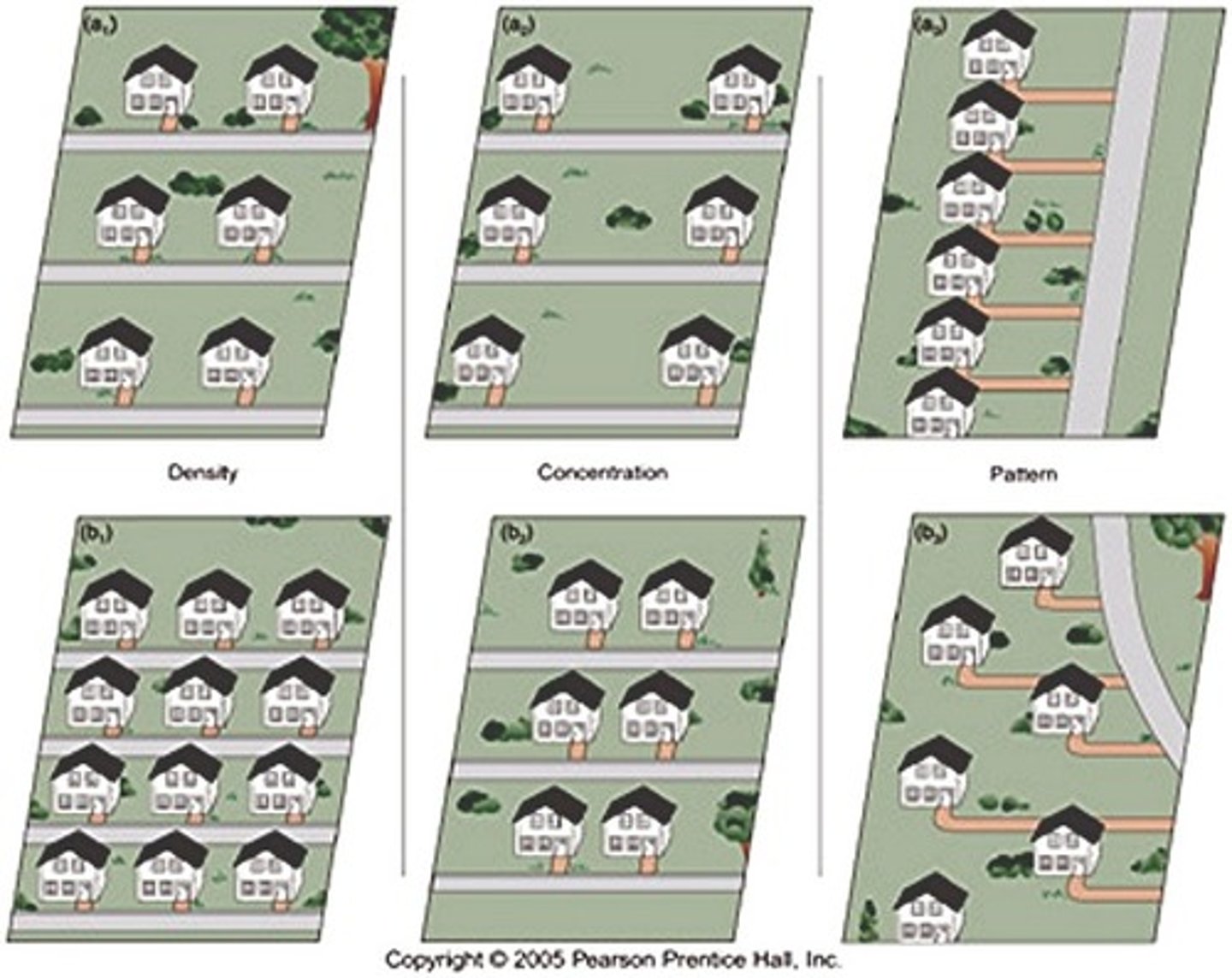
3 Types of Distribution
density, concentration, and pattern
Absolute distance
describing how far a distance is quantitative units of distance (miles, kilometers, etc.)
Absolute location
describing where something is using the exact site on an objective coordinate system
Capitalism
an economic system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled mainly by private owners for profit, rather than by the state - limited government control of the economy

Cartography
the science and art of drawing maps

Case study
detailed observations that provide insight into a group of people in a specific area

Census
an official count of individuals in a population (in the USA, it happens every 10 years)

cold war [lower case]
a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats short of open warfare

Cold War [upper case]
the state of political hostility that existed between the Soviet Union and the US and their allies from 1945 to 1990

Communism
an economic system in which all (or nearly all) trade and industry are collectively owned by the state and not by individual citizens - near total control of the economy by the government

Concentration
how closely packed together objects are
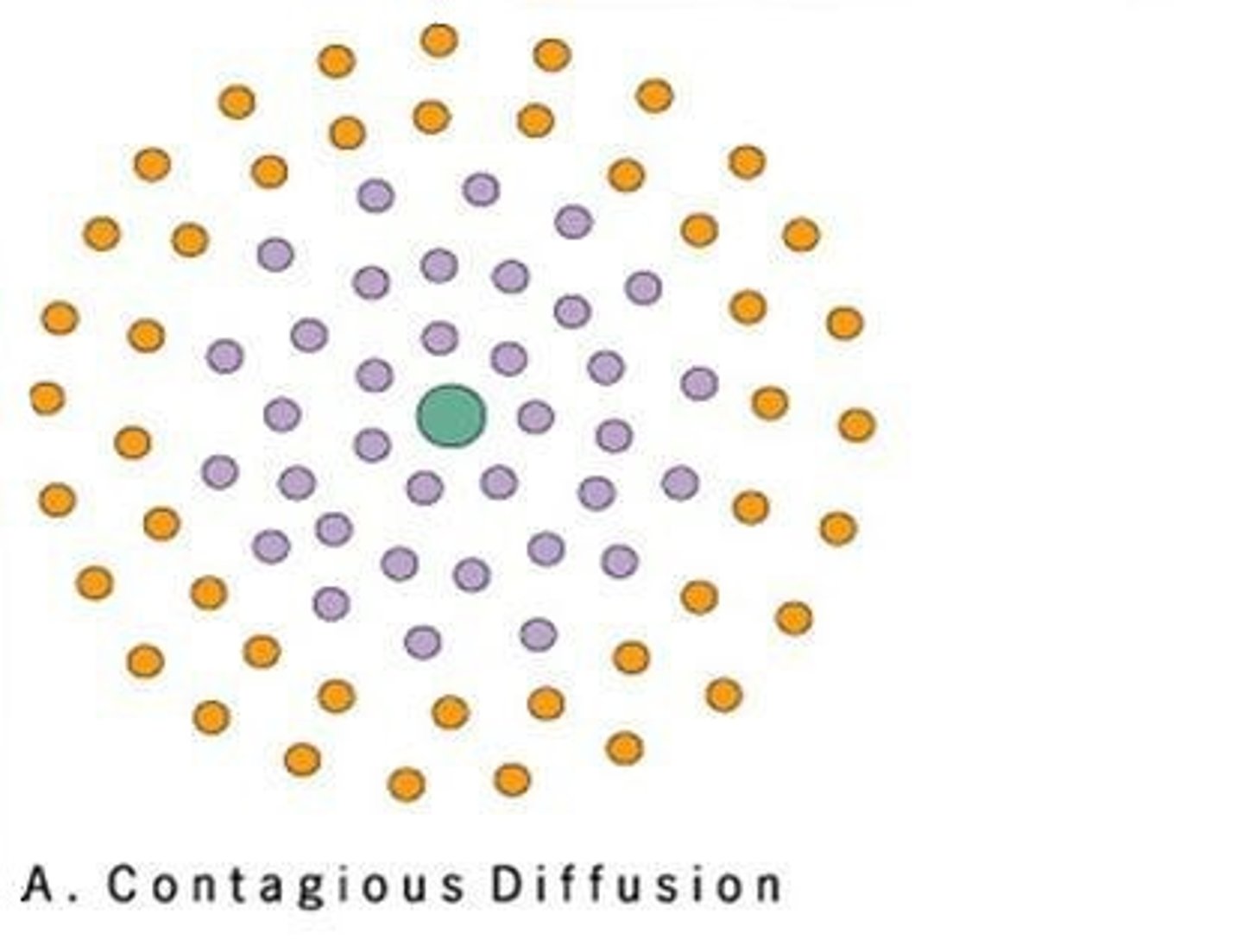
Contagious diffusion
when a cultural trend is transmitted from person to person from an original source to numerous others, similar to a virus or viral video
Cultural Landscape
the title of our textbook and more importantly, the visible changes that humans make to the enviroment including buildings, crops, and signs

Culture
the social heritage of a group or their way of life - major components are language, religion, ethnicity, food, and roles

