evolution paletzki
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
evolution
the cumulative change in the heritable characteristics of a population
heritable characteristics are encoded by
genes and are transferred by alleles
evolution requires a ___ of change and a consequential ___ for change
source, mechanism
sources of change may include
genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities, sexual reproduction and meiosis, and gene flow (migration)
mechanisms for change may include
random events (genetic drift), directional forces (natural selection or artificial selection)
germline mutations
occur in sex cells and can be passed to offspring
crossing over
DNA segments are exchanged between homologous pairs (meiosis)
independent assortment
separation of the homologous pairs is random (meiosis)
random fertilization
the fusion of two haploid gametes is also random (meiosis)
gene flow
describes the movement of alleles between different populations
gene flow can alter the diversity of a population via
immigration or emigration
how does gene flow create variation
by introducing genes from an alternative population source
populations that are in close proximity will show
less variation (less divergence)
distant populations typically show a
greater level of variation
genetic drift
a change in the composition of a gene pool due to chance events
genetic drift is greater when the population is
smaller (more prone to change)
natural selection as a mechanism for change
a change in the composition of a gene pool as a result of the presence of differentially selective environment pressures
artificial selection as a mechanism for change
humans determine the favorability of a particular trait (may involve selective breeding or transgenic techniques)
speciation
the formation of a new and distinct species in the course of evolution
what leads to speciation
mechanisms of change will reduce variation and increase the degree of genetic divergence between geographically isolated populations
speciation occurs when
populations cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring
scientific theory
a well supported explanation of how the world works
scientific evidence
evidence which serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis
evidence for evolution can be demonstrated by identifying
similarities in unrelated organisms (common ancestry)
evidence for evolution can be demonstrated by showing
a change in characteristics between current and ancestral species
evidence for the process of evolution include:
fossil records, comparative anatomy, selective breeding, biogeography, and DNA (molecular)
fossils
the preserved remains or traces of organisms from the remote past
fossil record
totality of fossils (discovered and undiscovered)
law of fossil succession
over time changes occurred in ancestral organisms, with different species appearing within the fossil record in a systematic order
