Selection and Maintaining variation
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is balancing selection?
NS can maintain alleles at intermediate frequency between 0-1
maintains two or more alleles in a population
Ex: allele favored in dry area and different allele favord in a wet area
in species as a whole, both alleles maintained by NS at intermediate frequencies
Why are alleles said to be balanced (balanced selection)?
stable equilibrium state is reached
What happens when the equilibrium is disturbed?
selection will return them back to this state
(unless environment has too strong of an affect —> causes genetic drift)
What is balanced polymorphisms?
maintaining heterozygotes and keeping recessive allels in the population even if other is more fit
What are examples of balanced polymorphisms
heterozygote advantage
Frequency-dependent selection
What is heterozygote advantage
when heterozygote fitness > homozygote
Balancing selection allows both alleles to remain in population
What is sickle cell Anemia
• Red blood cell disorder in which there aren't enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout your body. •
Pain, anemia, chest syndrome, infections, organ damage
What did Dr. William Warrick Cardozo discover (1905-1962)?
• Sickle cell anemia was inherited. Almost exclusively among
people of African descent.
• Not all people having sickle cells were anemic.
• Sickle cell disease wasn’t always fatal, but no successful
treatment found.
What did Dr. Roland Scott discover (1909-2002)?
• Pediatrician, treated many children with sickle cell anemia.
• Published on incidence of red cell sickling in newborns, lead
to implementation of screening tests.
• Had Congress pass Sickle Cell Anemia Control Act of 1971
providing federal funding for research and treatment
What is Malaria?
Parasite, Plasmodium, causes disease in humans and transmitted by
mosquitoes. Extreme flu-like symptoms can be reoccurring and fatal.
• Endemic to same region as sickle cell anemia
What are those with AA genotype venerable to?
Malaria likes circular blood cells
Don't get any sickle cell disease --> but plasmodium that causes symptoms of malaria are most complete in circular blood cells
What is heterozygote in Malaria and Sickle Cell?
A= normal hemoglobin, S= distorted hemoglobin
AS heterozygote has advantage
No sickle cell disease and some protection form Malaria
AA: Lack sickle cell, vunerable to malaria
aa: protected from malaria, have sick-cell disease
Why does Aa (AS) more protected from sickle cell disease and Malaria?
Don’t get malaria as bad: some sickle cell that can’t attack the plasmodium
Fewer symptoms of sickle cell anemia because they have circular blood cells
In regions: 40-50% of people are heterozygotes
What is frequency-dependent selection?
• The relative fitness of genotypes are not constant but vary with their frequencies in the population
• Fitness of a genotype increases as its frequency decreases
What is the highest form of fitness in negative frequency-dependent selection?
• Highest fitness when rare
Can maintain a stable balanced polymorphism
How do Right-mouthed and Left-mouthed perissodus show negative frequency-dependent selection?
Right mouthed fish always bites prey on the left
Left mouth bites fish on right side
If phenotype is more common in a year --> victims can learn behavior to be ready when one side is more common --> when prey react faster to one side, the one side decreases in population from more food
Other side: prey less likely to expect them --> fish with left mouth is less common but survive more because fish doesn't expect them
Causes shift in phenotype dominance and strategy
Negative slection: Maintains different states in population
If a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, we can conclude that:
nonrandom mating has occurred
natural selection has occurred
One of the assumption of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium has been violated?
Evolution has occurred because one or more of the assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium has been violated
D : the most complete answer
What is one way to solve competition?
Forming a niche
What are galls in plants?
expansion of the stem of plants
protective structure that fly creates in plants by exuding chemical in plants that changes how it grows
Eggs hatches and grows --> releases chemicals that protect the eggs inside the gall
How did evolution impact the wasp in reference to galls?