Density
the number of things divided by the measurement of area
Diffusion
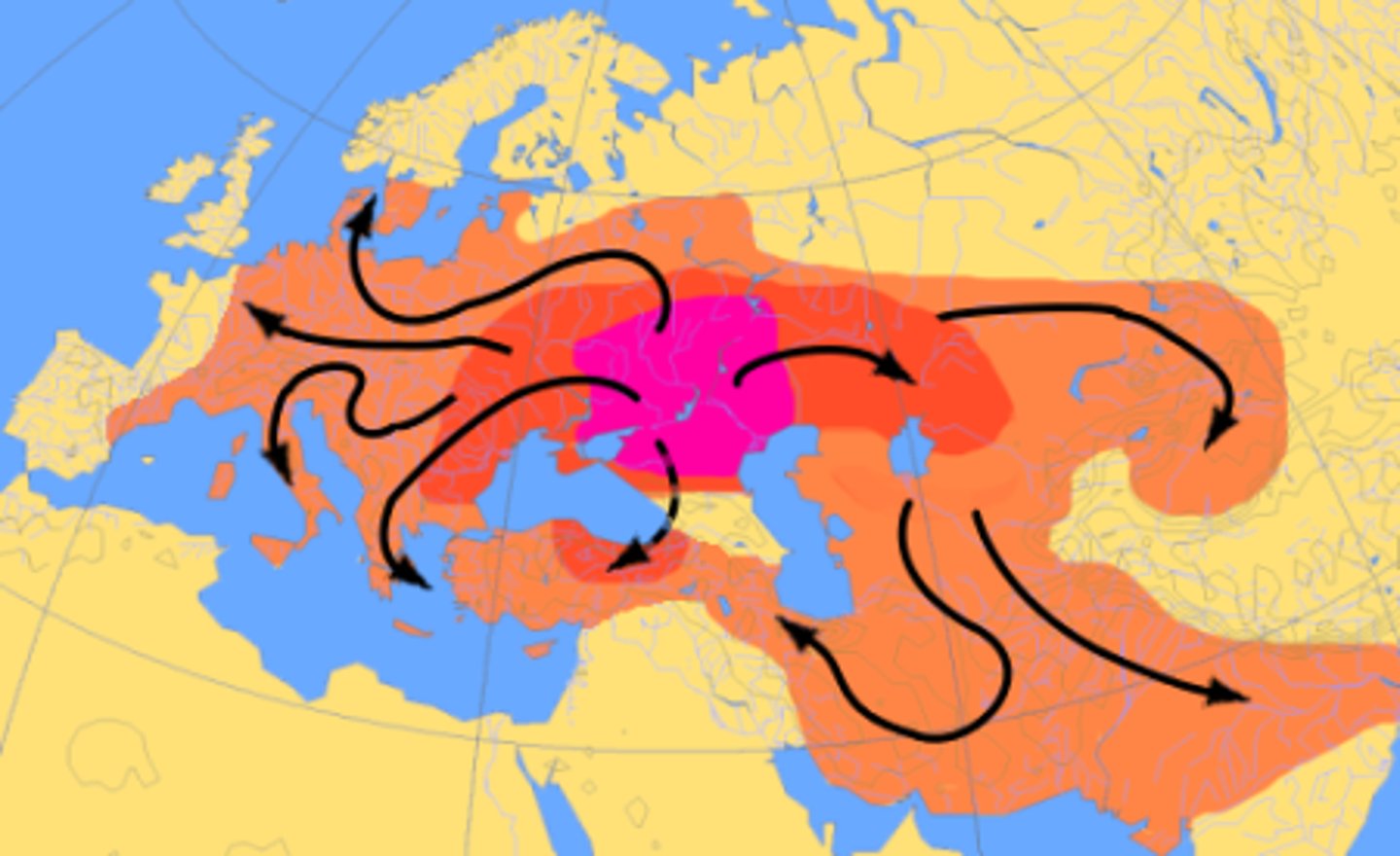
a feature or idea that is spread from its originating place, outward - the 3 types are contagious, hierarchical, and stimulus diffusion

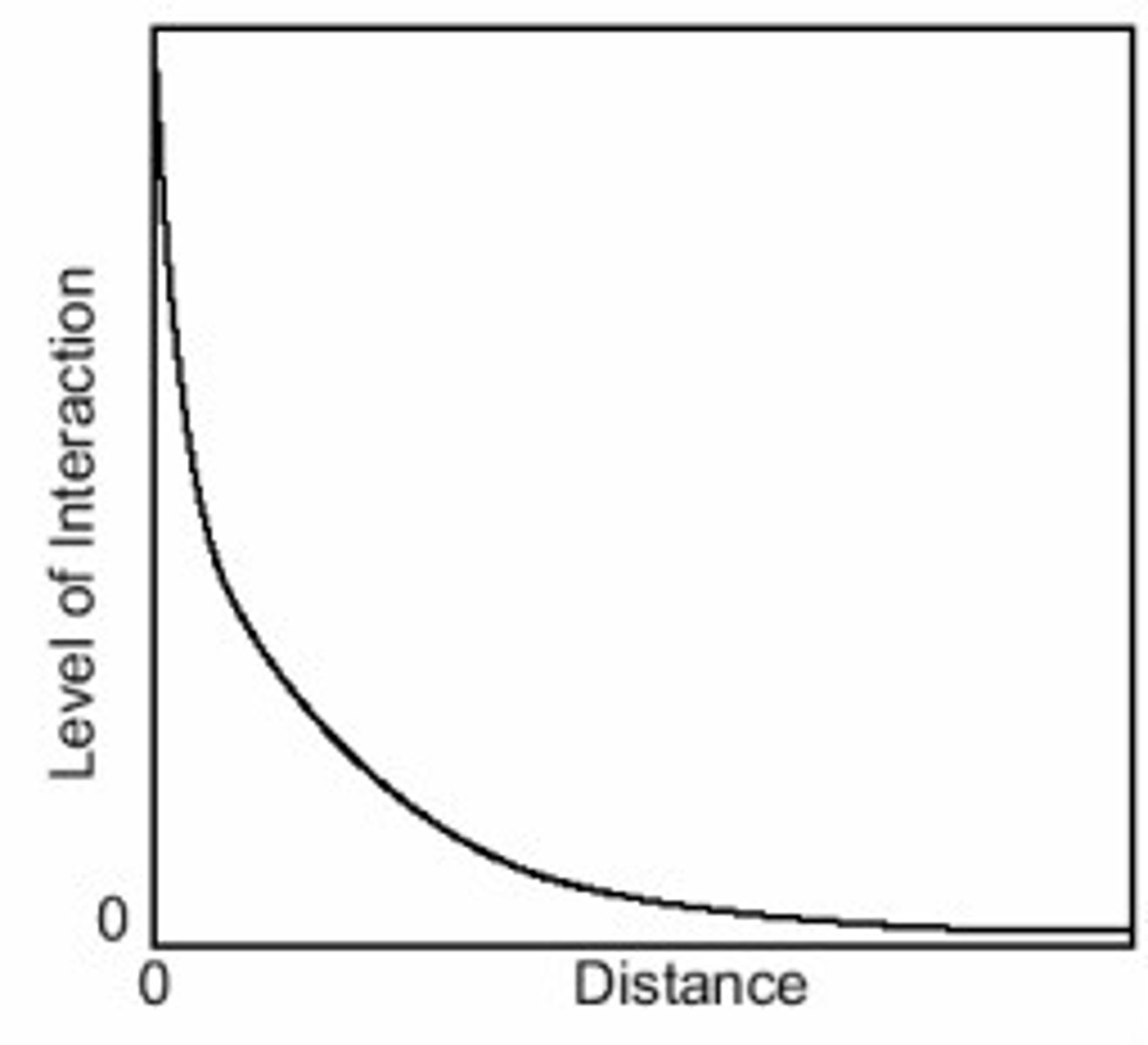
Distance decay
the idea that the interaction between two places declines as the distance between them increases
Environmental determinism
the belief that a physical environment is THE reason that some societies are strong while others are weaker
Environmental possibilism
the belief that a physical environment plays a role in the development of a society, but is NOT the ONLY factor at work
Expansion diffusion
a trend is spread from its originating place, outward
Formal region
a region that is based entirely on something that can be identified and documented or measured - all government areas are this because they share a government
Friction of distance
a metaphor that explains that effort must be used to overcome distance

