Seedless Plants: Evolution and Characteristics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Algal Ancestry
Plants evolved from charophytes in Archaeplastida.
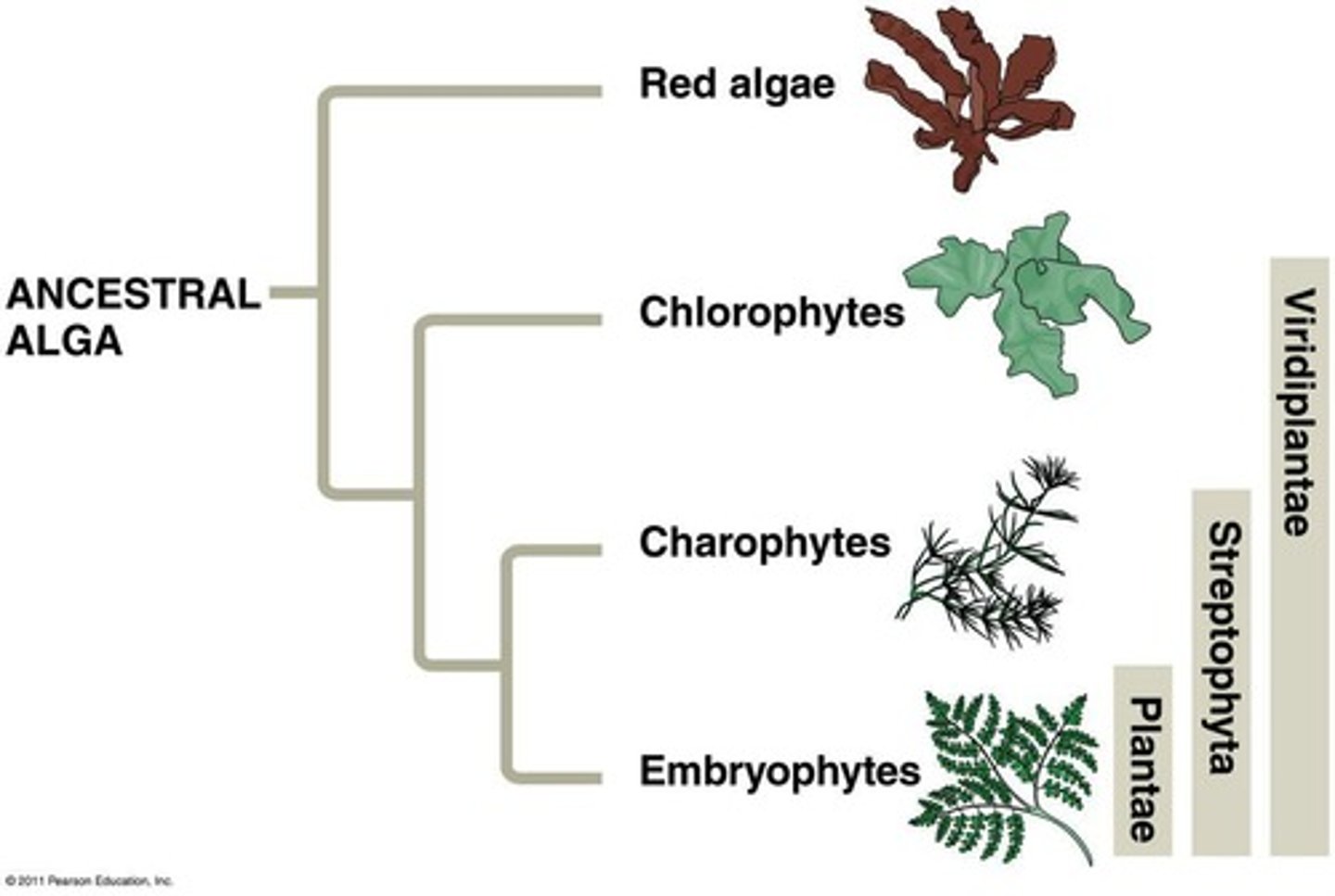
Green Algae
Includes chlorophytes and charophytes, ancestors of plants.
