Sepsis & Septic Shock: Key Terms and Definitions for Medicine
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
what is the surviving sepsis campaign?
international collaborative effort between the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), & the International Sepsis Forum (ISF)
- goal is to reduce mortality from severe sepsis & septic shock
why should the terms bacteremia, septic syndrome, & septicemia not be used in chart documentation or clinical literature?
bc they are not clearly defined
what is systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)?
can have a variety of causes
*meets >/= 2 of the below criteria:
- temp > 38 C (100.4 F) or < 36 C (96.8 F)
- HR > 90 bpm
- RR > 20 bpm
- WBC > 12 or < 4 or 10% bands
what is sepsis?
life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response (SIRS) from infection
- SIRS + infection w/ elevated NEWS score or acute change in total SOFA score >/= 2 points resulting from infection
what is the most common form of vasodilatory shock?
septic shock
what is septic shock?
subset of sepsis in which profound circulatory, cellular, & metabolic abnormalities greatly increase risk of mortality
- sepsis + vasopressor dependent BP & lactate >/= 2 mmol/L despite adequate fluid resuscitation
what is the national early warning score (NEWS2)?
- respiratory rate, O2 sats, supplemental O2 status
- SBP
- pulse
- level of consciousness or new confusion
- temperature
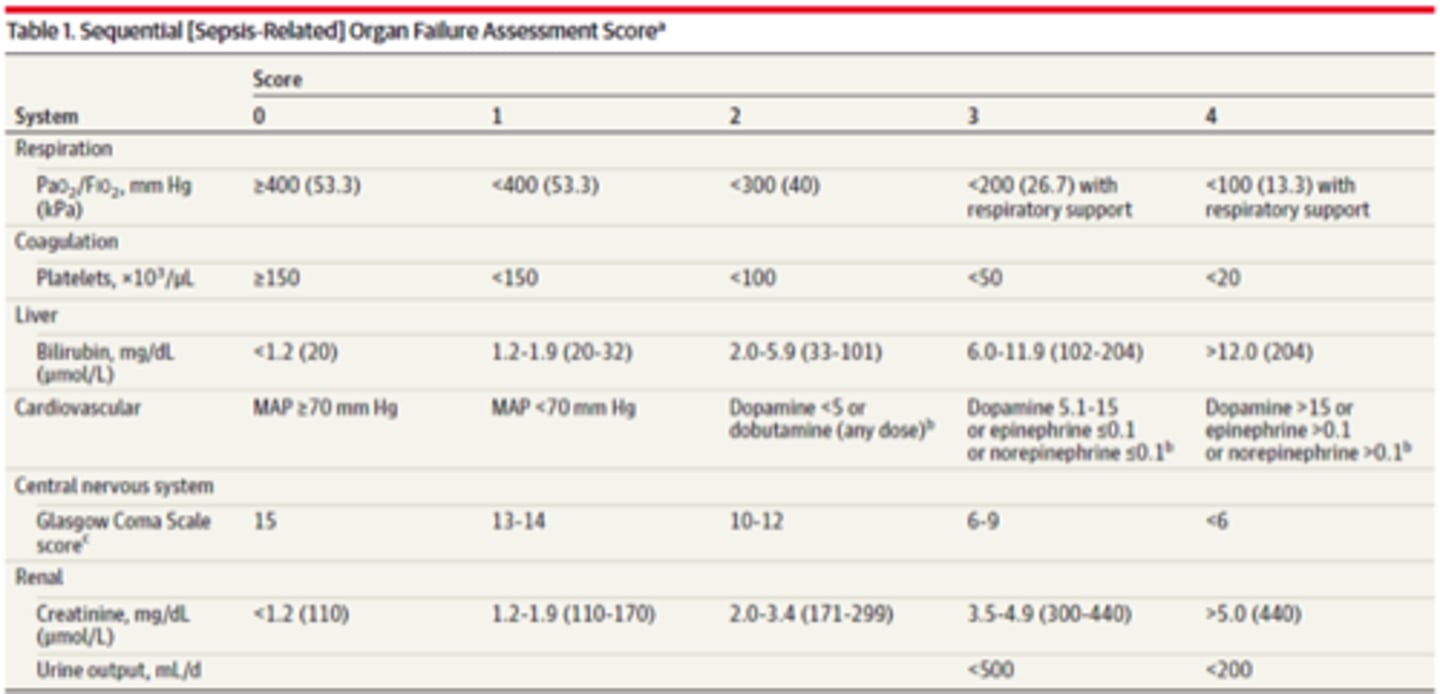
what is the sequential organ failure assessment score (SOFA)?
