Health History & Physical Assessment
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Comprehensive Admission Assessment
health assessment done when someone is admitted
Ongoing Partial Assessment
regular mini checks to track progress
Focused Assessment
looks at a specific issue
Emergency Assessment
life threatening or unstable issue
Health Assessment
collect, validating, and analyzing data
either subjective or objective data
includes two components → health history and physical assessment
Subjective Data
what the patient is telling you
sensations or symptoms, feelings, perceptions, desires, preferences, beliefs, ideas, values, and personal information
Interviewing
requires professional and interpersonal skills
establishes rapport and trusting relationship with the client
gathers info on developmental, psychological, physiologic, sociocultural, and spiritual status
can help identify changes and collaborate interventions or strengths that can help with client
Preintroductory Phase
review patients chart before the meeting
Introductory Phase
say “hello” and explain what you’re doing, build trust
Working Phase
ask questions and gather health history
Summary and Closing Phase
wrap up and make sure the patient understands everything
Objective Data
what you can see, hear, or feel during the physical exam
use your senses and tools like a stethoscope or thermometer
Assessment Equipment
gloves and gowns
sphygmomanometer (BP cuff) and stethoscope
thermometer
watch with second hand and penlight
ophthalmoscope and otoscope
ruler or a tape measure
doppler and ultrasound
tongue depressors, cotton balls, and tuning fork
Non Verbal Communication
appearance, demeanor, facial expression, attitude, listening
Verbal Communication
open ended questions and closed ended questions
validating, clarifying (for more info), reflective, sequencing, and directing (clear concise responses asking about a specific issue)
Non Verbal Communication to Avoid
excessive or insufficient eye contact
distraction and distance
standing
Verbal Communication to Avoid
biased or leading questions
rushing through the interview
readings the questions straight from paper
Gerontologic Considerations
slower responses, sensory changes, skin changes, have multiple chronic conditions, fatigue easily
ex: a 75 year old may not show typical fever response in infection - you must look for confusion or changes in behavior instead
Cultural Considerations
communication style, pain expression, modesty and gender roles, and health beliefs
ex: a patient from East Asia might not openly complain about pain due to values of endurance
Emotional Considerations
anxiety or fear, depression, anger or frustration, and mental health conditions
ex: a patient with anxiety may have difficulty focusing on questions so use a calm tone and simple instructions
Interaction with Anxious
be calm and explain things clearly
