Anatomy L4 Exam 1 Senses, Eye Anatomy
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
the ____ and interprets nerve impulses from sensory receptors that detect environmental changes
central nervous system
CNS
what are the 5 different types of sensory receptors?
pain receptors = nociceptors
chemoreceptors
thermoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
photoreceptors – rods and cones in eye
what is refered pain?
pain that may seem to be coming from a different area of the body than the one actually being stimulated
example of refered pain?
heart attack
-may experience pain in the left arm or jaw but really whats stimulating that pain is the heart
acute pain fibers
characteristics
type of pain
where is it felt?
thin and myelinated nerve fibers that conduct nerve impulses rapidly
mostly produce sharp pain
sensed as coming from the skin
chronic pain fibers
characteristic
type of pain
where is it felt?
thin and unmyelinated nerve fibers that conduct impulses more slowly
mostly produce dull, aching pain
sensed as coming from deeper within the body
what organs/accessory structures are stored in the orbit cavity of the skull?
eyelids
lacrimal glands
extrinsic muscles
eye
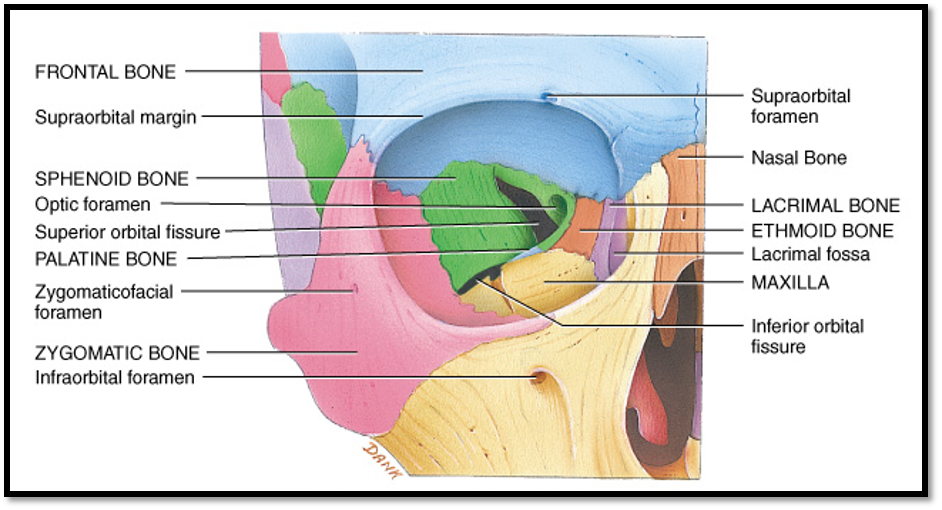
what bones are on the medial wall of the orbit?
Maxilla bone
Lacrimal bone
Ethmoid bone
Palatine bone
Sphenoid bone
Frontal bone
all the bones EXCEPT for zygomatic
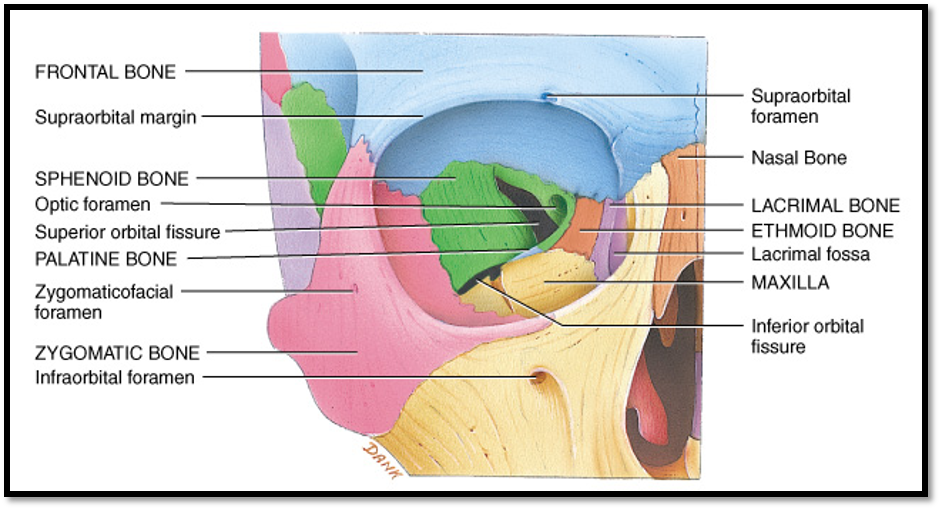
what bones are on the lateral wall of the orbit?
