Unit 1 Review
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
interstate=state to another state; intrastate=state to itself
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Initiative
A procedure by which voters can propose a law or a constitutional amendment.
Referendum
oppose a law passed by their legislature, and if enough people support it, they can call for a vote to defeat that law
US v Lopez
Arrest: Alfonso Lopez was arrested for carrying a concealed handgun to school, violating the federal Gun-Free School Zones Act.
Legal Challenge: He appealed, arguing the law was unconstitutional as it exceeded Congress’s power under the Commerce Clause.
Supreme Court Ruling: The Court ruled the law unconstitutional, stating gun possession in a school zone did not substantially affect interstate commerce.
Outcome: Lopez's conviction was overturned, but the case limited Congress's regulatory power over local non-economic activities.
participatory democracy
citizens have the power to decide directly on policy and politicians are responsible for implementing those policy decisions (initiatives, referendum, town hall)
elite democracy
privileged classes acquire the power to decide by a competition for the people's votes (electoral college, judges in supreme court)
pluralist democracy
Group based activism by nongovernmental interests striving to impact political decision making (interest groups, influence politicians through monetary donations)
brutus 1
U.S. Constitution would give too much power to the federal government (collect taxes, trump state courts, large republic with numerous representatives, necessary and proper clauses, supremacy clause), making it difficult to represent the diverse interests of the people and leading to potential tyranny; participatory
Federalist 10 (response to brutus 1)
the fear was unfounded because in a large republic, the presence of many factions will prevent any one faction from becoming dominant; pluralist
Challenges of Articles of Confederation
One vote for each state regardless of size (equality), no executive or judicial branches of government, no power to tax (economy), no power to regulate interstate commerce (economy), 9/13 required to pass laws, unanimous consent to amend the articles, no uniform currency (economy), had to ask states for troops for an army
Confederacy
states were independent entities linked together for limited purposes
bicameral legislature
house of rep apportioned by population, senate apportioned with 2 senators for each state
Laws for slavery
3/5th compromise for representation and taxation, slave trade can't be touched for 20 years then after it can be abolished
How does state legislatures work
California has 40 senate and 80 assembly in the state legislature so 21/40 and 41/80 have to say yes in order for them to get 1 approve vote for the state of California. Once 38/50 state legislatures have the approve vote, the amendment is approved
Legislative branch
propose and make laws
executive branch
enforce laws
judicial branch
interpret constitutionality of laws
checks and balances
Legislative can impeach president and judges, Executive can veto legislation and nominate judges, Judicial can declare president actions or laws unconstitutional
stakeholder
anyone vested interest in the outcome of policymaking (us)
Stakeholders can influence legislative branch
Pay lobbyists to meet with representatives to persuade them to vote in the group's interest or citizens can write emails to representatives
Stakeholders can influence Executive branch
file complaint with bureaucratic agencies run by executive branch, use the courts to challenge unjust or unconstitutional laws or appeal to wrongful convictions
Article 1 - Legislative
House: 25+ years, US citizen for 7+ years, resident; sole power of impeachment—majority; act as prosecutors
Senate: 30+ years, US citizen 9+ years, resident; conducts impeachment trials; act as jury—2/3 to convict and remove from office
Article 1, Section 7
bills raising revenue originate in the House, president can sign or veto (presentment clause), 2/3 of Congress to override a veto
Article 1, Section 8
Expressed powers of Congress; tax, spend, borrow, make and enforce laws, coin money, declare war, raise an army and navy, regulate interstate and foreign commerce, create lower federal courts, establish postal routes, control district of Colombia
Article 1, Section 9
Limits on Congress; Habeas Corpus: Cannot be suspended unless in rebellion/invasion; No Ex Post Facto Laws: Can’t criminalize acts retroactively; No Bills of Attainder: No punishment without trial; No Titles of Nobility: U.S. can't grant nobility titles; Other Limits: No export taxes, no spending without approval.
Article 1, Section 10
Limits on States: No Treaties/Currency: States can't make treaties or coin money; No Ex Post Facto/Bills of Attainder: States can’t pass these laws either; No Tariffs/Armies: States can't impose tariffs or have peacetime armies.