Interaction with Angry
stay safe and let them vent
Interaction with Depressed
be understanding
Interaction with Manipulative
set clear boundaries
Interaction with Seductive
be professional and get help if needed
set clear boundaries
Sensitive Topics
death or sexuality
be respectful, don’t judge, and refer to someone else if you are unsure
Health History
biographical data → name, age, insurance info
reasons for seeking healthcare
history of present health concerns
past health history
family health history
review of body systems
lifestyle and health practices
developmental level
COLDSPA
mnemonic to analyze pain
character, onset, location, duration, severity, pattern, associated factors/how it affects the client
Review of Systems
integumentary system
HEENOT system (head, ears, eyes, nose, and throat)
respiratory system
cardiovascular system
abdominal system
breast and axillae
male and female genitalia (rectum, anus, prostate, vagina)
musculoskeletal system
neurologic system
sometimes also mental/emotional status
Setting Up Environment
make sure the room is private, quiet, warm, and well lit
Preparing Yourself
check your feelings
create a calm and supportive environment - don’t bring stress into the exam room
wash your hands and wear gloves if needed or any other PPE
Preparing the Client
explain whats going to happen
be respectful
offer privacy when they change clothes
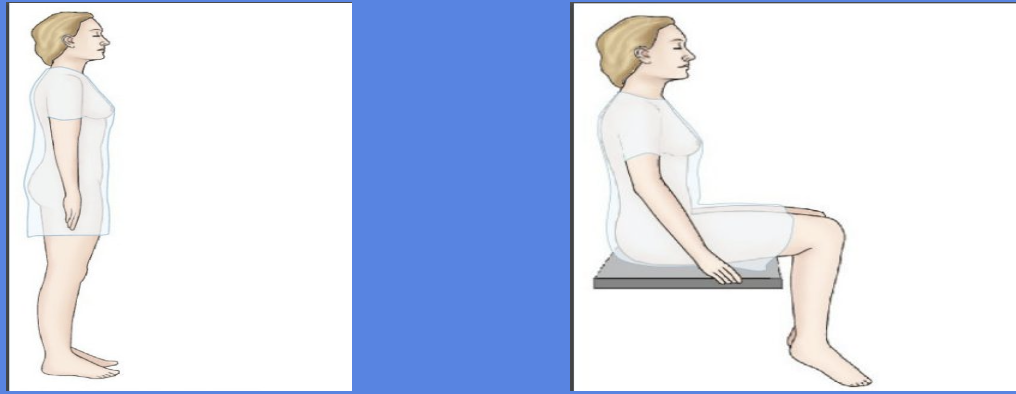
Standing and Sitting
for posturing and lung checks
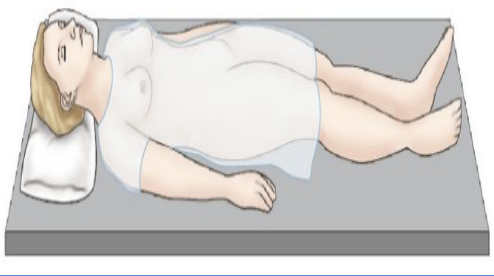
Supine
for general exams
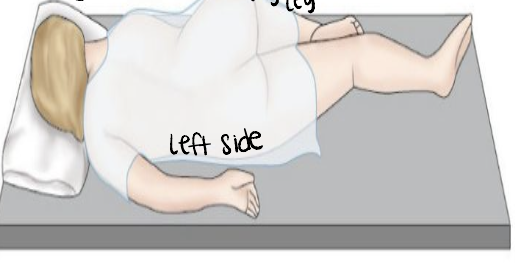
Sims
left side for rectal temp and enemas → laying on left side with right leg bent
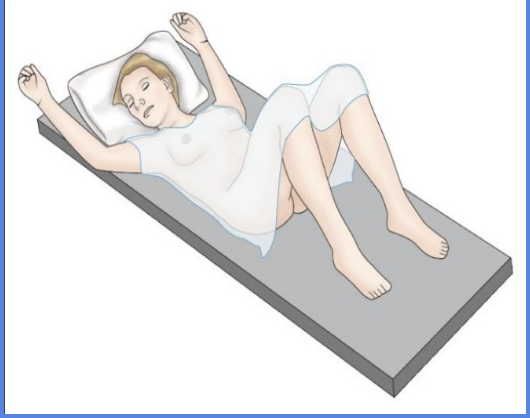
Dorsal Recumbent
Knee Chest
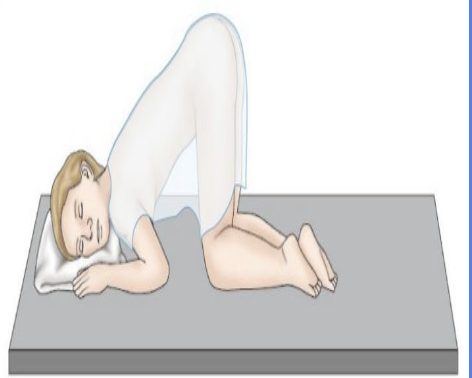
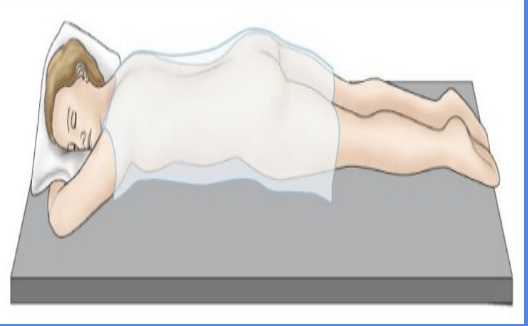
Prone
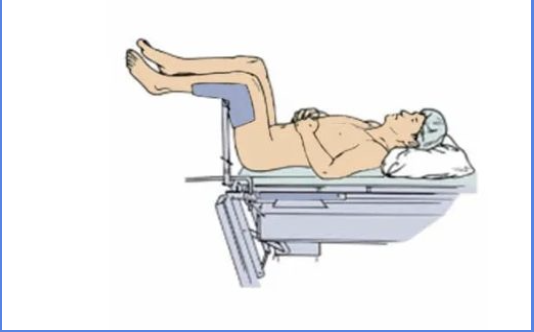
Lithotomy
for pelvic exams
Physical Assessment
nurse must have knowledge on types and operation of equipment
prepare yourself and the client for the exam
properly preform techniques
inspection → look
palpation → touch
percussion → tap
auscultation → listen
Inspection
uses sense of vision, smell, and hearing
room at comfortable temperature with good lighting
look and observe before touching
completely expose part being examined while draping the rest of client
note characteristics and compare appearance of symmetric body part
Palpation
light → 1 hand
deep → 2 hands
consists of using parts of the hand to touch and feel for the following characteristics - fingertips, dorsal, or palmar surface used
texture → rough or smooth
temperature → warm or cold
moisture → wet or dry
mobility → fixed, movable, still, vibrating
consistency → soft, hard, fluid filled
strength of pulses → strong, weak, thready, bounding
size → small, medium, large
shape → well defined, irregular
degree of tenderness
Fingerpads
