CH 3 Derivatives (DONE)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Long & Short Hedges
A long futures hedge is appropriate when you know you will purchase an asset in the future and want to lock in the price
A short futures hedge is appropriate when you know you will sell an asset in the future and want to lock in the price
Arguments in Favor of Hedging
Companies should focus on the main business they are in and take steps to minimize risks arising from interest rates, exchange rates, and other market variables
Arguments against Hedging
Shareholders are usually well diversified and can make their own hedging decisions
It may increase risk to hedge when competitors do not
Explaining a situation where there is a loss on the hedge and a gain on the underlying can be difficult
Basis Risk
Basis is usually defined as the spot price minus the futures price
Basis risk arises because of the uncertainty about the basis when the hedge is closed out
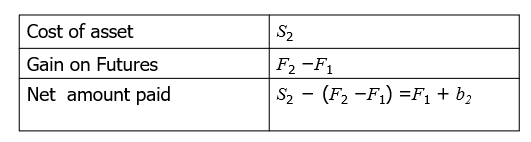
Long Hedge for Purchase of an Asset
Define
F1 : Futures price at time hedge is set up
F2 : Futures price at time asset is purchased
S2 : Asset price at time of purchase
b2 : Basis at time of purchase
Short Hedge for Sale of an Asset
Define
F1 : Futures price at time hedge is set up
F2 : Futures price at time asset is sold
S2 : Asset price at time of sale
b2 : Basis at time of sale

Choice of Contract
Choose a delivery month that is as close as possible to, but later than, the end of the life of the hedge
When there is no futures contract on the asset being hedged, choose the contract whose futures price is most highly correlated with the asset price. This is known as cross hedging.
Optimal Hedge Ratio (equation 3.1)
Ignoring daily settlement of futures (or assuming forwards are used) , the proportion of the exposure that should optimally be hedged is
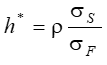
where
σS is the standard deviation of ΔS, the change in the spot price during the hedging period,
σF is the standard deviation of ΔF, the change in the futures price during the hedging period
ρ is the coefficient of correlation between ΔS and ΔF.
Optimal Number of Contracts (equation 3.2)
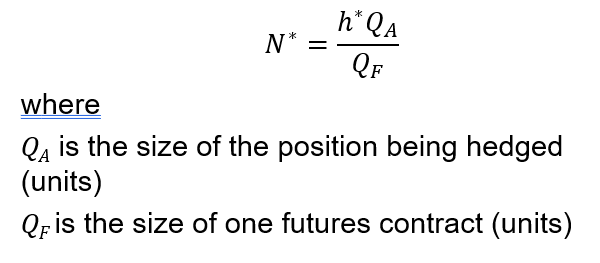
Example (Example 3.3)
Airline will purchase 2 million gallons of jet fuel in one month and hedges using heating oil futures
From historical data σF =0.0313, σS =0.0263, and ρ= 0.928
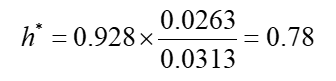
Example continued
The size of one heating oil contract is 42,000 gallons
Optimal number of contracts is
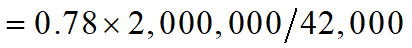
which rounds to 37
Optimal Number of Contracts When Contract Is Settled Daily
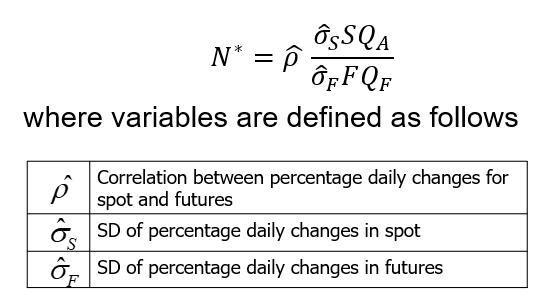
An Alternative Expression for N* when there is daily settlement (equation 3.3)

Daily Settlement
Day to day changes in N* are small and often ignored
Tailing the hedge involves dividing N* by one plus the amount of interest that will be earned over the remaining life of the hedge
Hedging Using Index Futures
(equation 3.4)

Example
Index futures price is 1,000
Value of Portfolio is $5 million
Beta of portfolio is 1.5
What position in futures contracts on the index is necessary to hedge the portfolio?
Changing Beta
What position is necessary to reduce the beta of the portfolio to 0.75?
What position is necessary to increase the beta of the portfolio to 2.0?
Why Hedge Equity Returns
May want to be out of the market for a while. Hedging avoids the costs of selling and repurchasing the portfolio
Suppose stocks in your portfolio have an average beta of 1.0, but you feel they have been chosen well and will outperform the market in both good and bad times. Hedging ensures that the return you earn is the risk-free return plus the excess return of your portfolio over the market.
Stack and Roll
We can roll futures contracts forward to hedge future exposures
Initially we enter into futures contracts to hedge exposures up to a time horizon
Just before maturity we close them out an replace them with new contract reflect the new exposure
etc
Liquidity Issues (Business Snapshot 3.2)
In any hedging situation there is a danger that losses will be realized on the hedge while the gains on the underlying exposure are unrealized
This can create liquidity problems
One example is Metallgesellschaft which sold long term fixed-price contracts on heating oil and gasoline and hedged using stack and roll
The price of oil fell.....