Veterinary Immunology: Bacterial and Fungal Infection Responses
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are the two main types of immune responses involved in combating bacterial infections?
Innate response and adaptive response.
In the immune response to bacteria and fungi, what induce inflammation, cytokine release, and complement activation?
TLRs
__ has dendritic and macrophages to ingest invading bacteria and to trigger T & B cell responses
Acquired Immunity
What are the five basic mechanisms of the acquired immune response to bacterial infections?
1. Neutralization of toxins by antibodies.
2. Killing of bacteria by antibodies and complement.
3. Opsonization of bacteria by antibodies and complement.
4. Intracellular destruction by activated macrophages.
5. Direct killing by cytotoxic T cells and NK cells.
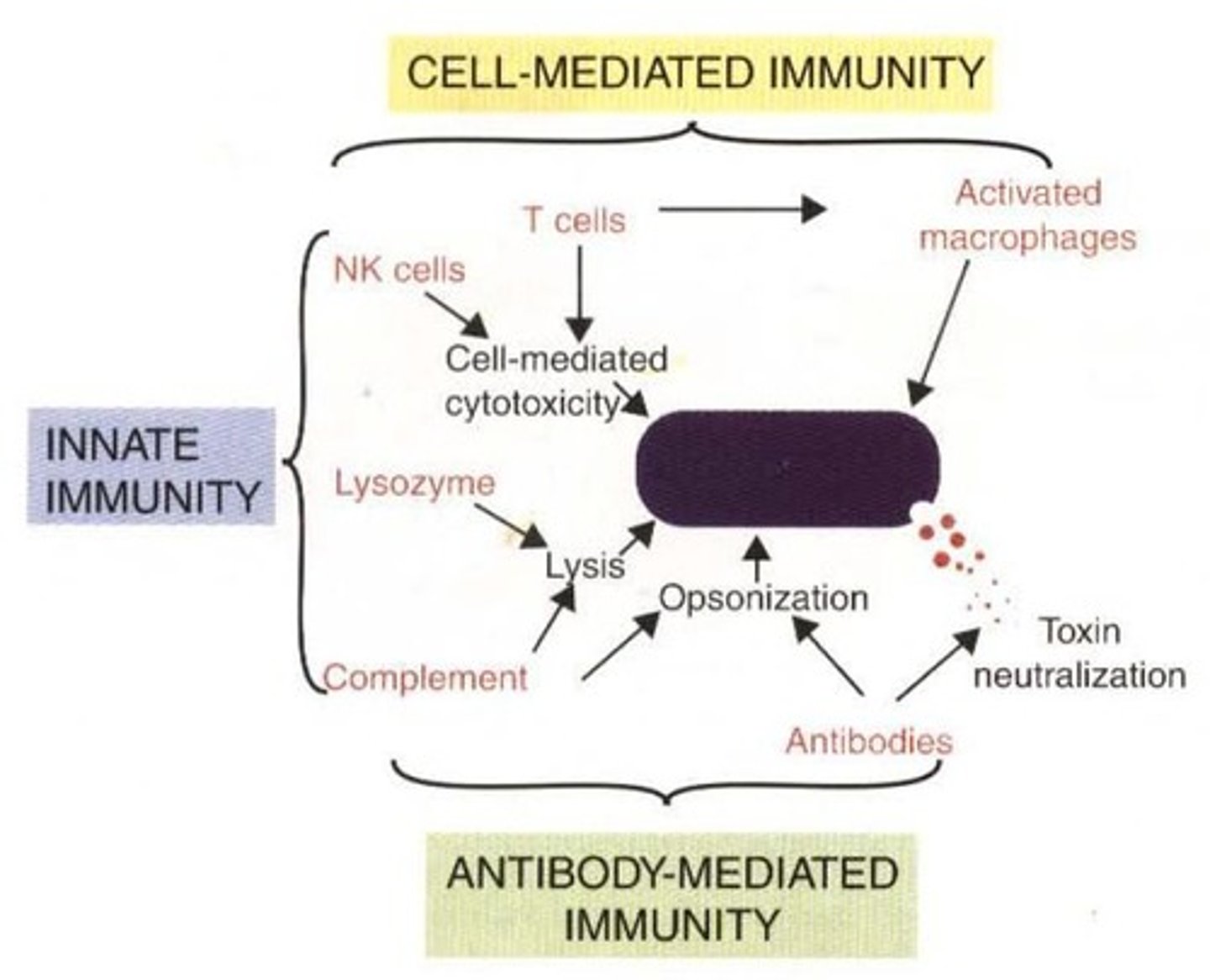
Immune response neutralize toxins from toxigenic bacteria by preventing the toxin from binding to its receptors on target cells by _
Antibodies
In toxigenic bacteria immunity, when the toxin is already combined with its receptors, antibodies will still be ineffective in reversing it.
