World History - Unit 1 World Religions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Buddhism
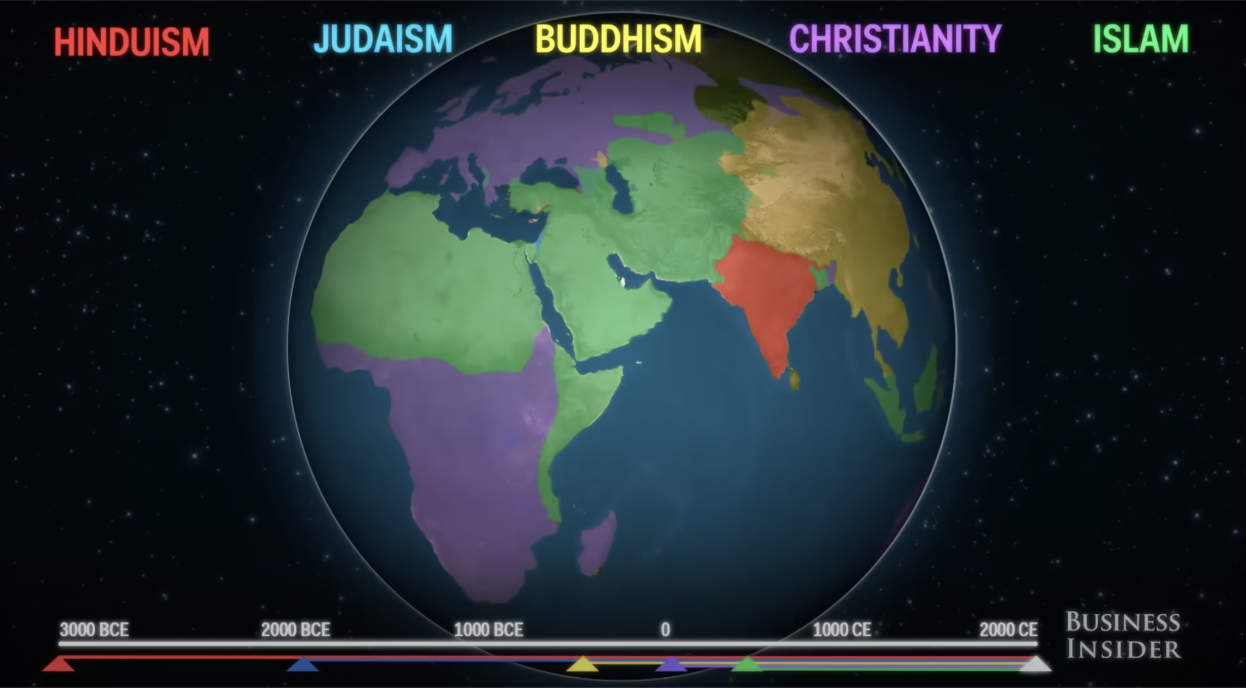
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 600 million/China, Japan, and Korea (East Asia and Southeast Asia) |
Year Founded | 6th c. BCE |
Founder | Siddartha Buddhama |
Place of Worship | Stupet Shrines/Temples |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | None; it’s founded on morals not on who to worship |
Holy Book | Tripitaka |
Basic Beliefs | Four Noble Truths, The Eightfold Path, & Nirvana |
Christianity
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 2.4 billion/North & South America, Europe, and Africa (Largest religion) |
Year Founded | 30-33 CE |
Founder | Jesus of Nasarac |
Place of Worship | Church |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | Monotheist |
Holy Book | The Bible |
Basic Beliefs | The Ten Commandments and Jesus is the son of God. |
Hinduism
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 1.2 billion/India and Nepal |
Year Founded | 2300-2400 BCE |
Founder | No one founder |
Place of Worship | Temple |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | Polytheist |
Holy Book | The Vedas |
Basic Beliefs | Reincarnation and Karma. |
Islam
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 1.9 billion/Southwestern & Central Asia, parts of America, Europe, and parts of Africa |
Year Founded | 610 CE |
Founder | Muhammad |
Place of Worship | Mosque |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | Monotheist |
Holy Book | The Qu’ran |
Basic Beliefs | The Five Pillars of Islam |
Judaism
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 15 million/US, Israel |
Year Founded | 1800 BCE |
Founder | Abraham |
Place of Worship | Synagogue |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | Monotheist |
Holy Book | The Torah |
Basic Beliefs | The Ten Commandments |
Confucianism
# of followers / Area most practiced today | 6 to 9 million/East Asia, and China |
Year Founded | 6th c. BCE |
Founder | Confucists |
Place of Worship | Temple of Confucists |
Monotheist/Polytheist? | None; it’s founded on morals not on who to worship |
Holy Book | The Analex |
Basic Beliefs | The Five Basic Beliefs and The Golden Rule |
Monotheist
Belief that there is only one God
Polytheist
Belief that there are multiple Gods
Beliefs of Buddhism
- Founded in India around 500 BCE by Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha)
- Main teachings: eliminate desire (craving), as it is the cause of suffering in the world
- No single authority or sacred book
Key Beliefs (Four Noble Truths):
1. Life is suffering
2. The origin of suffering is desire (craving/attachment)
3. Suffering can end through eliminating wants/needs
4. The path to the end of suffering and achieving Nirvana is to follow the Eightfold Path
Eightfold Path:
1. Right Understanding (View)
2. Right Intention (Thought)
3. Right Speech
4. Right Action
5. Right Livelihood
6. Right Effort
7. Right Mindfulness
8. Right Concentration
Beliefs of Christianity
- Originated in Palestine in 30–33 CE
- Based on the life and teachings of Jesus
- Belief that Jesus was the Son of God, who died for people’s sins so they could be saved in the afterlife
- Monotheistic: Belief that there is only one God
- Christianity originally developed as a part of Judaism
Beliefs of Hinduism