Multicellularity
Characteristic shared by green algae and plants.
Cellulose Cell Walls
Plants and green algae have cellulose-based structures.
Chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll a & b for photosynthesis.
Starch Storage
Plants and algae store energy as starch.
Desiccation
Risk of drying out for land organisms.
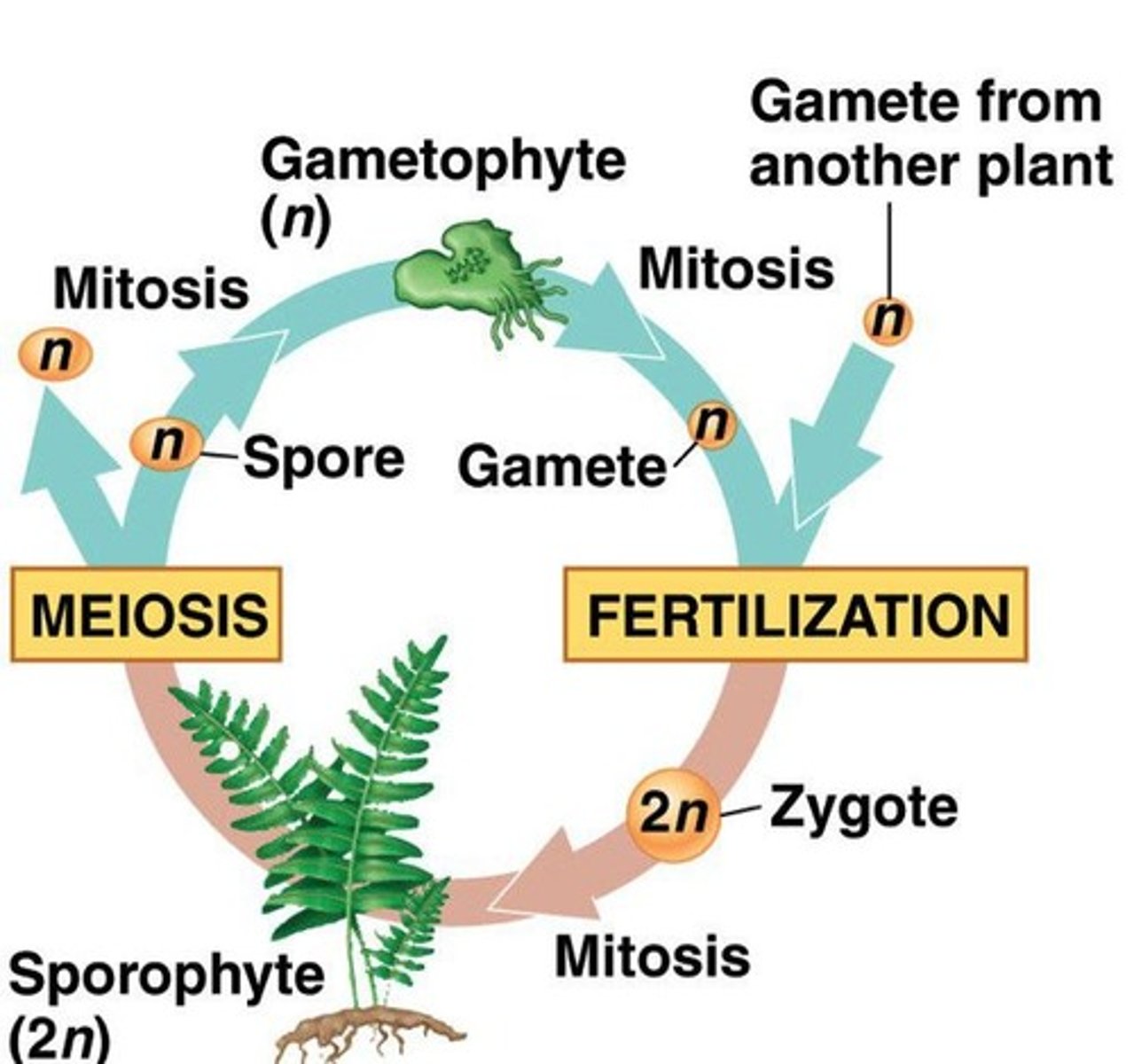
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle alternates between haploid and diploid stages.