conditions required for fossilization to occur
preservation of remains, exposed to high pressure to promote mineralization, subjected to anoxic (low oxygen) conditions to prevent decomposition
how can fossils be dated
according to the age of the rock layer (strata) in which they are found
relative age
estimates the age of the fossil by looking at where the fossil is in the rock layer
absolute age
use isotopes and half-lives to determine a more accurate age of the fossil
transitional fossils
any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group
homologous structures
share a common basic structure despite being used in different ways
adaptive radiation
when a single species or small group of species rapidly diversifies into many new species (ex. darwin’s finches)
vestigial structures
Structures that have no apparent function and appear to be residual parts from a past ancestor
why are vestigial structures evidence of evolution
they suggest that an organism changed from using the structure to not using the structure
comparative embryology
studies the similarities and differences in the embryonic development of different species to understand evolutionary relationships and how animal body plans originated
selective breeding
a form of artificial selection where humans breed animals w/ desirable characteristics to increase the frequency of these traits
why is selective breeding evidence of evolution
it leads to exaggeration of these traits in domesticated animals compared to their wild counterparts
biogeography
the distribution of life forms over geographical areas
why is biogeography evidence of evolution
related species tend to be in close physical proximity
how is molecular (DNA) evidence of evolution
DNA comparisons between species suggest how closely related they are, the more similar an organism’s DNA is to another the more closely related they are
evolution
the cumulative change in the heritable characteristics of a population
gene pool
a combination of all the genes (including alleles) present in a reproducing population or species
large gene pool
higher levels of genetic diversity
gene pool compositions change over time
genetic drift + natural selection
allele frequency
the prevalence of a particular allele in a population of organisms. it is calculated as a percentage of the alleles in a gene pool
bottleneck effect
when an event reduces population size by an order of magnitude, the surviving population is smaller and has less genetic variability (greater genetic drift)
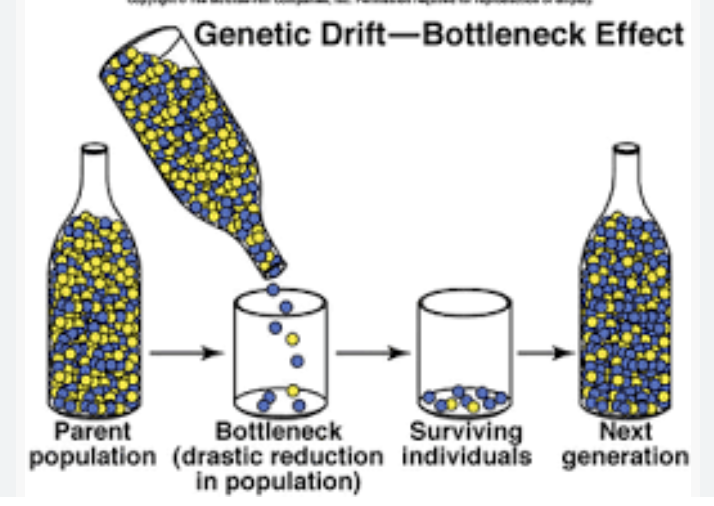
founder effect type
when a new population is established by a small subset of a larger population (resulting in less genetic variation and greater genetic drift)
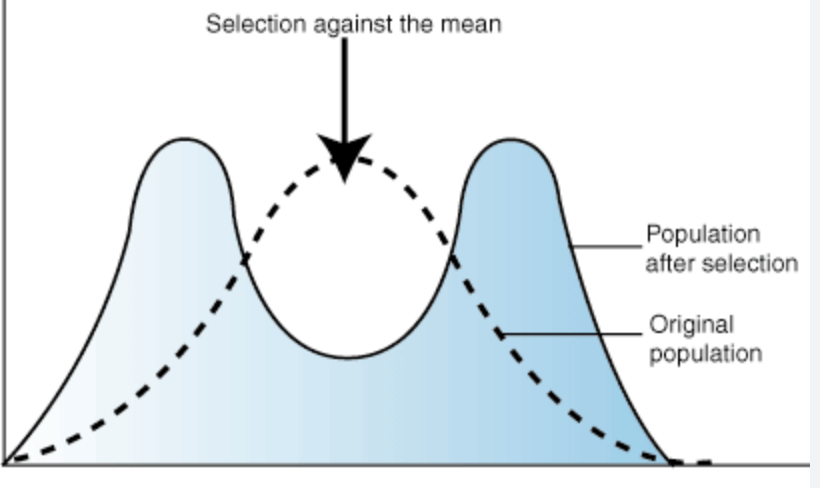
stabilizing (type of natural selection)