__________________ mediators help eradicate the infection
pro-inflammatory
1 multiple choice option
__________________ mediators control the inflammatory response to keep it under control
anti-inflammatory
1 multiple choice option
what develops if anti-inflammatory mediators cannot balance the inflammatory response?
SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome)
gram-___________ bacterial cell walls contain pro-inflammatory endotoxins released when cells proliferate & die
negative
1 multiple choice option
gram-___________ bacterial cell walls also contain proinflammatory endotoxins, but they typically are not as potent
positive
1 multiple choice option
components of the pathophysiology of sepsis:
- persistent & widespread inflammation
- loss of capillary endothelial integrity
- vasodilatory shock
- activation of coagulation cascade
what does the persistent & widespread inflammation in sepsis cause?
activation of the inflammatory cascade (cytokines, interleukins, tumor necrosis factor alpha, complement, histamine, neutrophils)
- this causes vasodilation & endothelial damage
what does the loss of capillary endothelial integrity in sepsis cause?
the capillaries to vasodilate & become "leaky"
- maldistribution of blood flow, shunting & O2 use, & reduced stroke volume
what does the vasodilatory shock in sepsis cause?
increased capillary permeability which leads to 3rd spacing of fluid, peripheral & pulmonary edema
- vasodilation decreases venous return to the ❤︎, reflex tachycardia, decreased SVR, & altered microvascular circulation
what does the activation of the coagulation cascade in sepsis cause?
this results from damage to the endothelial lining
- initial insult = hypercoaguable state; intravascular thrombosis & ischemic injury
- secondary insult = hypocoaguable state; potential for disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC) to develop
sepsis is a ___________________!!
medical emergency
- it is important to recognize sepsis when it occurs!
treatment & resuscitation for sepsis must begin ___________!
immediately
what can be done to help interrupt the pathogenic sequence (which could lead to septic shock) & avoid organ failure?
rapid elimination of source of infection medically w/ early initiation of aggressive antimicrobial therapy &/or surgically
what are the surviving sepsis campaign (SSC) bundles?
groups of interventions that improve mortality better when implemented as a group in a timely manner
what is the SSC 1-hr bundle?
1. measure serum lactate immediately; remeasure if > 2 mmol/L
2. obtain blood cultures x 2 aerobic & anaerobic ASAP & preferably prior to antibiotics
3. start broad spectrum antibiotics ASAP (goal w/i 1 hr)
4. initiate IV fluid resuscitation for hypotension or lactate >/= 4 mmol/L
5. maintain MAP >/= 65 w/ fluid resuscitation &/or vasopressors if unresponsive to fluid
as part of the SSC 1 hr bundle, measure serum lactate immediately & remeasure if _____ mmol/L
> 2
as part of the SSC 1 hr bundle, obtain _________________ x 2 aerobic & anaerobic ASAP & preferably prior to antibiotics
blood cultures
- obtain other relevant cultures related to source identification (urine, wound, etc..) as appropriate
as part of the SSC 1 hr bundle, start broad spectrum _____________ ASAP (goal w/i 1 hr)
antibiotics
as part of the SSC 1 hr bundle, initiate __________________________ for hypotension or lactate >/= 4 mmol/L
IV fluid resuscitation
as part of the SSC 1 hr bundle, maintain MAP _______ w/ fluid resuscitation &/or vasopressors if unresponsive to fluid
- higher MAP goals may be appropriate for some patients
>/= 65
if persistent arterial hypotension occurs despite the above measures, multiple measures to reassess volume status & tissue perfusion should be implemented, such as:
- focused exam (vitals, cardiopulmonary exam, capillary refill, pulse, & skin findings)
- CVP measurement (goal = 8-12 mmHg if possible)
- urine output measurement (goal >/= 0.5 mL/kg/hr)
- ScvO2 measurement (goal >/= 70%)
- bedside cardiovascular ultrasound
- dynamic assessment of fluid responsiveness w/ passive leg raise or fluid challenge
rapid fluid resuscitation will reverse _______ of hypotension
~ 50%
MAP =
1/3 (SBP) + 2/3 (DBP)
what is a normal MAP?
70-100 mmHg
what is MAP an indication of?
global perfusion pressure
the body's ability to auto-regulate blood flow is lost when MAP ______.
< 65
MAP _______ is necessary for adequate cerebral perfusion
>/= 60
for IV fluid resuscitation therapy, how should the initial fluid bolus be given?