Haplontic Life Cycle
Dominant haploid stage, typical in some algae.
Diplontic Life Cycle
Dominant diploid stage, typical in humans.
Gametophyte
Haploid generation producing gametes in plants.
Sporophyte
Diploid generation producing spores in plants.
Walled Haploid Spores
Spores with protective walls against desiccation.
Multicellular Gametangia
Structures producing gametes in land plants.
Sporophyte Embryos
Develop within female gametophyte for protection.
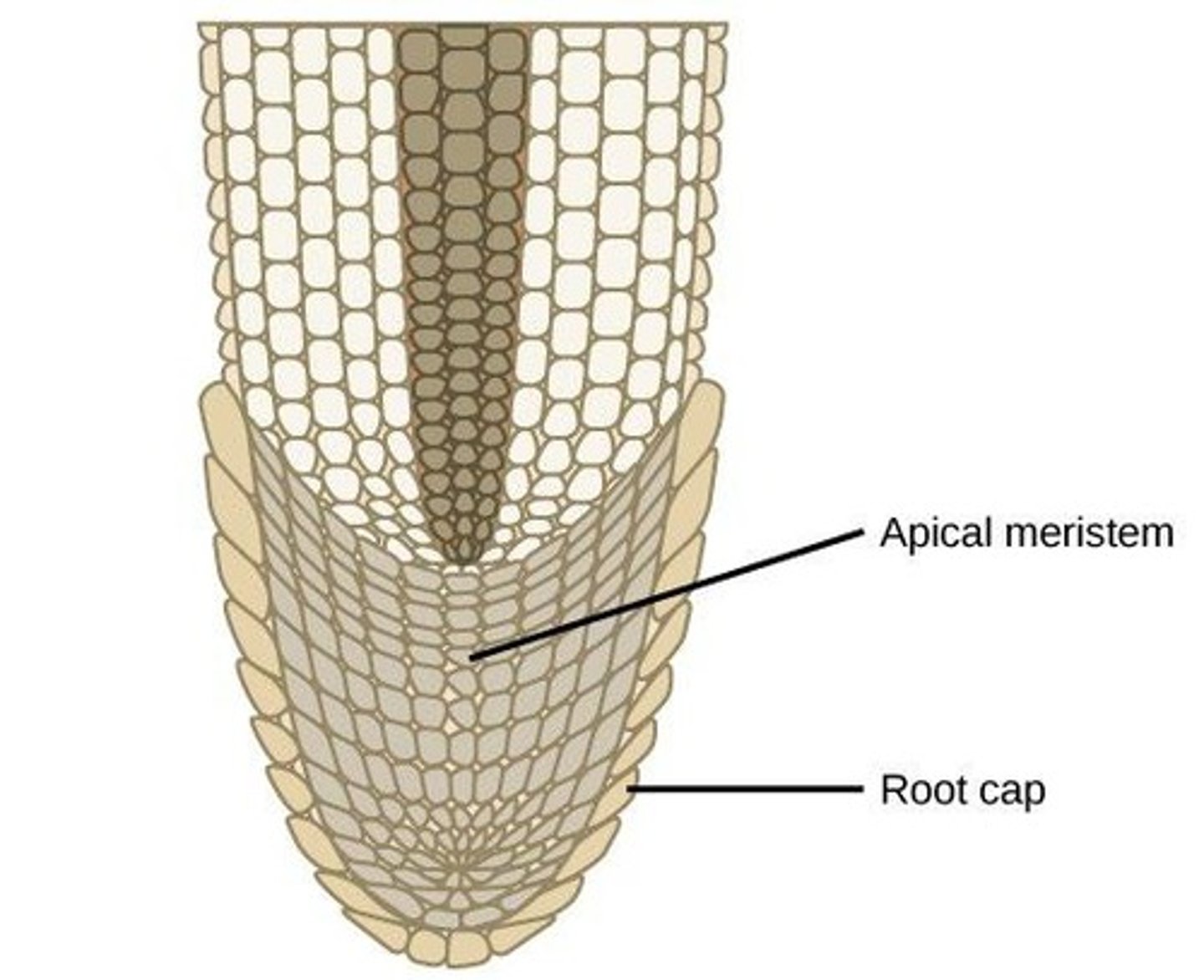
Apical Meristem
Tissue at tips of roots and shoots.