Zygomatic bone
Frontal bone
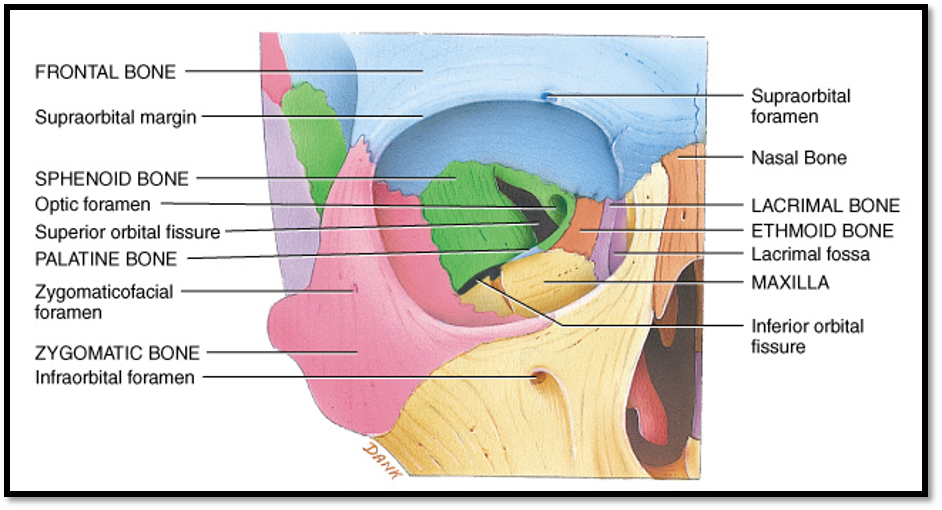
what bones are on the superior wall of the orbit?
Frontal bone
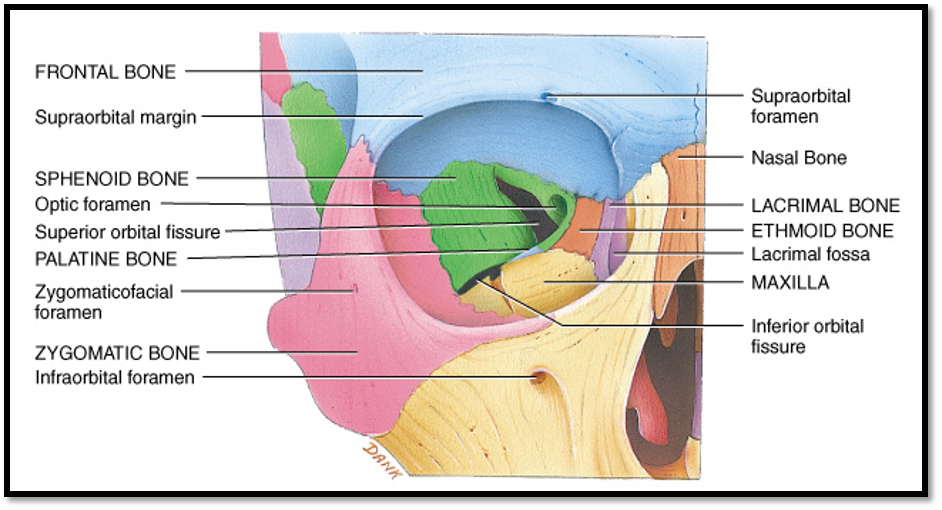
what bones are on the inferior wall of the orbit?