False
This immunity is mediated by antibodies directed against the surface antigens of the bacteria
Immunity to Invasive Bacteria
The immune response to invasive bacteria: __ enhances phagocytosis by marking bacteria for recognition by neutrophils and macrophages.
Opsonization
What portion of the opsonin layer binds to the surface of invasive bacteria?
C3b
Antibodies against the __, neutralize the antiphagocytic properties of the capsule in capsulated bacteria.
K antigen
Antibodies against _ act as opsonins to enhance phagocytosis in nonencapsulated bacteria
O antigen
Bacterial capsules can hinder phagocytosis, and antitoxic immunity is slow to develop. What bacteria can this be seen?
Anthrax
This immunity against bacterial capsule is protective, but slow to develop & toxin production is prolonged, making phagocytic cells struggle to eliminate the toxins
Antitoxic immunity
What type of vaccine is used against animal anthrax and why?
An unencapsulated toxigenic strain of B. anthracis given in spore form.
In the immune response, _ increase their thermotolerance so cells can function at high temperature; they are highly antigenic & readily processed by antigen-presenting cells
Heat-Shock Proteins (HSPs)
This response is the major defense against bacterial pathogens
Anti-HSP response
HSPs are present in all organisms at very low levels at normal temperature
True
What induces HSP production?
Mild stress
What bacteria can travel from cell to cell without being exposed to ECF?
Listeria monocytogenes
_ survive within macrophages by growing inside macrophages, travel between cells, resist lysosomal enzymes, or manipulate host cytokine responses.
Intracellular bacteria
This is the most effective in inhibiting macrophage activation. __ does it by inhibiting macrophage activation, suppresses oxidant production, and downregulates antigen processing, which then reduce MHC class II expression
IL-10
Vaccines containing killed bacteria are not protective against __, because they do not stimulate the appropriate helper T cell populations needed for protective immunity.
