Social Studies 30-1 - Unit 2: Liberalism + Conservatism
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Classical Liberalism
The focus on the rights and freedoms of the individual in society. The role of the government should be limited to the protection of individual rights and private property.
Luddism
- Groups of usually unskilled workers who destroyed the machinery that had replaced them
- Named after Ned Ludd, the leader of the movement
- Movement was burnt out by 1817 following the British government's enforcement of laws prohibiting machine-breaking
Modern Liberalism
- Involves government action
- All individuals valued equally
- Development of programs to help the disadvantaged
- Desire to share benefits and develop wisely
- Allowing for individual growth and development in conjunction with networks of mutual assistance for all of society
Industrialization
The stage of economic development during which the application of technology results in mass production and mass consumption within a country. This is accompanied by urbanization and changes in national living standards.
=> The development of industries for the machine production of goods.
Laissez-faire Capitalism
"Leave it alone!"
- Individuals need to be given the freedom to make their own decisions
- Individuals selfishness and competitiveness will inadvertently improve their own societies
- Free markets, fair competition, wise consumers, and profit-motivated producers
- A minimum of government involvement is favoured
Free Market
An economic system in which prices and wages are determined by unrestricted competition between businesses, without government regulation or fear of monopolies.
Classical Conservatism
- Reactionary; return to the better past
- Hierarchy; people do not have equal abilities
- Government should be chosen by limited electorate
- Humanitarian government; the government should care for the welfare of others
- Stability is kept through law and order, customs, and traditions
=> Tradition, human imperfection,
Modern Conservatism
Stresses the importance of personal responsibility, free markets, limited government, personal freedom, preserving tradition, and maintaining social hierarchy.
Authoritarian Conservatism
A political ideology that seeks to uphold order, tradition and hierarchy, often with forcible suppression of radical and revolutionary enemies.
=> Combines conservative views on culture and social issues with an emphasis on obedience to authority and order; strict authority is necessary to prevent chaos
=> A powerful government or ruler is required to enforce laws and uphold stability
New Right
Conservative political movements in industrialized democracies that have arisen and stress "traditional values," often with a racist undertone.
=> Ideological trend with conservatism that blends market individualism with social authoritarianism
Egalitarianism
A political principle that holds that all people should be treated as equals and allowed equal civil, social, political, and economic rights under the law.
Libertarianism
A political ideology that is opposed to all government action except as necessary to protect life and property.
=> NO government!
Monopoly
The exclusive ownership or control of trade in a particular good or service.
Oligopoly
A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market.
Progressivism
A 1920s movement in the United States, usually associated with President Theodore Roosevelt, that reacted to the perceived abuses of laissez-faire capitalism by large corporations. Progressives favoured “a square deal” for average citizens and used legislation and some regulation of the marketplace to achieve this.
=> Social reform
Labour Unions
An organization of workers that acts to protect workers' rights and interests.
=> "Organized" labour; bargain and negotiate for better conditions
=> Actions often defined as illegal and conspiracy
=> Power of a strike
Collective Bargaining
The process by which a union representing a group of workers negotiates with management for a contract.
Suffragette Movement
Universal suffrage!
- Focus on gaining the right to vote for women; action against employment and education discrimination
- Nellie McClung's Mock Parliament
Feminism
A concern of the need for equality across sex and gender.
=> First-wave feminism; the fight for Universal Suffrage
Dominion Elections Act
The right to vote to all European-Canadians.
=> Men and women 21 years of age or older
=> Indigenous Peoples did not gain the right to vote until 1960
Reactionary
- Tending to oppose change
- Idealizes the past and accepts economic inequality
Radical
- Tending to embrace change
- Favouring drastic political, economic, or social reforms
=> GRADUAL change
Revolutionary
- Tending to embrace change
- Involving or causing a complete or dramatic change
=> IMMEDIATE change that could involve violence
Reform
To make changes in (typically a social, political, or economic institution or practice) in order to improve it.
