Mucles Lab 2 Exam
1/71
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
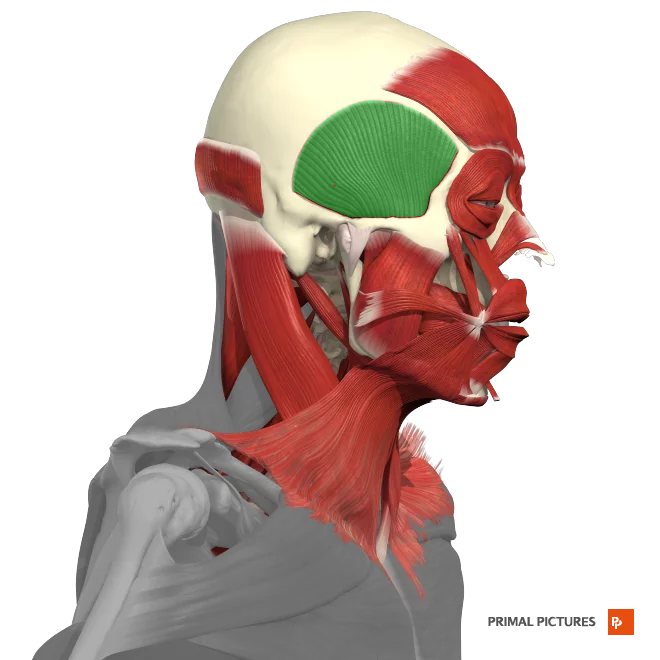
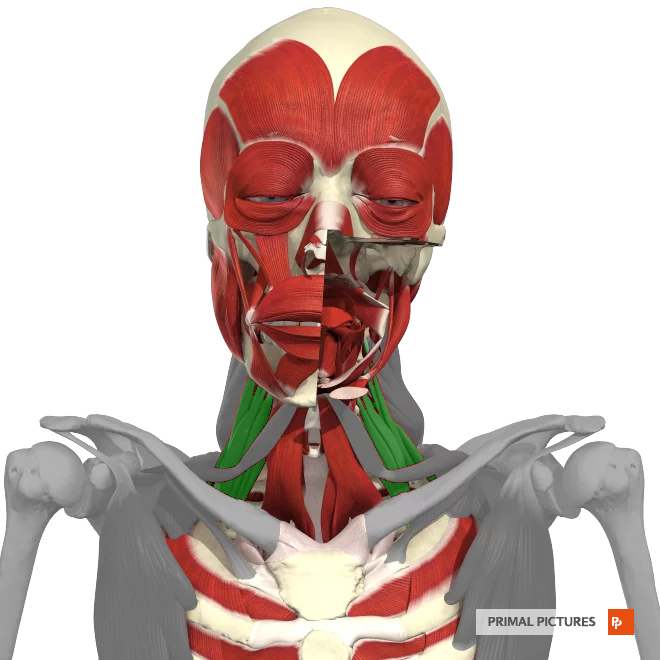
Temporalis
The __________ is a muscle located on the side of the head, responsible for closing the jaw and aiding in chewing.

Masster
_______ Elevates the mandible
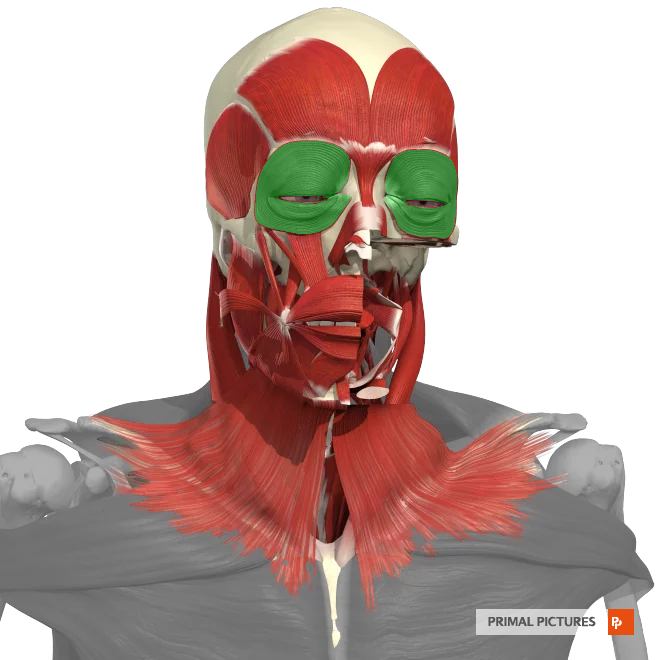
Orbicularis Oculi
Muscle surrounding the eye, closes eyelids

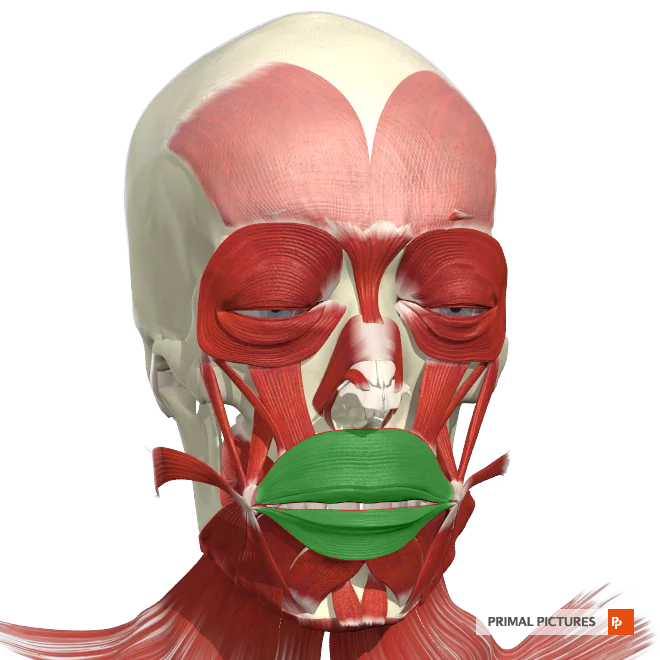
orbicularis Oris
The __________ is a muscle located around the mouth, responsible for controlling the movements of the lips, such as puckering, smiling, and kissing.
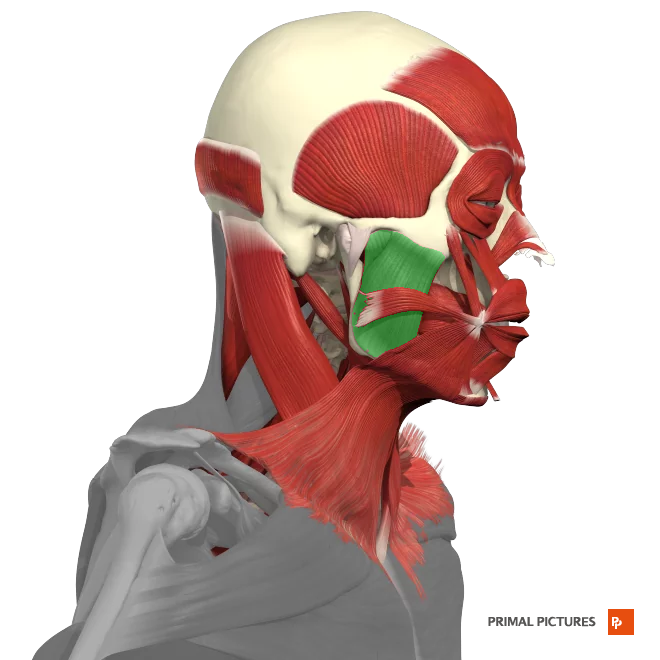
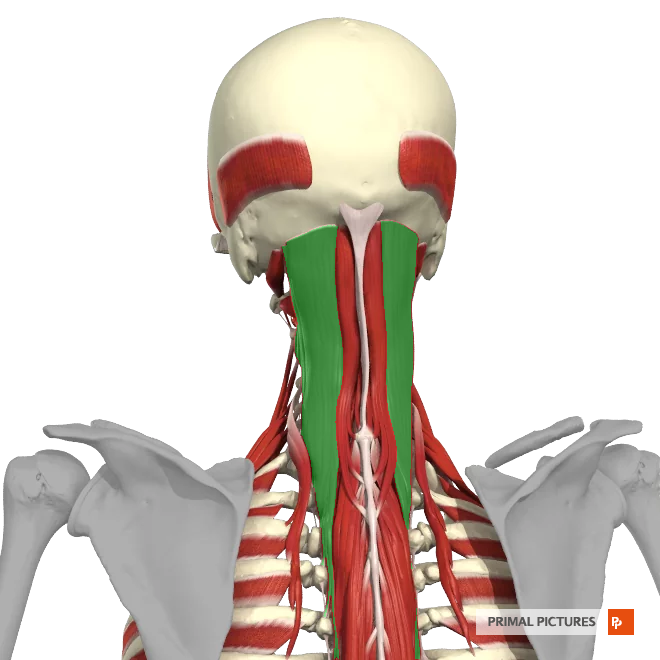
sternalcleidomastoid
The __________ is a large muscle located in the neck that runs from the sternum and clavicle to the mastoid process of the skull.
-rotation of the head
- lexion of the neck.

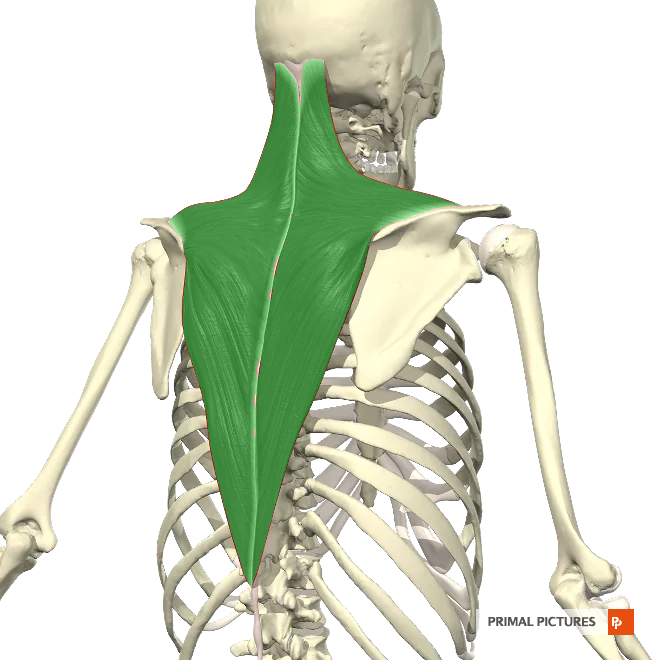
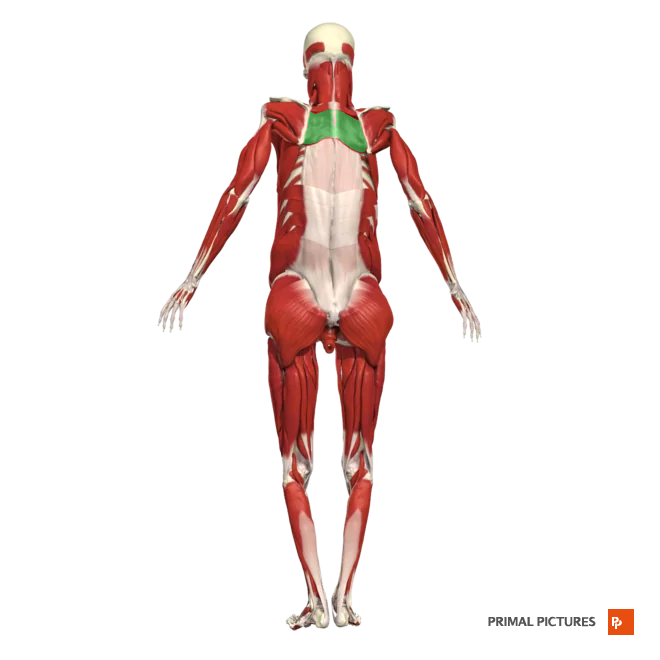
(upper) Trapezius*
The__________ muscle stabilizes and moves the shoulder blades. It allows shrugging and scapulae retraction. Shoulder raises and rows strengthen this muscle, improving upper back strength and posture.