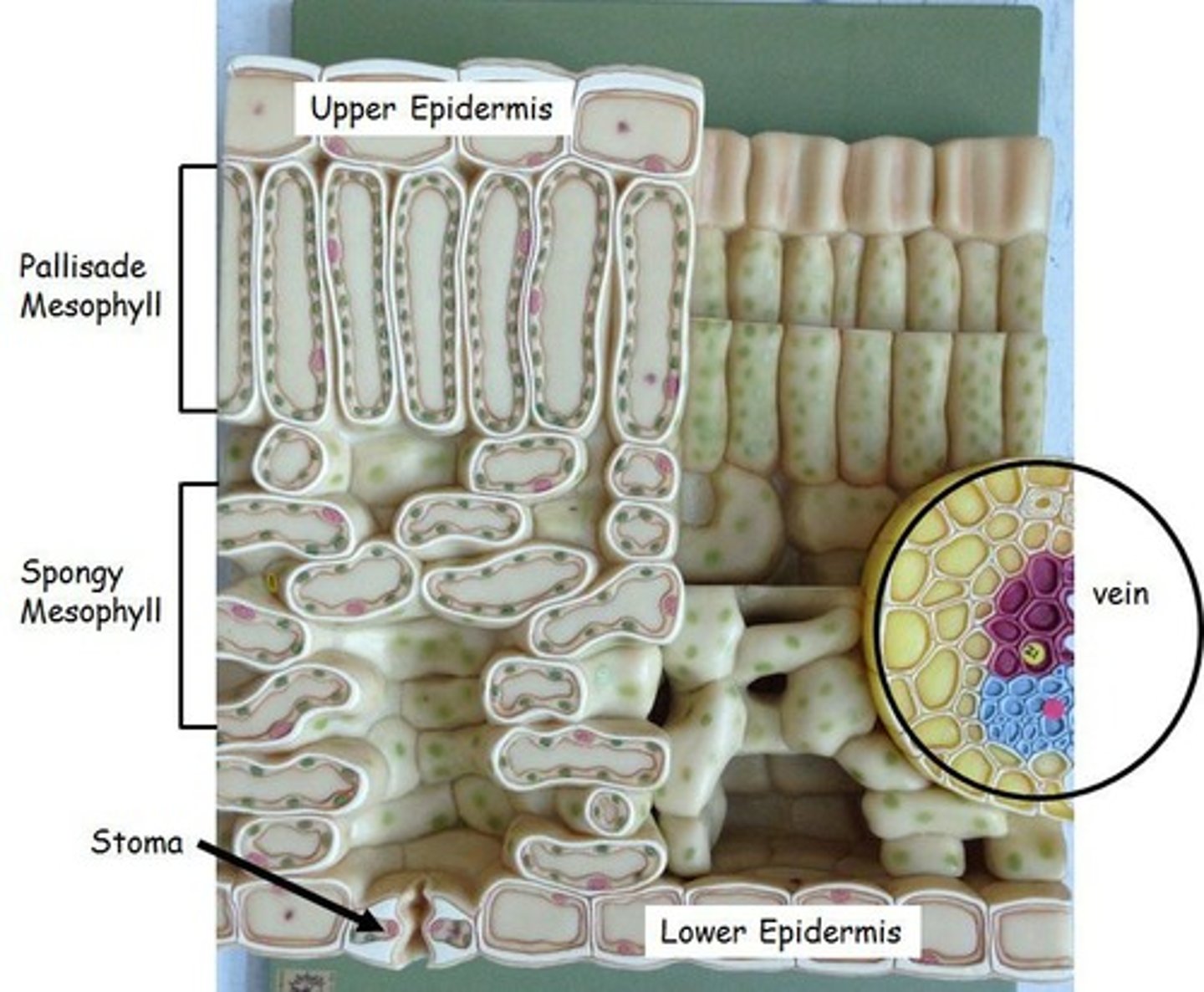
Waxy Cuticle
Layer preventing water loss in plants.