Maxilla bone
Zygomatic bone
Palatine bone
what is another word for eyelid?
palpebrae
what do meibomian gland secrete and where?
aka tarsal glands
lipid rich product keep the eyelid from sticking together
what is the nasolacrimal duct?
where does it drain to?
a duct going from the lacrimal bone region to the inferior nasal turbinate (located in the spetum)
drains to the inferior nasal turbinate
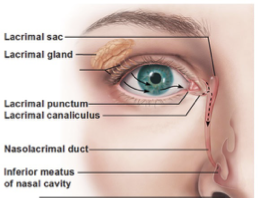
what is the lacrimal apparatus composed of?
lacrimal gland
lacrimal canaliculi
lacrimal sac
nasolacrimal duct
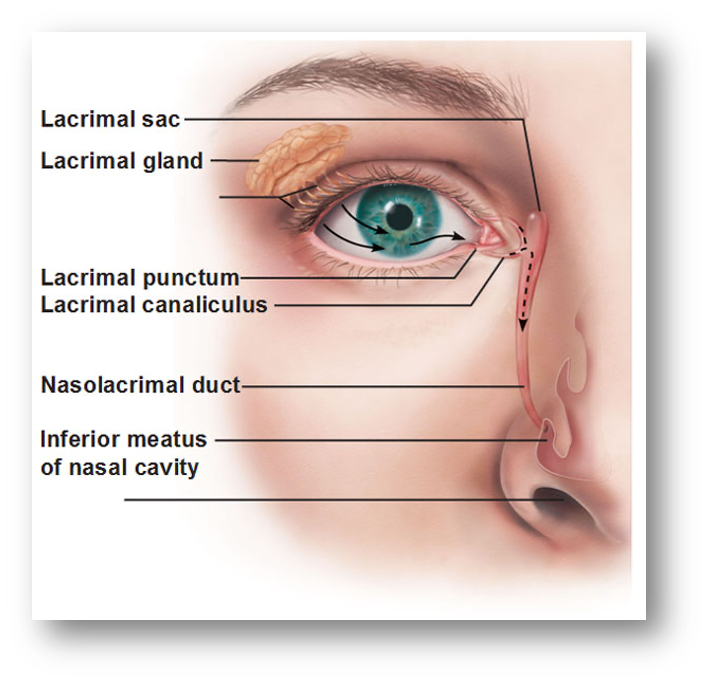
where is the lacrimal gland located in the orbit?
what is it also known as?
superior and lateral to the eye
superiolateral gland
what hormone do tears have?
lysozyme, which kills bacteria
what are the 2 different conjunctiva located in the eye?
palpebral conjunctiva
bulbar/ocular conjunctiva
what does the palpebral conjunctiva cover?
the inner surface of the eyelid
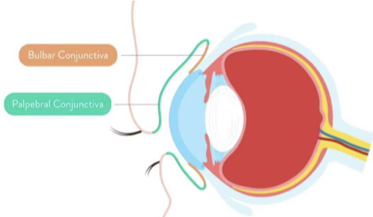
what does the bulbar/ocular conjunctiva cover?
cover the anterior surface of the eye, and extend to the edge of the cornea
basically covers the sclera
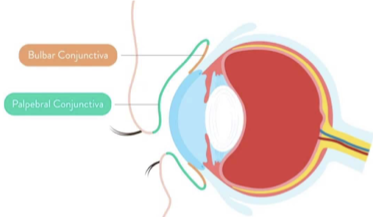
what is the function of the conjunctiva in the eye?