Functional region
a region based around a node or focal point - terrestrial radio broadcasts are an example of this
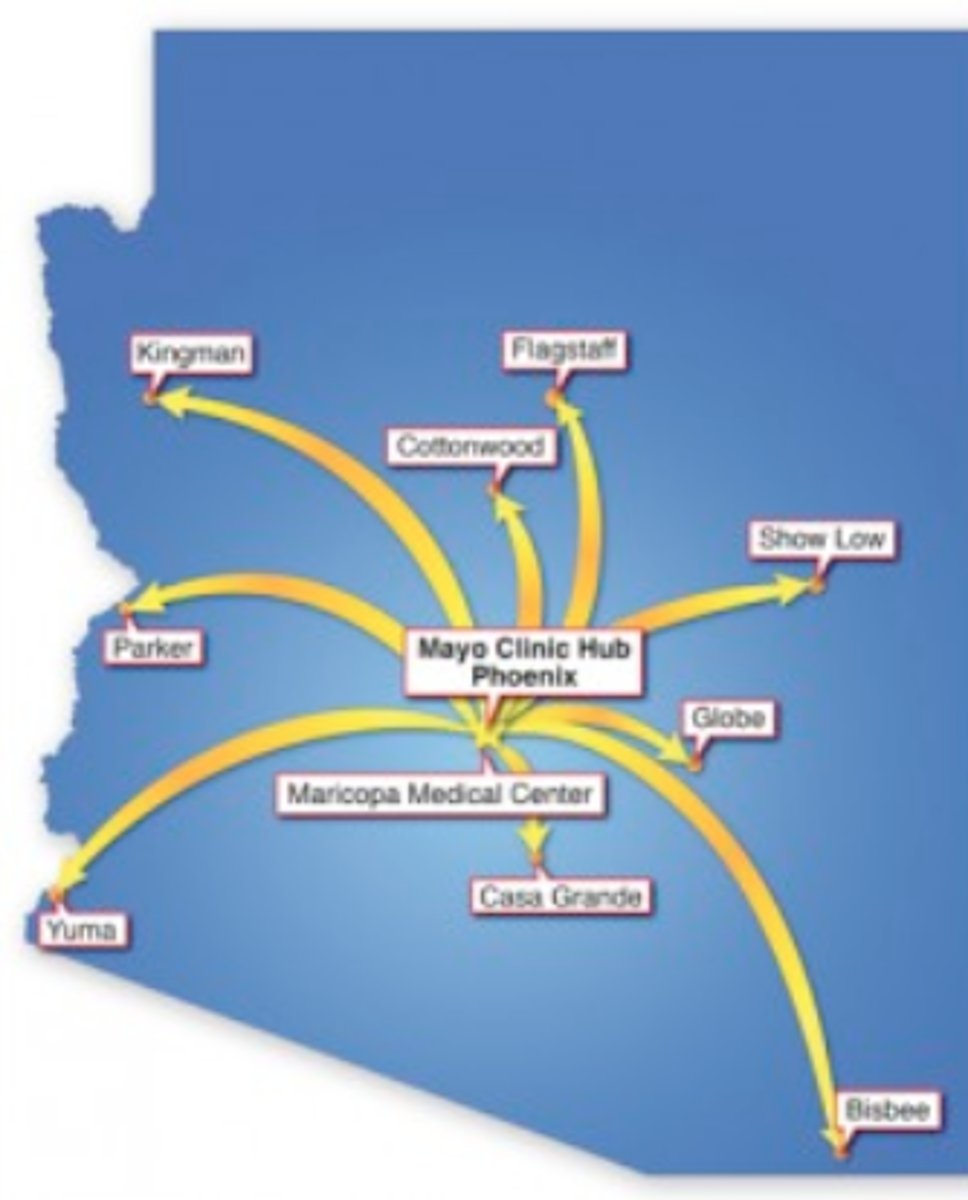
Geospatial
relating to data that is specific to one location

GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
software that captures, manages, analyzes, and displays data that is collected geographically
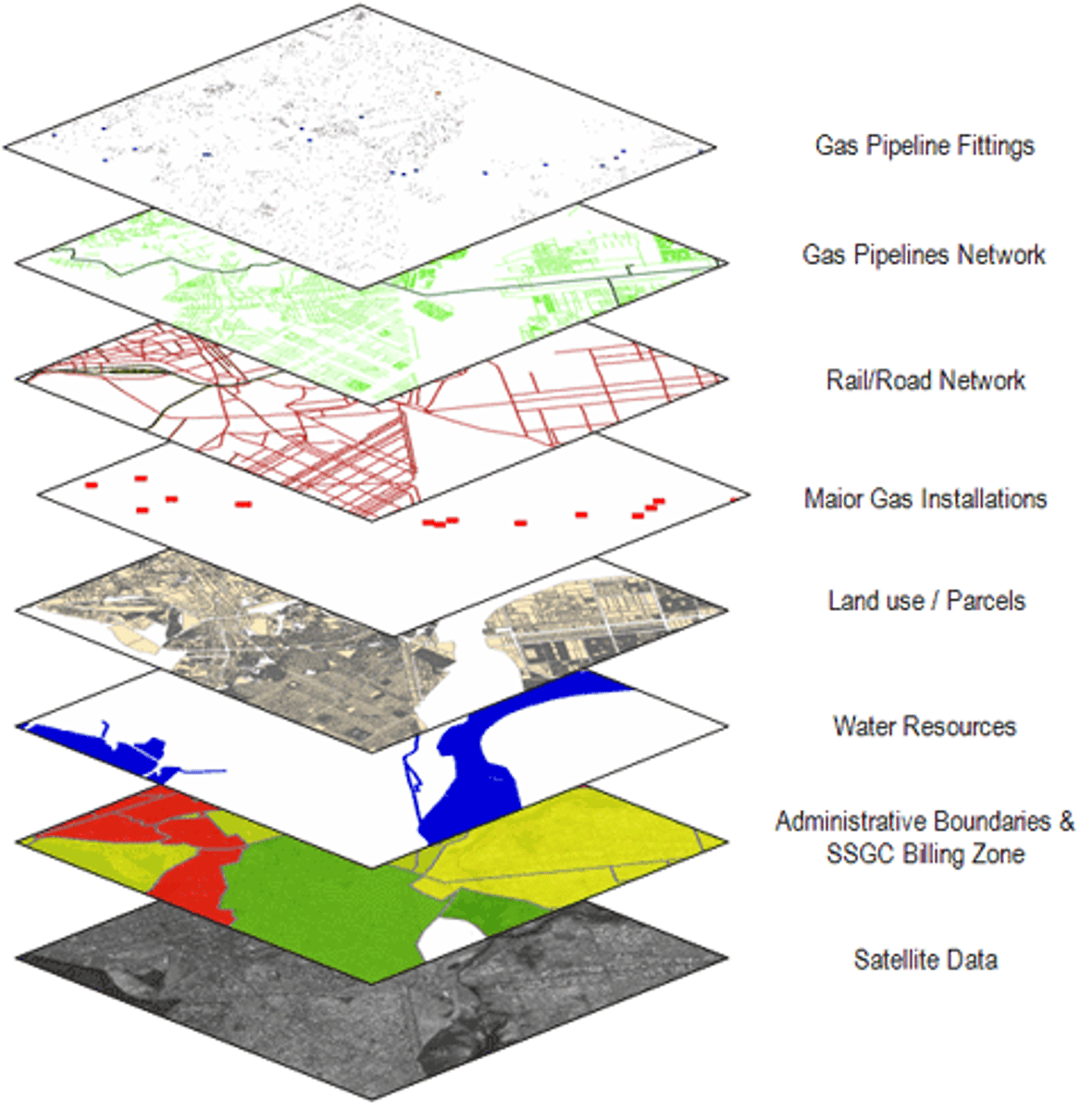
Globalization
worldwide integration and development which results in the expansion of international cultural, economic, and political activities

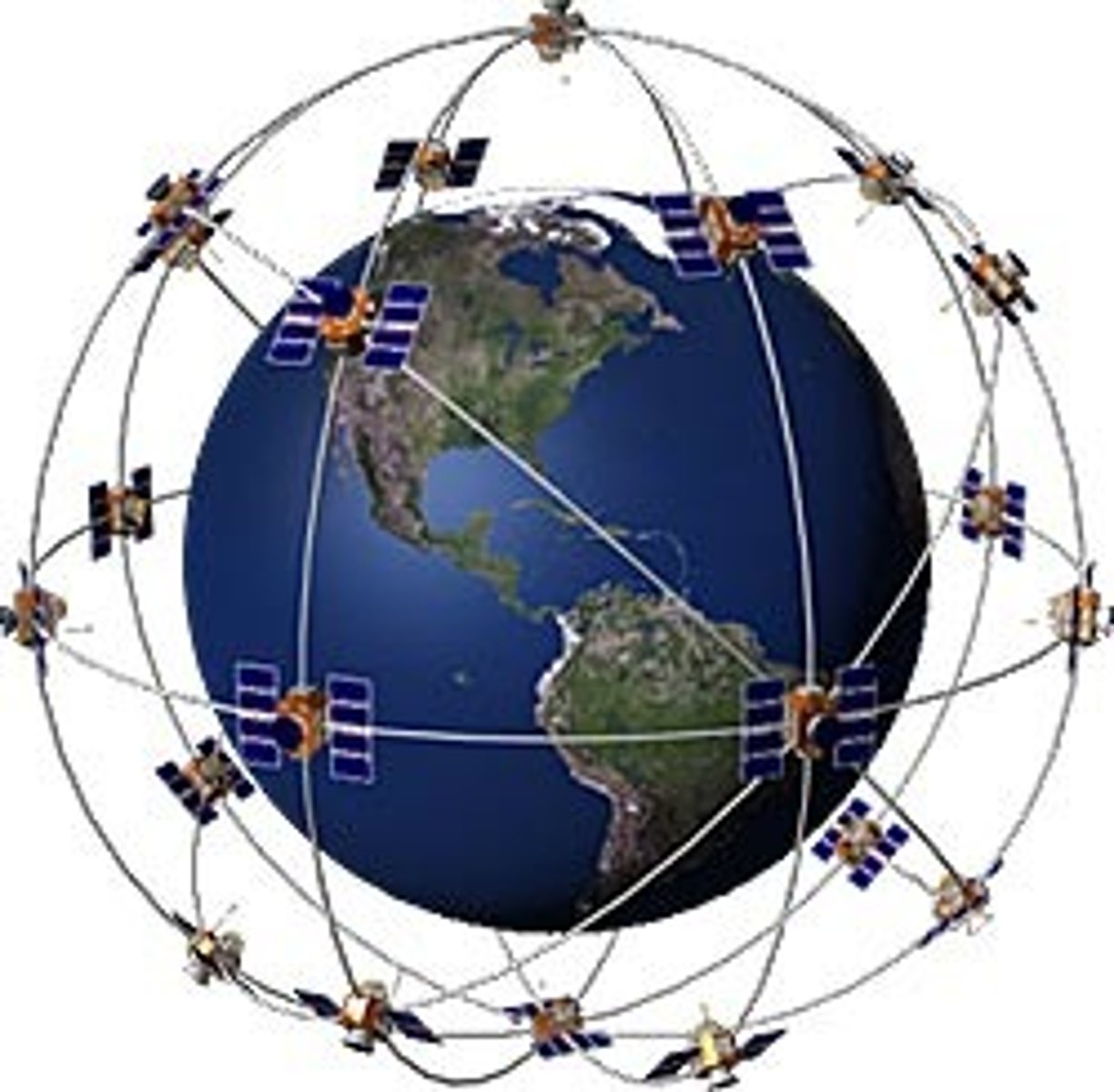
GPS (Global Positioning System)
a system that measures distance from a series of satellites to determine location on the planet
Gravity Model of Spatial Interaction
the most important model in geography - (population1 x population2)/distance squared - the interconnectedness of 2 places depends on their distance and population