an intermediate phenotype is featured over the extremes
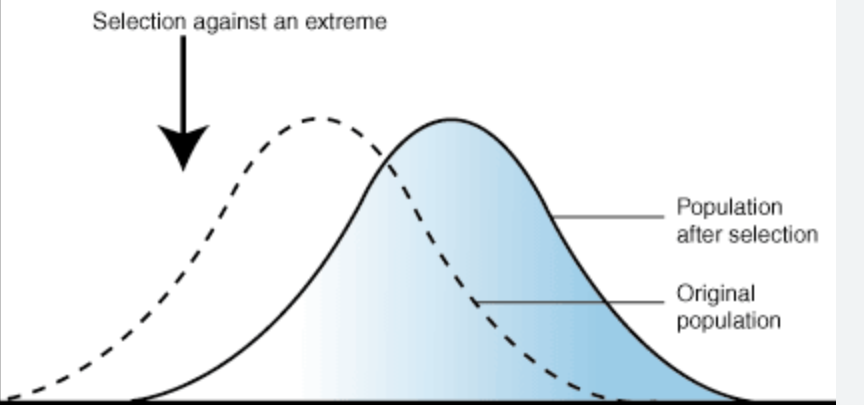
directional (type of natural selection)
one phenotypic extreme is selected at the expense of another
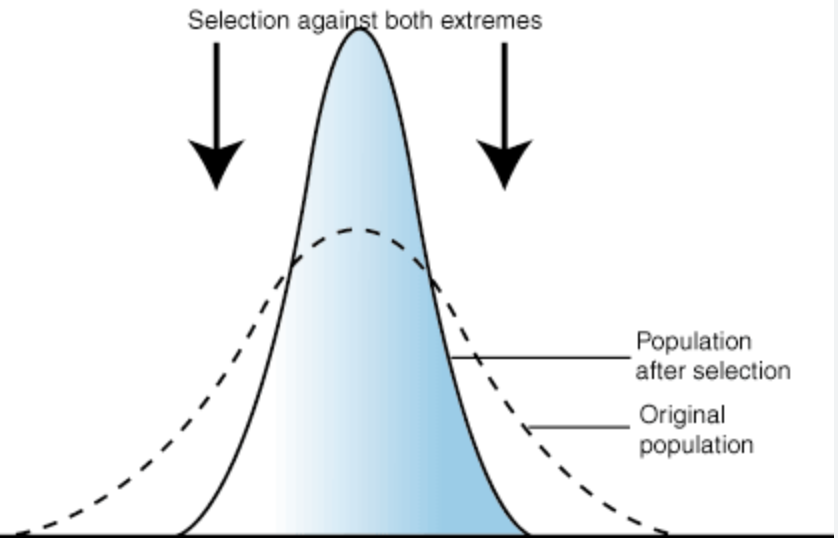
disruptive (type of natural selection)
both extremes are selected over an intermediate phenotype
hybrid
an offspring of two animals or plants of different subspecies, breeds, varieties, species, or genera
pre-zygotic
occurs before fertilization can occur
temporal mechanism
populations differ in periods of activity or reproductive cycles (pre-zygotic)
behavioral mechanism
populations exhibit different specific courtship behaviors (pre-zygotic)
geographic mechanism
populations occupy different habitats or niches within a region (pre-zygotic)
post-zygotic
occurs after fertilization
hybrid inviability mechanism
hybrids produced but fail to develop to reproductive maturity (post-zygotic)
hybrid infertility
hybrids fail to produce functional gametes (post-zygotic)
hybrid breakdown mechanism
F1 hybrids are fertile, but F2 generation fails to develop properly (post-zygotic)
allopatric speciation
divergence due to geographical isolation
sympatric speciation
divergence within same geographical location
phyletic gradualism
speciation results from continuous change occurring at a constant pace
punctuated equilibrium
speciation results from abrupt bursts that intersperse periods of stability
r-strategist
many offspring, short energy/time for raising and producing, frequently changing habitat, short lives (ex. mouse)
k-strategist
few offspring, lots of energy/time for raising and producing, stable environment, long lives (ex. humans)
william paley
wrote a book called ‘natural theology’ which influenced darwin
what ship did darwin go on
the HMS beagle, traveling south america, australasia, and africa
charles lyell
darwin read his theories while on the HMS beagle, learning that the Earth's features were formed by gradual, ongoing geological processes, not catastrophic events.
thomas robert malthus
darwin read his essay on the principle of population, who’s arguments were the final clue for darwin: a relationship between the environment and the reproduction of populations
alfred russel wallace
sent a letter to darwin in 1858, wallace had also discovered natural selection and they published a joint letter.
john baptiste lamarck
incorrectly theorized that evolution happened by acquired characters. (ex. giraffes would stretch their necks to reach trees, get longer necks, then pass on the long necks to their offspring0
james hutton
used geology to prove the world was much older than just a few thousand years old
analogous structures
structures with different origin and structure but are adapted for the same purposes are called
four points of darwin’s theory of evolution
overproduction, variation, adaptation, and selection