keeps bacteria and foreign material from getting behind the eye
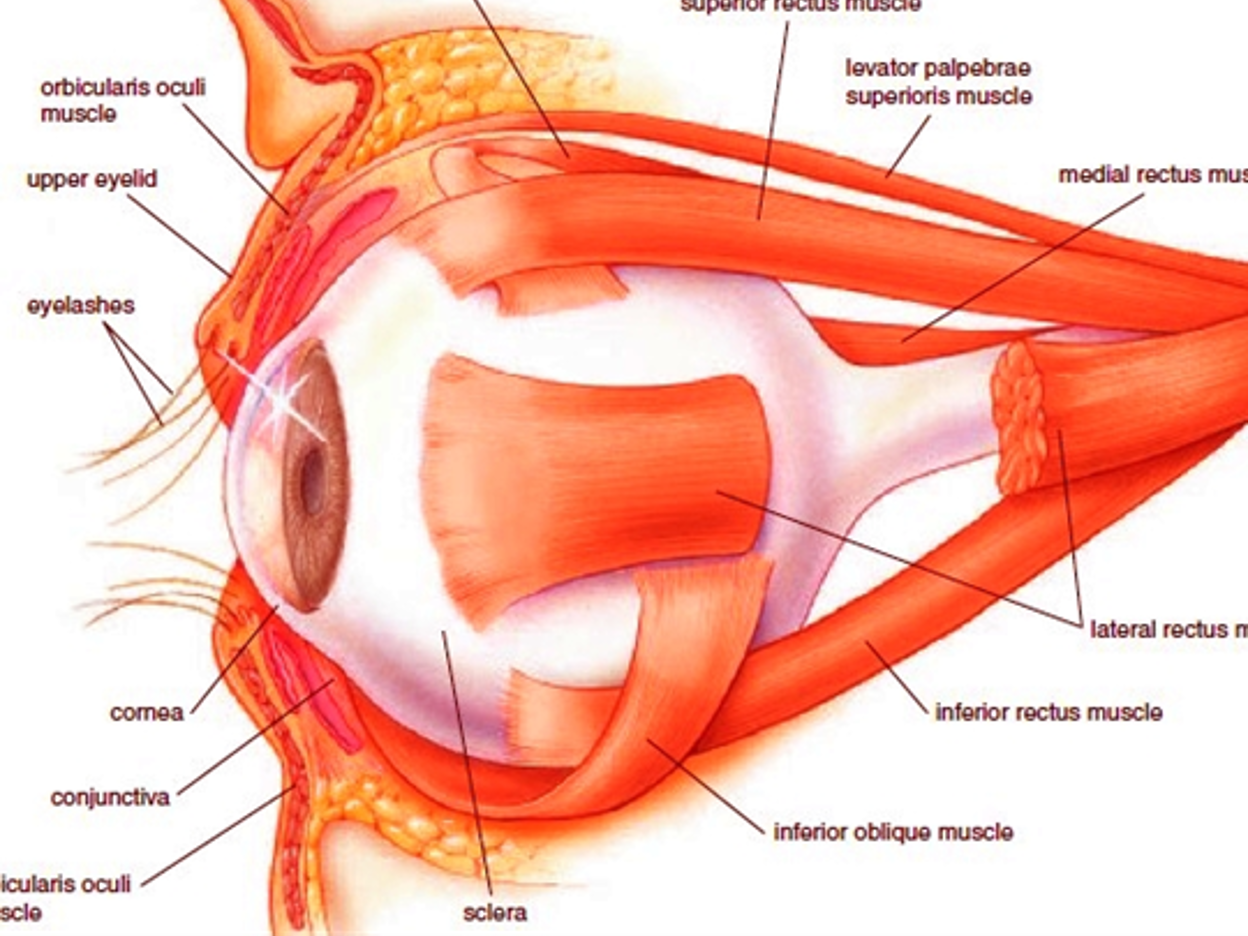
what are the muscles of the eye?
orbicularis oculi m.
levator palpebrae superioris m.
SR
SO
MR
IR
IO
what are the 3 layers of the eye?
fibrous tunic (outter layer)
vascular tunic (middle layer)
nervous tunic (innermost layer)
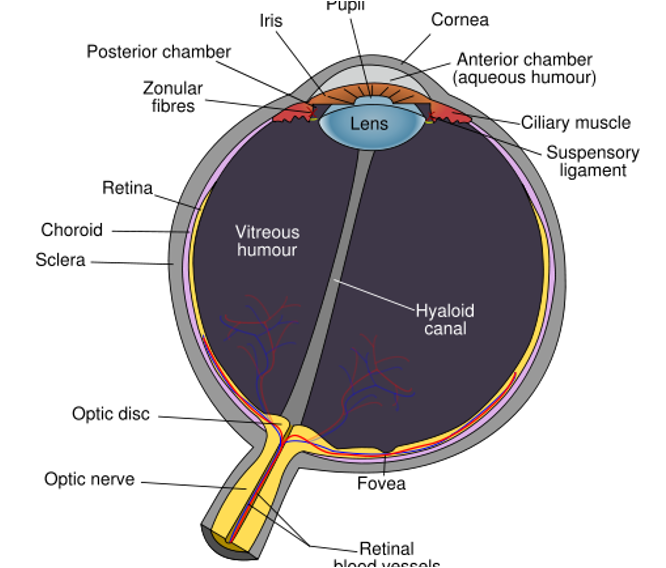
what is in the fibrous tunic?