Hearth
a source of culture (where a culture began)
Hierarchical diffusion
the spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places
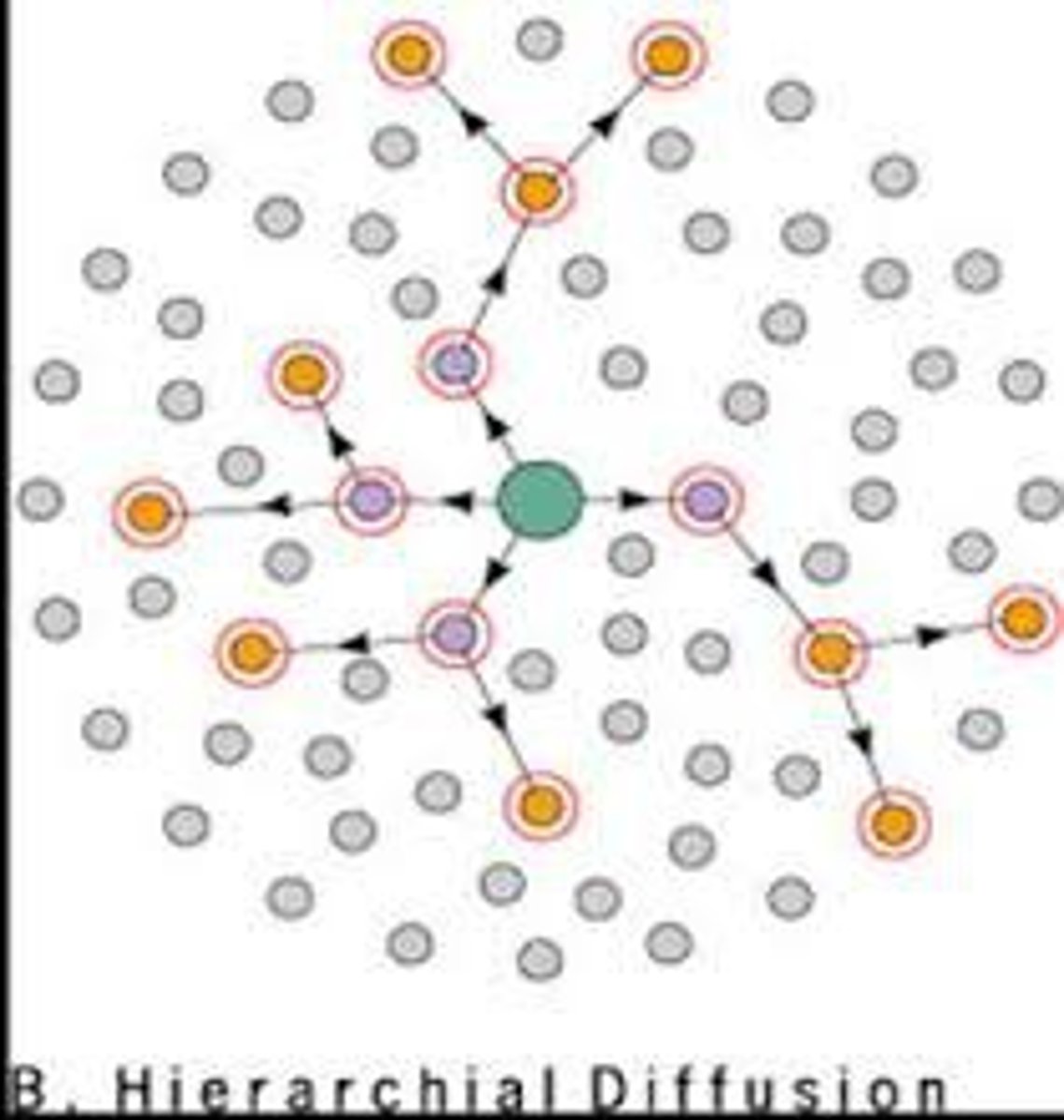
Infrastructure
the basic facilities and installations that help a government or community run, including roads, schools, phone lines, sewage treatment plants and power generation

Natural resource
a physical material constituting part of Earth that people need and value

Projection
a method of taking a 3D object and putting in on a 2D plane
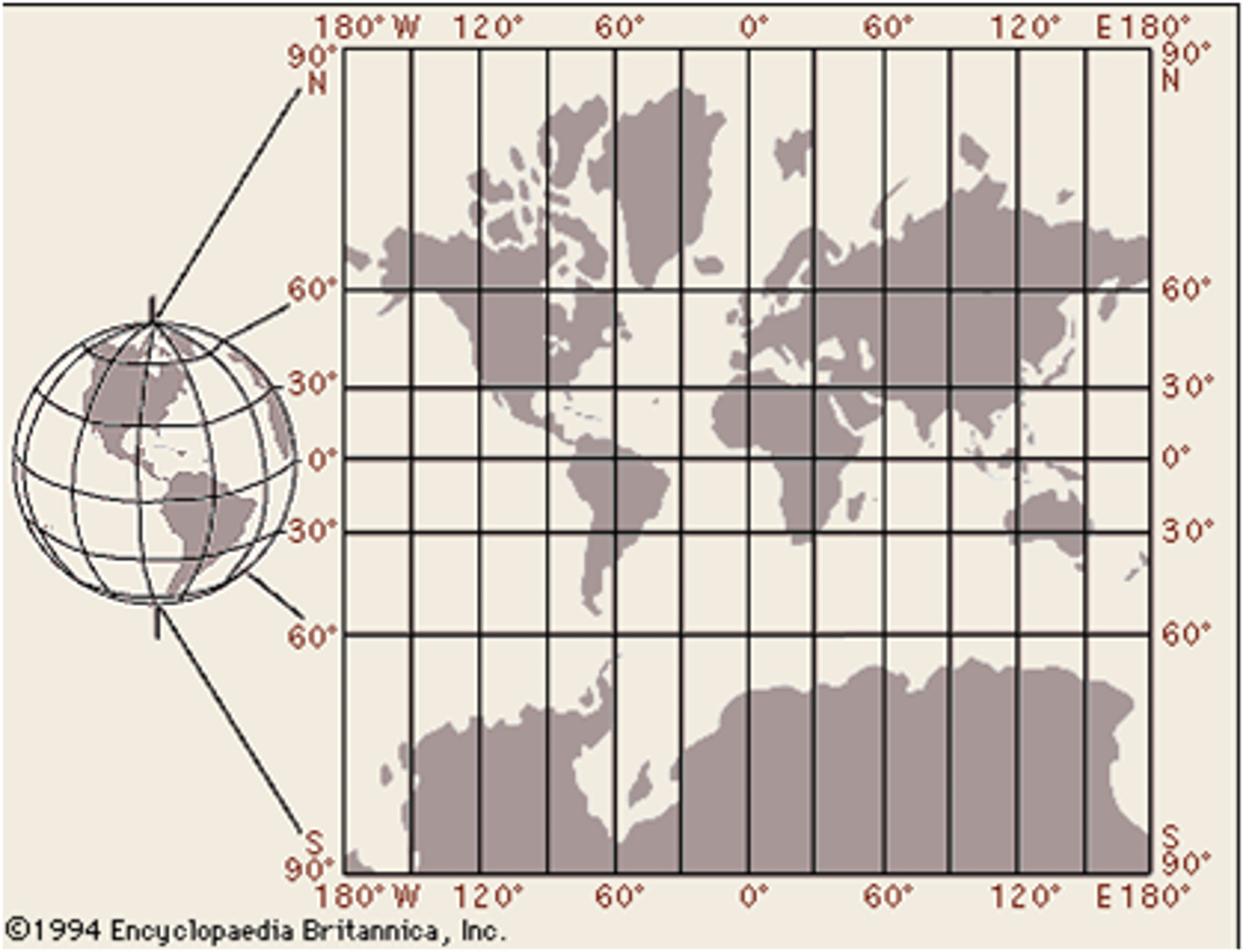
Qualitative data
subjective information that is opinion based, is usually descriptive, and often expressed as text
Quantitative data
objective data that is fact based, usually measurable and usually expressed in numbers
Reference map
maps that emphasizes the location of places (without data attached)