Levator Scapulea
Elevates the scapula
rotates the scapula downward
laterally flexes neck
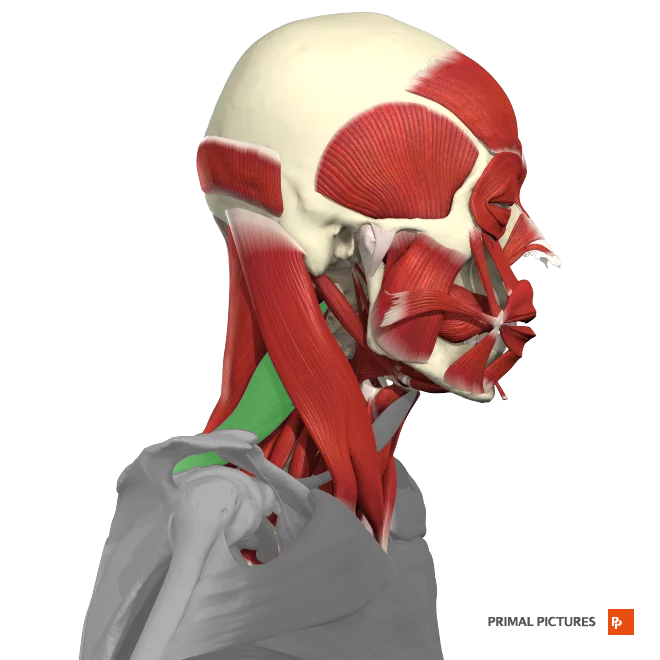
Scalenes
Elevation of the ribs
Lateral flexion of the neck
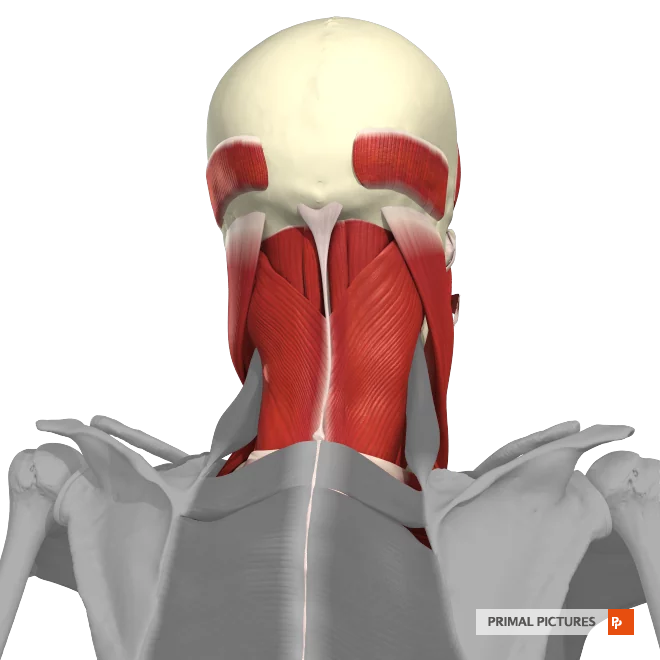
Splenius Capitis
Rotation of the head
Extension of the head
Deltoid
Abduction of the arm at the shoulder laterally
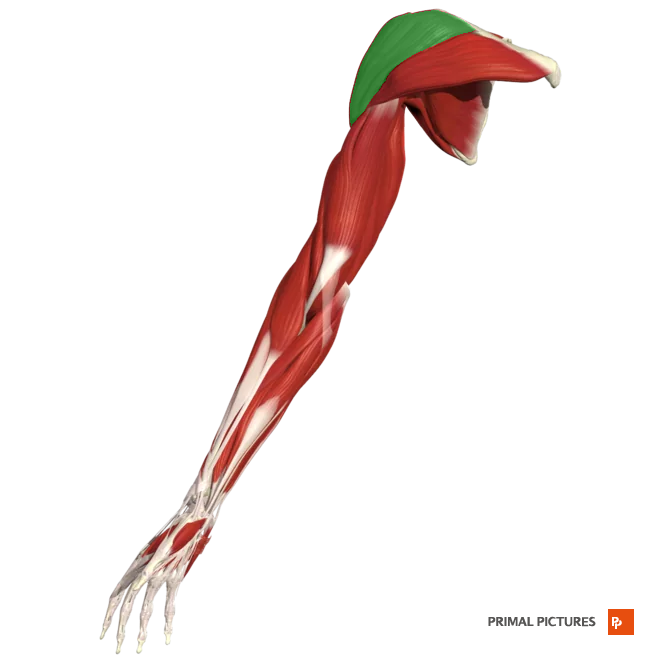

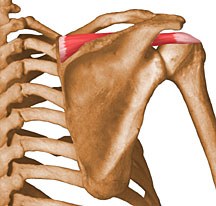
Supraspinatus
Abduction of the arm at the shoulder
Origin: supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle (hummerus)
Infraspinatus
infraspinous fossa of scapula
origin: Infraspinous fossa of scapula
insertion: greater tubercle (humerus)
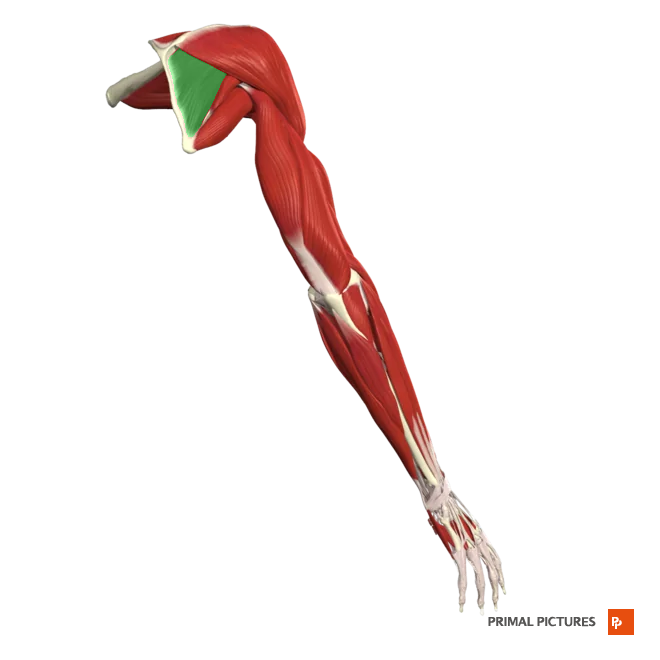
Teres Minor
Laterally rotates and extends arm at shoulder joint
Origin: Inferior lateral border of scapula
Insertion:greater tubercle (humerus)
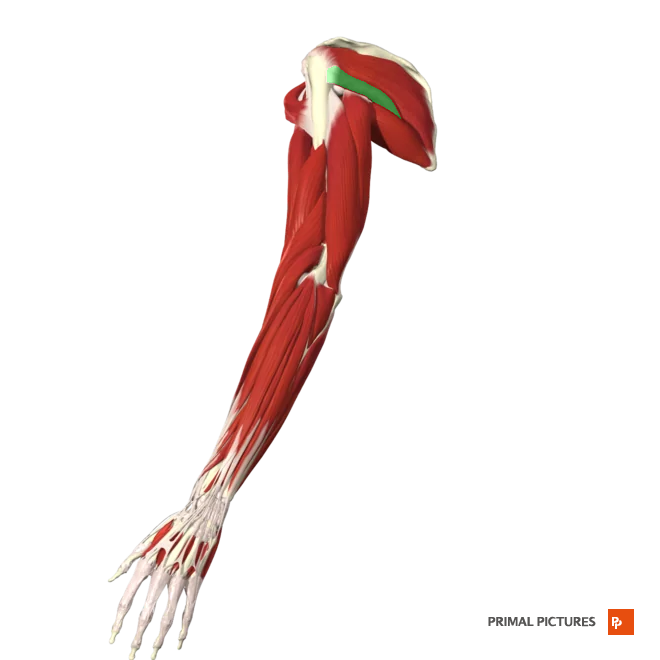
Teres Major
Extends the arm at the shoulder
Assists in adduction and medial rotation of the arm at the shoulder
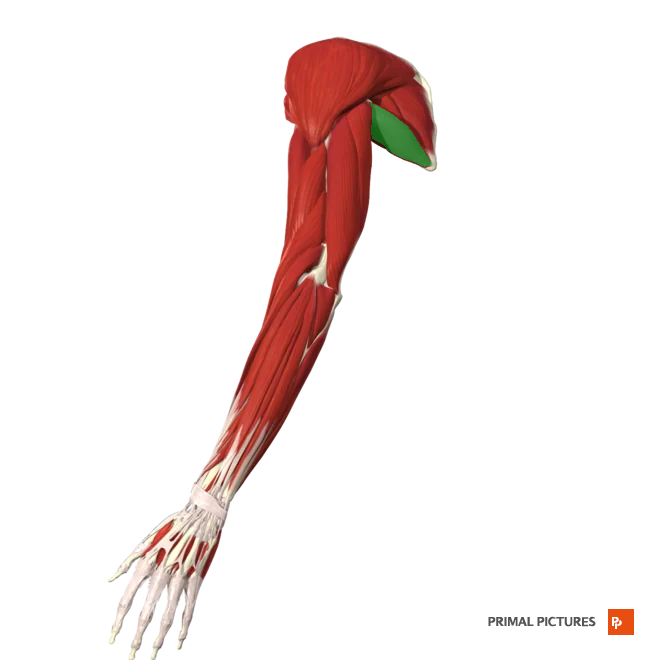
Subcapularis
Medially rotates arm at shoulder joint
Origin: Subscapular fossa of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle
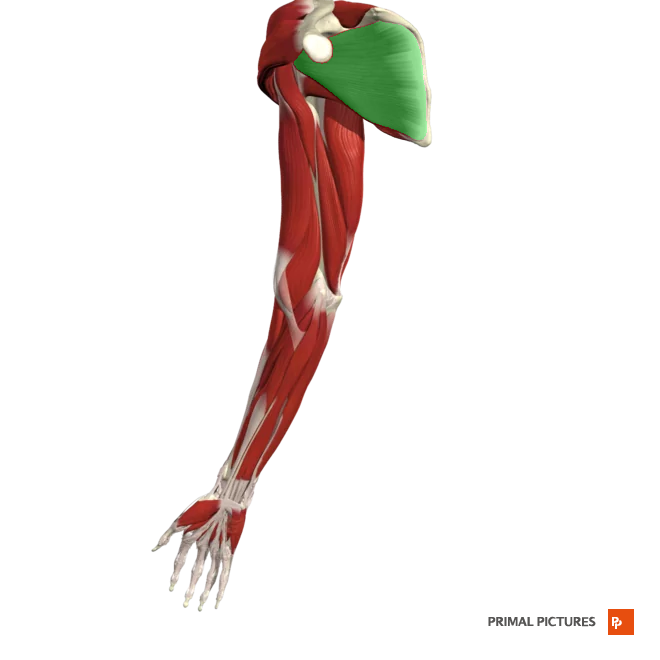
Rotator Cuff Muscles
The _______ consists of four muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis) that stabilize and move the shoulder joint, enabling rotation and abduction.