Intracellular bacteria
What vaccine is effective against intracellular bacteria?
Vaccines with live bacteria
The difference of live and dead bacteria vaccines against intracellular bacteria is due to their __
Differential stimulation of helper T cell populations
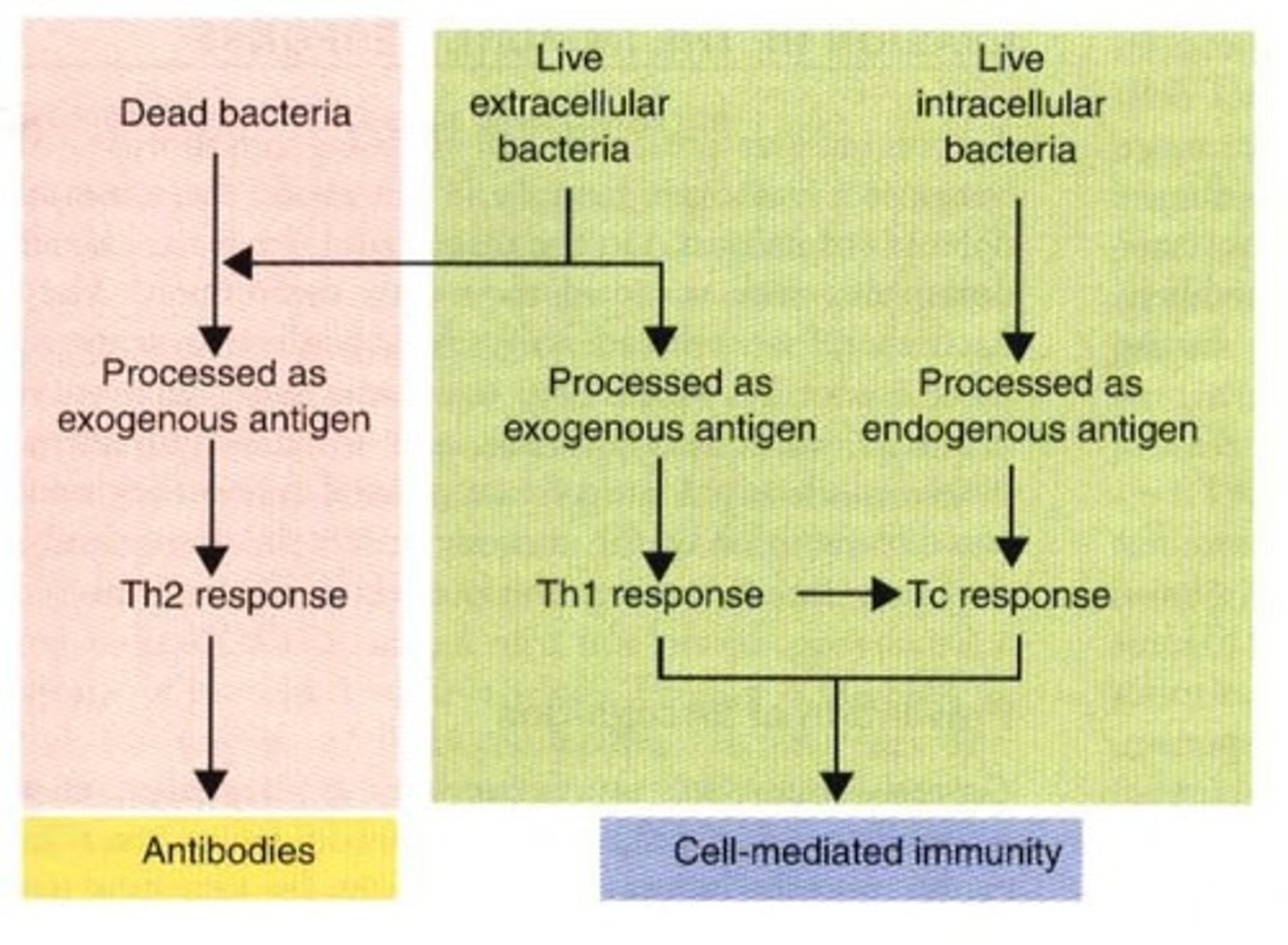
Live B. abortus stimulated Th1 cells to secrete __, which activates macrophages to kill intracellular microbes
IFN-γ
Dead Brucella organisms stimulate __ production to a greater extent than the live bacteria, which causes more inflammation and fever
IL-1
What innate immune mechanisms are involved in the response to fungal infections that results to neutrophil attraction?
Alternative pathway activation of the complement system
In fungal infections, neutrophils can’t fully digest them due to?
large hyphae or pseudohyphae
Small fungal fragments/spores can be destroyed by __
Macrophages & NK cells
Fungal infections can be later destroyed by __
T-cell mediated mechanism/acquired immunity
They primarily function in fungal infections by activating macrophages and promoting epidermal growth & keratinization
T-cells
Some T & NK cells exert direct cytotoxic effect on yeasts such as __
C.neoformans & C. albicans
What factors influence the development of diseases related to bacterial infections?
Host response, presence of damaged tissues, bacterial location, and bacterial virulence.
What is the consequence of a shift in the balance between host immunity and bacterial virulence?
It can result in disease or death.
What is the role of dendritic cells and macrophages in acquired immunity to bacterial infections?
They ingest invading bacteria and trigger T and B cell responses.
What is the effect of bacterial toxins on the immune response?
The immune response must neutralize toxins in addition to eliminating the bacteria.
What is the significance of the complement system in bacterial immunity?
It enhances opsonization and phagocytosis, and can directly kill bacteria.
What mediate inflammation and coordinate the immune response to bacterial infections
Cytokines