Region
a place larger than a point and smaller than a planet that is grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
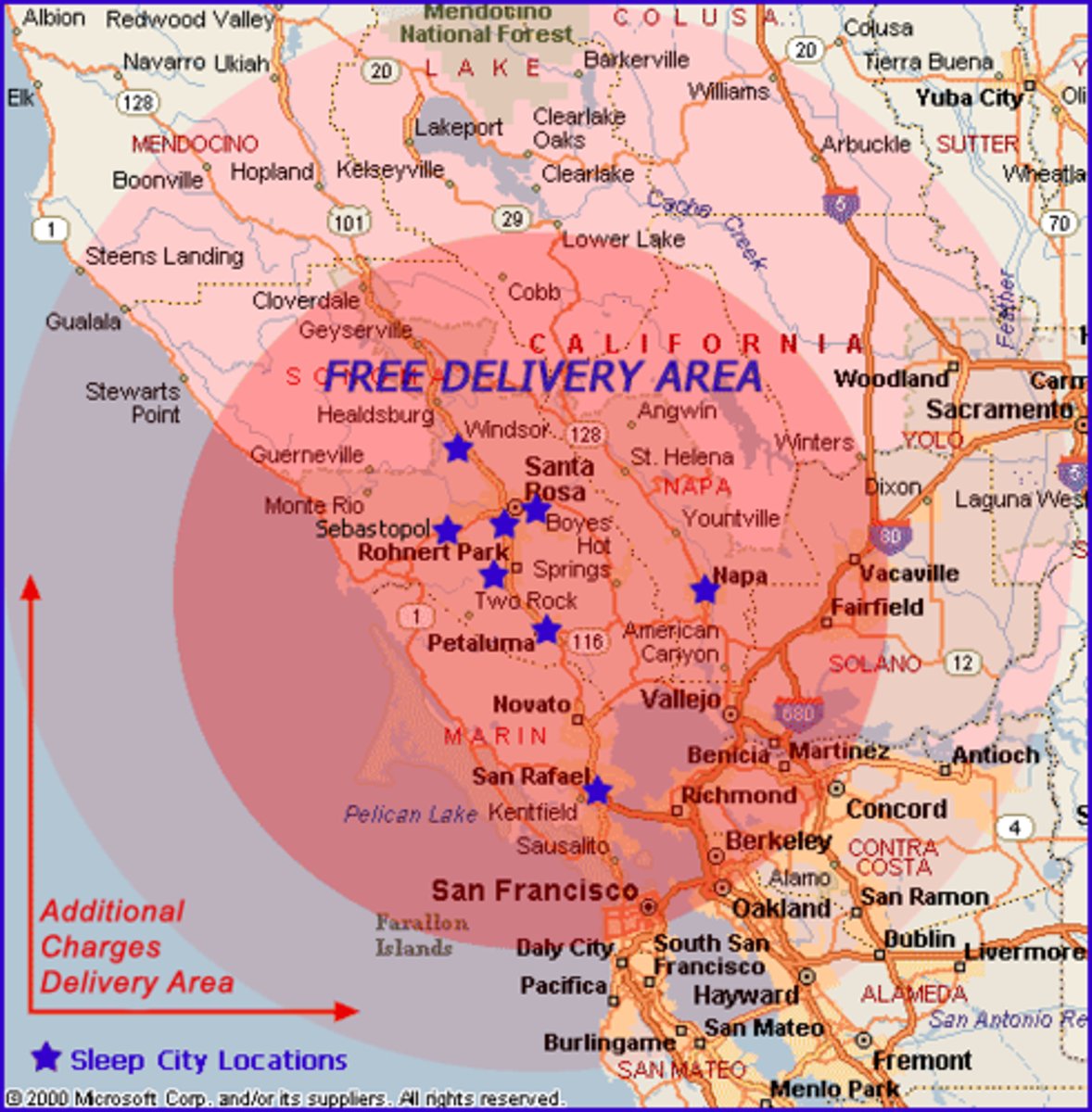
Relative distance
describing the distance between locations using qualitative terms or non-traditional measurements of distance (one hour north of)