Coracobrachialis
Flexes and adducts arm at shoulder joint
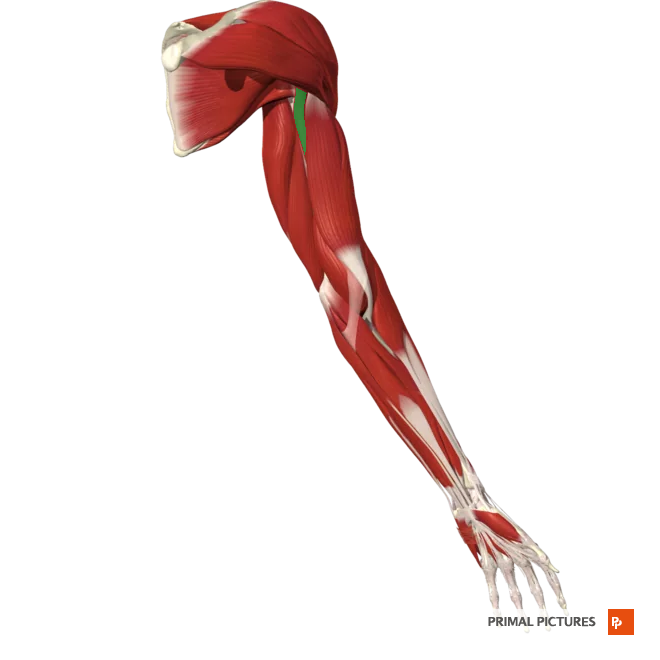
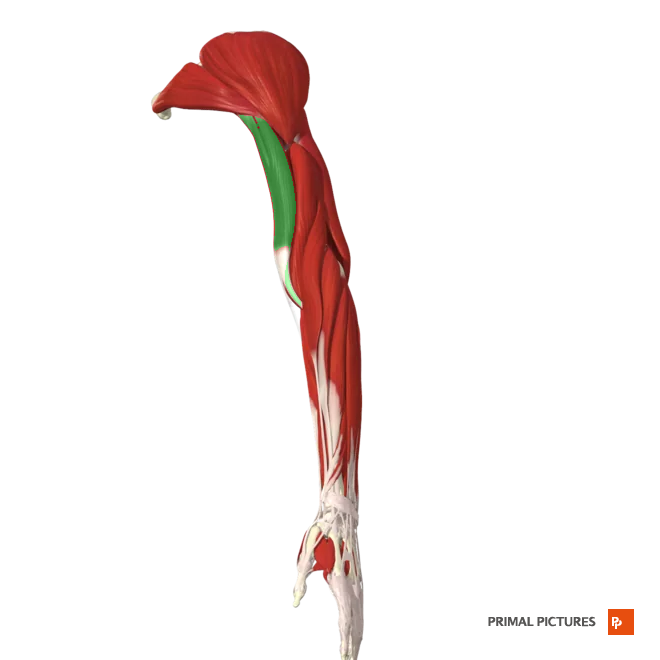
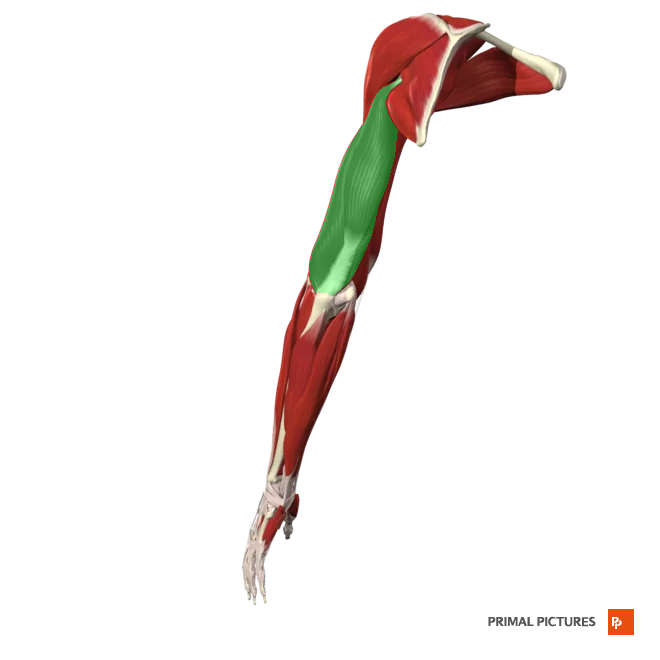
Biceps Brachii
Flexes and supinates the forearm
Insertion:Radial tuberosity
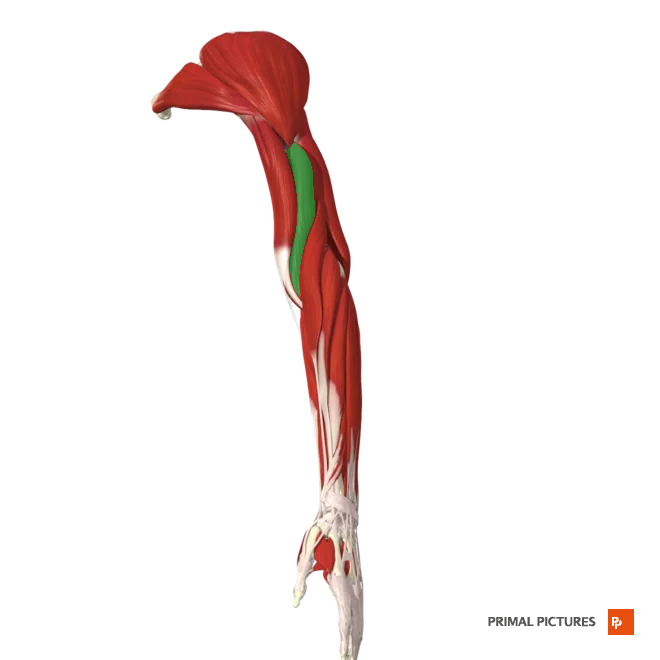
Brachialis
Flexes forearm at elbow joint
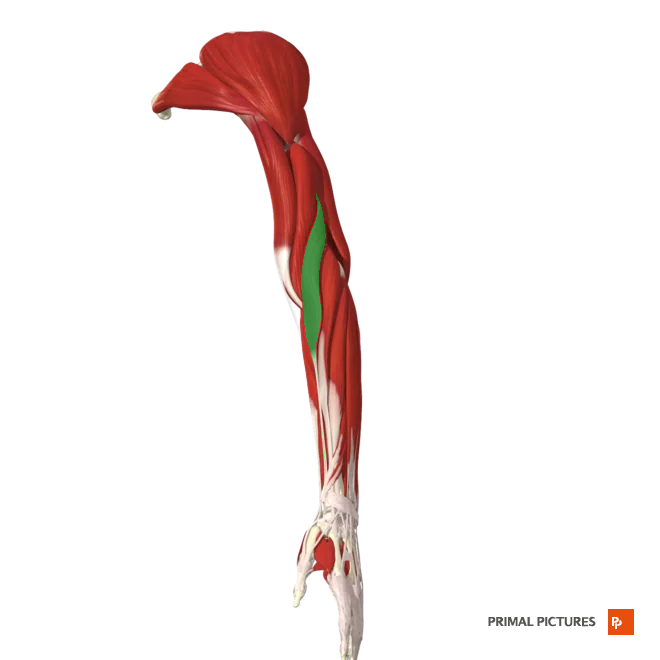
Triceps brachii
extends forearm at elbow
extends arm at the shoulder
Insertion:Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna

Brachioradialis
Flexes forearm at the elbow
Insertion:Styloid process of the radius
pronator Teres
Pronates forearm at radius
weakly flexes forearm at elbow
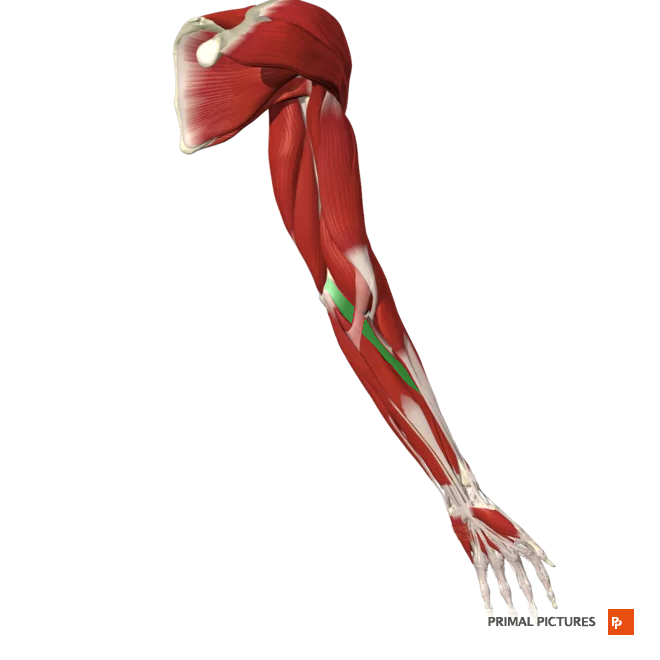

Flexor Carpi Radialis
Flexes and adducts hand at wrist
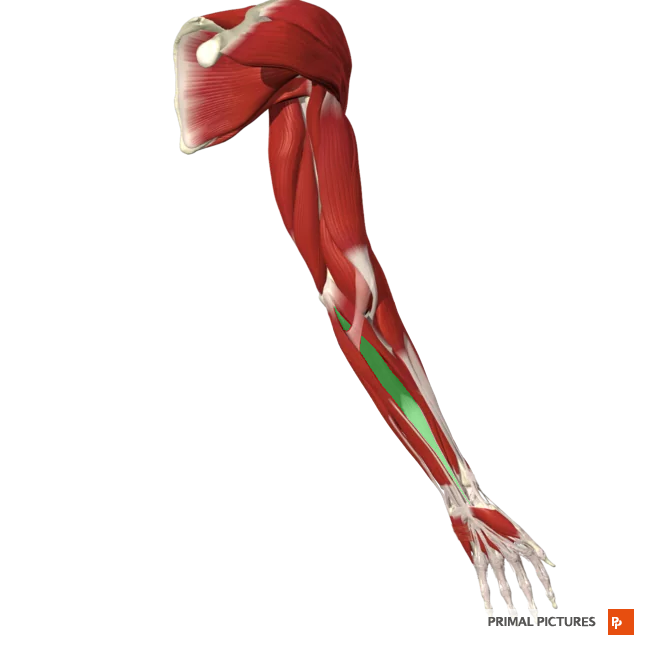
Palmaris Longus
weakly flexes and abducts hand at wrist
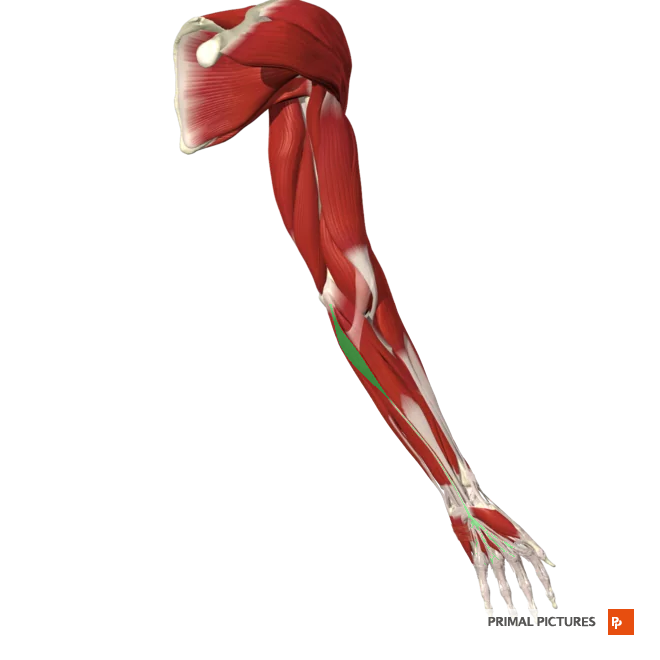

Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexes and adducts hand at wrist
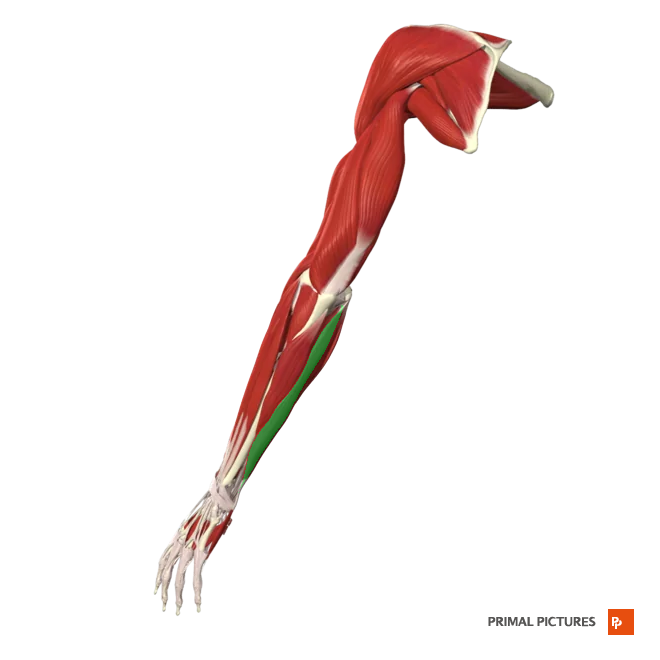
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Extends and abducts hand at wrist
