The heart and blood vessels (Health and disease)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
An organ that pumps blood around the body in a double circulatory system. Blood enters the right and left atrium and the atria contrasts which forces blood into the ventricle and it contrasts and forces it out ( right to the lungs where gas exchange takes place and left to the body)
Four chambers(left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle, valves)
NOTE: LOOK AT THE LEFT AND RIGHT LIKE YOU ARE LOOKING AT A PERSON
Structure of the heart
coronary artery- branch out of the aorta to the muscle of heart providing oxygen for respiration which gives it energy for contraction
The vena cava- blood goes through the vena cava into the right atrium
The pulmonary artery- is where the blood flows out of the heart to the lungs
The pulmonary veins- is where blood flows through to the left atrium into the heart
Aorta- blood flows out through the aorta to the rest of the body
Valves- between the atriums and ventricles; prevents back flow of blood
NITE: left side has a thicker muscle wall because it needs to provide a lot of energy to force the blood to the rest of the body
Function and structure of each blood vessel
It’s a group of cells that controls the natural resting heart rate; located in the right atrium
Function and location of the pacemaker
Are electrical devices used to correct any irregularities in the heart rate
What’s an artificial pacemaker
Artery: has a thicker wall and small linen to transport the flow of high pressurised blood to the rest of Body
blood in the arteries travel in surges every time the heart beats
The vein: has a less thick wall but wider lumen to transport the flow of low pressurised blood into the body
contains valves
The capillaries: located around the lungs; consists of red blood cells which contains haemogoblin
allows diffusion of oxygen, glucose and waste products
Thin cell walls
How does the structure of the three blood vessels relate to their functions
22400 divided by 4= 5600ml/min
5600 times 60= 336000 ml/hr or 336 L/hr
At rest, about 22,400ml of blood flows through the aorta every 4 mins. Calculate the hourly rate of blood flow through the aorta
Blood flow divided by time
Equations for calculating rate of blood flow
when breathing, oxygen goes through the trachea ( rings of cartilage to prevent collapsing during inhalation)
Into the bronchi and subdivides to the bronchioles which connects to tiny air sacs called the alveoli(microscopic )is the site of gas exchange
Structure of the lungs
alveoli causes the lungs to have a huge surface area
Thin cell walls for rapid diffusion
When oxygen is diffused into the bloodstream, it’s rapidly removed which shows the concentration gradient is steep
Good blood supply
This adaptations means that oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream rapidly and CO2 diffuses into the air rapidly
How are the lungs adapted for gas exchange
When breathing fresh oxygen is taken into the alveoli and CO2 which means the concentration gradient will be high and that increases its rate of diffusion
How does breathing increase the rate of diffusion in the lungs
Blood is a tissue consisting of plasma in which the white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets are suspended
define blood
transports carbon dioxide( produced during aerobic respiration) from the body to the lungs to be breathed out
It transports waste(urea) from the liver tot the kidney to be excreted as urine
Transports soluble digestion products (glucose) from the small intestine to other organs
They carry antibodies, antitoxins, hormones, nutrients, protein and waste products
Functions of plasma
Function- carries oxygen from the lungs to other organs
Adaptations
biconcave disk which provides a large surface area for oxygen
No nucleus which means more space haemoglobin
Contains haemoglobin that carries the oxygen to the organs from the lungs( when it carries oxygen it becomes oxyhaemoglobin)
Functions and adaptations of the red blood cells
They engulf pathogens (phagocytosis)
They produce antitoxins
They produce antibodies
They contain nucleus that contains the DNA to provide instructions for it to do its job
