HLTH110-HCC-radio
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
angi/o
vessel
cervic/o
neck, cervix
fluor/o
emitting or reflecting light
ili/o
ilium (hip bone)
is/o
same, equal
later/o
side
lumb/o
lower back, loin
medi/o, mes/o
middle
phot/o
light
roentgeno/o, radi/o
x-ray, radioactivity
sacr/o
sacrum
son/o
sound
thorac/o
chest
tom/o
to cut, section, or slice
xer/o
dry
cine-
movement
echo-
reflected sound
infra-
below
intra-
within, inside
inter-
between
supra-
above, over
ultra-
beyond, excess
-ar
pertaining to
-er, -or
one who
-gram
a record (noun)
-graphy
process of recording (verb)
-graph
instrument to record
-lucent
to shine
-meter
instrument for measuring, measure
-osis
condition
-opaque
obscure, hidden
-therapy
treatment
Angio (abbreviation)
angiogram
AP, A/P
anterior/posterior (front to back)
PA, P/A
posterior/anterior (back to front)
Ba
barium
CT
computed tomography
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
PET
positron emission tomography
FB
foreign body
LBP
low back pain
LAT
lateral
C-spine
cervical spine (neck portion and/or the x-ray of this area)
T-spine
thoracic spine (mid portion of the back and the x-ray of this area)
L-spine
lumbar spine (lower back and the x-ray of this area)
CXR
chest x-ray
ECHO