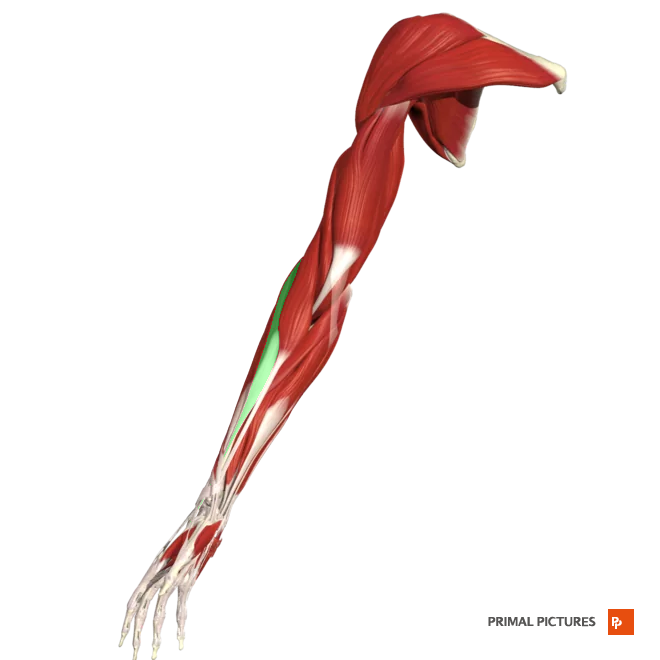
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Extends and abducts hand at wrist
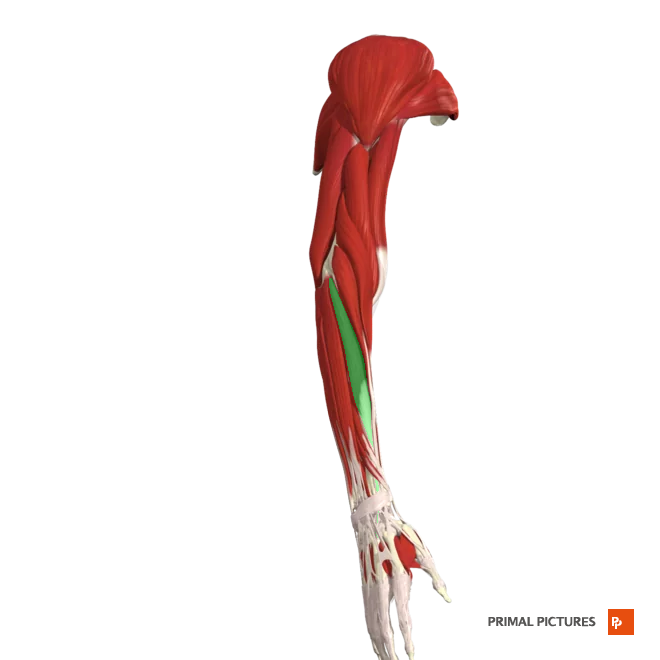
Extensor Digitorum
Extends medial four digits at the metacarpal joints and secondarily at the phalangeal joints
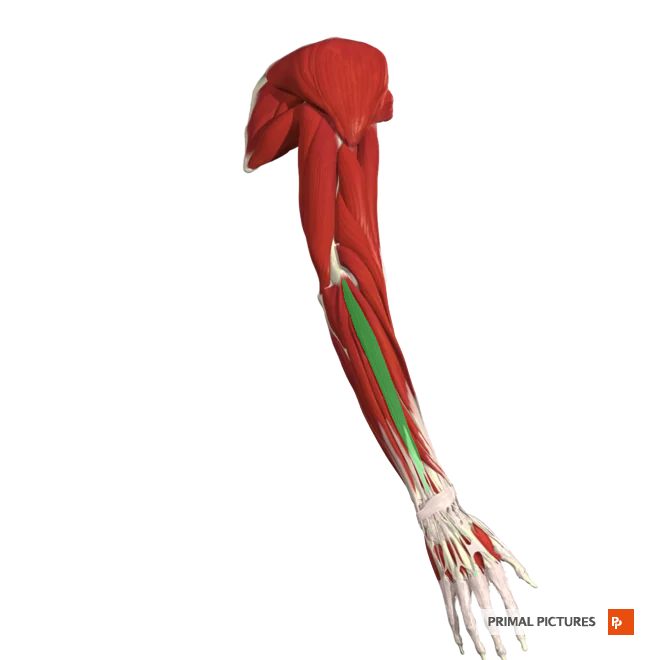
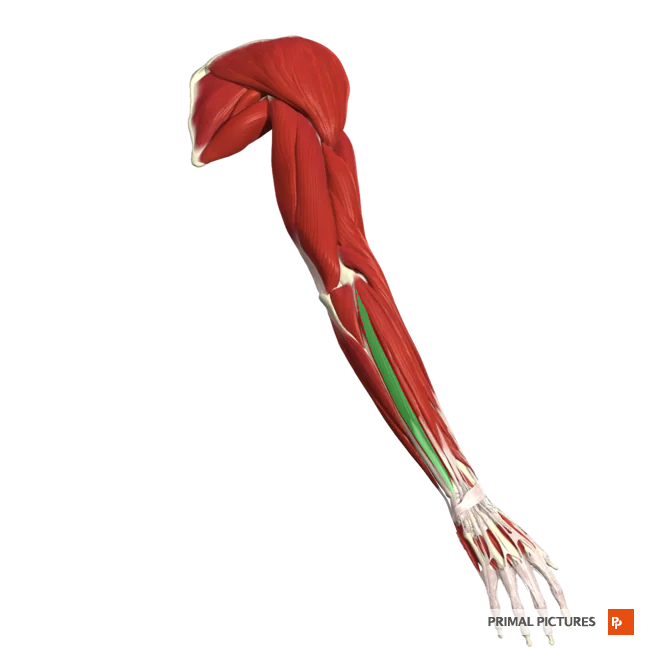
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Extends and abducts hand at wrist
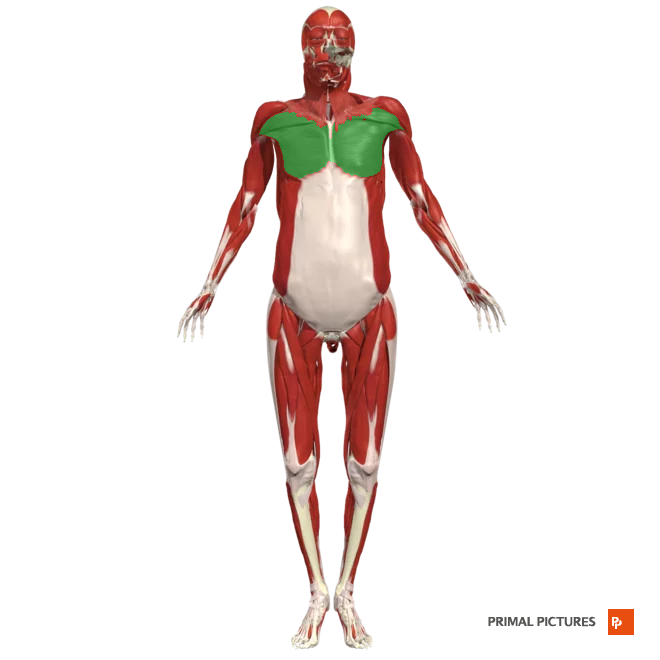
Pectoralis Major
Medialy rotates arm at the shoulder
Insertion: at the lateral lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
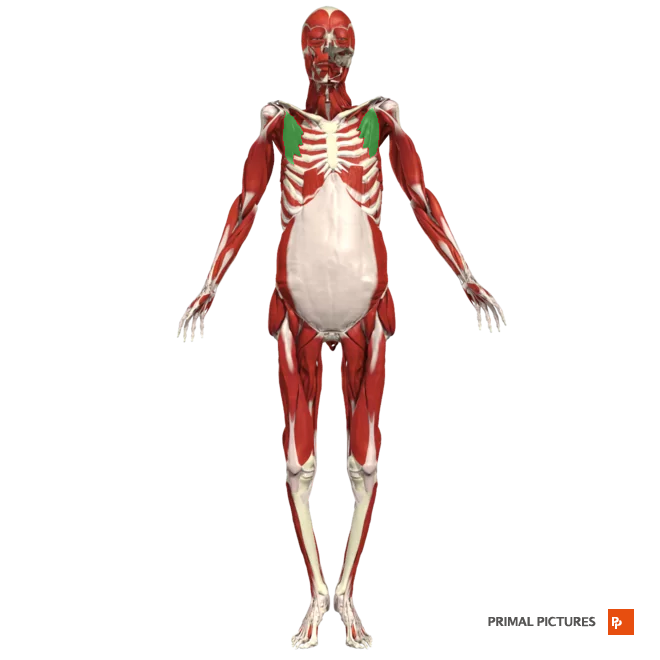
Pectoralis minor
Abducts scapula and rotates it downwards
Insertion:coracoid process of the scapula
Serratus Anterior
abducts the scapula and rotates upwards (protraction)
Insertion:the anterior surface of the medial border of the scapula
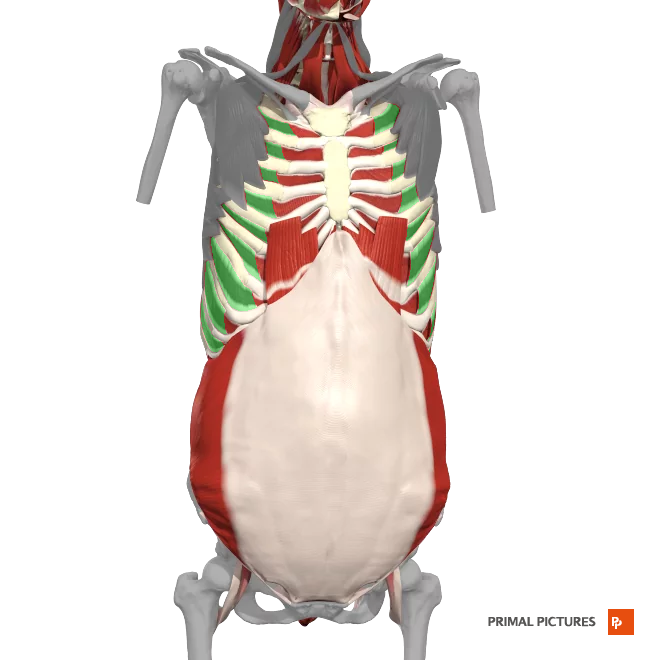
External intercostals
Elevates the ribs
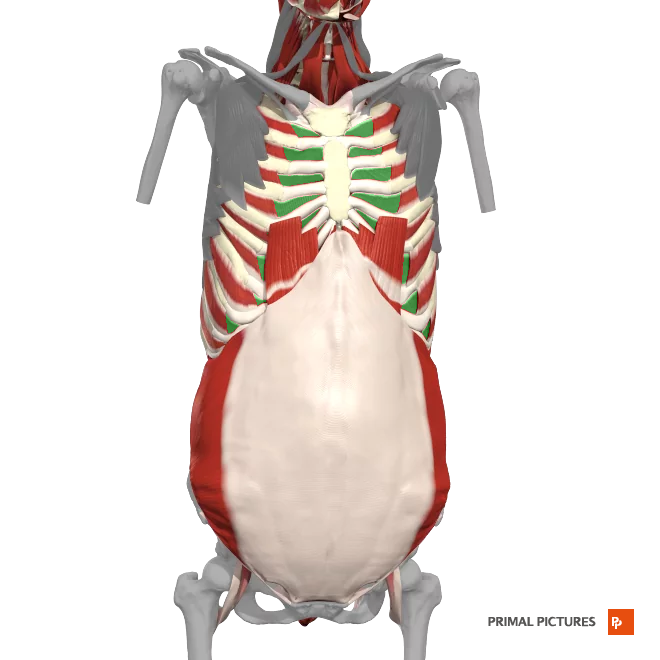
Internal intercostals
Depresses the ribs
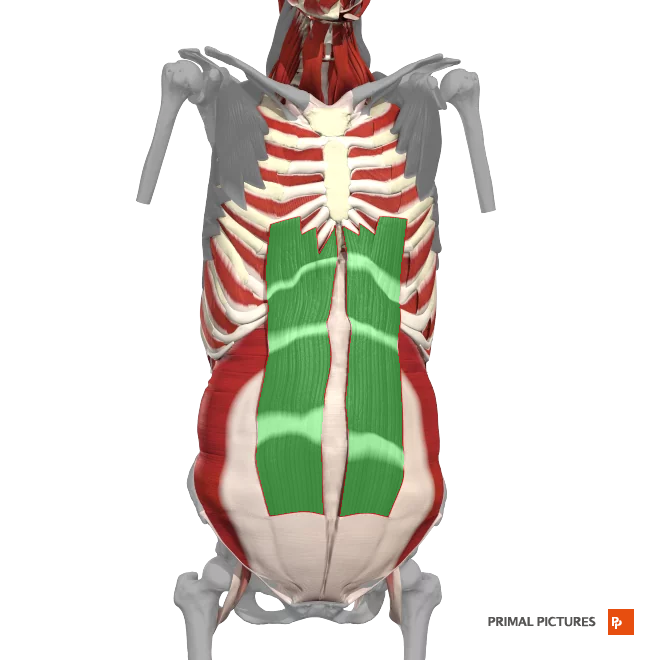
Rectus Abdominis
Flexion of the trunk
