ch 52 malnutrition and obesity
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what does leptin do
- tells parts of body that ur full
- decreases w weight loss so feel constantly hungry
brain gut axis
serotonin?
- 95% of serotonin is in your enterochromaffin cells lining the GI tract
- to increase serotonin, you need tryptophan - from turkey, cheese, eggs, nuts, seeds, salmon, and whole grains
- more serotonin = a healthier stomach.
what do diet sodas cause
- metabolic syndrome and belly fat
preventing constipation in older adults
- consume plenty of water and fiber to prevent or manage constipation
- other beverage choices can include: unsweetened fruit or veggies juice, low fat or fat free milk, or fortified soy beverages
action alert for weight
- measure at the same time each day pref before breakfast
- hf and renal disease cause weight gain
- dehydration and cancer cause weight loss
- weight is the most reliable indicator of fluid gain or loss
what is BMI
- divides pts weight in kgs by height in meters squared
- many limitations
- judgmental terms like morbid obesity
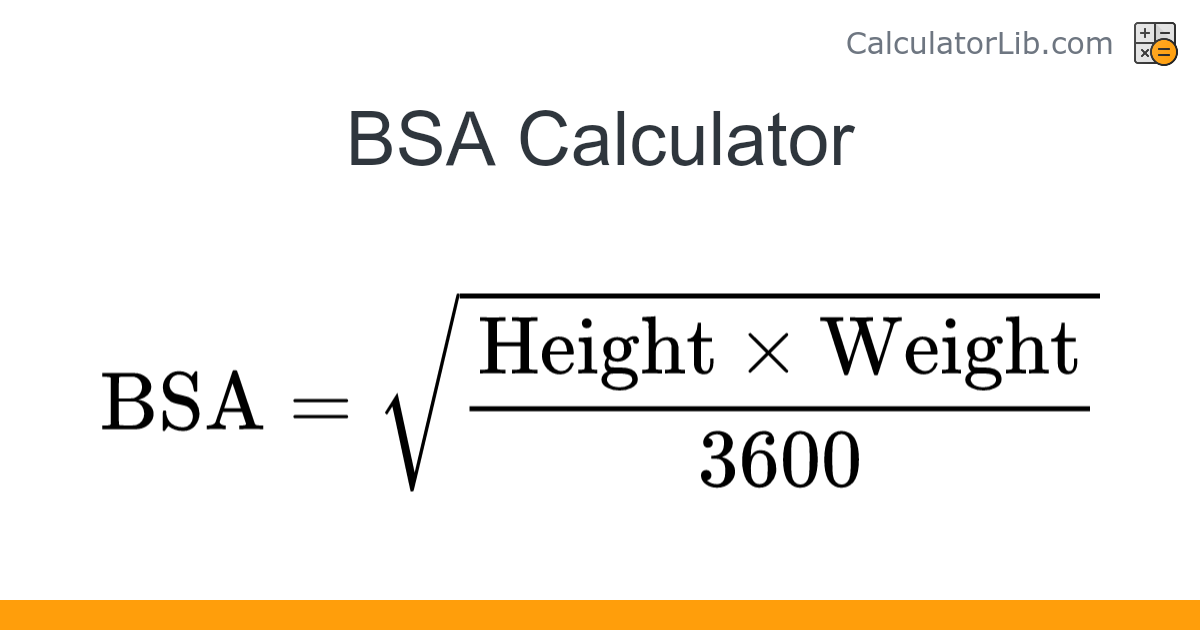
what is BSA
- body surface area
- used for appropriate med dosages and iv titration
- sq root of height in cm x weight in kg/3600
- used in peds

what are skinfold measurements
- measure triceps and subscapular skinfolds
- can use midarm or midcalf circumferences measurements
older adults and body weight and bmi
- weight and bmi increase through adulthood until 60yo
- often become less hungry, eat less, even if they are healthy
- others continue usual eating patterns and are at higher risk for obesity, esp older females
- do not assume that an older adult automatically eats less
- personalize nutritional assessment to accurately assess eating patterns for every pt
bmi ranges?