Welfare Capitalism
Initiatives by industrialists to provide workers with non-monetary rewards to head off the growing demand for labour unions; also refers to government programs that would provide social safety nets for workers.
=> A classical liberal economic system combined with worker's rights
Factory Acts
Britain
- Changed minimum age of labour from 9 to 12
- Regulated working hours
- Improved working conditions in factories
=> Shift toward welfare capitalism
Trust
A group of corporations run by a single board of directors.
Welfare State
A state in which the economy is capitalist, yet the government uses policies and programs to modify the market forces to ensure economic stability and a basic standard of living for its citizens.
Income Disparity
The difference in earnings between the rich and the poor.
Classical Economics
The theory that free markets will restore full employment without government intervention.
=> Free markets can regulate themselves
Keynesian Economics
- John Maynard Keynes
- Economy is UNSTABLE
- Idea of inflation/recession, rise and fall CAUSED BY CONSUMER DEMAND
- Felt that few individuals can predict the market
- Increase government involvement by manipulating money available to producers/consumers
=> INFLATION; increase taxes and interest rates, decrease government spending
=> RECESSION; decrease taxes and interest rates, increase government spending
=> Deficit spending
Thatcherism
Similar to Regan, wanted to reinvigorate the British economy through private enterprise.
=> Tough on unions
Reaganomics
The economic policies of the Ronald Reagan US presidency, which advocated less government intervention in the economy and pro-industry, anti-labour, anti-regulation, anti-environmental regulations policies.
Fiscal Policy
The direct taxing and spending functions of government.
=> Taxes, government spending
Monetarism
A school of economic thought that focuses on the need for governments to control the amount of money in circulation.
=> Friedman + Hayek
Monetary Policy
Actions taken by the central bank of a country to control money.
=> Interest rates, printing money
Supply-side Economics
- Producers and entrepreneurs grow markets
- Government-led economy can't predict demand
- Demand is a response
- Steady supply can be maintained, and price can be adjusted to meet demand
- Government has limited power
Demand-side Economics
The idea that government spending and tax cuts help an economy by raising demand.
=> A school of thought based on the idea that demand for goods drives the economy
=> Government has more power
Trickle-down Economics
- Government economic policies that include reduced income and business taxes, reduced regulation (controls on business), and increased government spending on the military
- Also known as supply-side economics
- Generally these policies favour industry, assuming that if industry (wealthy) prospers then everyone will prosper as wealth “trickles down” to the ordinary workers and consumers
Nationalization
The changing of something from private to state ownership or control.
Privatization
The process of converting government enterprises into privately owned companies.
Neoconservatism
- An ideology that emerged as a reaction against modern liberal principles
- Challenge modern liberal principles and favour a return to particular values of classical liberalism
- Other ideas challenge both classical and modern liberal principles and favour values identified as “family values” and traditional values, often resting on a religious foundation.
New Deal
- Economic policies put in place by US president Franklin D. Roosevelt
- Give government a more significant role in the regulation of the economy and in providing social “safety net” programs
=> Creation of Alphabet Agencies and Mixed Economy
=> Relief, recovery, and reform
=> Deficit spending
Square Deal
A domestic program created by Theodore Roosevelt to offer consumer protection, control corporations, and conserve natural resources.
=> Both labour and capital must be treated fairly
=> Prevent large companies from abusing their control over the marketplace
=> Elkins Act and the Hepburn Act; used to stop railroads from offering special treatment to some businesses, like the Standard Oil Company
The Sherman Anti-Trust Act
- Created by William Howard Taft
- Prevent monopolies and collusion between competing companies
- Prevent anti-competitive behaviour; an entity cannot own two or more competing companies
=> Clayton Act makes this work with labour unions
Theodore Roosevelt
- Curb the excess of laissez-faire capitalism
- Creation of "square deal"
- National Progressive Party; equal suffrage and better working conditions, no child labour
Franklin D. Roosevelt
- First to convert to Keynes' theories
- Massive public works programs to put people to work
- Shift to welfare state and mixed economy
- Creation of "new deal"
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC)
An agency, established as part of the New Deal, that put young unemployed men to work building roads, developing parks, planting trees, and helping in erosion-control and flood-control projects.