sclera
cornea
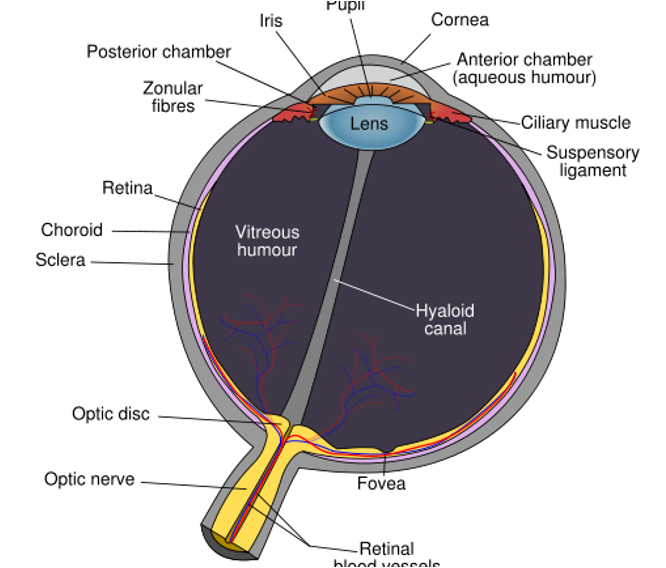
what is in the vascular tunic?
uveal tract
iris
ciliar body
choroid
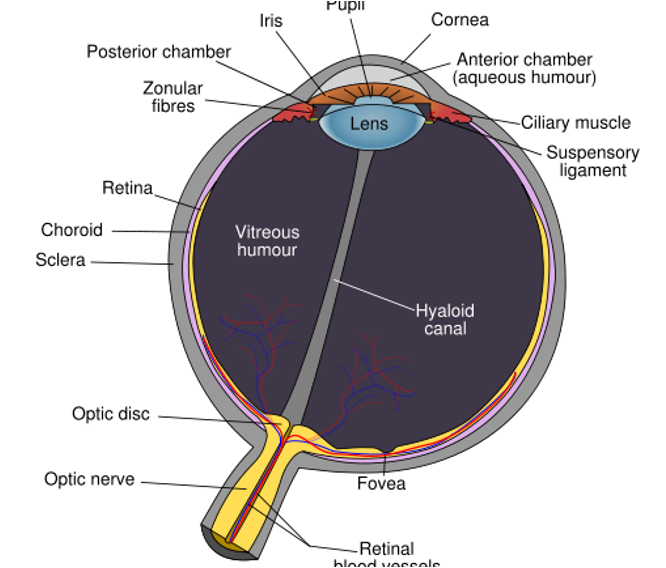
what is in the nervous tunic?
retina
optic nerve (CN 2)
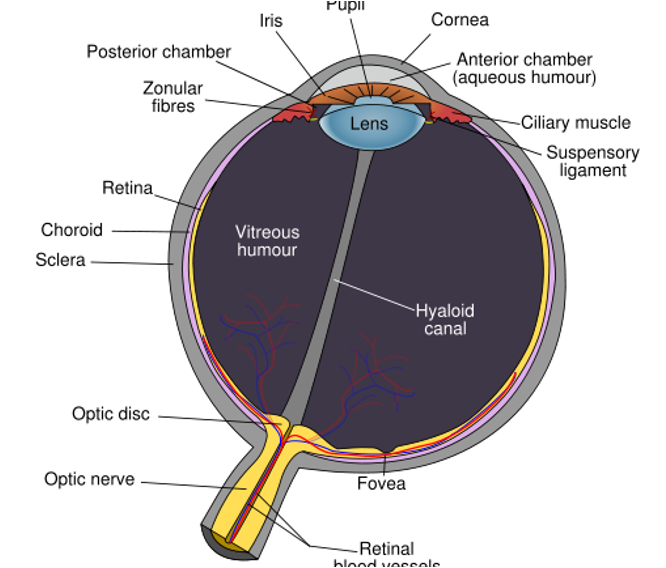
what are the two major divisions of the eye?