- Hinduism has no founder, no single book of faith, and no single set of teachings
- Belief in reincarnation: every soul is reborn
- Goal: to live in a manner that will cause each reincarnation to be better than the life before, ultimately reaching Moksha (liberation from rebirth)
- Karma: the effects of a person’s actions that determine their future in this life or the next
- Polytheistic religion
Beliefs of Islam
- Islam began to develop around Abraham
- Based on the ministry of Muhammad and the words that Allah (God) gave to the world through him
- These teachings were written down to create the Qur’an
- Worship the same God as Christianity and Judaism
Five Pillars of Islam:
1. Declaration of Faith (Shahada): Belief that there is no god but God, and Muhammad is the messenger of God
2. Prayer (Salat): Pray at prescribed times five times per day (dawn, noon, mid-afternoon, sunset, after dark)
3. Almsgiving (Zakat): Donate to community members in need
4. Fasting (Sawm): During daylight hours of Ramadan, the 9th month of the Islamic calendar, requirement to fast
5. Pilgrimage (Hajj): Make at least one visit to Mecca (present-day Saudi Arabia)
Sunni and Shi’a:
- After Muhammad’s death, there were questions over leadership
- Abu Bakr (Muhammad’s closest friend) was selected as new leader (Sunni)
- A smaller group supported Ali ibn Abi Talib, Muhammad’s cousin (Shia)
Beliefs of Judaism
- One of the oldest and smallest monotheistic religions
- Founded ~1800 BCE in Israel
Fundamental Beliefs:
- There is only one God, who watches over and cares for His people
- God loves and protects His people but also holds people accountable for their actions/choices
- People serve God by studying the Torah and living by its teachings
Beliefs of Confucianism
The importance of order and harmony – Confucianism emphasizes that society functions best when everyone knows their role and fulfills their responsibilities.
Filial piety (xiao) – Respect and devotion to one’s parents and ancestors is central; family is seen as the foundation of society.
The Five Relationships – Human relationships should be based on respect, duty, and proper behavior:
Ruler ↔ Subject
Parent ↔ Child
Husband ↔ Wife
Older sibling ↔ Younger sibling
Friend ↔ Friend (the only equal relationship)
Ren (humaneness or benevolence) – People should act with kindness, compassion, and empathy toward others.
Li (rituals, propriety, etiquette) – Following proper rituals, traditions, and social norms helps maintain order and respect.
Education and self-cultivation – Learning, moral development, and self-discipline are essential to becoming a virtuous person.
The role of the ruler – A ruler should lead by moral example, not by force, so the people will naturally follow with loyalty and respect.
👉 In short: Confucianism focuses on morality, respect, proper behavior, education, and strong family values as the path to a harmonious society.
By Numbers (World Population of Followers)
- Christianity: 2.4 billion
- Islam: 1.9 billion
- Hinduism: 1.2 billion
- Buddhism: 500 million
- Judaism: 15 million
- Folk/Traditional religions (African traditional religions, Chinese folk traditions): 400 million
- Other religions (Jainism, Shintoism, Zoroastrianism, Taoism, etc.): 58 million
Eightfold Path:
The Buddhist path to enlightenment consisting of Right View, Intention, Speech, Action, Livelihood, Effort, Mindfulness, and Concentration.