John Maynard Keynes
An English economist who advocated the use of government monetary and fiscal policy to maintain full employment without inflation.
=> Keynesian economics
Milton Friedman
- American economist
- Promoted the idea of free trade and condemned government regulation and socialism
Friedrich Hayek
An economist known for his defence of free-market capitalism and work in the theory of money and economic fluctuations.
Stock Market Crash
October 29, 1929
- Everyone borrowed money
- Stock market dropped, panic selling
- Economic crash
Bank Run
This occurs when too many people try to withdraw their savings from a financial institution.
Great Depression
CRASH on October 29, 1929
- Economic boom; bought on credit
- USA is creditor nation; other countries are borrowing from the USA
- Panic selling => stock prices plummet
Crownest Pass
- United Mine Workers of America, regrouped as Mine Workers Union of Canada
- Mine management lowered hours and wages
- Joined Workers Unity League sponsored by Communist Party; strike
- "Red conspiracy"
- Both sides won?
Smoot-Hawley Tariff
This dramatically increased the cost to import goods into the United States.
=> Isolationism post depression
Dust Bowl
- Massive drought
- Mass-production of crops leads to failure to continue traditional methods to combat wind erosion of topsoil
- Topsoil blown away
Herbert Hoover
- Committed to Laissez-faire economics and classical liberalism
- Hoped that local authorities would help
- Small efforts to support the economy
=> Before Franklin D. Roosevelt
Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC)
- Government would lend money to small banks that were not part of the federal reserve
- Helps stop Bank Runs
R. B. Bennett
- Conservative Prime Minister
- Make-work projects to provide relief for the unemployed
- Cut government spending
The Business Cycle
- Based on a country's GDP (the value of all goods and services produced in a given year)
- Rise and fall of total jobs, production, and incomes
- Instability of the cycle
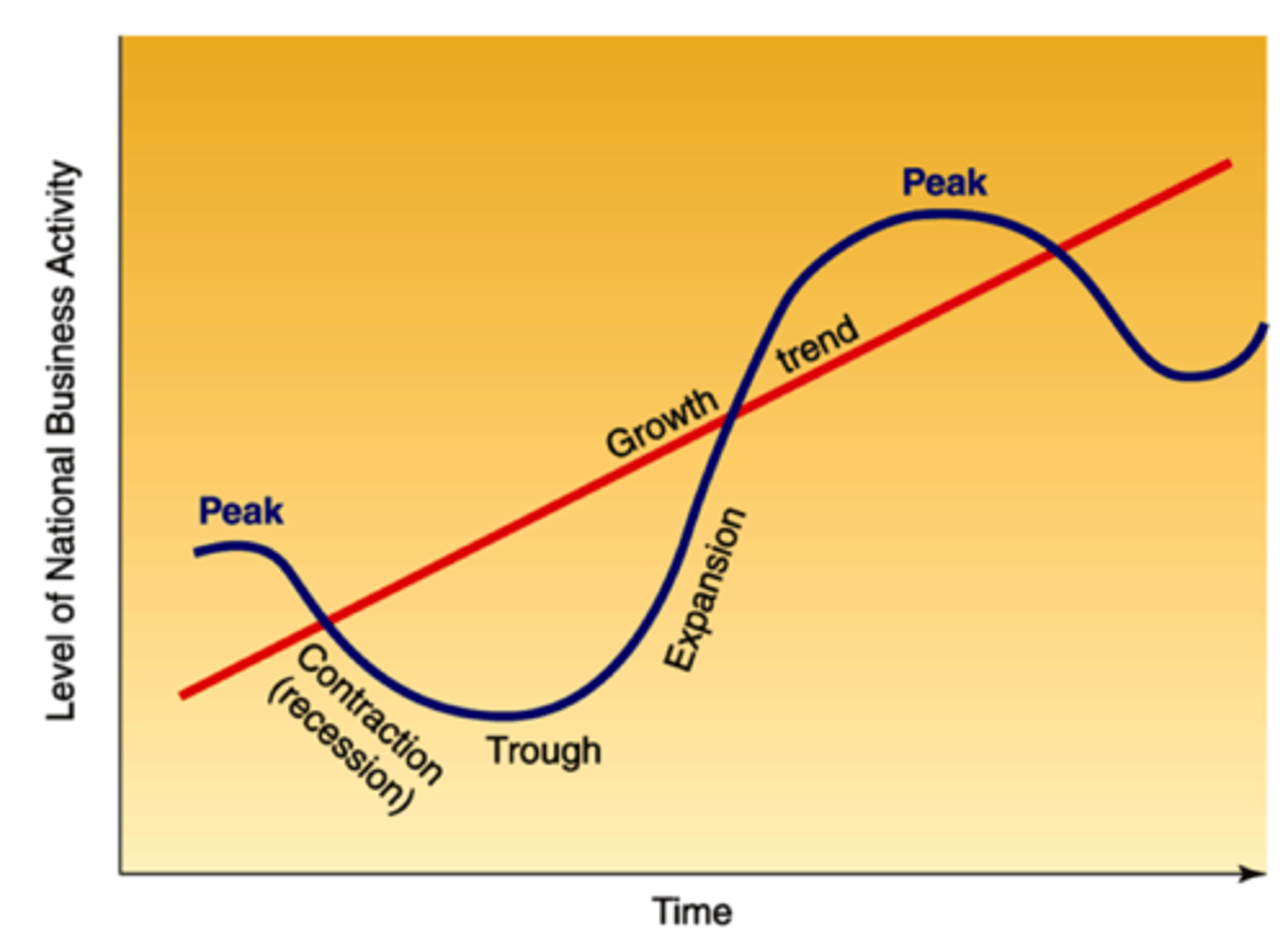
Recovery
INCREASING profits, prices, spending, and employment
- Expansion in the economy
- Replace worn out machinery
- Optimism
Inflation
A general and progressive increase in prices.
Boom/Peak
HIGH production, employment, income, stock prices, investments, demand
- Prices rising faster than wages
- High inflation
Recession
DECLINING profits, investments, production, sales
- Costs increasing
- Credit tightened
- Inventory accumulates
- Unemployment increases
Depression/Bust
SEVERE drop in wages, prices, interest rates, investments