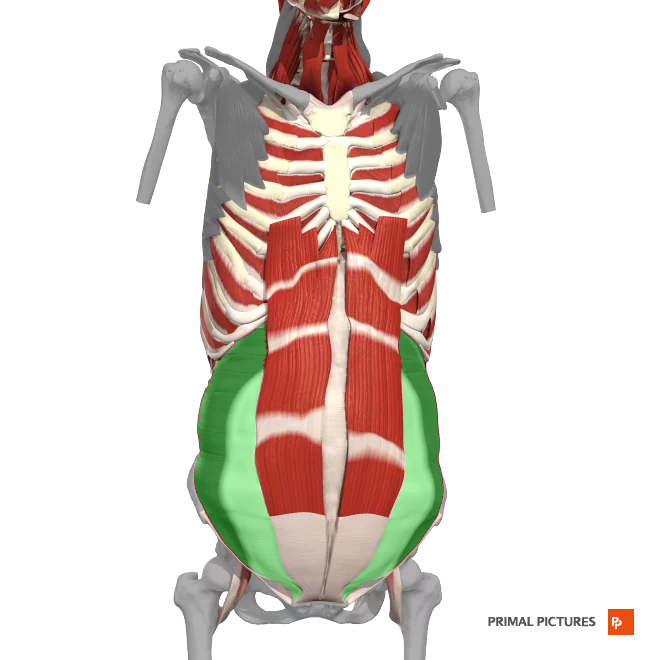
External oblique
Unilateral flexion of the trunk rotation of the trunk
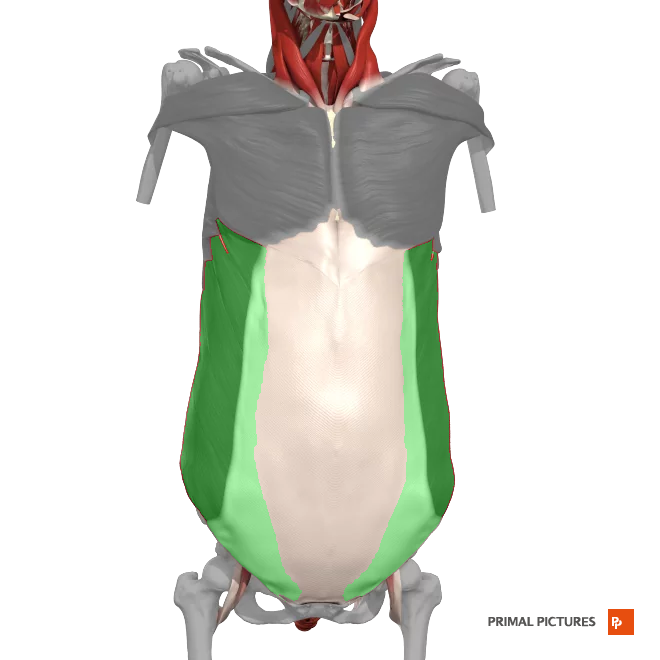
internal Oblique
rotates the trunk
laterally flexes vertebral column
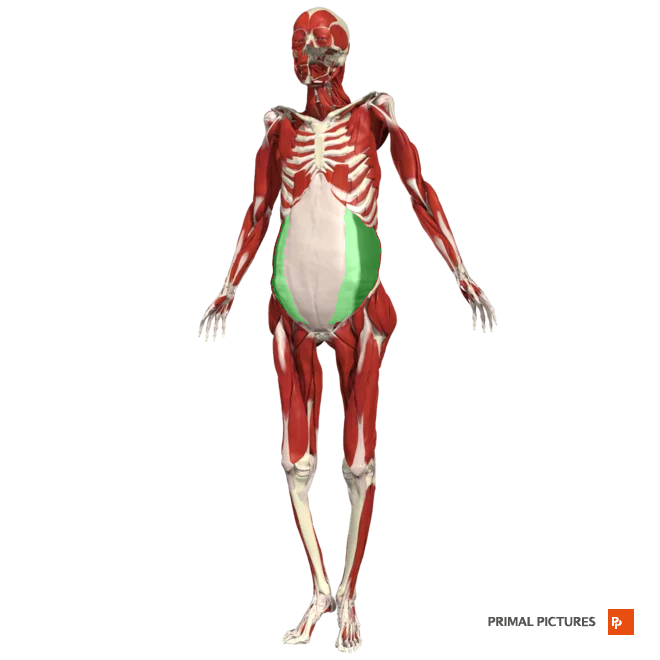
Transverse Abdominis
compression of the abdominal cavity
Rhomboids
origin: (minor) Spinous process of vertebrae c7- T1
(major) Spinous process of vertebrae T2-T5
Antagonist: stratus anterior
Latissimus Dorsi
medial rotation, abduction, extension
Insertion: intertubercular groove of the humerus.
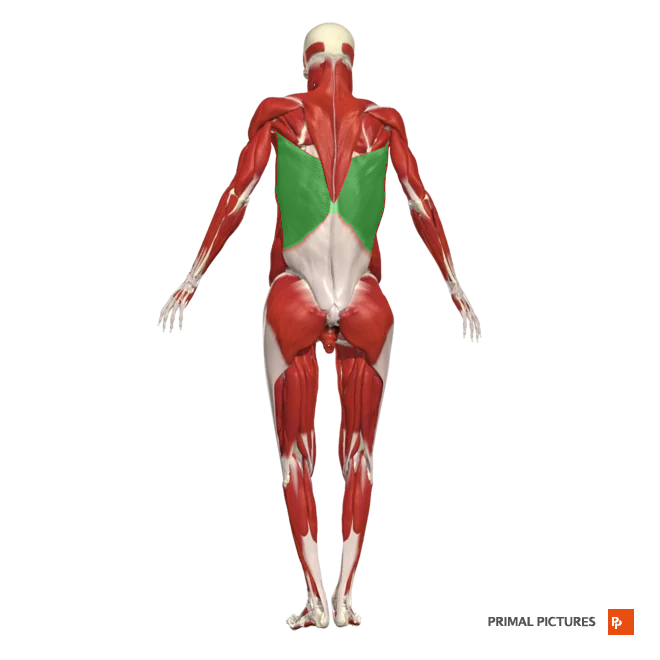
erector spinae
Group of muscles longissimus, iliocostalis, and spinalis
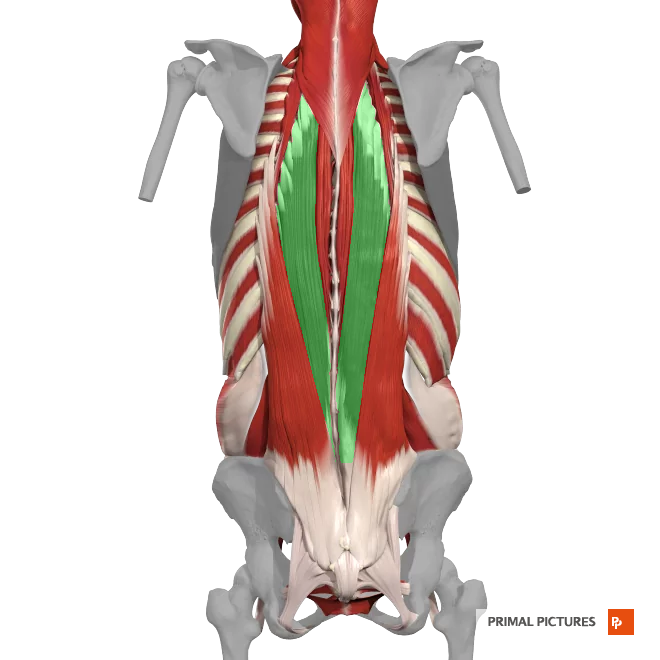
transverso- spinale
It consists of 3 major subgroups: semispinalis, multifidus and rotatores
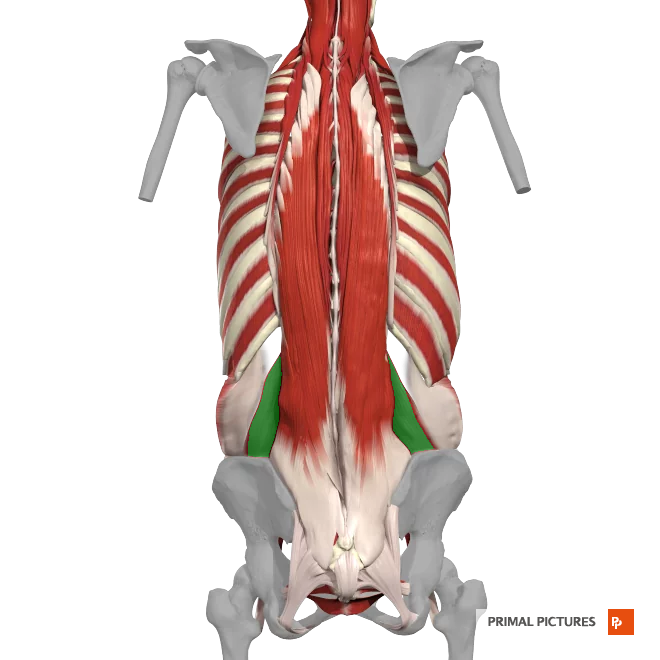
Segmental Muscles
Deepest layer. The levatores costarum, interspinales and intertransversarii muscles
Quadratus lumborum
Muscle located in the lower back, connecting the pelvis and the spine. It helps stabilize the spine, maintain posture, and assist in movements like bending and twisting.