Relative location
describing the position of a place as compared to (or relative to!) another landmark
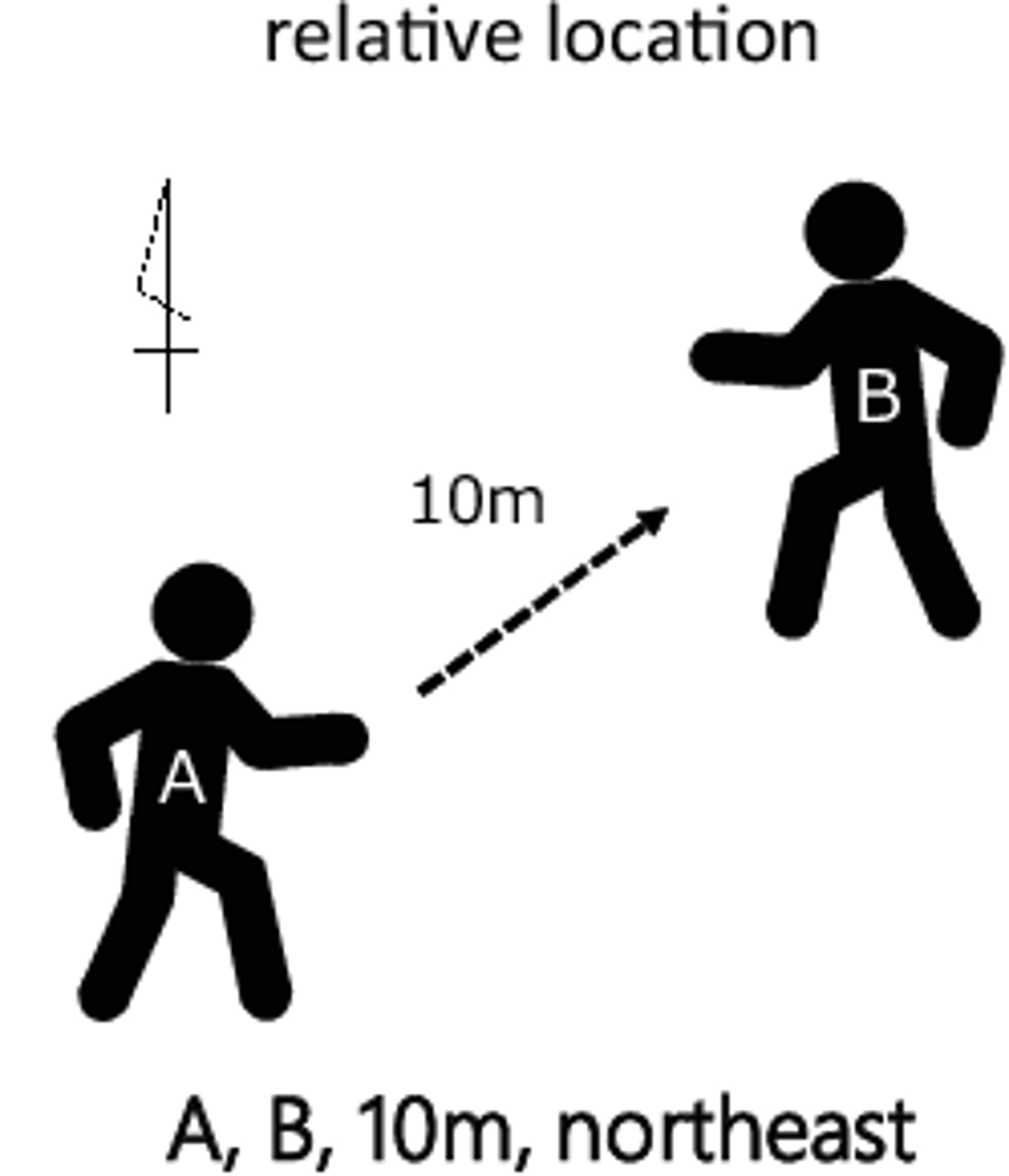
Relocation diffusion
the physical spread of a feature or trait by people migrating
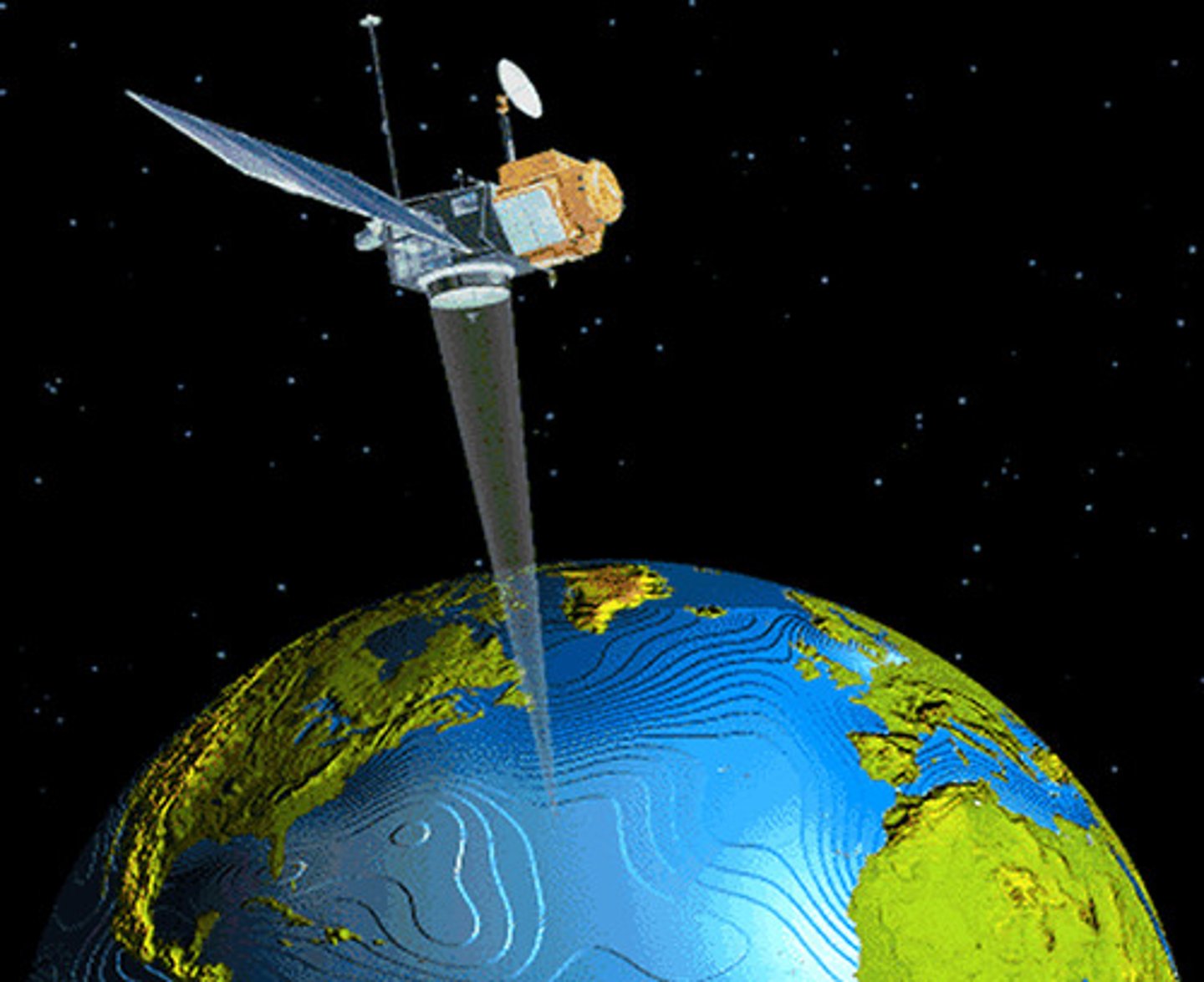
Remote sensing
the science of making measurements of the earth using sensors on airplanes or satellites
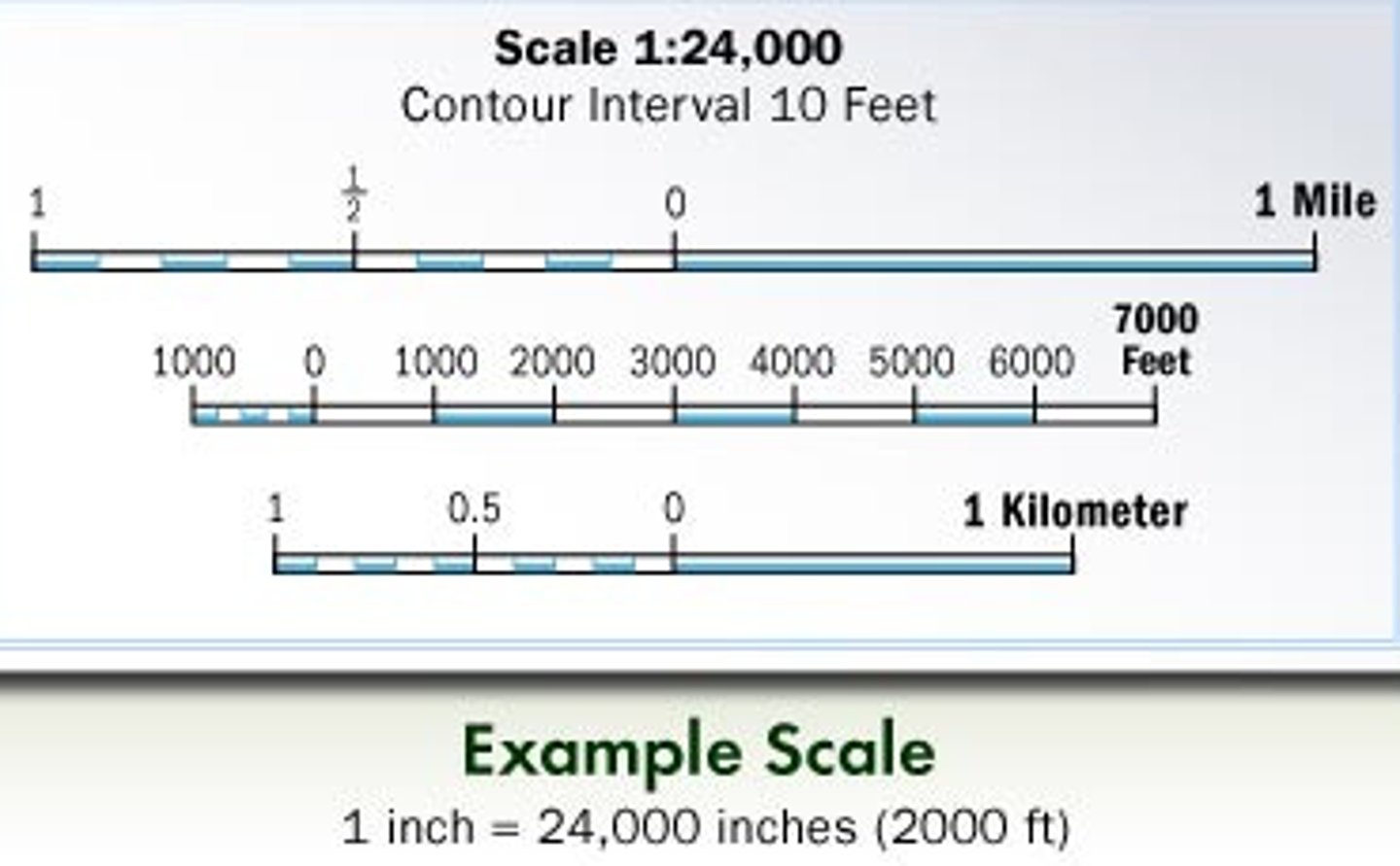
Scale
the relationship between the distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a specific map
Scale of analysis
how zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data
Socialism
an economic system in which trade and industry are partially collectively owned by the state and partially privately owned by individual citizens - partial control of the economy by the government