- Right Understanding
- Right Intention
- Right Speech
- Right Action
- Right Livelihood
- Right Effort
- Right Mindfulness
- Right Concentration
Five Pillars:
The five core practices of Islam: Shahada (faith), Salat (prayer), Zakat (charity), Sawm (fasting during Ramadan), Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca).
- Shahada (Declaration of Faith)
- Salat (Prayer 5x daily)
- Zakat (Charity)
- Sawm (Fasting during Ramadan)
- Hajj (Pilgrimage to Mecca)
Four Noble Truths:
Life is suffering; the cause of suffering is desire; suffering can end; the way to end suffering is the Eightfold Path.
1. Life is suffering
2. Suffering is caused by desire/attachment
3. Suffering can end by eliminating desire
4. The way to end suffering is the Eightfold Path
Ten Commandments:
Moral/religious laws given by God to Moses in Judaism and Christianity.
Matching Religious Texts to Religions
Torah →
Quran →
Bible →
Torah → Judaism
Quran → Islam
Bible → Christianity
Difference Between Sunni and Shia Muslims:
- Sunnis: Leadership to Abu Bakr (Muhammad’s close friend).
- Shia: Leadership should stay in Muhammad’s family → Ali (cousin/son-in-law).
Abrahamic Religions (oldest → newest):
1. Judaism
2. Christianity
3. Islam
Monotheistic, Polytheistic, or Neither
Judaism →
Christianity →
Islam →
Hinduism →
Buddhism →
Confucianism →
Judaism → Monotheistic
Christianity → Monotheistic
Islam → Monotheistic
Hinduism → Polytheistic
Buddhism → Neither
Confucianism → Neither
The Crusades were largely fought over:
Jerusalem
Importance of Jerusalem to Each Abrahamic Religion
a holy city for Jews, Christians, and Muslims, such as the Western Wall for Jews, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre for Christians, and the Dome of the Rock for Muslims
Judaism:
Jerusalem is the most sacred city in Judaism, considered the site where God's presence is closest on Earth. It is home to the Temple Mount, where the First Temple and the Second Temple stood. The Western Wall, the remaining structure of the Second Temple, is a place of pilgrimage and prayer.
Christianity:
The city is sacred to Christians as the location of Jesus's crucifixion and resurrection. Important sites for Christians include the Garden of Gethsemane, the Via Dolorosa, and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
Islam:
Jerusalem, known as Al-Quds, is the third holiest city in Islam. Muslims believe that Prophet Muhammad journeyed from Mecca to Jerusalem during his Night Journey and ascended to heaven from the Temple Mount. The city contains important Islamic sites, including the Dome of the Rock and Al-Aqsa Mosque.
Contested Capital: Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city.
Center of Power: Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions in Jerusalem.
What is Sufism?
Sufism is a mystical movement emerged within Islam that emphasizes personal spiritual experience. It stresses brotherhood, egalitarianism, and often mixes Islam with local religious traditions. Seen as a threat by many Muslim rulers as it could be used as a tool to resist rulers who were seen as too oppressive or too powerful.
Why did Hinduism appeal to rulers in South Asia over other religions?
Hinduism appealed to rulers in South Asia because it had a powerful priestly class (the Brahmins) with whom rulers could form alliances. The religion supported the idea of patronage of temples and religious orders, which helped rulers legitimize and consolidate their authority.
In Southeast Asia, many rulers embraced Buddhism, leading to which groups of people earning political influence?
In Southeast Asia, when rulers embraced Buddhism and established monasteries, monks and nuns from those monasteries gained considerable political influence in the states.
The Song Dynasty in China emphasized Confucianism, particularly the relationship between _____ and _______.
ruler, subject
Why did Catholic priests typically encourage people to follow kings and princes?
Catholic priests generally encouraged people to obey kings and princes because those rulers were believed to rule with God’s approval, so obedience to secular rulers was seen as part of moral and religious duty.
What made the Pope unique compared to other priests? Why was the Pope a threat to kings and other rulers?
The Pope was unique because he was both a religious and political figure; he could charge taxes, raise armies, and had a spiritual authority to excommunicate people. He was a threat because through excommunication, the Pope could remove someone from the Christian community, which could provoke rebellion or undermine a ruler’s legitimacy. This meant that powerful kings could be challenged by the Pope’s decisions.
In Sub-Saharan Africa, both _________ and _________ power was often held by more local, rather than centralized, authorities.
political, religious
List 2 reasons that the Mongols allowed different religious practices within their Empire.
1. To keep the peace in a vast empire that included people of many faiths
2. As a form of “celestial insurance”—sponsoring many faiths just in case one turned out to be the “true” religion.
World Map