wasp: created specialized structure to puncture egg inside of gall —>eats the fly larvae
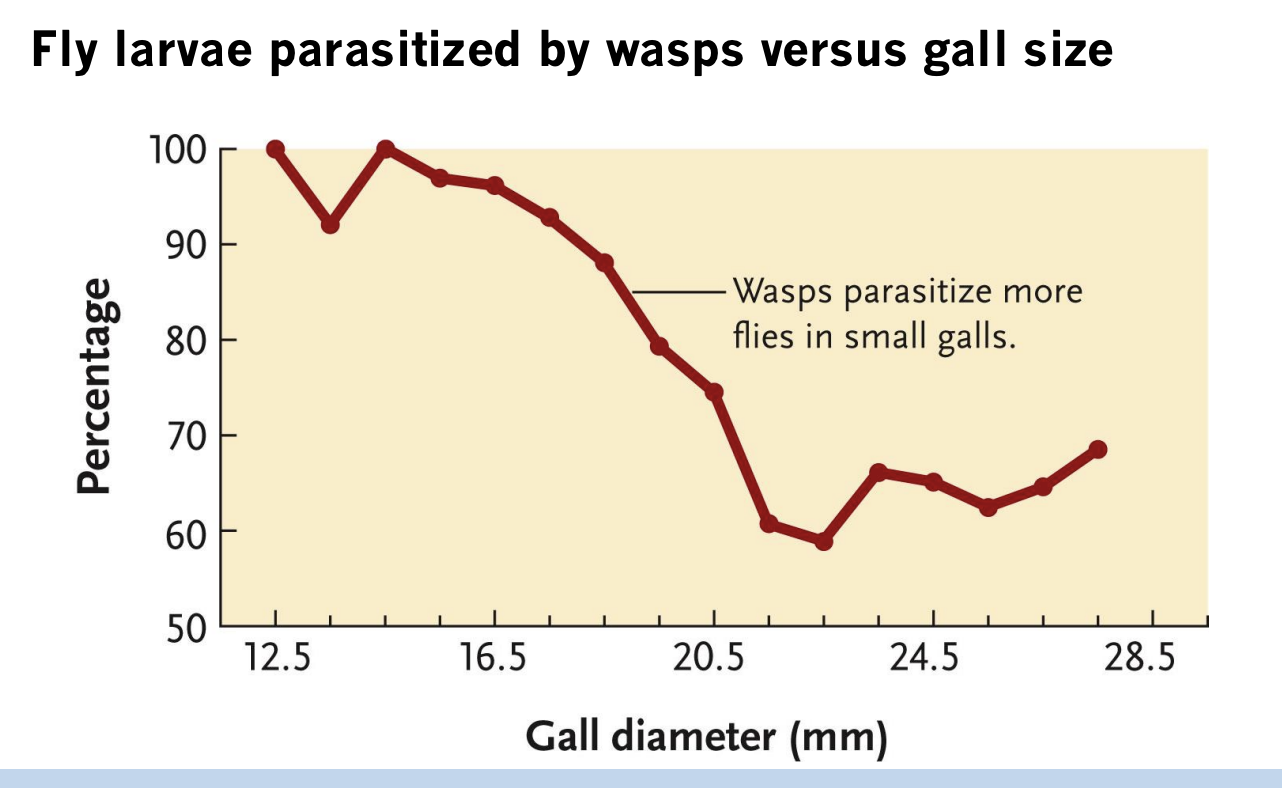
What does this graph show?
Higher likelihood of fly being killed by parasite wasp when it produces a gall that is smaller in diameter
Which directions are maintenance of variation and natural selection pressures?
comes from all sides
rarely from one direction of a long time
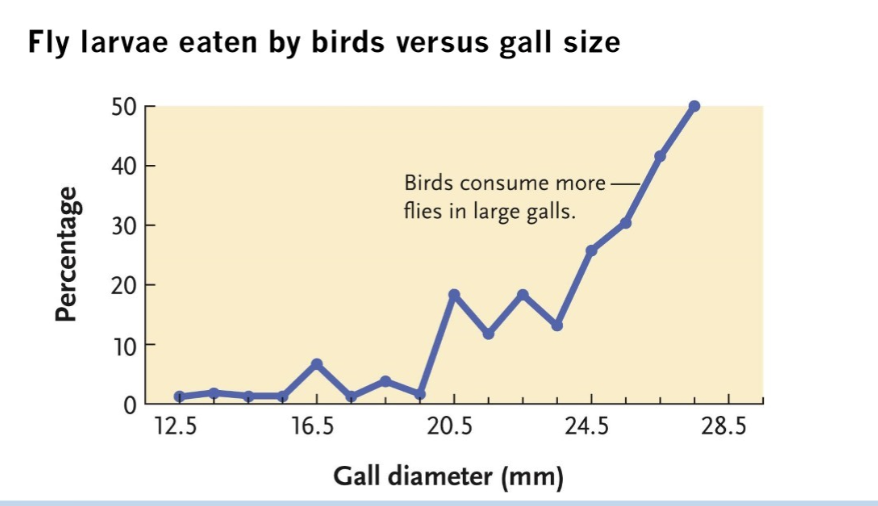
What does this show about gall preferences in the bird (Downy woodpecker)?
Too small gall --> birds can land on them --> birds prefer larger galls
What do you think will be the effect on the flies that survive and emerge from the galls?
A. Stabilizing selection will maintain the same average size of fly
B. Directional selection will shift the mean towards larger flies
C. Directional selection will shift the mean towards smaller flies
D. Disruptive selection will result in a bimodal distribution with two distinct means, one for small flies and one for large flies.
wasp selecting for smaller, birds selection for larger
A: two pressures on the sides push fly size to an optimum middle
opposing forces can lead to stabilizing selection
Are selective pressures constant?