Spatial
it's not as complicated as it sounds - a fancy word for describing how things are organized in space
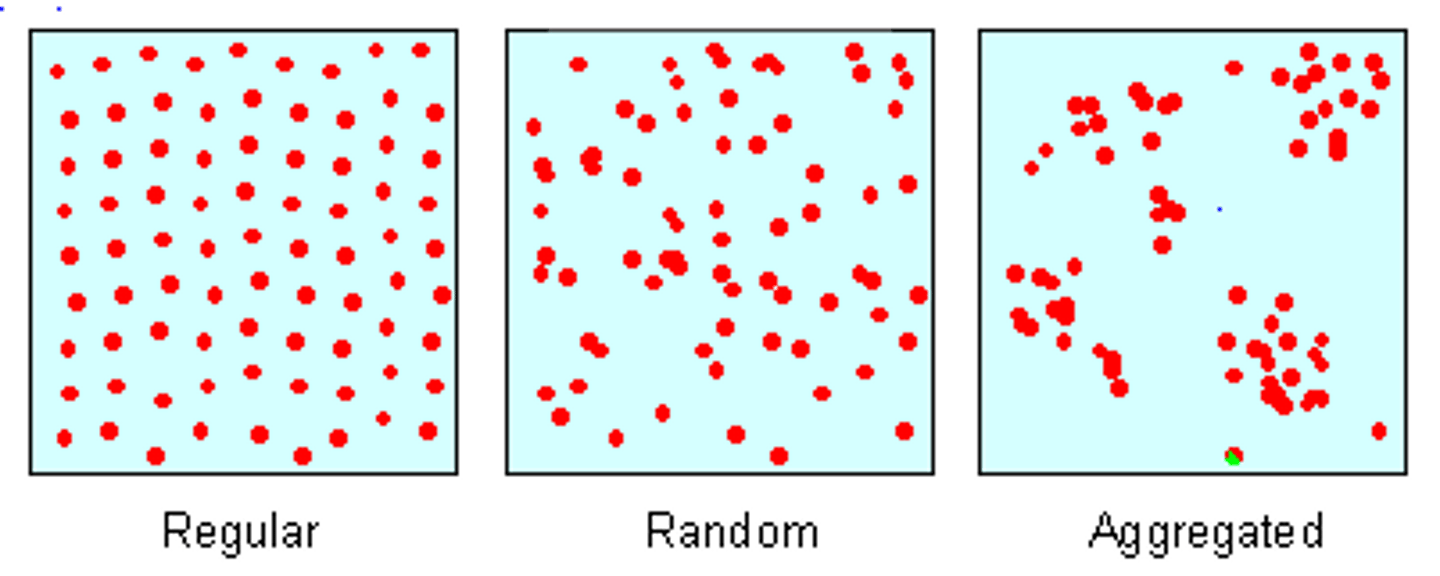
Spatial distribution
arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface
Spatial Interaction
the flow of goods, people, or information among places, in response to localized supply and demand
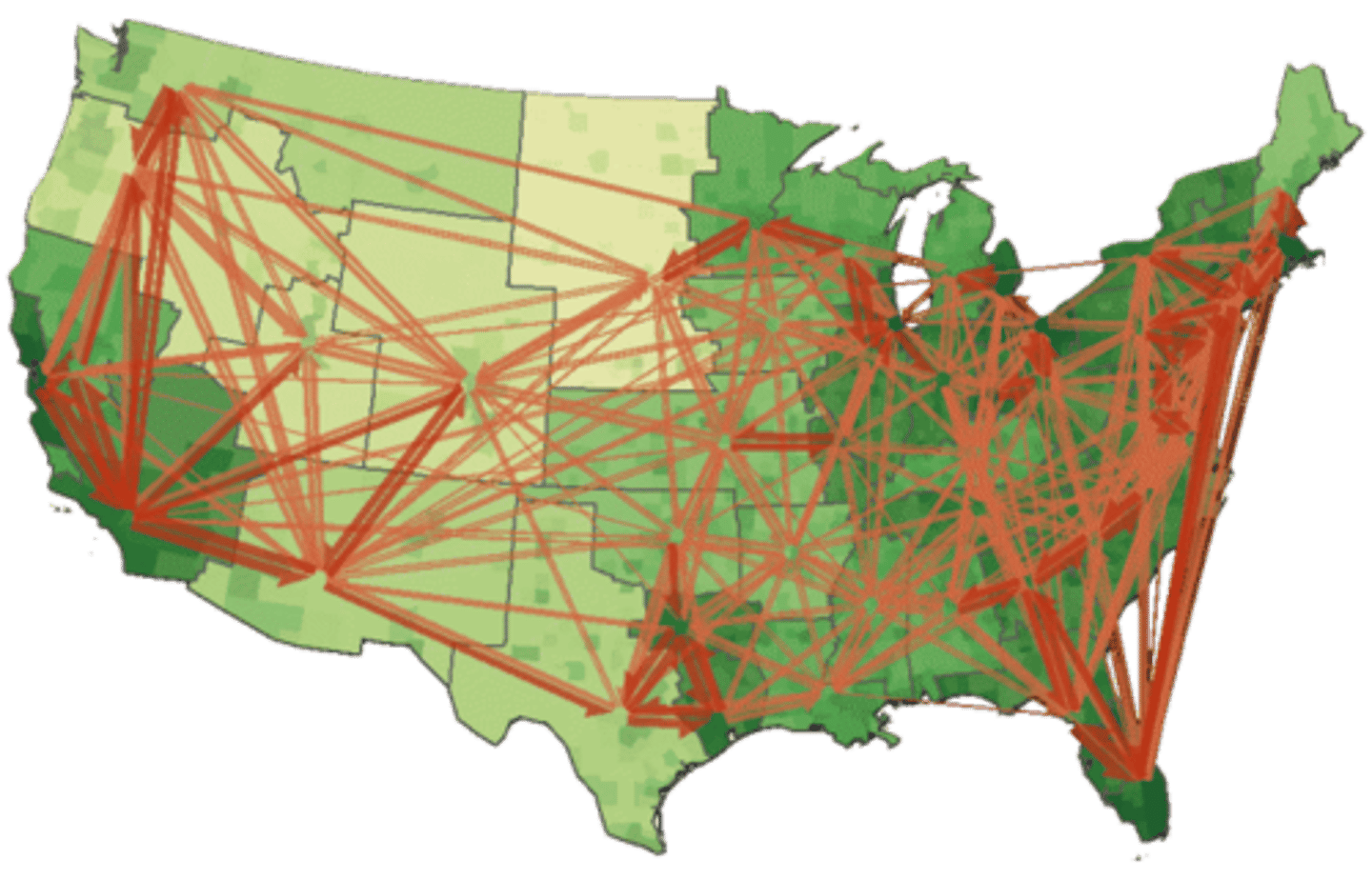
Stimulus diffusion
when a feature or idea spreads, but is changed by those adopting the idea

Sustainability
the goal of the human race reaching equilibrium with the environment; meeting the needs of the present without while also leaving resources for future generations

Temporal
relating to time

Thematic maps
a map that displays not only locations but maps a topic or theme of information with the location
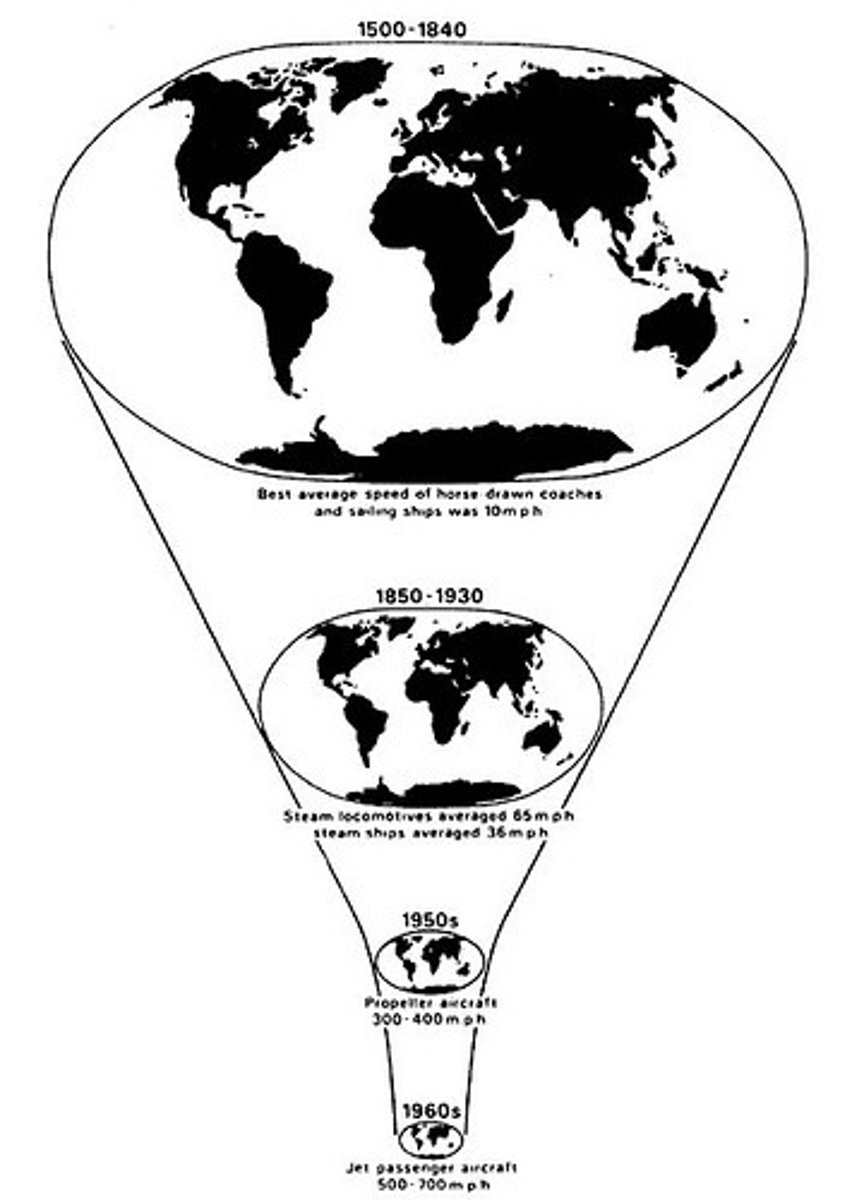
Time-space compression
the idea that the world feels smaller than it used to because of increased technology in transportation and communication
Toponym
a place name