Article 2
Executive Branch; Commander in Chief of Armed forces, makes treaties with approval of 2/3 Senate, does state of the union
Article 3
Judicial Branch; life tenure
Article 4
Relations among states and federal government; full faith and credit clause (respect other states actions), extradition (fugitives who flee must return to the state they committed the crime), privileges and immunities clause (states cannot discriminate against citizens of other states), republic form of government, congress admits new states and administers US territories
Article 5
Amendment Process; 2/3 Congress or state convention for proposal; ¾ of state legislatures or conventions to ratify
Article 6
Supremacy Clause, federal government over state
Article 7
Ratifying the Constitution; Constitution would take effect once nine out of the thirteen states ratified it.
Social Contract
Society as a whole would agree to give up its most extreme rights so that their natural rights are protected by government; Concerned about a strong central government turning into a tyrannical monarchy again.
Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.
Shay's Rebellion
1786-1787 uprising led by Daniel Shays, fueled by economic hardship and unpaid Revolutionary War veterans. Farmers protested high taxes and debt, highlighting weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation and leading to calls for a stronger federal government
Power vs Influence
formal authority to make others do something; shape others' decisions
Government vs Politics
institution where public policy decisions are made; process which these decisions are made
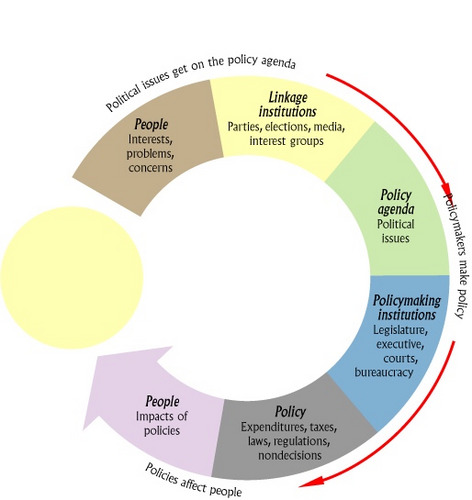
Policymaking System
people, linkage institutions, policy agenda, policymaking institutions, policy, people
Divine Right Theory
rulers claim their authority comes from God, making their power absolute and unquestionable
Social Contract theory
government is formed through a contract where people consent to give up some freedoms in exchange for protection and order
Thomas Hobbes
Leviathan (key work): "state of nature" leads to chaos and a state of war where people can harm each other; to protect their lives, people must consent to create a powerful state that maintains order and security
John Locke
Second Treatise of Government: "state of nature" people have perfect freedom but may face threats to their property so a govt should be formed; it must protect natural rights and is based on popular sovereignty and consent of the governed; if it fails people have the right to dissolve it
Jean Jacques Rousseau
direct democracy where citizens directly make laws
Republicanism
A form of government in which people elect representatives to create and enforce laws
Virginia Plan
representatives apportioned by population
New Jersey Plan
representatives apportioned equally, 1 vote
Charles A. Beard
the Founding Fathers as self-interested individuals primarily motivated by economic concerns, believing they crafted the Constitution to protect their own property and wealth rather than purely for democratic ideals.
Robert Roach
democratic nationalism, emphasizing popular sovereignty and democratic principles in the formation of the American government
Katzenbach v. McClung (1964)
Ollie’s Barbecue, a restaurant in Birmingham, Alabama, refused to serve Black customers, citing its right as a private business.
Supreme Court Decision: The Court upheld the Civil Rights Act of 1964, ruling that Congress had the authority to prohibit racial discrimination in public accommodations because it substantially affected interstate commerce.
Heart of Atlanta Motel v. United States (1964)
Background: The Heart of Atlanta Motel in Georgia refused to rent rooms to Black customers, challenging the Civil Rights Act.
Supreme Court Decision: The Court ruled that the motel's operations affected interstate commerce, allowing Congress to prohibit racial discrimination in public accommodations
Formal way the Constitution becomes more democratic overtime
amendment process (Article 5); example: 13,14,15,17,19,23,24,26 amendment
Informal way the Constitution becomes more democratic overtime
changes interpretation; example: 1965 voting rights act (ended literacy tests), changing political practices