Psoas major
Acts together with iliacus for flexion of thigh at hip
rotates thigh laterally
flexes trunk on the hip (sitting up in a supine position)
Insertion:lesser trochanter of the femur
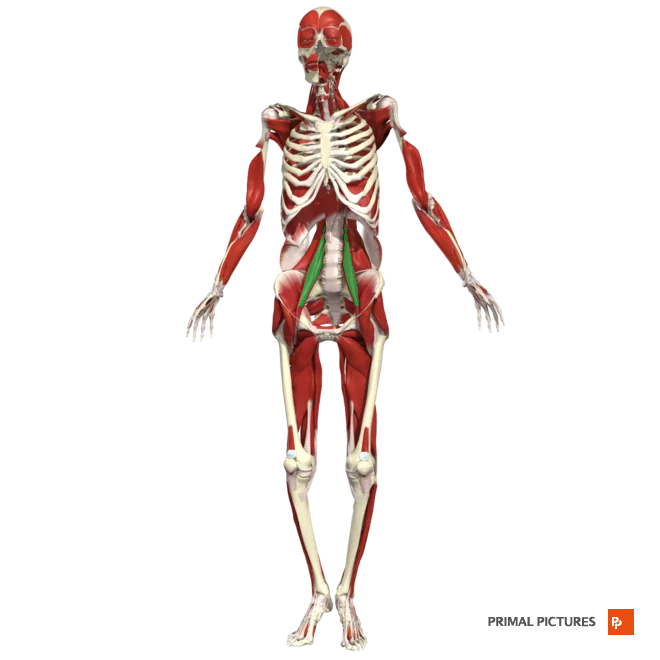
Iliacus
Acts together with psoas for flexion of thigh at hip
Insertion:Iliac fossa
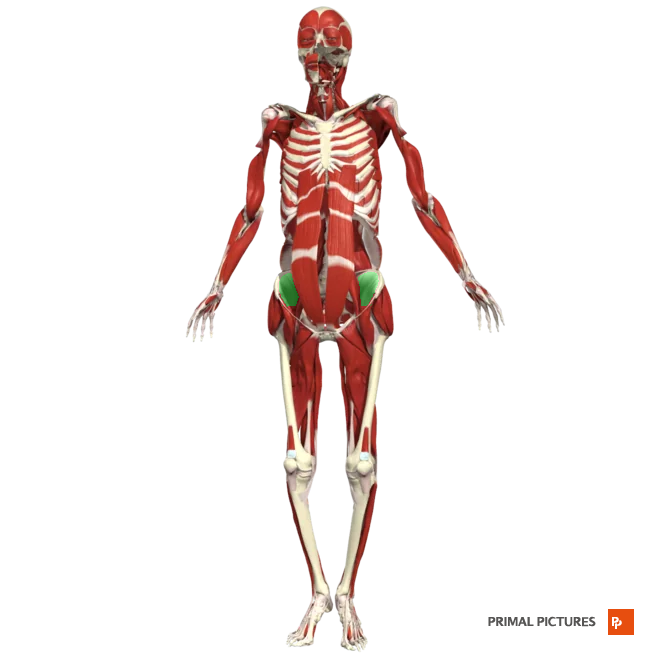
Pectineus
Flexes and adducts thigh at hip
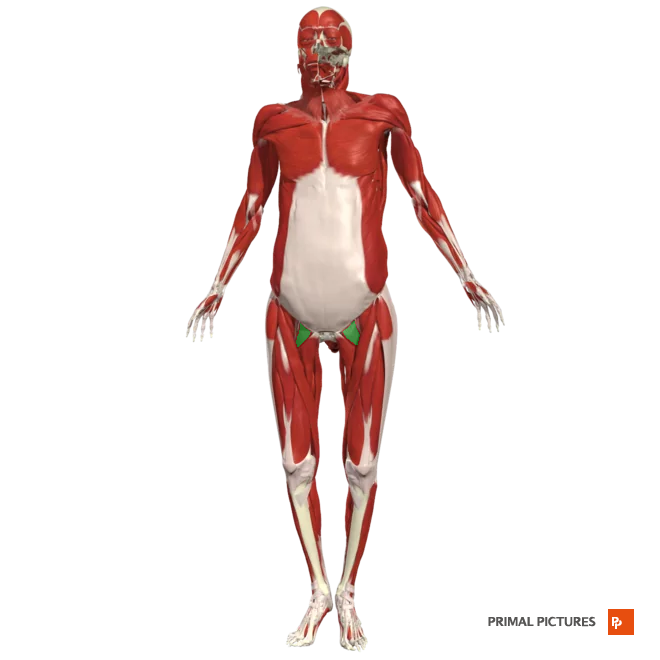
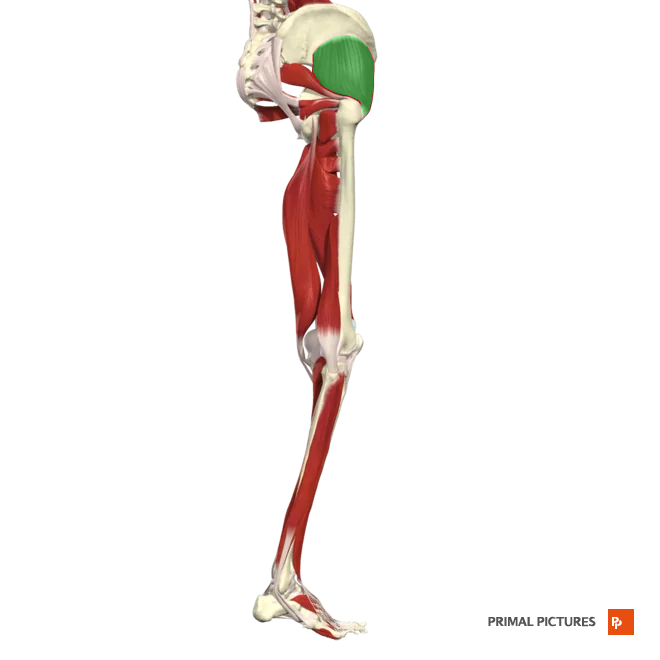
gluteus maximus
Extends and laterally rotates hip
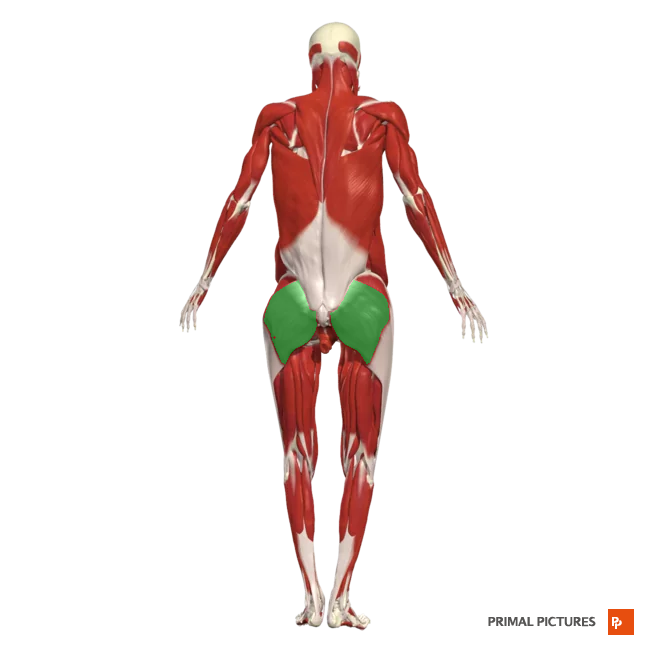
gluteus medius
abducts and medially rotates hip
Insertion:lateral surface of the ilium
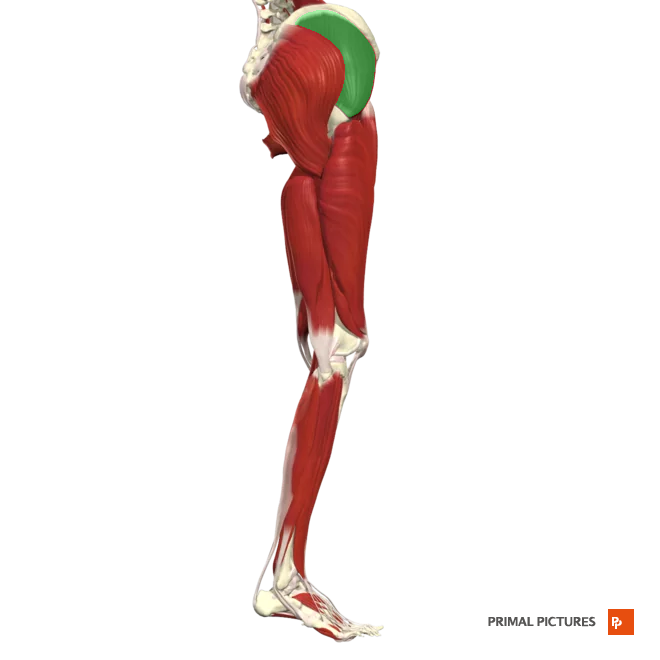
gluteus minimus
Abducts and medially rotates hip
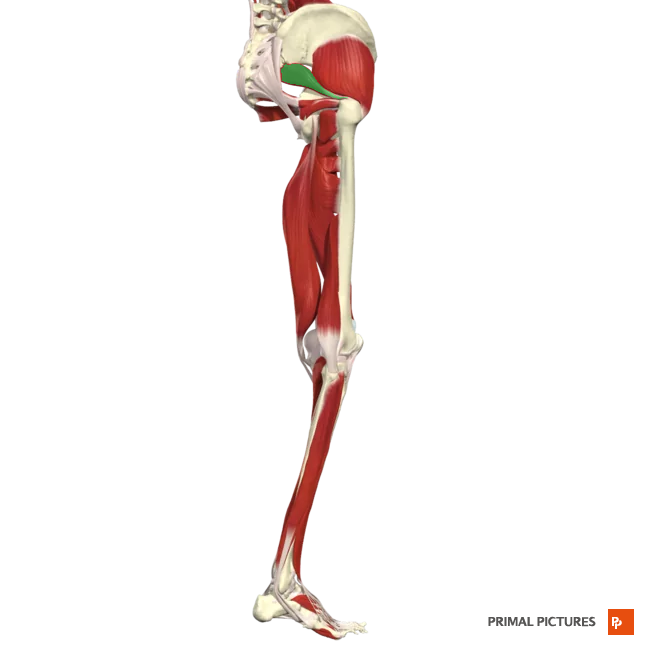
piriformis
Laterally rotates and abducts hip
Insertion:apex of the greater trochanter
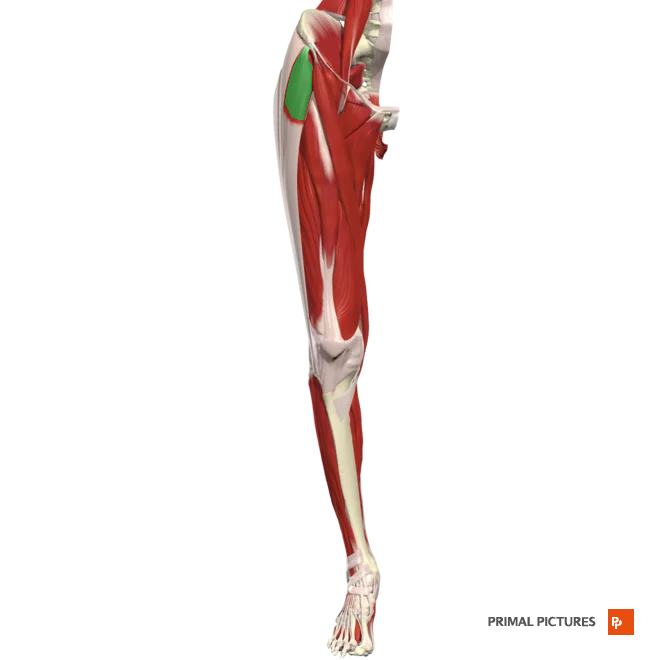
tensor fasciae latae
Flexes and abducts hip
sartorius
Laterally rotates thigh at hip
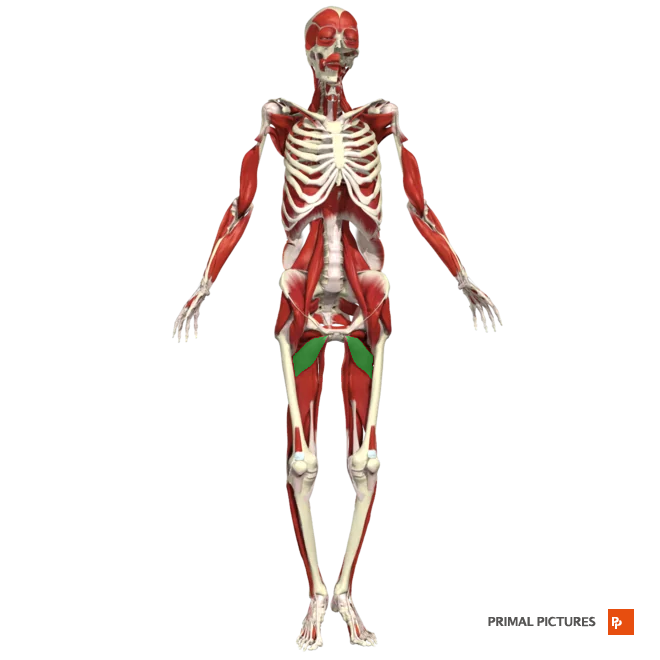
Adductor brevis
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip and rotates thigh
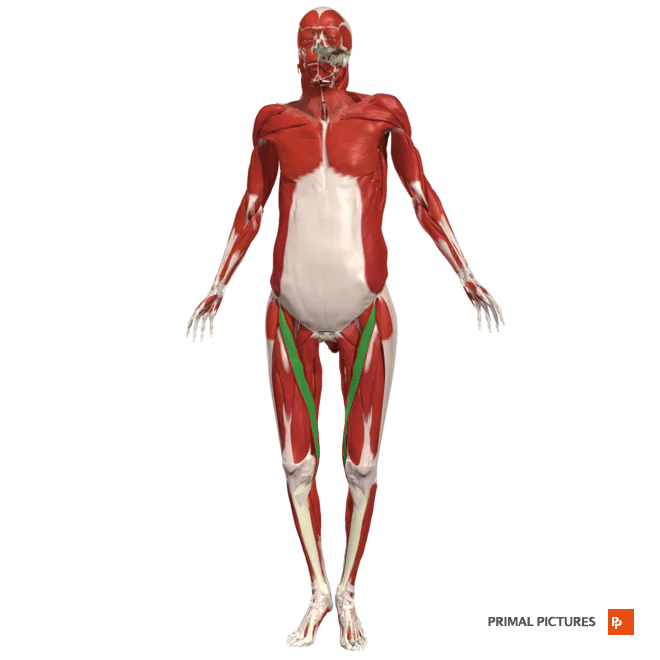
adductor longus
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip and rotates thigh