- Economic activity at an all time low
- Low production and demand
- Massive unemployment
Deflation
- The prices of goods drop, but people still won't buy out of fear
- Not a lot of money is moving through the economy
Post-war Consensus
- Period in British politics
- Maintain welfare state; creation of "social safety net"
Social Safety Net
The many programs that the federal government provides to protect Americans against economic and social misfortune.
=> Employment insurance, child care, healthcare, elderly care
=> Prevent individuals from slipping through the cracks of society
Stagflation
A period where there is no economic growth, but prices increase.
=> Recession and high inflation at once
Deficit Financing
When a government is paying out more money than they are getting from tax revenue.
Maurice Duplessis
- Premier of Quebec
- Padlock Law => padlock buildings used for communist activity
- Created provincial income tax, funds to expand infrastructure, high minimum wage, opponent of organized labour, did not like social programs
Edmund Burke
- Developed classical conservatism
- Called for older forms of democracy
- Uninformed masses should be left out of political thought; trained professionals should be used instead
- "Ordered liberty"
- Rejection of Rousseau and ideas of equality in the French Revolution
- Government should represent the legacy of the past as well as the well-being of the present
Chartism
- Named after the "People's Charter"
- Prior to the movement, only males who owned property could vote
- Fought for male suffrage; empower working class
- Did not meet their goals
- Focus on using changes to law to expand liberty
=> Universal suffrage for men, equal-sized electoral districts, secret ballot, ability to join parliament without owning property, pay for MPs, annual elections
John Locke
- Government powers are derived from the consent of the governed and in which the government serves the people
- Also said people have natural rights to life, liberty and property
Adam Smith
- Wealth of Nations
- Called for an economic system that allowed for people to act on their self-interest
- "Invisible hand"
Margaret Thatcher
- British conservative Prime Minister
- Decrease government involvement, increase economic freedom
- Privatization
- Hard on labour unions
Blair's Third Way
- A moderate platform
- New form of a mixed economy
- Increase spending on healthcare and education, increase national minimum wage
- Introduces fee for post-secondary education
- Contrast to Thatcher
Mixed Economy
An economic system combining private and public enterprise.