echocardiogram (U/S of the heart)
Fx
fracture
RT
radiographic technologist, right
sono (abbreviation)
sonogram, ultrasound
U/S, US
ultrasound
XRT
radiation therapy (treatment with radiation)
contrast studies
Radiopaque materials are injected to obtain contrast with surrounding tissue when shown on x-ray film
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
tracer studies
radiograms that show activity, metabolism
uptake
absorption of substances into cells
oblique
at an angle
transverse, axial plane
horizontal (cross-sectional) plane dividing the body into upper and lower portions
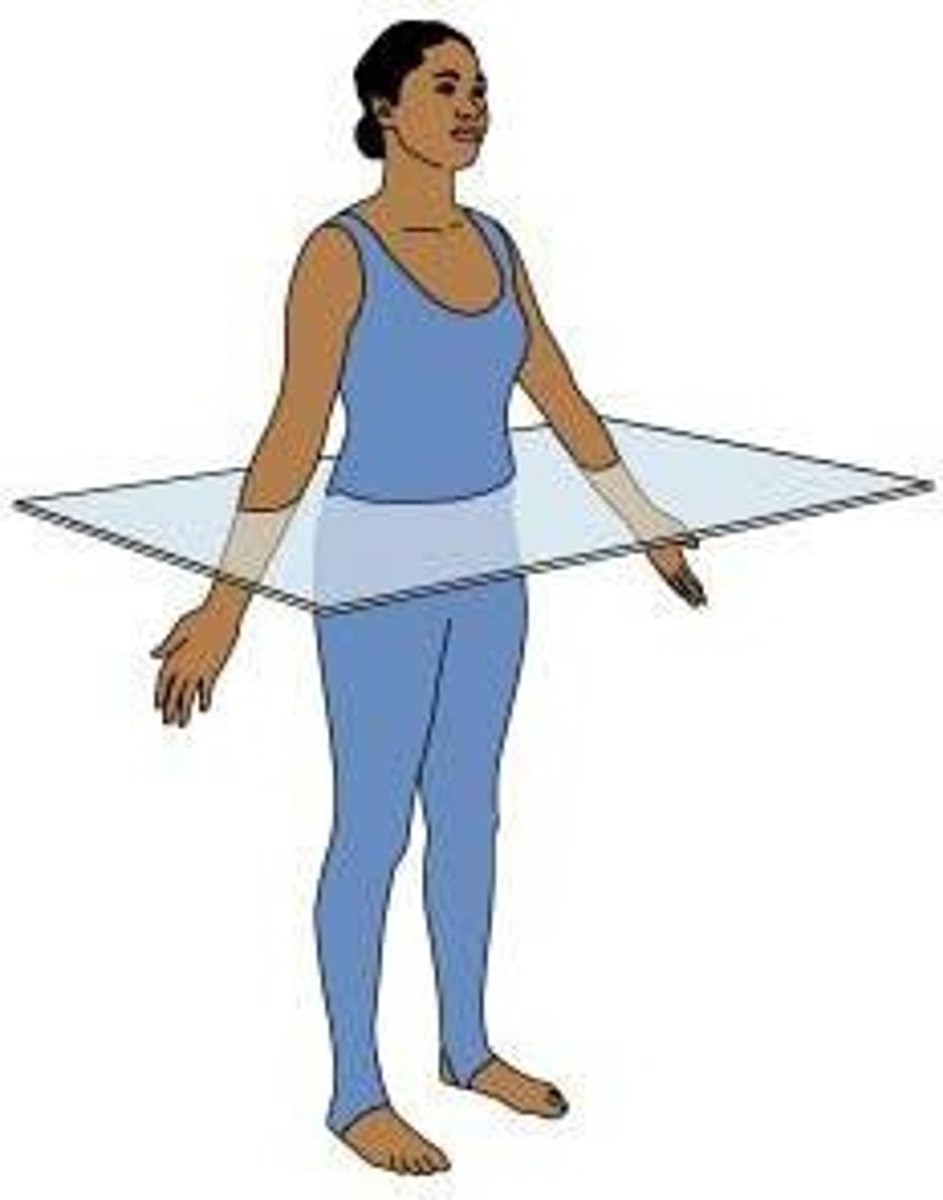
frontal (coronal) plane
vertical plane dividing the body or structure into anterior and posterior portions
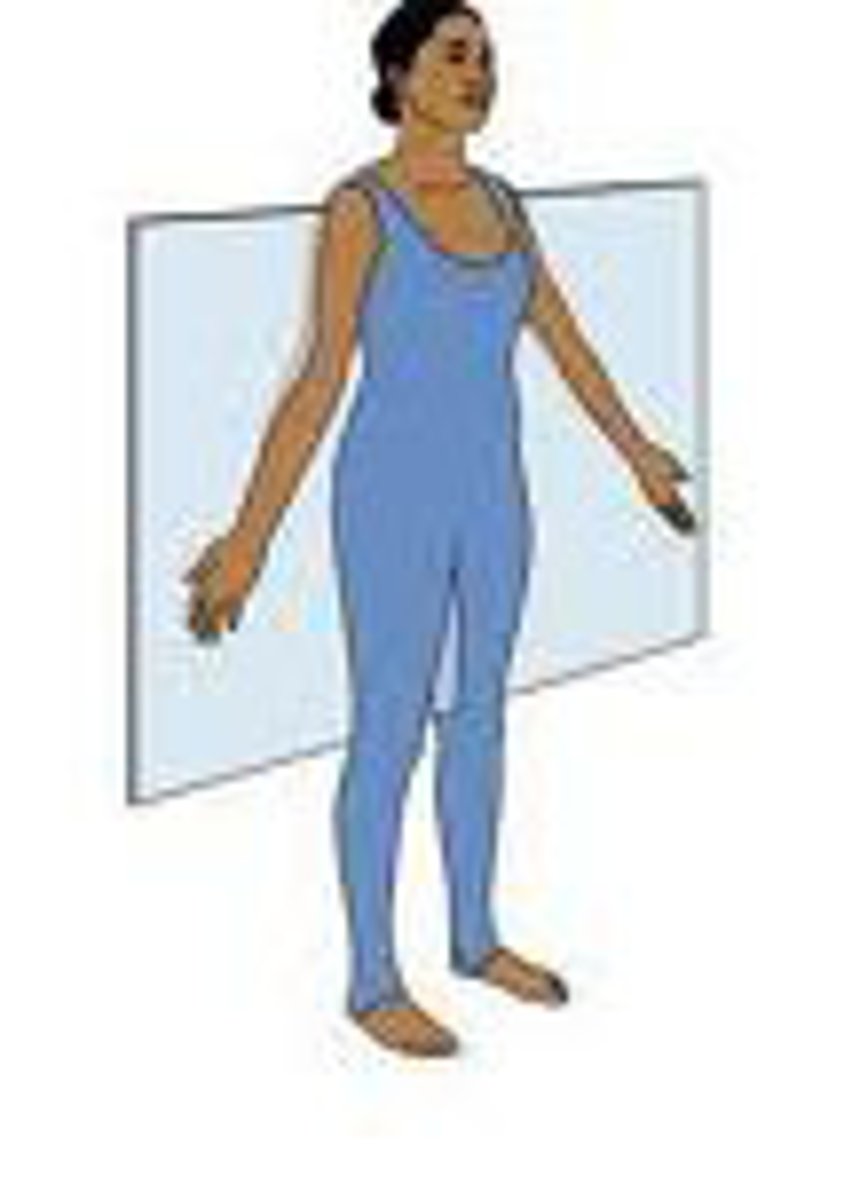

sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
radiographer
one who takes x-rays
radiologist
physician who specializes in the use of x-rays, ultrasound, and magnetic fields in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
contrast studies
substance/dye is used to distinguish organs from another
half-life
amount of time it takes for a substance to lose half its potency
tracer studies
radiograms that show activity/metabolism
uptake
absorption of substances into cells