Uneven development
unequal distribution of people, resources, and wealth within a region

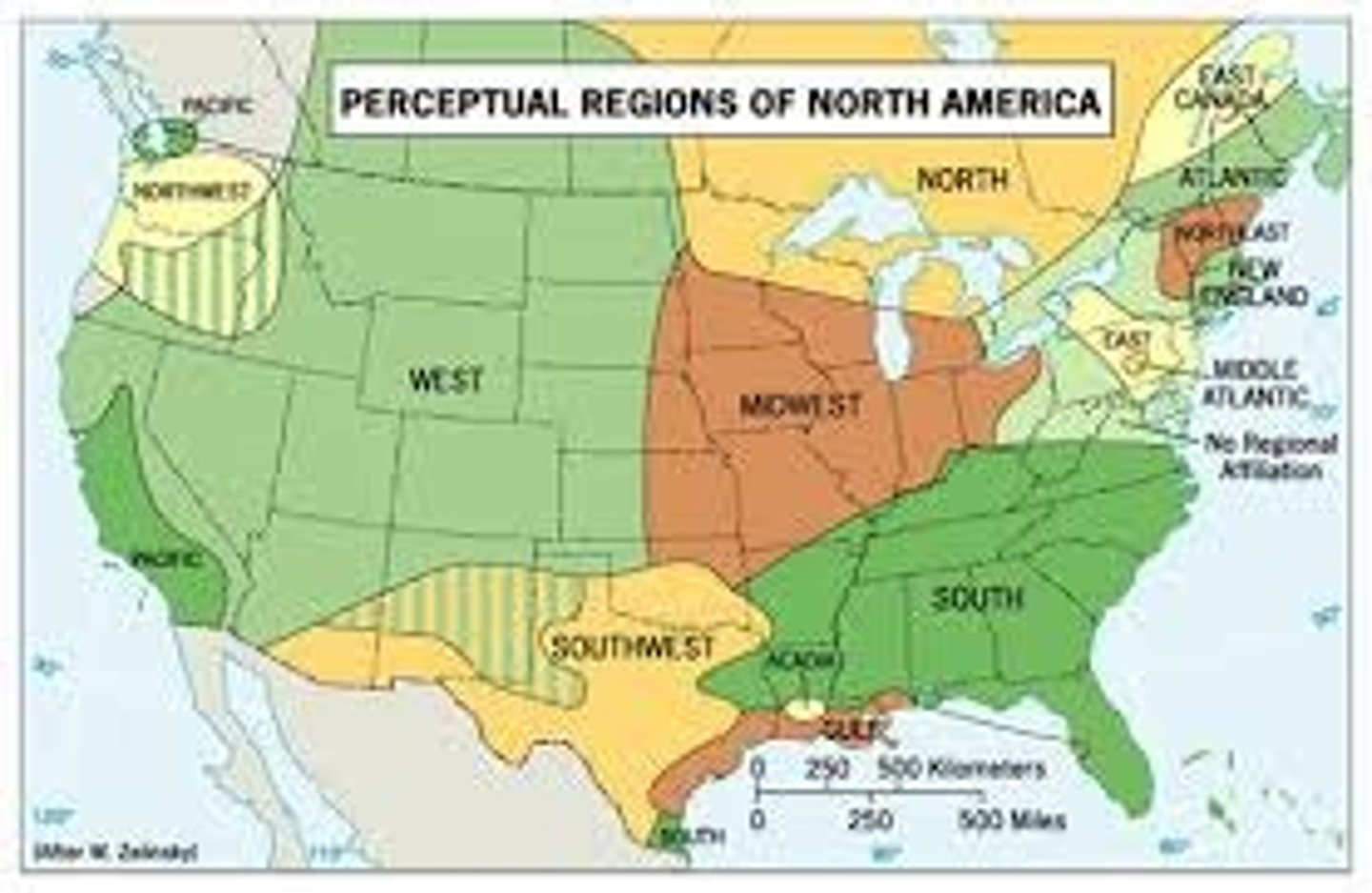
Vernacular/perceptual region
an area that shares a common qualitative characteristic, it's only a region because people believe it's a region
antinatalist policies
Government policies to reduce the rate of natural increase. Think: China's One Child Policy or India's controversial forced sterilization of men in the 1970s.
arable land
Land that is suitable for agriculture (growing crops)
arithmetic growth
Linear increases at a constant rate (1,2,3,4...)
asylum seeker
Someone who has migrated to a new country to be legally recognized as a refugee
arithmetic (crude) population density
The total number of people divided by the total amount of land area; the least useful measure of population density
brain gain
The opposite of brain drain; opening up new opportunities and bringing business experience and special skills
brain drain
Large-scale emigration by talented people (usually from LDCs to MDCs)
carrying capacity
The number of people an area can support on a sustained basis. Not a consistent figure, it depends largely on the area's level of technology.
chain migration
Migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members (earlier "links") of the same nationality previously migrated there
cohort
A population group unified by a specific common characteristic such as age or sex and subsequently treated as a statistical unit.
constrictive population pyramid
A top-heavy population pyramid with higher proportions in older age groups indicates a declining population. This may result from a long period of below replacement fertility, alongside low death rates.
crude birth rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
crude death rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
degenerative disease
a disease most associaetd with old age; causes a breakdown of the body cells, tissues, and organs as it progresses
demographic momentum
The tendency for a population to continue growing after a fertility decline due to so many young people entering their childrearing years
demographic transition (theory)
The process of a change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth rates, high crude death rates, and low rates of natural increase (yielding a low total population) to a condition of low crude birth rates and death rates, and low rates of natural increase (yielding a higher total population).
density
The frequency (number of times) with which something exists within a given unit of area (Example: 10 people per sq. kilometer)
dependency ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
distance decay
The diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
doubling time
The length of time (in years) needed to double the population; can be calculated with the Rule of 70.
emigration
Migration from a location
endemic
A disease that is constantly present to a greater or lesser degree in people of a certain class or in people living in a particular location
epidemic
A widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time.
expansive population pyramid
Young populations that have a typical 'pyramid' shape, with a broad base indicating high proportions of children. Indicates a population undergoing rapid growth.
epidemiologic transition
The process by which the pattern of death and disease in a population is transformed from one of high mortality among infants and children and episodic famine and epidemics to one of degenerative and chronic illnesses affecting principally the elderly
exponential (geometric) growth
A pattern of growth that shows greater increases with passing time (1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128... vs. 1,2,3,4...); forms a J-curve when graphed and characterizes population growth following the Industrial Revolution.
family planning
the practice of regulating the number or spacing of children through the use of birth control
female infanticide
The intentional killing of baby girls due to the preference for male babies and from the low value associated with the birth of females (a problem in the past in India and China where there has been a son preference)
forced migration
Migration that involves the involuntary movement from one's home, when people have no choice but to migrate (example: slavery)
gravity model
A model that states spatial interaction- including migration- is directly related to the size of the populations and inversely related to the distance between them
guest worker
a foreign laborer living and working temporarily in another country
immigration
Migration to a location
Industrial Revolution
The process of change from an agricultural and handicraft (cottage) economy to one dominated by industry and machine manufacturing. These technological changes introduced new ways of working and living and fundamentally transformed society. This process began in Britain in the 18th century and from there spread to other parts of the world.
infant mortality rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1-year-old for every 1,000 live births in a society; provides insight into the level of development of a country, its healthcare system, and the status of women.
infectious disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen (bacteria or virus) and that can be spread from one individual to another.
internal migration
Migration within the borders of a country.
internally displaced persons (IDP)
A forced or reluctant migrant who has fled their home as a refugee but who has not migrated across an international border.
interregional migration
Migration from region to another region. Example: Moving from Moreno Valley, Ca. to San Francisco, Ca. (the region of Southern California to Northern California).
intervening obstacles
Any force or factor that may limit human migration. Example: A migrant attempting to immigrate to the U.S. legally from the United States will encounter a complicated set of legal hurdles. A migrant attempting to immigrate to the United States illegally will have to navigate challenges that conclude border patrol agents, a harsh desert border environment, and exploitative "coyotes" (smugglers).
intervening opportunities
A feature (usually economic) that causes a migrant to choose a destination other than his original one. (Part of Lee's Model of Migration )
intraregional migration
Migration within the same region (example: moving across town).
LDC
A country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development
life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live
Thomas Malthus
Argued that food production would not be able to keep up with population growth (exceeding the carrying capacity), resulting in disease, famine, war, and calamity.
MDC
A country that has progressed relatively far along a continuum of development.