Underweight: less than 18.5
Normal weight: 18.5 to 24.9
Overweight: 25 to 29.9
Obesity: 30 or higher
assessing older adult for undernutrition physical concerns
- chronic conditions/illness
- constipation
- decreased appetite
- poor dentition
- drugs: prescription and otc can impair taste and appetite
- failure to thrive
- impaired eyesight
- pain that is acute or persistent
- weight loss
what is failure to thrive
combo of 3-5 symptoms:
- weakness
- slow walking sped
- low physical activity
- unintentional weight loss
- exhaustion
assessing older adult for undernutrition psychosocial concerns
- inability to prepare meals due to fx decline, fatigue, knowledge deficit, memory
- decrease enjoyment of meals
- depression
- income (ability to afford food)
- loneliness!!!
- proximity to sources of nutrient dense foods
- transportation access to get to sources of nutrient dense foods
ex of protein energy malnutrition
- marasmus
- kwashiorkor
- starvation
what is marasmus
- calorie malnutrition in which body fat and protein are waster, serum protein is preserved
what is kwashiorkor
- lack or protein quantity and quality w adequate calories
- common in children
what is starvation
- complete lack of nutrients
what to do for the pt w undernutrition
consult with?
help do what?
- consult a RD who can assist meeting nutritional needs while the pt is hospitalized as well as help w planning for continues nutritional health after discharge
- using complementary abilities of other team members optimizes health and pt care
what is important to watch for w pts w eating disorder
LABS - this is what kills them. Especially potassium (cardiac/dysrhythmias) for anorexia patients. Put them on a heart monitor and watch their potassium.
complications of undernutrition
- reduced CO; reduced vital capacity in lungs
- cold intolerance
- diarrhea/vomiting
- impaired protein synthesis
- susceptible to disease
- dry flaky skin; various types of dermatitis
- poor wound healing
- decreased activity tolerance; decreased muscle mass; weakness
- impaired fx ability
- substance misuse
meals in the healthcare setting
elderly?
- undernutrition can result when meals provided by the hospital are different than what the PT usually eats
- identify specific food preferences that the PT can eat and enjoy that are in keeping w personal cultural practices
- ⅓ of elderly will develop some type of malnutrition while admitted which increases hospital stay. Advocate for nutrition for them. You can eat with them, it helps them.
action alert dysphagia
- assess for difficulty or pain w chewing or swallowing
- unrecognized dysphagia is common in older adults and can cause undernutrition, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia
promoting nutrition intake environment
- remove bedpans, urinals, and emesis basins from the environment
- eliminate or decrease offensive odors as much as possible
- decrease environmental distractions
- admin pain meds or antiemetics at least 1 hr before mealtime
promoting nutrition intake comfort
- allow the pt to toilet before mealtime
- provide mouth care before mealtime
- ensure eyeglasses and hearing aids are in place during meals
- remind assistive personnel to have pt sit in chair if possible during mealtime
how to promote nutrition intake in hospital - function
- ensure that meals are visually appealing, appetizing, and at apropriate temps
- if needed, open cartons and packages and cut up food
- observe during meals for food intake and document percentage consumed
- encourage self feeding
- eliminate or minimize interruptions during mealtime for nonurgent procedures or rounds
tx for eating disorders
- meal management
- nutritional supplements: can be full of sugar, encourage smoothies
- total enteral nutrition
- drug therapy: Marinol, Megace and vitamins
TPN
what is it?
care of TPN? (12)
- IV (PICC lines, central lines, and Midlines - not peripheral) when a patient cannot effectively use the GI tract for nutrition
No medications goes into the TPN bag
Check TPN solution with orders, 2nd nurse verify
Monitor IV pump for accurate rate
If TPN runs out, administer D10W or D20 W until available
Do not increase rate, if administer dose late
Daily weights, Monitor I&O
Monitor glucose and electrolytes daily (2 most common electrolyte imbalances are K+, NA . Monitor labs frequently)
Administer insulin as ordered
Assess IV site
Change tubing every 24 hours
Change the dressing every 48 hours for a gauze dressing change and 7 days for a transparent dressing change.