finds discriminations like pulses, texture, size, consistency, shape, or crepitus (air under skin respiratory)
Ulnar or Palmar Surface
feels vibrations, shrills/thrills (chest vibration), or fremitus (vibrations when saying 99 that weaken further down the body)
Dorsal Surface
feels temperature
Percussion
used to elicit pain, determine location/size/shape, determine density, detect abnormal masses, and elicit reflexes
types → direct, blunt, and indirect or mediate
elicits resonance, hyperresonance, tympany, dullness, or flatness
Direct Percussion
tapping directing on the body part
ex: tapping on sinuses
Blunt Percussion
hitting body air hard with fit
ex: palpating kidneys with a light punch
Indirect Mediate Percussion
placing your hand on the body part and tapping that with your fingers
ex: respiratory exams
Resonance
low pitch and hollow normal sound
Hyperresonance
louder booming lower pitch sound, air in thoracic cavity
Tympany
high pitch and hollow sound over areas of air in the abdomen
Dullness
dull sound heard over an organ
Flatness
no sound if tapping over bone
Stethoscope
earpieces into outer canal with binaurals angled down toward the nose
before use warm diaphragm and bell, explain what you are doing and answer questions, and avoid listening through clothes
Diaphragm
the larger side used to hear high pitch sounds like breath sounds, normal heart sounds, and bowel sounds
use it with firm pressure
Bell
smaller side used to hear lower pitch sounds
use with low pressure to hear heart murmurs and bruits (whooshing over carotid area)
Auscultation
requires use of a stethoscope
sounds rated on intensity (loud/soft), pitch (high/low), duration, and quality (musical/cracking/raspy)
eliminate distractions or competing noise and expose body part being used
Questions to Self
did i do the exam properly?
are the findings normal or not?
should i ask more questions or check other body systems?
should i call the doctor or provider?
Flushing
redness
caused by blushing, alcohol, fever, injury, or infection
Cyanosis
bluish color
due to cold envi and cardiac or respiratory disease
Jaundice
yellowish
caused by liver disease
Pallor
paleness
due to anemia
Ecchymosis
purplish discoloration
Petechiae
small hemorrhagic spots caused by capillary bleeding
Lesion
diseased or injured tissue
Turgor
fullness or elasticity of the skin
Bruits
abnormal swooshing or blowing sounds heard over a blood vessel
Edema
excess fluid/swelling of tissue
tested by pressing into skin, skin will have indent
Dehydration
decreased skin elasticity and skin folds return slowly
Pupillary Reaction
darken room and briefly shine light into eyes → pupils should constrict
Accommodation
place object 10-15cm from patients nose and most closer and farther away
closer → pupils constrict
farther away → pupils dilate
Convergence
hold finger 6-8 inches from face and move closer → pupils cross