Secondary Compounds
Chemicals providing protection against herbivores.
Mycorrhizae
Fungal associations aiding plant nutrient uptake.
Adaptations to Land
Structural support and reproduction strategies for survival.
Advantages of Land
Higher CO2, light, minerals; less competition.
Disadvantages of Land
Desiccation risk and lack of buoyancy.
Walled haploid spores
Spores protected by sporopollenin for air dispersal.
Sporangium
Multicellular structure producing haploid spores.
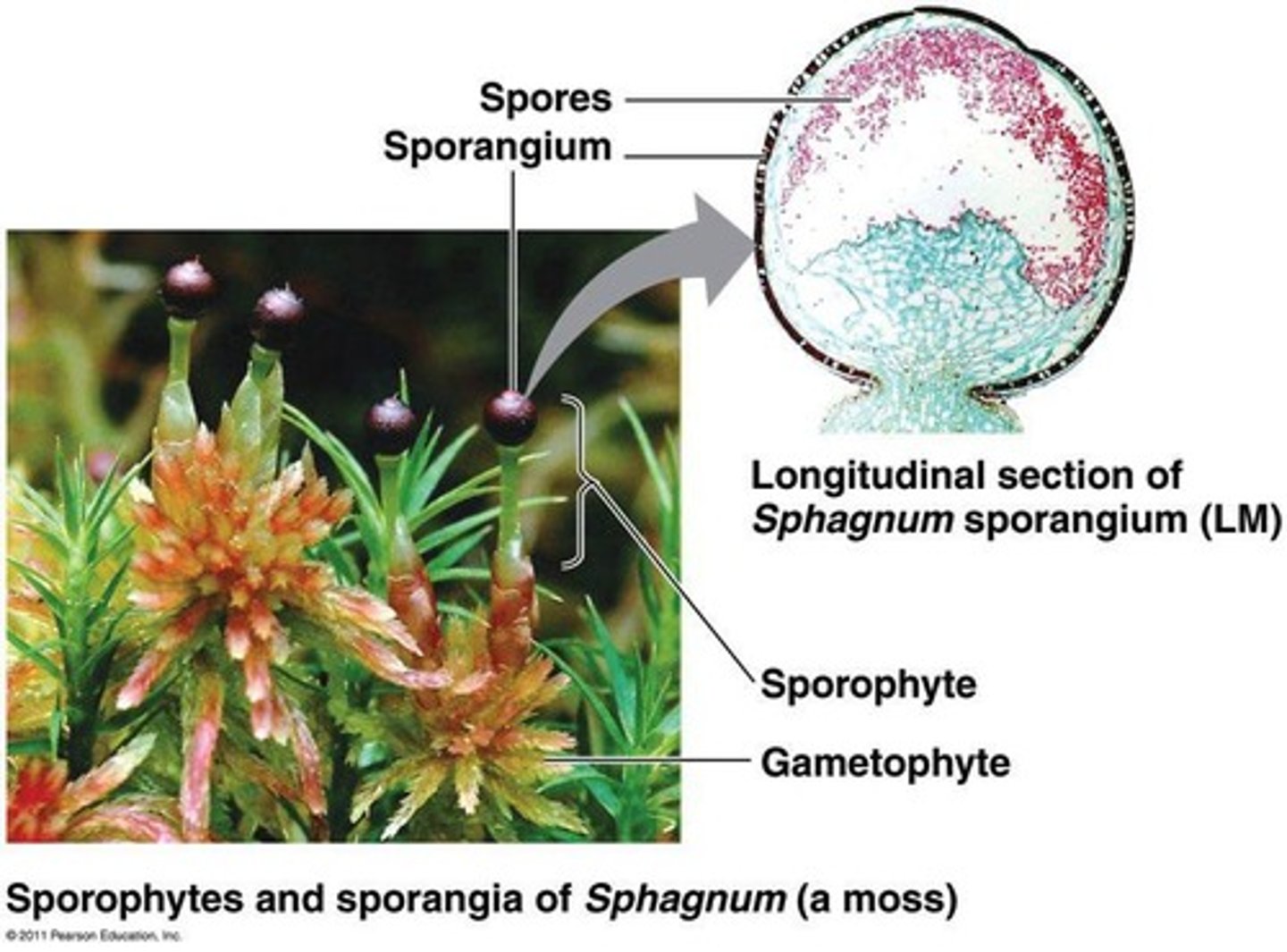
Sporophyte
Diploid phase producing spores via meiosis.
Gametophyte
Haploid phase producing gametes for reproduction.
Multicellular gametangia
Structures protecting gametes in land plants.
Antheridium
Male gametangium producing sperm cells.
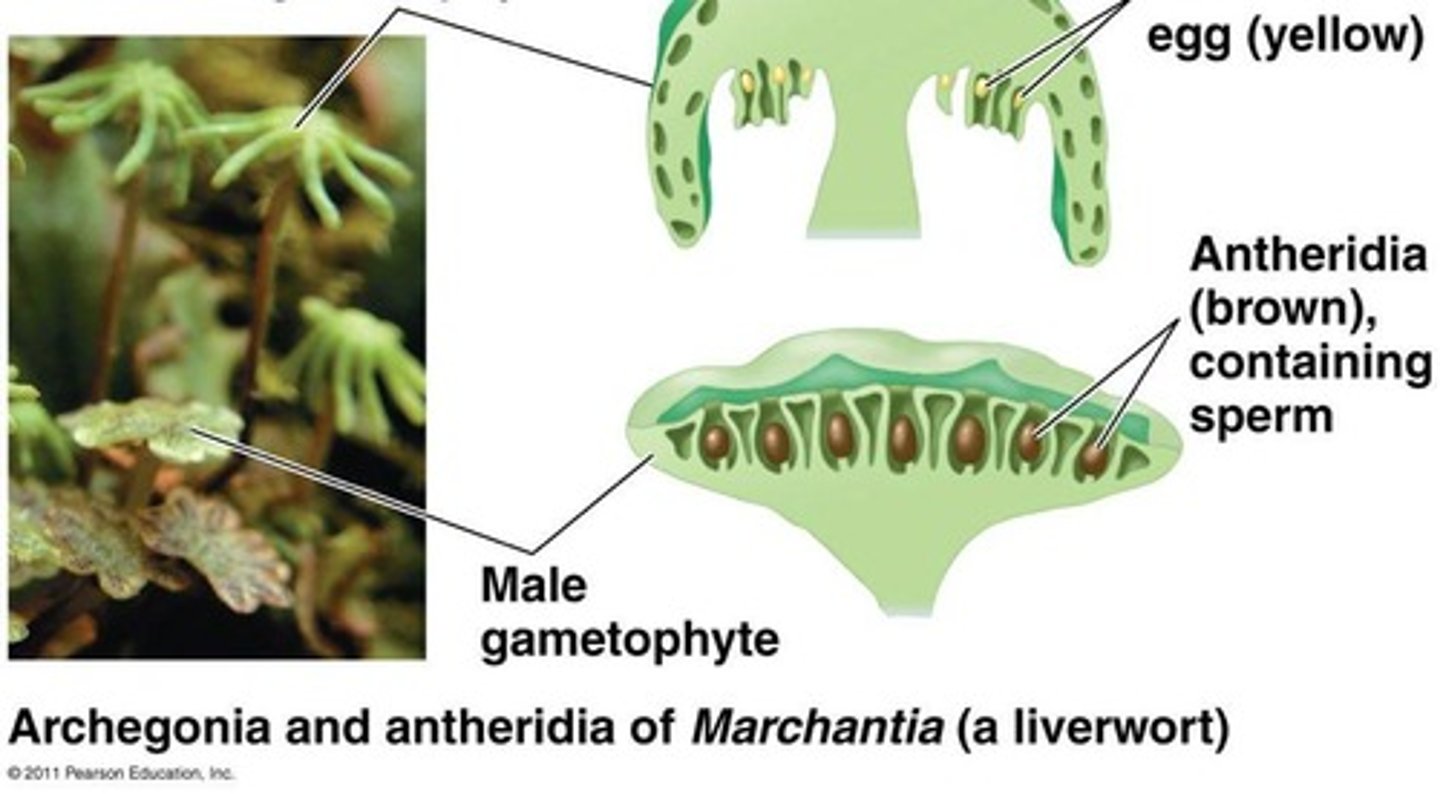
Archegonium
