Edexcel A-Level Geography - Coasts EQ1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what is the littoral zone?
the wider coastal zone, including coastal land areas and shallow parts of the sea offshore
what are the sub-divisions of the littoral zone?
- offshore
- nearshore
- backshore
what is offshore?
beyond the influence of breaking waves
what is nearshore?
intertidal and within the breaker zone; used for fishing, trade and leisure
what is backshore?
above high tide and the influence of normal wave patterns; may have a storm beach futher up
what are the characteristics of rocky coasts?
- subject to erosion
- steep or vertical in profile
- formed of resistant rocks
- attacked by weathering and mass movement
- high energy environment
what are the characteristics of plain coasts?
- deposited landscapes of sand, shingle and mud (estuarine)
- low, flat landscapes, often poorly drained
- dominated by processes of accretion - coastline advances seaward
- often low energy environment
what is primary coastline?
dominated by land based processes ( deposited from rivers or lava flows)
what is secondary coastline?
dominated by marine erosion and depositional processes
what is an emergent coastline?
where the coast is rising relative to the sea level - due to tectonic uplift
what is a submergent coastline?
areas flooded by rising sea levels and/or subsiding land
what is tidal range?
microtidal = 0-2m
mesotidal = 2-4m
macro tidal = over 4m
what is a low energy coastline?
sheltered coasts with limited fetch and low wind speeds
- small waves
what is a high energy coastline?
exposed coasts facing prevailing winds with a long fetch
- powerful waves
what are the elements of coastal geological structure?
Strata - different layers of exposed rock
Deformation - degree of tilting and folding by tectonic activity
Faulting - factoring that may have moved rocks from their original positions
what are the two main types of coastline (caused by geological structure)?
Concordant and Discordant
what is a concordant coastline?
when rock strata runs parallel to the coastline
what is a discordant coastline?
when different rock strata intersect the coast at an angle, so rock type varies along the coastline
what are the examples of concordant coastlines?
Dalmation coast in the Adriatic Sea
- limestone has been folded by tectonic activity into a series of anticlines and synclines that trend parallel to the coastline
- the syncline basins have been drowned by sea level rise
- the anticlines have produced long, narrow offshore islands
Haff coastline in the southern Baltic Sea
- long sediment ridges topped by sand dunes run parallel to the coast just offshore
- lagoons (haffs) are created between ridges ad the shoreline
what is the description of discordant coasts?
dominated by headlands and bays
- less resistant rocks are eroded to form bays
- more resistant rocks remain as headlands protruding into the sea
what is wave refraction?
In deep water, wave crests are parallel. As water shallows towards the coast, waves slow down and wave height increases.
In bays, wave crests curve to reflect their shape and wave height decreases
- wave action is concentrated on headlands
what are cliff profiles influenced by?
- Resistance to erosion of the rock
- Dip of rock strata in relation to the coastline
what else can influence cliff profiles?
- faulting to expose rocks to erosion
- natural cracks in the rock (jointing and fissures)
describe the igneous rock type
Granite, Basalt and Dolerite
- very slow recession (<0.1 cm per year)
- the rocks are crystalline - strong and resistant
- granite has few joints for erosion to exploit
describe the metamorphic rock type
Slate, Schist and Marble
- slow recession (0.1-0.3 per year)
- rocks are generally resistant
- some may have crystals oriented in one direction or may be folded and faulted - so have areas of weakness
describe the sedimentary rock type
Sandstone, Limestone and Shale
- moderate to fast recession (0.4-10cm a year)
- Rocks are clastic (stick together in layers) and less resistant
- rocks with many natural bedding planes (strata) such as Shale, are the most vulnerable
describe the unconsolidated rock type
Boulder Clay and Sand
- very fast recession (2-10m per year)
- very weak materials, easily eroded
why is permeability an important factor?
permeable rocks allow water to pass through (sandstone and limestone)
impermeable rocks do not allow water to pass through (clays, mudstone and most igneous and metamorphic rocks)
what are the key points of stability?