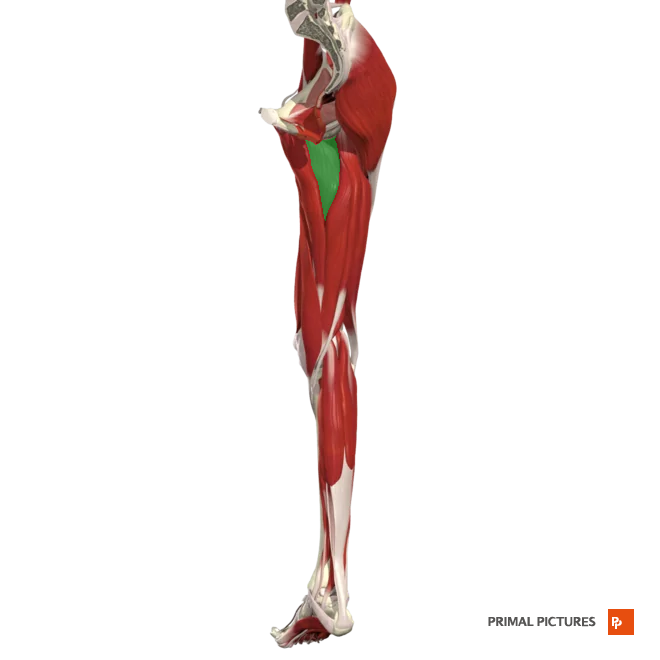
adductor magnus
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip and rotates thigh
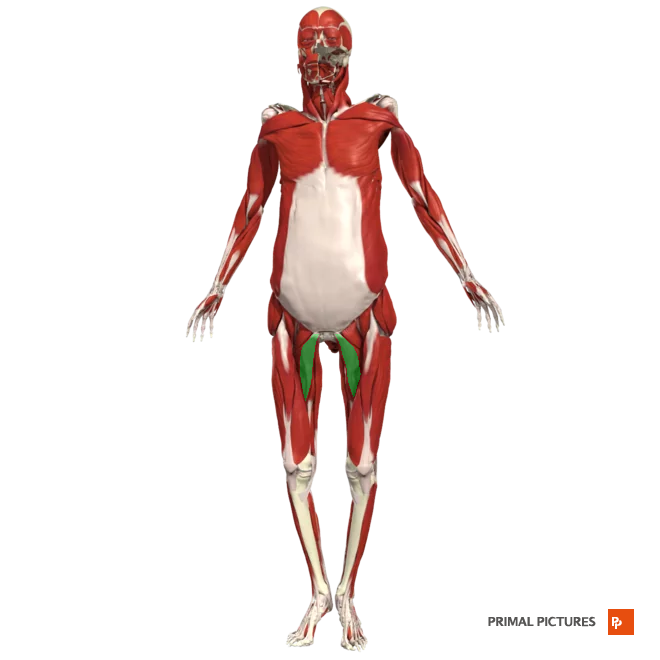
gracilis
Adducts thigh at hip
Medially rotates thigh
Flexes leg at knee
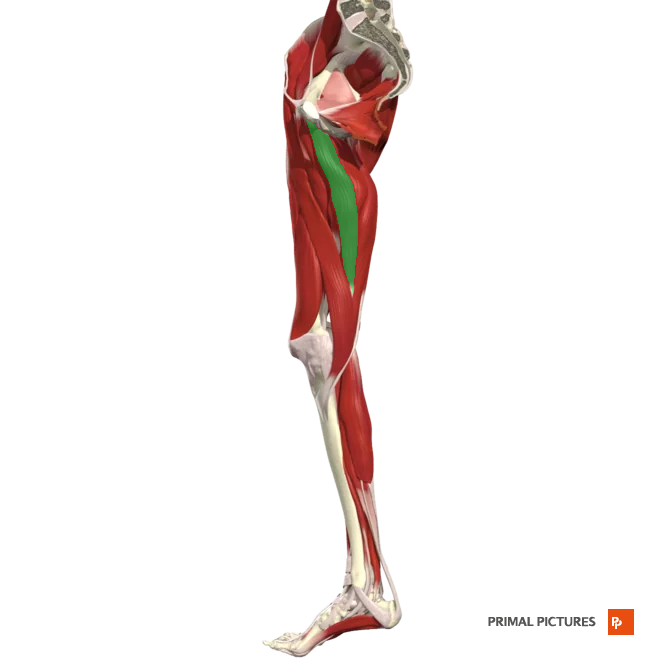
rectus femoris
Extends leg at knee
Flexes thigh at hip
Origin: plevis anterior inferior illiac spine
Insertion:the base of the patella
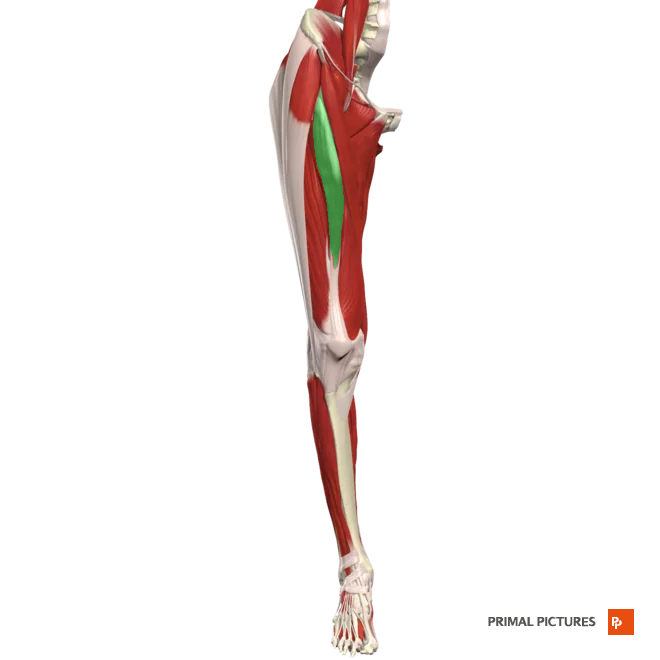
vastus lateralis
Extends leg at knee
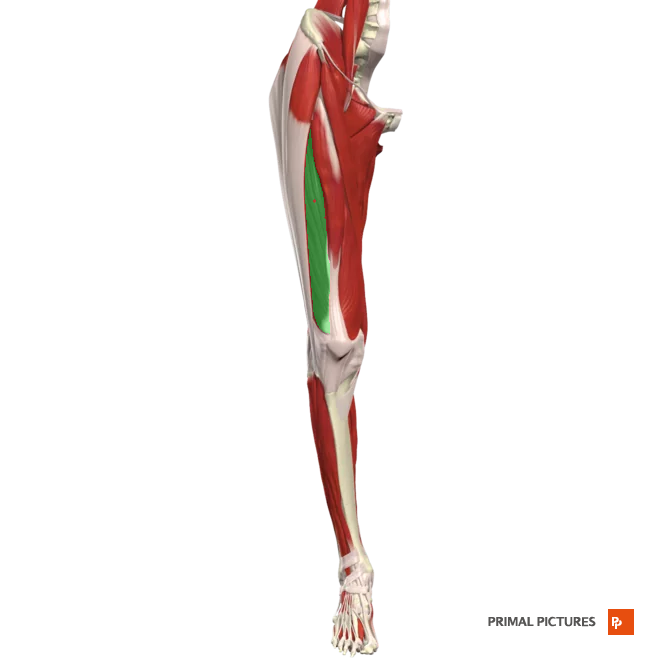
vastus medialis
Extends leg at the knee
Origin:plevis anterior inferior illiac spine
Insertion: the base of patella via the quadriceps femoris tendon
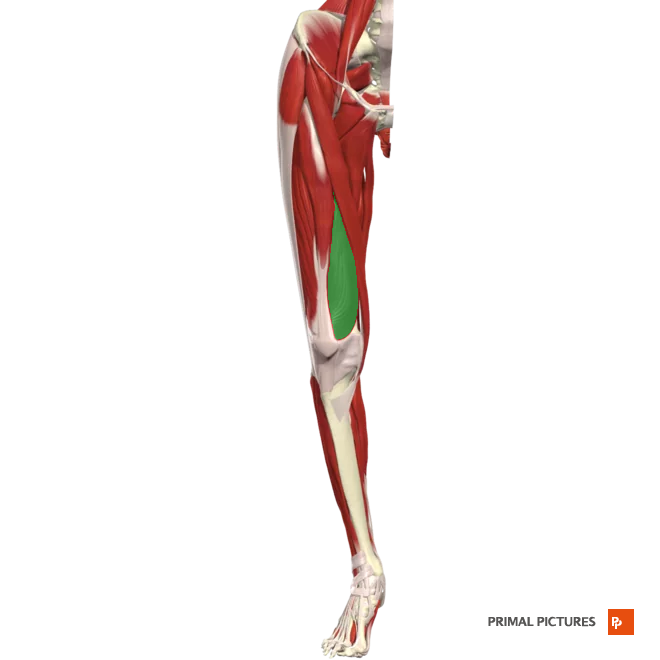
vastus intermedius
Extends leg at the knee
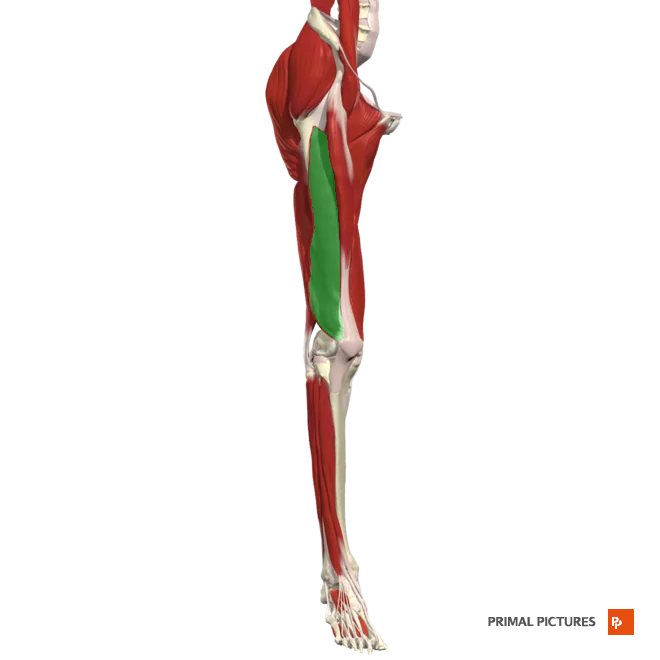
Semitendinosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at the hip
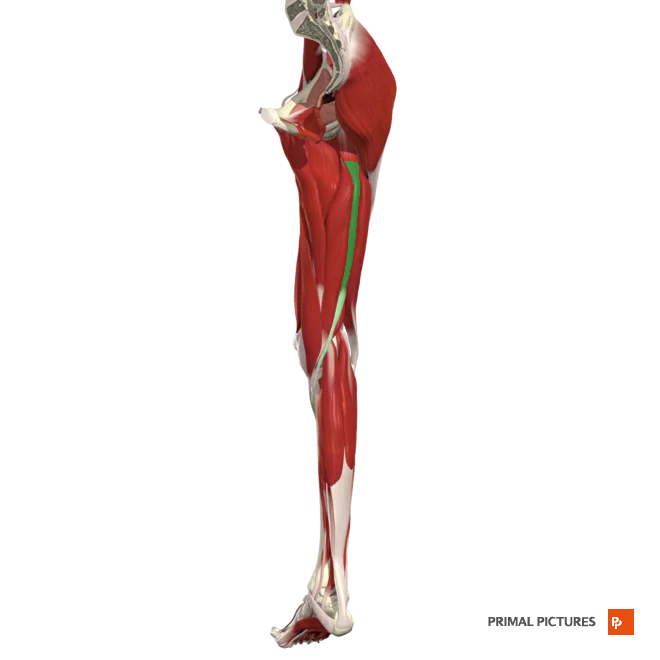
semimembranosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at hip
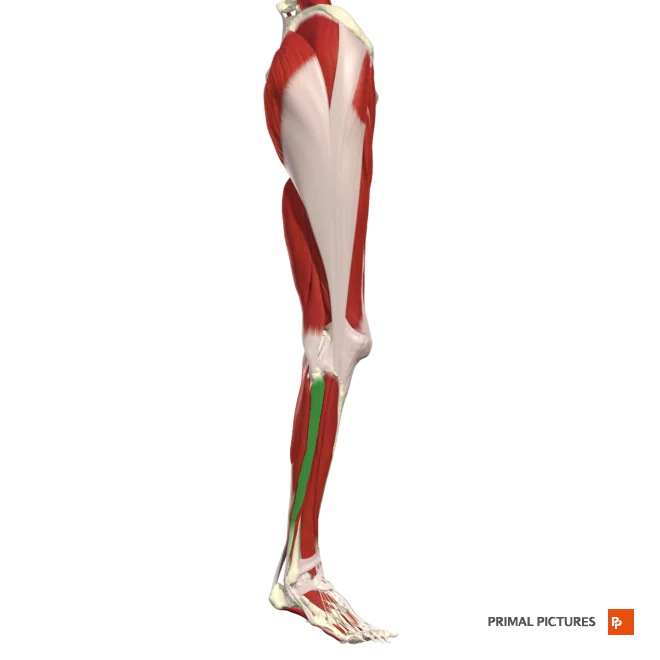
Fibularis longus
Plantar flexion at ankle
Everts the foot at intertarsal joints
fibularis brevis
Plantar flexion of foot at ankle
everts (pronates) foot at intertarsal joints
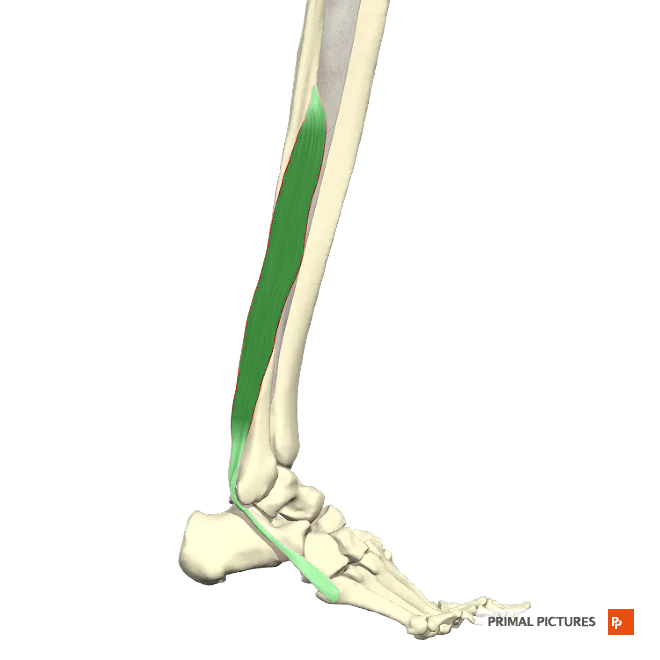