anterior cavity
posterior cavity
visceral body
visceral cavity
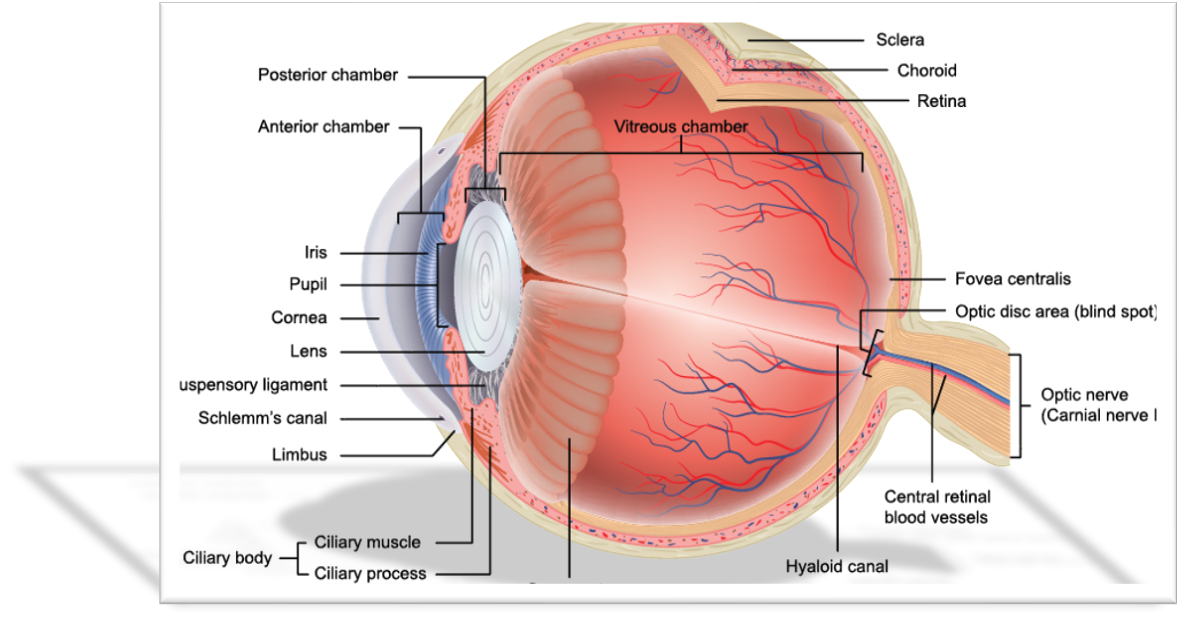
is there a subdivision of the anterior cavity?
yes
the anterior chamber and posterior chambers
what fluid is found in the anterior cavity?
aqueous humor
IN BOTH anterior and posterior chambers
what secrets aqueous humor?
the ciliary body
what is the circulation pathway of the aqueous humor?
flows from posterior chamber → through pupil → anterior chamber
whats the function of aqueous humor?
maintains intraocular pressure (IOP)
what divides the anterior cavity into chambers?
the iris
what causes glaucoma if it gets blocked?
canal of schlemm
what is the canal of schlemm?
the route that aqueous fluid of anterior chamber escapes
what structure divides the eye into the two major cavities?
the ciliary body and lens
what is the visceral body also called?
visceral chamber
posterior cavity
what does the visceral body/cavity contain?
Lens
Ciliary body
Retina
Choroid
Sclera
Optic n. (CN II)
what fluid is found in the vitreous body?
vitreous humor
what does the sclera not cover?
cornea
the cornea is
transparent
avascular
strongest refracting element of the eye
is the cornea continuous with the bulbar conjuctiva?
yes
what does the cornea cover?
iris
pupil
anterior chamber
function of the cornea
aids the lens with focusing
where does the iris lie?
in between the cornea and lens
what 2 muscles are in the iris? what do they do?
Sphincter pupillae m.
circular m., pupillary sphincter m.
Dilator pupillae m.
radial m., pupil dilator m.
