ATP +basics 5.1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
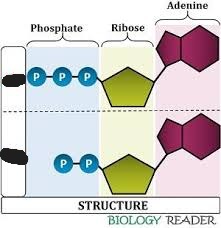
ATP
ADP
what is the reversible reaction between ADP and ATP
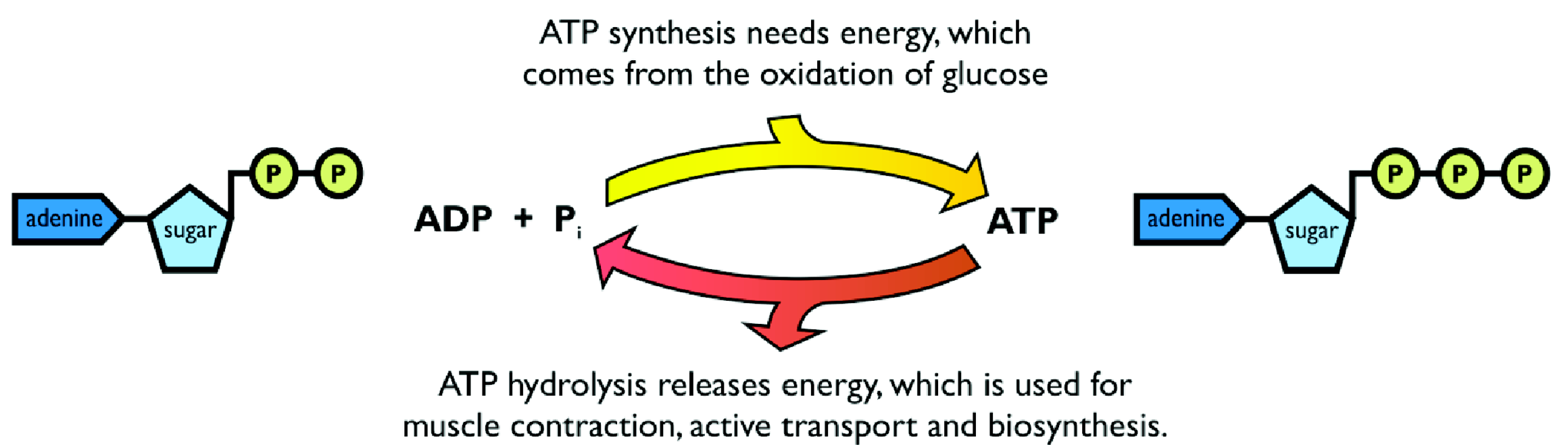
what enzyme helps to catalyse the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP +Pi and what’s its other name
ATPase enzyme other name is stalked particles
define OILRIG
Oxidation
Is
Loss
Reduction
Is
Gain
of electrons
why is ATP better than glucose as an energy store
its very soluble so the energy it contains can be released easily and quickly over
They store less energy individually but as these small packets of easily-released energy are more useful to cells and can be used to do simple common jobs, as the next paragraph shows. An analogy would be that small change (ATP) is often more useful than large bank notes (glucose).
over 30 ATP can be synthesised from one glucose molecule
what is ATP used for
The processes in a cell that require energy can be put into three groups:
• Muscle contraction and other forms of movement, such as cilia, flagella, cytoplasmic streaming, etc. Each step of the muscle crossbridge cycle costs one ATP molecule.
• Active transport. Each shape change in an active transport protein pump costs one ATP molecule.
• Biosynthesis– building up large molecules from smaller ones, e.g. protein synthesis, DNA replication, starch synthesis, etc. Each monomer added to a growing polymer chain costs one ATP molecule.