If TPN is not on time, do not attempt to catch up by increasing the rate
TEN
what is it?
care for TEN/tube feeding? (11)
Tube placed into the stomach or jejunum, peg tube
NG tubes can be used less than 4 weeks w bolus or cyclic feedings
- blood glucose management bc high in sugar
- HOB should be 30 degrees during feeding and 1 hr after the feeding for bolus, continuously maintain semi-fowlers for pts receiving continuous: to prevent aspiration
- Check residuals before administering meds & PER FACILITY
- Daily weight, I&O
- X-ray confirmation
- Change tubing and feeding 24-48 hrs
- Labs: BUN, electrolytes, Hct, prealbumin, & glucose
- Obstructed (clogged) tube most common problem
- Flush tube with 30 ml of water every 4 hrs, before & after administration of meds, and after interruption of TEN
- Ensure correct prescribed rate (ml/hr)
tube care feeding and maintenence
- NG: use soft flexible small bore feeding tube
- if gastrostomy or jejunostomy tube is usesd assess insertion site for signs of infection and excoriation, rotate tube 360 degrees each day and check in and out play of about 1/4 inch
- document residual vol Q6h by aspirating stomach contents into syringe
- for continuous cyclic feeding: add only 4hrs of product to the bag at a time to prevent bacteria growth, closed system is preferred and each set should be used no longer than 24hrs
- label cans w date and time opened, cover and keep refrigerated, discard unused open cans after 24hrs
action alert enteral tubes and aspiration
- if enteral tubes are misplaced or become dislodged the pt is likely to aspirate
- life threatening comp w ten esp w older adults
- observer for fever and signs of dehydration (dry mucus membranes, decreased urinary output)
- auscultate lungs q4-8hrs to check for decrease breath sounds esp in lower lobes
- pts may become sob and report chest discomfort
- if xray confirms, tx w antibiotics is started
action alert gastrostomy or jejunostomy
- if a gastrostomy or jejunostomy tube cannot be moved while performing regular assessment, notify hcp immediately bc the retention disk may be embedded in the tissue
- cover site w a dry, sterile dressing and change the dressing at least once a day
maintaining a feeding tube w occlusion
- risk for occlusion: delivering multiple meds w out flushing inbetween, not flushing before and after overall med admin, using longer tubes, and small diameter tubes
- consult w pharmacist to be sure meds are compatible w nutrition formula and can be cleared from the tube w appropriate flushing
- collab w HCP to use liquid meds instead of crushed ones when possible unless liquid form causes diarrhea
- do not mix drugs w the deeding product before giving, crush tablets as finely as possible and dissolve in warm water (+ for unclogging)
- flush tube w 30ml water using at least a 30ml syringe to prevent tube rupture at least Q4hr, before and after med admin, after interruption of enteral nutrition
- if tubing becomes clogged: use 30ml of water applying gentle pressure w 50ml piston syringe
- as final attempt to unclog, enzyme declogging kits or devices can be used by experiences nurse
- if unclogging is unsuccessful replacement of tube recommended
critical rescue refeeding syndrome
- life threatening comp r/t fluid and electrolyte shifts during aggressive nutritional rehab in the pt w starvation
- s/s: hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, hf, peripheral edema, rhabdomyolysis, seizures, hemolysis, resp insuff
- contact HCP immediately
critical rescue fat emulsions
- monitor for fever, increased triglycerides, clotting problems, multisystem organ failure which may indicate fat overload syndrome esp in pts who are critically ill
- respond to these s/s by d/c iv infusion and reporting changes to hcp immediately
what is central obesity
increases r/f for what?
measurements?