Functions of the white blood cells
Tiny fragments of the cell that helps the blood to clot
They stop bleeding
Stop microorganisms from getting into open wound
Functions of platelets
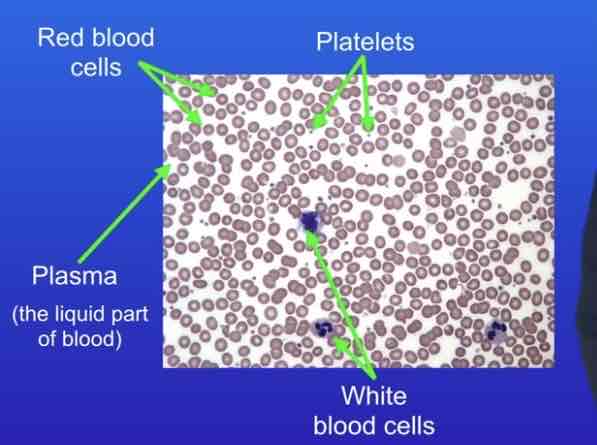
Identify the types of blood cells
single cell thick( allows diffusion)
Permeable
Small lumen to allow
to diffuse nutrients
How does the structure of capillaries relates to its functions
Layers of fatty materials builds up inside the coronary arteries, narrowing them. This reduces the flow of blood In the coronary artery causing lack of oxygen in the heart muscle
Explain coronary heart disease
stents are used to kept the coronary arteries open
Statins are used to reduce the blood cholesterol levels which slows down the rate of fatty materials deposit
Uses of stents and statins
Both requires surgery which could cause infections
Both could cause blood clotting
Mechanical- last a long time
Biological- wouldn’t last a long time
disadvantages of mechanical and biological valves
Adv of stents
surgery is quick
Lasts a long time
disadvantages
Could cause blood clot
Could cause infections
Advantages of statins
Reduces bad cholesterol and increases good cholesterol
Avoids other cardiovascular diseases
Disadvantages
could cause side effects(kidney failure)
Needs to be taken regularly
Advantages and disadvantages of stents and statins
Biological heart transplant
Disadvantages
might take a long time to find a heart donor
Immune system might reject
Artificial heart
Might cause blood clothing
They aren’t long-term
Advantages
Allows real heart to rest as an aid to recovery
To keep patients alive whilst awaiting heart transplant
Wont be rejected by immune system
Disadvantages and Advantages of heart transplant
Is the state of physical and mental wellbeing
What’s health
They are most likely to suffer from infectious diseases
What happens if a person has a defect in their human system
Cancer
What does virus living in cells trigggers
When the immune system tries to hard to fight off against pathogens it damages tissues in the process could cause allergies such as asthma and skin rashes
How are allergies caused
Several physical ill health could lead to depression, chronic anxiety and other mental illness
How does health link to mental well-being
Parasites, fungi, bacteria and viruses
How can communicable diseases be spread
HPV- causes cervical cancer
List a type of disease that may cause another disease
communicable Disease
Non communicable Diseases
Stress
Poor diet
Life situations
Factors that causes ill health
A diet high in fat but low in vegetables increase the level of certain types of cholesterol in the blood and increases the rate of fatty materials building up in the coronary arteries
A diet high in salt increases blood pressure
Effects of bad diet
Carcinogens causes lung cancer
Lease to emphysema causes a low quality of life
Smoking when pregnant causes miscarriage and low body mass
Effects of smoking
when pregnant could cause fatal alcohol syndrome( physical disabilities and other mental problems )
In adults, causes liver cirrhosis and cancer
Mentally;
Addiction
Memory loss
Effects of alcohol
Alcohol causes obesity which causes type 2 diabetes
Link between obesity type 2 diabetes and alcohol
A radioactive gas that increases the risk of lung cancer
What’s radon
carcinogens
Ionising radiation
Risk factors of cancer
As the number of cigarettes smoked per day increases, the risks for developing lung cancer also increase. positive correlation
Describe this graph
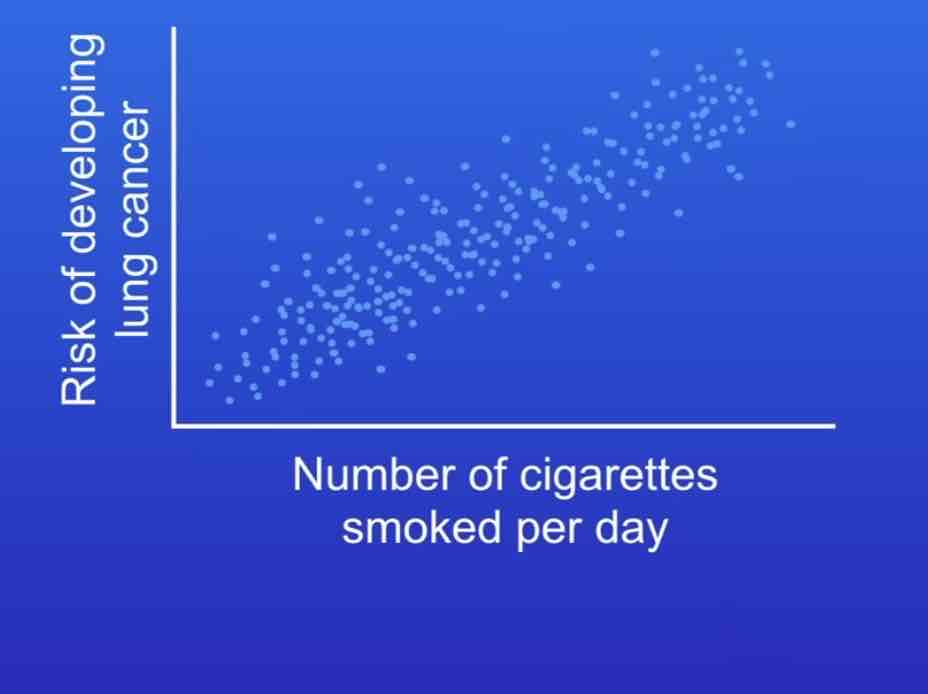
No
Does correlation prove cause
it means that smoking increases the risks of lung cancer
What does scientist mean when they say that smoking is a causal mechanism for lung cancer
To prevent bias in sampling it’s better to take as random and large number of sample as possible
How to prevent bias in sampling
Sampling might be systematic in that it is carried out at regular time intervals. When working with samples of human populations, studies must take account of possible variations owing to differences: between the sexes. resulting from people of different ages taking part.
Principles of sampling