30 ml/kg IV crystalloid w/ each liter over 30-60 mins
- reduce volume/rate as appropriate per fluid status
for IV fluid resuscitation therapy in sepsis, which is preferred LR or NS?
LR may be preferred
1 multiple choice option
can 5% albumin be considered when patients require substantial amounts of crystalloid?
YES
1 multiple choice option
are hetastarch products recommended due to increased risk of AKI?
NO
1 multiple choice option
additional fluid resuscitation may be provided _____________
as needed
titrate rate of IV fluid resuscitation therapy to improve:
- heart rate
- urine output
- blood pressure
- lactate
- mental status
gram-positive bacterial sepsis account for about __________ of all cases of sepsis
40-50%
gram-negative bacterial sepsis account for about __________ of all cases of sepsis
30%
which gram-positive bacteria are most commonly seen in sepsis?
- staph aureus
- strep pneumoniae (25% mortality rate)
- coagulase-negative staphylococci (stpah epidermidis due to infected intravascular devices)
- enterococcus sp.
which gram-positive bacteria is seen in sepsis most often due to infected intravascular devices?
staphylococcus epidermidis
which is more likely to produce septic shock & has a higher rate of mortality: gram-negative or gram-positive bacterial sepsis?
gram-negative
1 multiple choice option
what are the most common gram-negative pathogens isolated in sepsis?
- e. coli
- psuedomonas aeruginosa
- others: klebsiella species, serratia species, enterobacter species, proteus species
anaerobic & miscellaneous bacterial sepsis account for about __________ of all cases of sepsis
5-39%
which has the highest mortality rate of all bloodstream pathogens: bacterial, fungal or viral?
fungal
2 multiple choice options
pathogens seen in fungal sepsis:
- candida species
- cryptococcus
- coccidioides
- fusarium
- aspergillus
when should you consider adding anti-fungal coverage?
*in patients w/:
- recent abdominal surgery
- chronic parenteral nutrition
- indwelling central venous catheters
- recent treatment w/ broad spectrum antibiotics
*or if pts are immunocompromised:
- chronic corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
- neutropenia
- malignancy
- organ transplant
what meds may be used for empiric fungal therapy?
- fluconazole
- echinocandins (caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin)
- amphotericin B lipid complex
when may echinocandins be preferred for empiric fungal therapy?
- in patients recently treated w/ antifungal agents
- if candida glabrate or krusei suspected
when should you consider empiric antiviral therapy w/ oseltamivir?
for patients w/ possible influenza
- treat any other viral infections w/ appropriate agents
in sepsis, aggressive treatment & appropriate antibiotic selection ________________.
improve survival
what is source control?
measures taken to remove a focus of infection and to restore optimal function at the site of infection
- ex: drain, debride, remove/change infected catheters, etc..
what is empiric therapy (broad spectrum) based upon in sepsis?
- site of infection
- most likely pathogens
- local hospital/community sensitivity patterns
you should reassess the patient ______
daily & de-escalate therapy (narrow the coverage) as soon as feasible
consider this w/ antimicrobial therapy in sepsis:
- how sure are you of the suspected site of infection?
- if your diagnosis is incorrect, you will have unknowingly narrowed your spectrum of coverage & put your patient at risk
ideally, start the _________ coverage possible until certain of the site of infection &/or causative pathogens have been identified
broadest
1 multiple choice option
in sepsis, broad spectrum regimens should cover:
- gram positives (enterococcus & MRSA)
- gram negatives (pseudomonas)
- anaerobes
what are the options for the broadest coverage possible until certain of site of infection &/or causative pathogens have been identified?
vancomycin +
ceftriaxone,
cefepime,
meropenem,
imipenem,
or
piperacillin/tazobactam
what are the abx of choice for a community-acquired urinary tract infection?
ciprofloxacin or piperacillin/tazobactam
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired urinary tract infection?
piperacillin/tazobactam or meropenem
what are the abx of choice for a community-acquired respiratory tract infection?