Female gametangium housing the egg.
Zygote
Fertilized egg developing into a sporophyte.
Apical Meristems
Regions of continuous cell division for growth.
Waxy cuticle
Protective layer preventing water loss in plants.
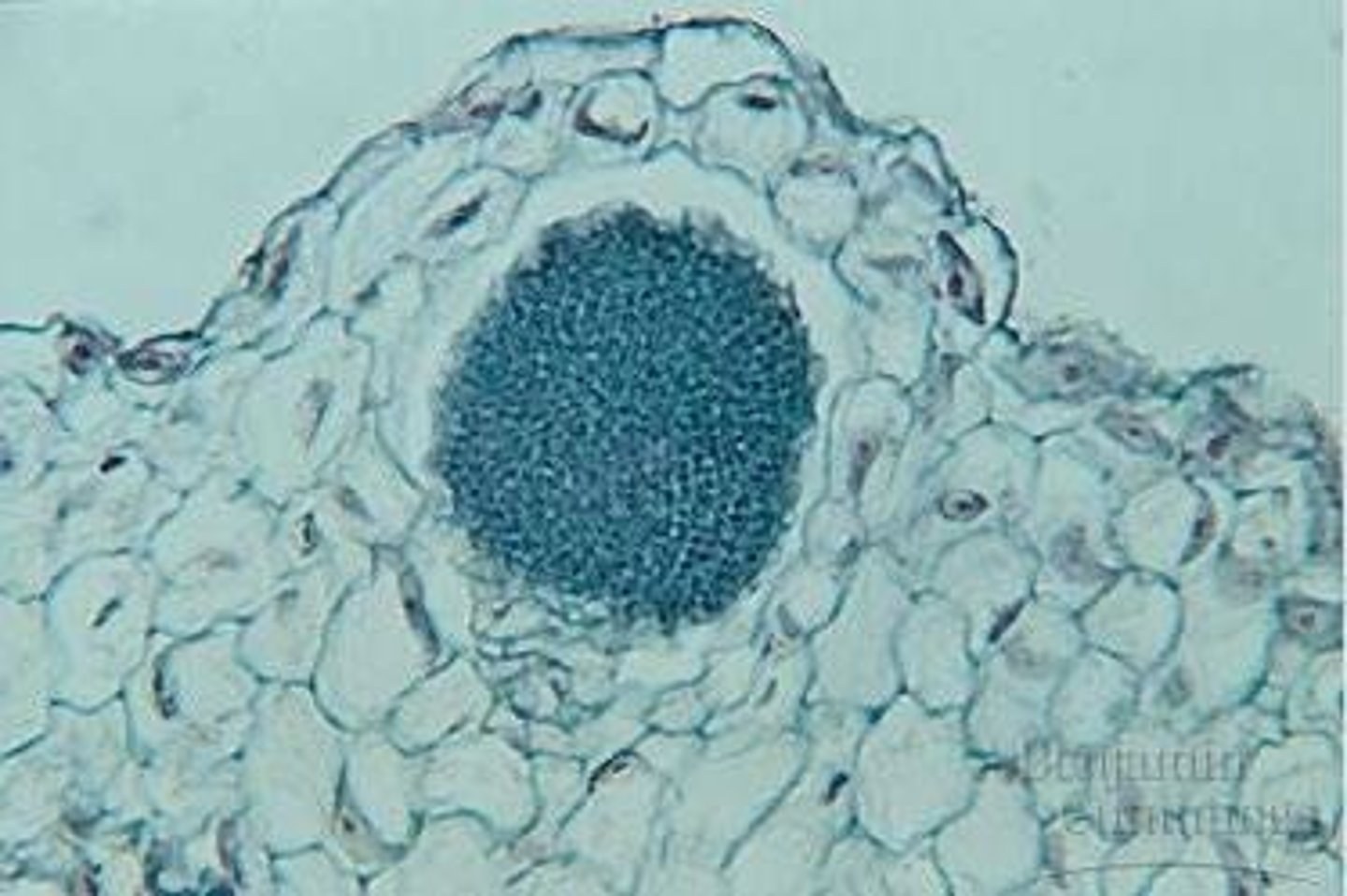
Stomata
Pores regulating gas exchange in leaves.
Secondary metabolites
Chemicals deterring herbivores and competitors.
Mycorrhizae
Fungal symbiosis aiding in nutrient absorption.
Bryophytes
Non-vascular plants with dominant gametophyte stage.
Rhizoids
Structures anchoring gametophytes, not true roots.
Anthocerotophyta
Phylum of hornworts with horn-like sporophytes.
Marchantiophyta
Phylum of liverworts, often thalloid or leafy.
Bryophyta
Phylum of mosses, most numerous non-vascular plants.
Sporophyte structure
Includes foot, seta, and capsule for spore release.
Capsule