BOTH innervated by CN III
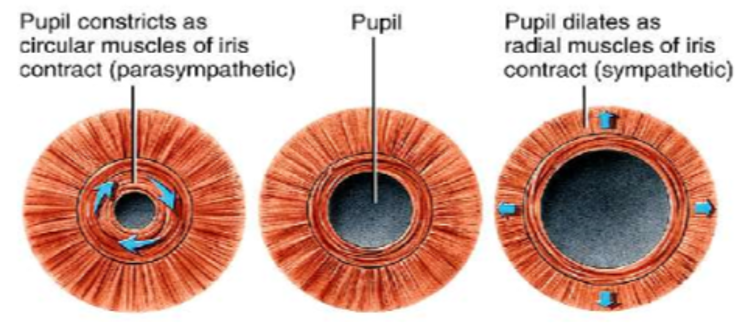
what is eye contraction called?
Miosis or myosis
what is eye dilation?
Mydriasis
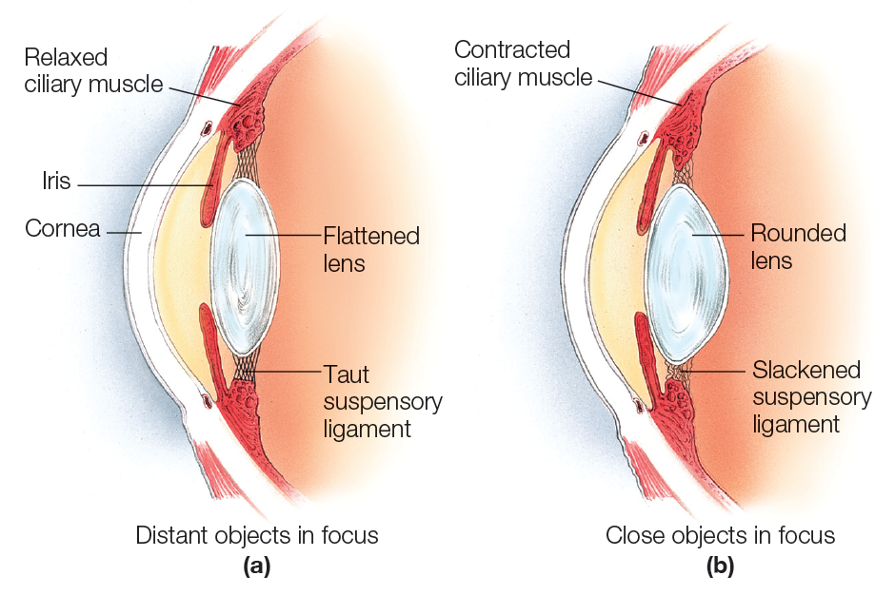
what happens to the lens when the pupils dilate and contract?
dilation: rounds
constriction: flattens
what structure in the retina creates the sharpest vision?
fovea centralis aka central depression
what does the retina have?
visual receptors
2 different types of cells:
rods
cones
rods
sensitive to light and allow for low light and dark vision
provide dark vision
cones
require more light
provides color vision
describe the layers of the retina
Primary neurons (outter layer)
rods and cones
Secondary neurons (middle layer)
bipolar cells
Tertiary neurons (innermost layer)
ganglion cells
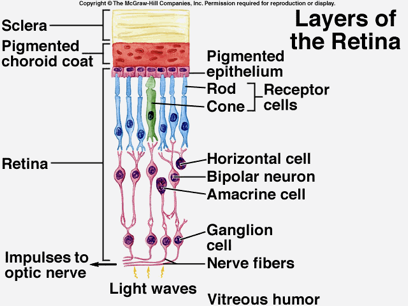
what is the blind spot?