define metabolism
the thousands of chemical reactions taking place in a cell
define metabolites
These are the intermediates in a metabolic pathway
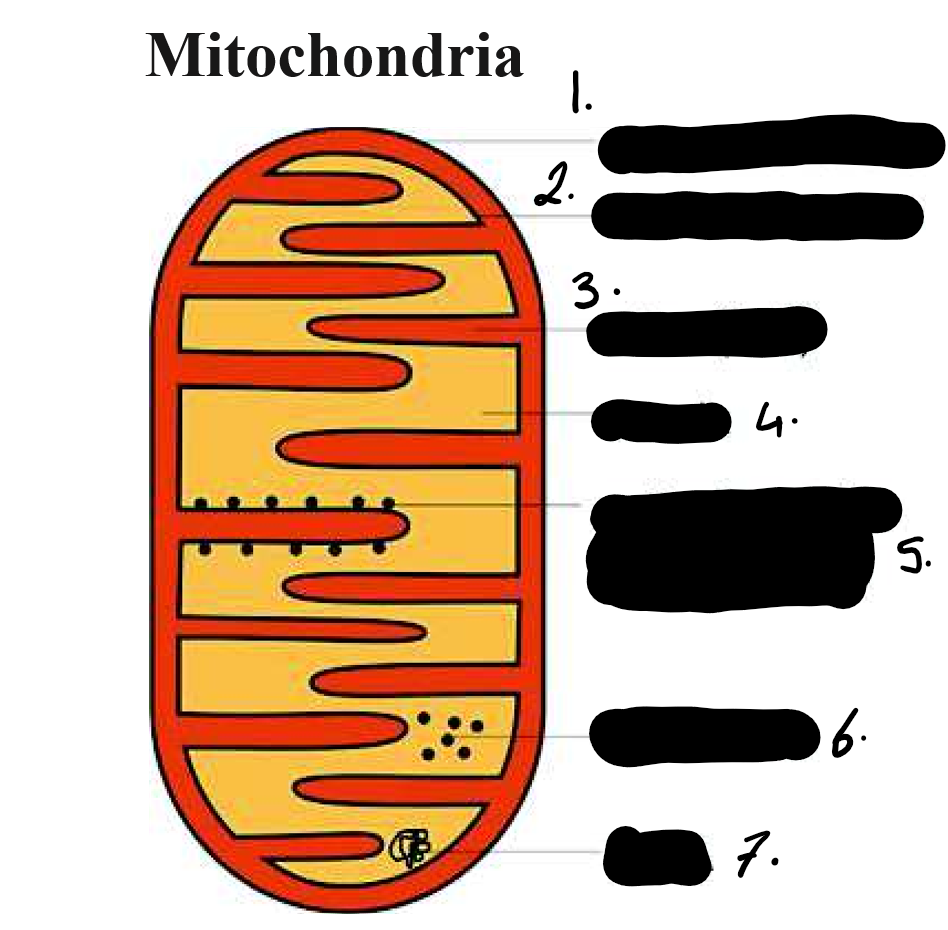
outer membrane
inner membrane
crista
matrix
stalked particles ( ATP synthase)
ribosomes
DNA
what are the 4 stages of respiration and where do they take place and are they anaerobic or aerobic
glycolysis (cytoplasm) anaerobic
Krebs cycle (mitochondria) aerobic
electron transport chain ( in mitochondria) aerobic
oxidative phosphorylation (inner mitochondrial membrane) aerobic/ electron transport chain
why is it beneficial to have the different stages occur in different areas
This compartmentation allows the cell to keep the various metabolites separate, and to control the stages more easily.
ATPase Vs ATP synthase
ATPase and ATP synthase are both enzymes that involve ATP, but they have opposite functions: ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and phosphate, releasing energy for cellular work, while ATP synthase synthesizes ATP from ADP and phosphate, using energy from a proton gradient
define decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is the removal of a carbon atom from a molecule in the form of carbon dioxide (CO₂).
hydrogen acceptor
receives a hydrogen and is reduced
dehydrogenase
enzymes that remove hydrogen
Dehydrogenases are enzymes that catalyse the removal of hydrogen atoms (H⁺ + e⁻) from a substrate eg GP being oxides loosing a hydrogen .
In biological systems, these hydrogens are usually accepted by coenzymes such as NAD⁺ or FAD.
cytochrome
member of the ETC they are proteins which pigmented with an iron group
cytochrome oxidase
an enzyme which receives e from the cytochromes they become reduced and cytochromes are oxidised.