=> Market-based system with some government involvement
Ronald Reagan
- Believed that stagflation of economy was caused by a growing deficit
- Supported supply-side economics and trickle-down economics
- Conservative
Socialism
The belief that resources should be controlled by the public for the benefit of everyone in society and not just by private interests for the benefit of private owners.
=> Focus on economic equality and cooperation, LEFT of spectrum
=> Private ownership = exploitation, state should direct economic activity, classless society
Utopian Socialism
A humanitarian movement that advocated the end of the conditions workers found themselves in during the Industrial Revolution.
=> Focused on character; if you can provide opportunities to grow character, you can create a better society
Eg) Robert Owen and New Lanark; communal system introduced to replace laissez-faire capitalism
=> Mandatory education, communal grocery stores, improved housing, worker incentive and penalty
Moderate Socialism
- A mentality of gradualness; meaning
political reforms brought about by gradual steps
- Put their faith in evolutionary socialism rather than
revolution
=> As seen in Fabian society and with Tommy Douglas (the voice of moderate socialism)
Democratic Socialism
A socialist movement that focuses on more political reform through democratic means in order to achieve economic equality.
=> Co-operative Commonwealth Party (CCF), Regina Manifesto => now the NDP
Communism
(Scientific Socialism, Marxism)
- Ideas associated with Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels
- Class struggle between the Proletariat and the Bourgeoisie for control over the Means of Production
- Command economy
- Abolition of private property; centralization of the means of production
=> Communist Manifesto
Manifesto
A public statement explaining the intentions, motives, or views of an individual or group
=> A public declaration of policies or intentions
Wealth Redistribution
The transfer of income and wealth (including physical property) from some individuals to others through taxation, land reform, or some other social mechanism.
=> Inflation redistributes wealth between borrowers and lenders
=> Equal society?
Karl Marx
- Father of Communism; Marxism is a radical
form of socialism
- Many of Marx’s ideas were socialist and collectivist in nature, but many of his ideas were used to create extreme forms of socialism
Command Economy
An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy.
Central Planning
A communist economic system in which the state explicitly allocates resources by planning what should be produced and in what amounts, the final prices of goods, and where they should be sold.
=> Decisions are made by a central authority rather than by market participants.
Fabians
- London, England
- Members were intellectuals, academics, and writers
- Advocated for the gradual reform of liberalism towards socialism through education and democratic reform
=> New and unknown
Proletariat
The workers!
Bourgeoisie
The owners!
Class Conflict
Marx's term for the struggle between capitalists and workers.
Class Struggle
The conflict of interests between the workers and the upper class in a capitalist society.
Neoliberalism
This embraces a return to free-markets and less government.
=> A return to the focus on the need for private enterprise and free markets.
Sweden
- Cradle to Grave state
- Have extensive social services that affect the
population (food allowance for each child, all levels of education free, medicine and prescriptions free, dental care)
=> HIGH tax rate; heavily affected by stagflation
Russia (USSR)
- Russia is behind; exploitation and inequality leads to the growth of support for Marxist ideas by individuals such as Lenin and the creation of many socialist parties
- Creation of the Bolsheviks (ultimately becomes Communist Party)
Bloody Sunday Massacre
- Protestors wanted basic liberal principles (a constitutional monarchy universal suffrage; a minimum wage)
- Cossacks killed at least 92 civilians
October Revolution and Manifesto
- General strikes grow in numbers across Russia
- First Soviets emerged
- Czar yielded and promised change
- Enter the Duma (parliament)