- if no pseudomonas suspected: ceftriaxone + levofloxacin or moxifloxacin
- if pseudomonas possible: piperacillin/tazobactam or
ceftazidime or
cefepime +
gentamicin or
ciprofloxacin
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired respiratory tract infection?
piperacillin/tazobactam or
ceftazidime or
cefepime
+/- gentamicin or
ciprofloxain
+/- vancomycin
what are the abx of choice for a community-acquired abdominal infection?
ampicillin/sulbactam or
ciprofloxacin + metronidazole or
ceftriaxone + metronidazole
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired abdominal infection?
piperacillin/tazobactam or carbapenem
+/- gentamicin
+/- vancomycin
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired skin/soft tissue infection?
piperacillin/tazobactam or carbapenem
+/- vancomycin
+/- daptomycin
what are the abx of choice for a community-acquired skin/soft tissue infection?
ampicillin/sulbactam + clindamycin or
ciprofloxacin + clindamycin
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired IV catheter infection?
vancomycin
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired infection of unknown origin &/or immunocompromised patient?
piperacillin/tazobactam or
ceftazidime or
cefepime or
carbapenem
+/- gentamicin
+/- vancomycin
+/- caspofungin
what are the abx of choice for a hospital-acquired infection of unknown origin &/or immunocompromised patient if severe PCN allergy?
ciprofloxacin + gentamicin + vancomycin
protocols for antimicrobial therapy in sepsis vary by:
- suspected pathogens
- hospital formulary
- resistance patterns
for any of the above hospital-acquired infections, when gentamicin is listed as +/-, when would you add it?
when pseudomonas suspected
for any of the above hospital-acquired infections, when vancomycin is listed as +/-, when would you add it?
when MRSA is suspected
for any of the above hospital or community-acquired infections, when would you consider adding antifungal?
high risk or immunocompromised patients
initiate ____________ therapy if fluid challenge fails to restore BP & organ function
vasopressor
should you delay initiating vasopressors while waiting for central line placement?
NO, give peripherally until central line can be placed
1 multiple choice option
what is the vasopressor of choice in sepsis?
norepinephrine (NE)
why is norepinephrine the vasopressor of choice in sepsis?
bc it's highly effective & there's less risk of tachycardia
vasopressin (ADH), is a direct vasoconstrictor ________ inotropic or chronotropic effects
without
1 multiple choice option
what may vasopressin help preserve?
blood flow to gut mucosa
when may vasopressin or epinephrine be added to NE?
prn to maintain adequate BP
epinephrine may be added to NE prn to maintain adequate BP, but it can also be __________________ prn
substituted
- (used instead of NE)
dopamine is an alternative vasopressor. when would it be used instead of NE?
in patients w/ a very low risk of tachycardia or in patients w/ bradycardia
should low-dose dopamine be used for "renal protection?"
NO
1 multiple choice option
phenylephrine is an alternative vasopressor. when would it be used instead of NE?
in patients w/ vasopressor-induced serious tachycardia or persistent hypotension
when may positive inotropes, dobutamine or milrinone, be added to vasopressor therapy?
if cardiac output (CO) is low despite fluids
norepinephrine (Levophed)
* a1: ++++
* B1: +++
* B2: +
* D: 0
* effects on HR: ↑
* effects on CO: ↑/0
* effects on SVR: ↑↑↑
epinephrine
* a1: +++
* B1: +++
* B2: ++
* D: 0
* effects on HR: ↑↑
* effects on CO: ↑↑
* effects on SVR: ↑↑
phenylephrine
* a1: ++++
* B1: 0
* B2: 0
* D: 0
* effects on HR: ↓
* effects on CO: ↑/0
* effects on SVR: ↑↑
dopamine 1-3 mcg/kg/min
* a1: 0
* B1: +
* B2: 0
* D: ++
* effects on HR: 0
* effects on CO: ↑/0
* effects on SVR: 0/↓
dopamine 5-10 mcg/kg/min
* a1: +
* B1: ++
* B2: 0
* D: ++
* effects on HR: ↑
* effects on CO: ↑
* effects on SVR: ↑
dopamine > 10 mcg/kg/min
* a1: +++
* B1: ++
* B2: 0
* D: ++
* effects on HR: ↑↑
* effects on CO: ↑
* effects on SVR: ↑↑↑
vasopressin
* a1: 0
* B1: 0
* B2: 0
* D: 0
* effects on HR: ↓
* effects on CO: 0/↓
* effects on SVR: ↑↑↑
what is the DOC in septic, cardiogenic, & hypovolemic types of shock?
norepinephrine (Levophed)
what is the DOC in anaphylactic shock, an alternate in septic shock, & may increase lactate initially (B2)?
epinephrine
which vasopressor may decrease HR due to uninhibited baroreceptor reflex from a1 effects?
phenylephrine
which vasopressor has more ADRs than NE, can induce dysrhythmias at any dose, & at low doses is NOT renal protective?
dopamine