- vegetation roots bind sediments together - making them more resistant to erosion
- when submerged, plants protect the surface from erosion
- plants protect sediment from wind erosion by reducing wind speed (friction)
- plants that grown as a succession in coastal environments (drought tolerant sand dunes) or halophytes (sand-tolerant salt marshes)
Sand dunes succession
- sand is deposited by the sea under low energy conditions
- wind may move he sand to build sand dunes further up the beach
- these become colonised by stabilising plants (Psammosere)
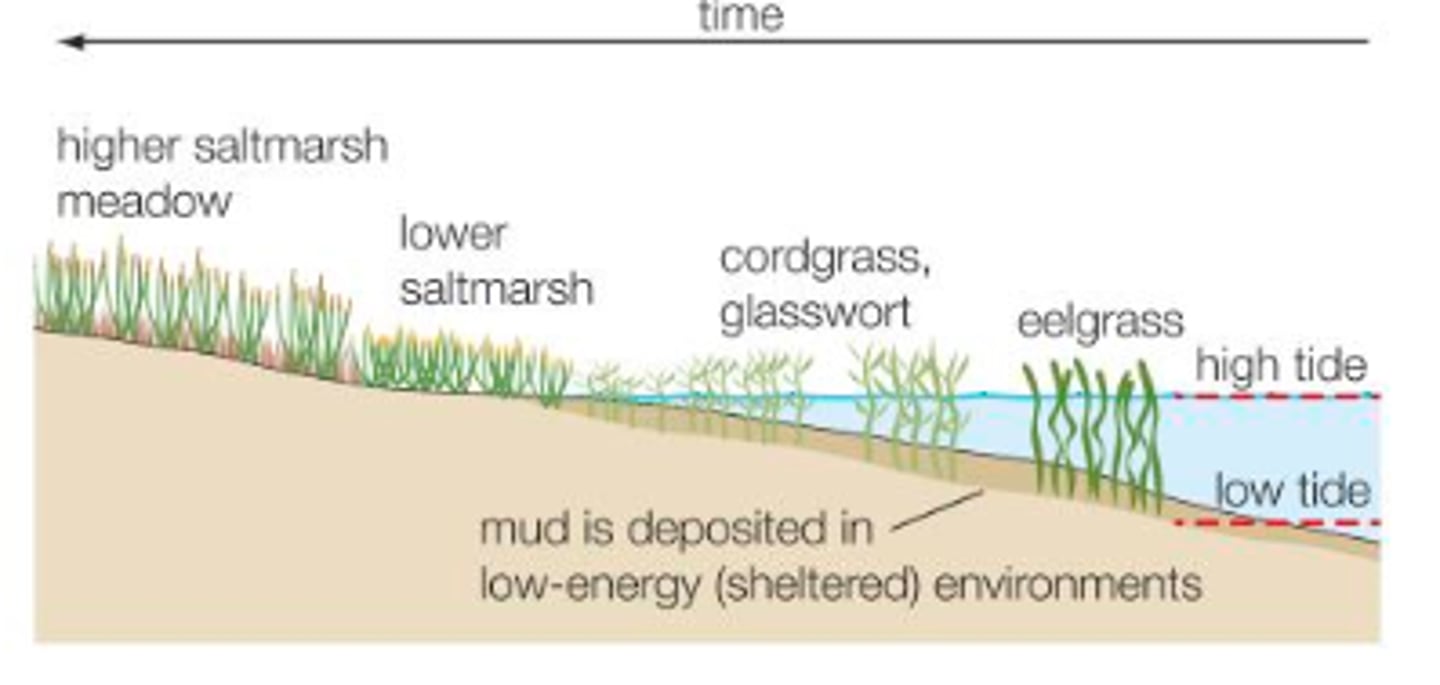
Salt Marsh succession
- sheltered river estuaries or zones in the lee of spits are areas where there are extensive accumulations of silt and mud - aided by flocculation and gentle tides
- inter-tidal areas are colonised by vegetation + halosere may develop over time (salt marsh)
- initial plants of the halosere (Eelgrass + Spartina + Sea Lavender) - tolerant of salt and regular inundation @ high tide