extensor digitorum longus
Dorsiflexes foot at ankle and extends distal and middle phalanges of each toe
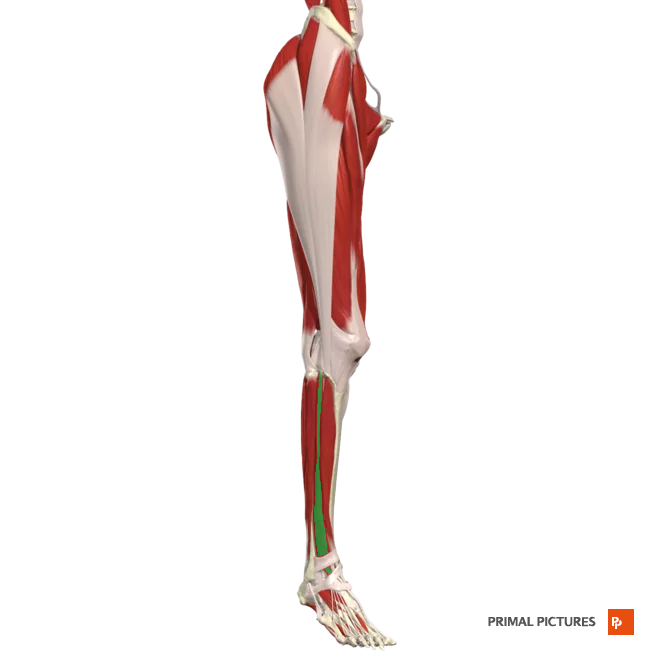
Tibialis anterior
Dorsiflexes foot at the ankle
Inverts (supinates) foot at interarsal joints
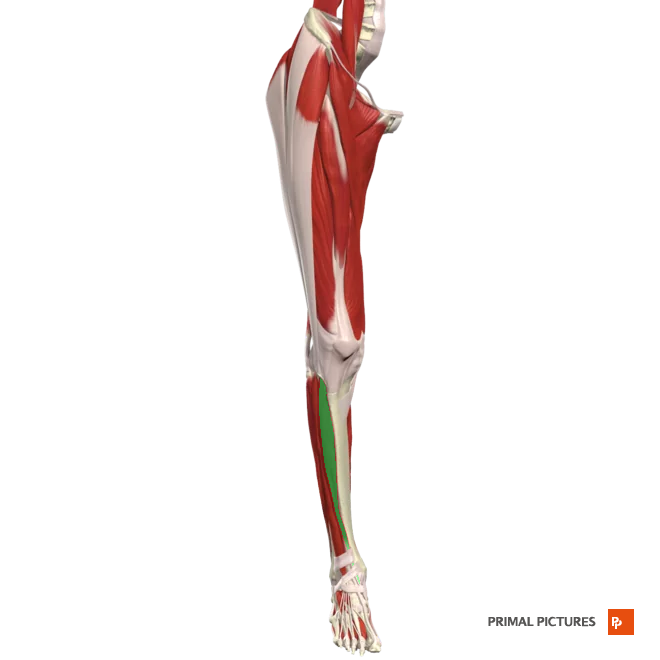
Popliteus
Flexes leg at the knee
Medially rotates tibia to unlock the extended knee
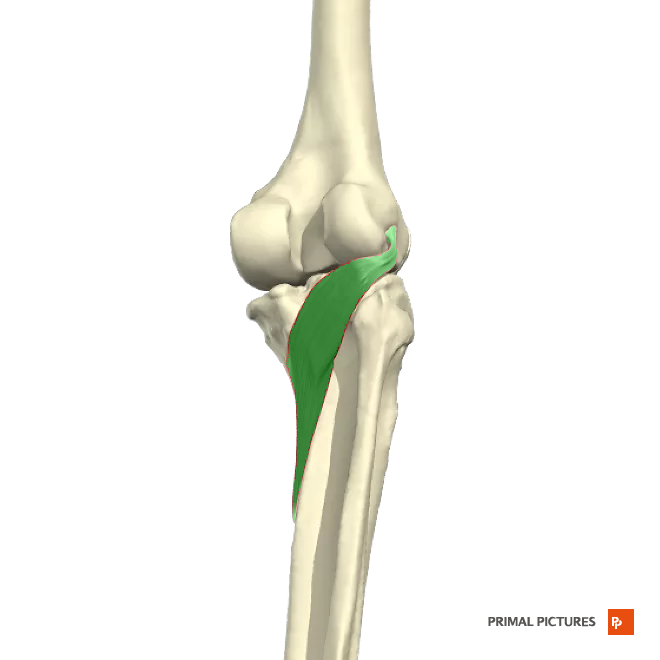
Gastrocnemius
Plantar flexion of foot at ankle joint and flexes leg at knee
Insertion: fuse to insert onto the calcaneus (heel bone) through the Achilles tendon (also known as the calcaneal tendon)
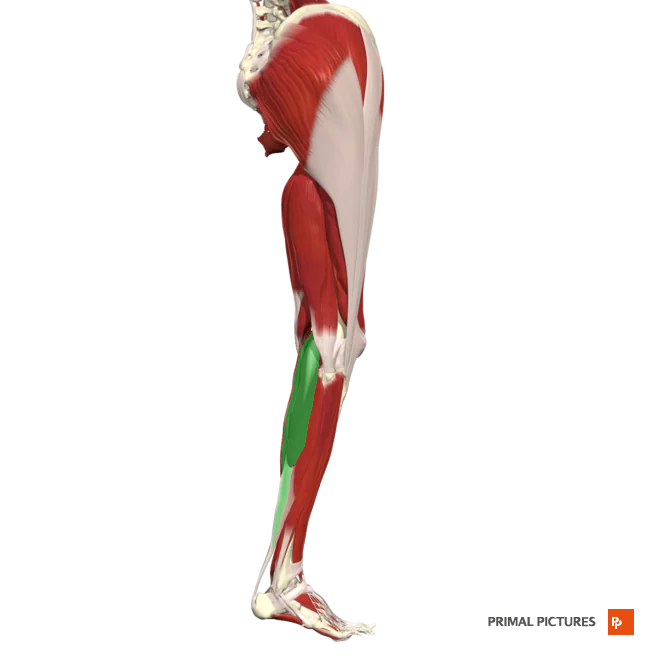
Soleus
Plantar flexes foot at the ankle joint
Insertion: fuse to insert onto the calcaneus (heel bone) through the Achilles tendon (also known as the calcaneal tendon)
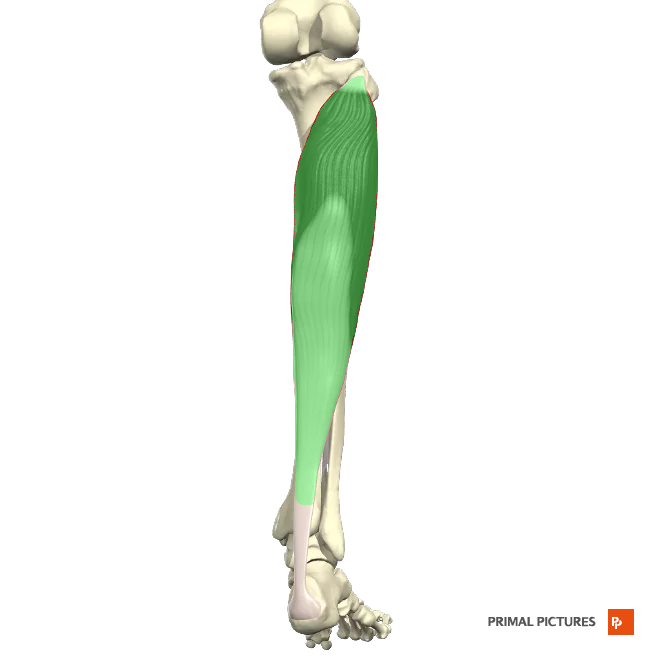
4 properties of muscular tissue.
-Electrical excitability
-Contractility
-Extensibility
-Elasticity
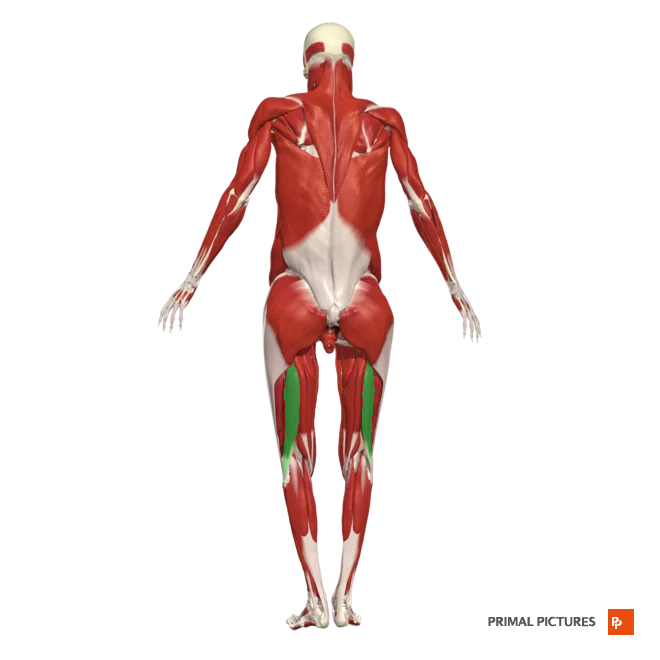
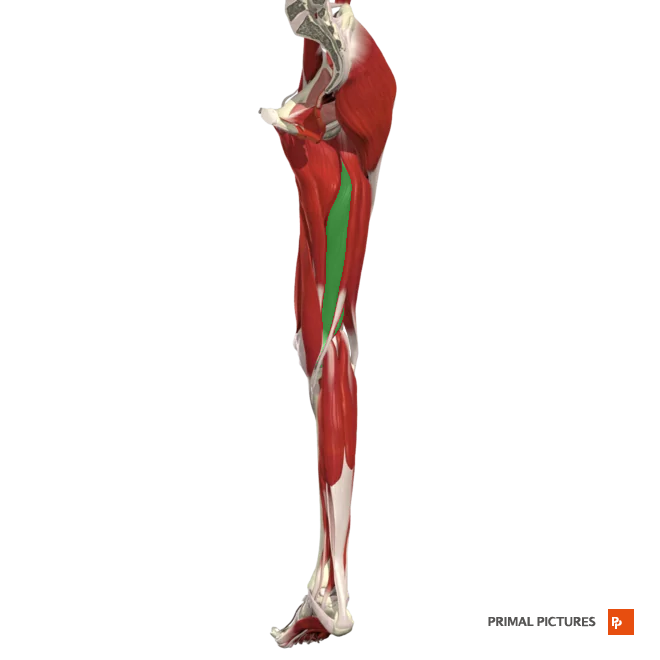
Biceps Femoris
Long h. origin: originates from the medial facet of the ischial tuberosity
Short h. origin: lateral lip of the inferior third of the linea aspera
Insertion: The lateral head of the fibula.