- distribution of excess body fat in the abdominal area
(a stronger risk/predictor of health)
- CAD, stroke, cancer, sleep apnea, DM2, sleep apnea, and early death
- if more inches than healthy range of waste circumference
healthy waist circumferences in women
men?
35 in or less
40 in or less
drugs that contribute to weight gain
- steroids
- estrogens
- hormones
- nsaids
- antihypertensives
- antidepressants
- antiepileptics
- oral antidiabetics
how to ask the pt if its ok to talk to them about elevated weight
R - Rapport
E - Environment
S - Safe
P - privacy
E - Encourage
C - Compassion
T - Tact.
a______ can decrease risk of CAD and DM2
5-10% weight loss
cutting out sugary carbonated beverages can
- cause weight loss over time
- If you drink one can daily, cutting it out saves nearly 1,000 calories per week. Over a month, that’s around 4,000 calories – equivalent to over a pound of body weight (3,500 calories equals about 1 pound of fat).
other benefits of cutting out soda
- improve blood sugar control
- reduce the risk of heart disease
- improve dental health
nonsurgical management of obesity
- diet programs (use percentages not numbers for weight)
- nutrition therapy
- exercise program
- drug therapy (glp1)
- behavioral management
- complementary and integrative health
surgical management of obesity (bariatrics)
- vertical banded gastroplasty
- gastric banding
- vertical sleeve gastroplasty
- biliopancreatic diversion w duodenal stitch
- roux-en-y gastric bypass
comp of bariatric surgery
- increased n/v
action alert bariatric surgery and NG tube
- some pts have to get ng tube esp after open procedures
- gastroplasty: NG tube drains both proximal pouch and distal pouch, closely monitor tube for patency, never reposition the tube because it can disrupt the suture line
- ng tube is removed the second day if pt passing gas
nutrition after bariatric surgery
- several weeks of pureed foods then solid food at week 8
- small meals and avoid high fat and sugar content
- takes 18-24mo for weight to stabilize
cv and resp care after bariatric surgery
- semifowlers to improve breathing and decrease risk for sleep apnea, pneumonia and atelectasis
- monitor o2 sats
- provide o2, bilevel or cpap or vipap ventilation per orders
- apply compression stocking and admin prophylactic anticoagulants to precent clots
GI care after bariatric surgery
- abdominal binder to prevent dehiscence for open surgeries
- observe for dumping syndrome
- provide six small feedings (clear then full liquids as ordered) and plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, collab w RD
- measure abdominal girth daily
GU care after bariatric surgery
Musculoskeletal care after bariatric surgery
- remove catheter w in 24hrs after surgery to prevent uti
- collab w physical therapist for transfers or ambulation assistive devices
- encourage turning q2hrs using weight bearing overhead trapeze
skin care after bariatric surgery
- observe folds for redness/hyperpigmentation, excoriation, or breakdown and tx early
- use absorbent padding between folds to prevent pressure and skin breakdown
- ensure tubes and catheters are not causing pressure on skin
critical rescue anastomotic leaks
- most serious complication and cause of death after gastric bypass
- s/s: increasing back, shoulder or abdominal pain, restlessness, unexplained tachycardia and oliguria
- contact surgeon immediately
what is dumping syndrome
- rapid emptying of gastric contents into small intestine
- s/s: tachycardia, abdominal cramping, distention, diarrhea, n/v, vertigo, sweating, pallor, palpitations
discharge teaching topics post bariatric surgery
including vitamin and mineral supplements
analgesics and antiemetic drugs
cover wound during shower or bath
avoiding lifting; activity progression
signs and symptoms to report: Fever; excessive nausea or vomiting; epigastric, back, or shoulder pain; red, hot, or draining wound(s); pain, redness/hyperpigmentation, or swelling in legs; chest pain; difficulty breathing
nutrition and exercise classes; follow-up visits with RD