neurosensory patch, it lacks photoreceptors (optic disc/optic nerve)
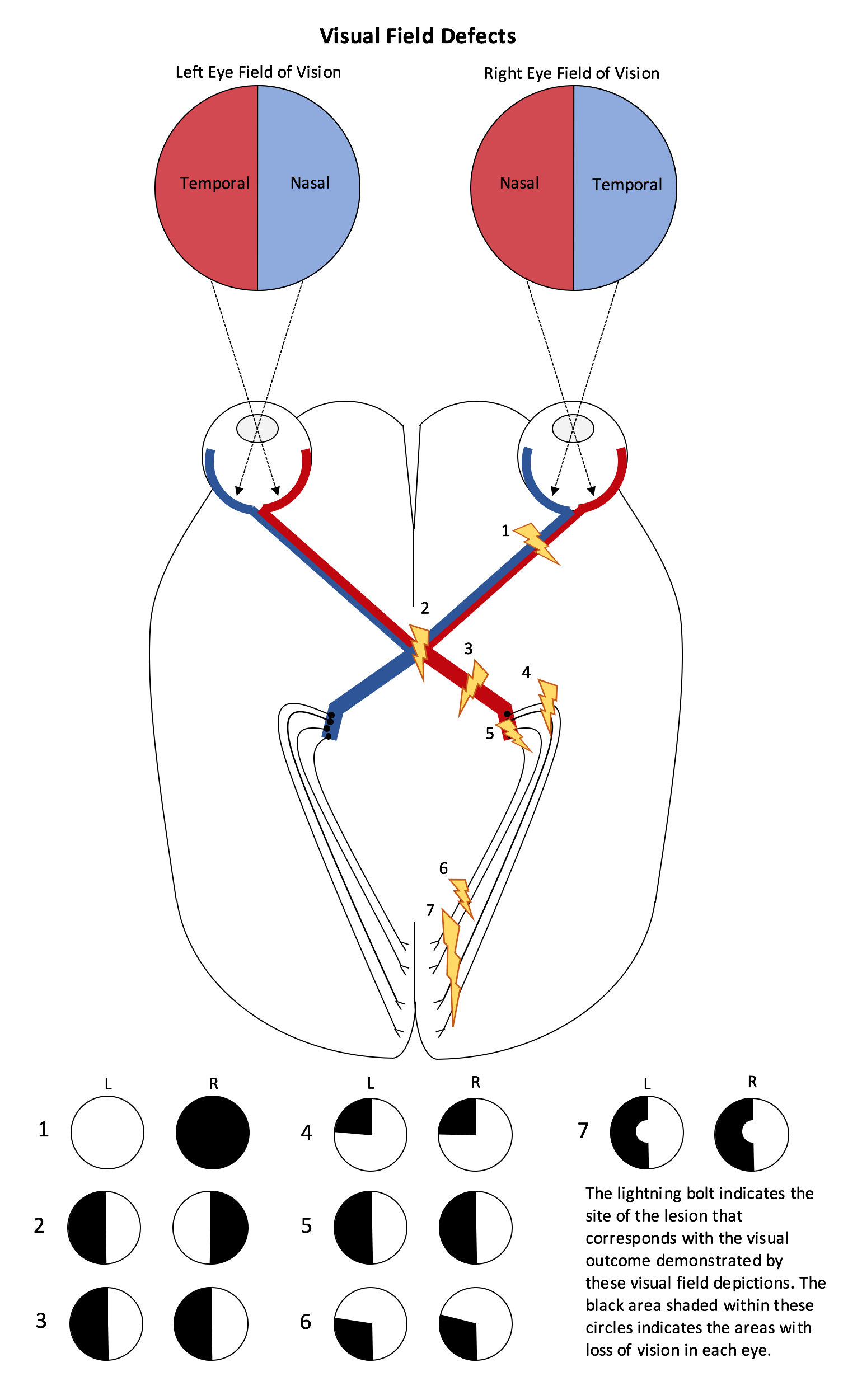
describe the pathway light takes from entering the eye to being processed in the brain
Light must pass through the Cornea
Then thru the Anterior Cavity
Then thru Pupil (a hole in the Iris)
Then thru the Lens
Then thru the Vitreous Cavity
Absorbed by the Retina, the Retina converts light energy into electrical energy
The electrical energy travels down the Optic Nerve
Crosses at the Optic Chiasm
Optic tract to lateral geniculate in thalamus
Then travels to the Visual Cortex of the Brain (occipital lobe)
If you cut the optic chiasm then you will have?
bitemporal hemianopsia
loss of vision in the outer temporal (sides) of both eyes
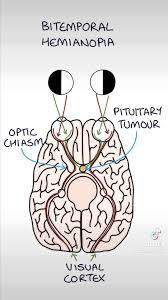
If we cut the optic nerve before it gets to the occipital cortex it is
homonymous hemianopsia
same half of the visual field is lost in both eyes