No, environment is always chaning what is fit
Ex: Shifts year to year depending on population of wasps/birds which can affect which side has more pressure
What can selection be based on?
Sexual selection
What is sexual selection?
Competition for mates
form of NS
Competition can be between rivals for the affection of a potential mate
What does sexual selection promote?
promotes traits that increases chance of reproductive opportunities
How are males more likely to be impacted by sexual selection?
more common in males to gain phenotypes for sexual selection
Relationship between NS and sexual selection
Balance and compromise is created between NS and Sexual selection
Ex: peacock feathers getting too long and being predated on --> drives selection towards smaller feathers (other direction)
Sexual selection can act opposite of NS
What is intersexual selection?
one sex (usually males) competing with one another to acsess of other sex (females)
focuses on competition between individuals
What is sexual dimorphism?
distinct difference in size or appearance between the sexes of an animal in addition to difference between the sexual organs themselves.
When does sexual cannibalism occur?
Adaptive male strategy if benefits of being eaten exceed male's expected future reproductive value
What possible benefits would cause selection of sexual cannibalism"?
Increased paternity
• Decreased likelihood of female remating
Ex: Evolution led to mating strategy --> male being eaten exceeds the males future reproductive value (low chance of meeting another female)
Matched fitness --> goal met
Negatives of sexual cannibalism
death and lost opportunity for future matings
Ex: male black widows unlikely to mate more than once, even in they survive copulation
Do females select males based off good genes?
Long male calls better?
or do females invest more in the offspring of more attractive males?
difficult to disentangle
What is the the pressure in most sexual selection?
phenotype: features under selection by environment (usually the female)
What factors are important to having successful offspring?
early survival (ex: tadpole survival)
Organism growth
Organism development
Why is faster organism growth better?
Lower chance off being eaten in youth
Why is there still variation when selection is so strong?
Not all females have strong preferences •
Females cannot always mate with the ‘best’ male •
Thus, short call males still have reproductive success •
Long call males have higher relative fitness, but this is not absolute
What can cause females to not be able to choose the best males?
physical barriers
Why is higher relativeness fitness not always absolute?
In future new predator/environment could change what is fit —> could be valuable in the future
What are adaptive traits?
Products of selection that increase relative fitness
What is adaptation?
Accumulation of adaptive traits over time
Adaptation hypotheses must be tested
Adaptation where do current structures come from?
Current structures came from previous structures
How do some traits arise in adaptation?
some arise by chance and not selection
Is Natural selection is a process which ensures that organisms are optimally suited to their environment?
False
Natural selection does not necessarily lead to an absolute optimum in a particular trait
Environment in the future can change --> no constant optimum
What does natural selection favour?
A competitive optimum (as good or better than alternatives)
Why doesn’t natural selection create perfect organisms?
Selection can act only on existing variation
evolution is limited by historical constraints
Adaptations are often compromises
Chance, natural selection, and the environment all interact
Example of compromise in Pandas?
human thumb bones corresponds to sixth finger (false thum) on panda hand
Why are adaptations often compromises?
Most environments have competing selective pressures
Environments constantly change over time
What are vestigial structures?
currently useless structures = ‘evolutionary leftovers’
Examples of vestigial structures in humans
Hair stands up to make furry animals look bigger —> humans lose hair —> hair still stands up
Wisdom Tooth: need for larger jaw (eating tough, uncooked food) no longer needed due to different diet
Appendix: Used to harbor microbiome and used to be important in past environment and diet
What are traits observed today a result of?
result of natural selection acting in the past
Which environment do generations adapt to?
each generation adapts to environment of parents
What can natural selection never anticipate?
environmental change
most studies evaluate phenotype not genotype
how does Urban evolution impact genetic diversity?
Humans change environment drastically --> too fast for species to adapt to
Can measure evolution due to urbanization
What is genetic isolation?
members of one species cannot exchange genetic material with members of another species
What is the molecular clock?
The observation of rate constancy in molecular evolution. The extent of genetic divergence at a gene in two taxa is thus a reflection of the time since the taxa last shared a common ancestor.
measures the changes in genome over time
What is molecular evolution?
When differences in population accumulate and diverge genetically (DNA sequences)
Evolution at the level of DNA, which in time results in the genetic divergence of population
What is the molecular clock determined from?
uses fossil record to set clock
uses region in DNA or protein that has a known rate of mutations over time (usually mitochondrial)
Is the molecular clock always constant?
no, varies from gene to gene
molecular clock data should be interpreted cautiously
Why is the molecular clock not always reliable?
rate of mutations depend on like generation time and population size
Example of molecular clock
Scientist knows gene knows gene changes bases by 2 bases every 25 million years
Observe species differs in DNA by four bases —> diverged from a common ancestor 50 million years ago