Sporangium at the tip of sporophyte.

Plagiochila deltoidea
Example of a leafy liverwort species.
Polytrichum commune
Example of a hairy-cap moss species.
Mosses
Bryophyta, nonvascular plants thriving in moist environments.
Pioneer species
First organisms to colonize nutrient-poor soils.
Sphagnum
Type of peat moss, forms important wetlands.
Peatlands
Wetlands that preserve organic material over time.
Tollund Man
Preserved ancient corpse found in peat bog.
Protonema
Initial stage of moss life cycle from germinating spores.
Bud
Develops from protonema, leading to mature moss.
Seedless vascular plants
Plants with vascular tissue but no seeds.
Vascular tissue
Specialized tissue for transporting water and nutrients.
Xylem
Vascular tissue transporting water and minerals.
Phloem
Vascular tissue transporting sugars and organic compounds.
Microphylls
Small leaves with single vascular strand, found in Lycophytes.
Megaphylls
Large leaves with branched vascular system in most vascular plants.
Sporophylls
Leaves modified to bear sporangia for spore production.
Homosporous
Producing one type of spore, typical in most SVPs.
Heterosporous
Producing two types of spores, seen in seed plants.
Strobilus
Cone-like structure of sporophylls in some plants.
Monilophytes
Phylum including ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns.
Whisk ferns
Plants with dichotomous branching and no true leaves.
Horsetails
Jointed stems with tiny leaves, homosporous.
Ferns
Diverse plants with large megaphylls and sori.
Sori
Clusters of sporangia on the underside of fern leaves.
Ecological importance
Seedless plants enhance soil formation and weathering.