Genetics: Mendel's Principles and Inheritance Patterns
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Genetics
the study of the patterns of inheritance, genes, and genetic variation
Gregor Mendel
Father of Genetics

P generation
first cross
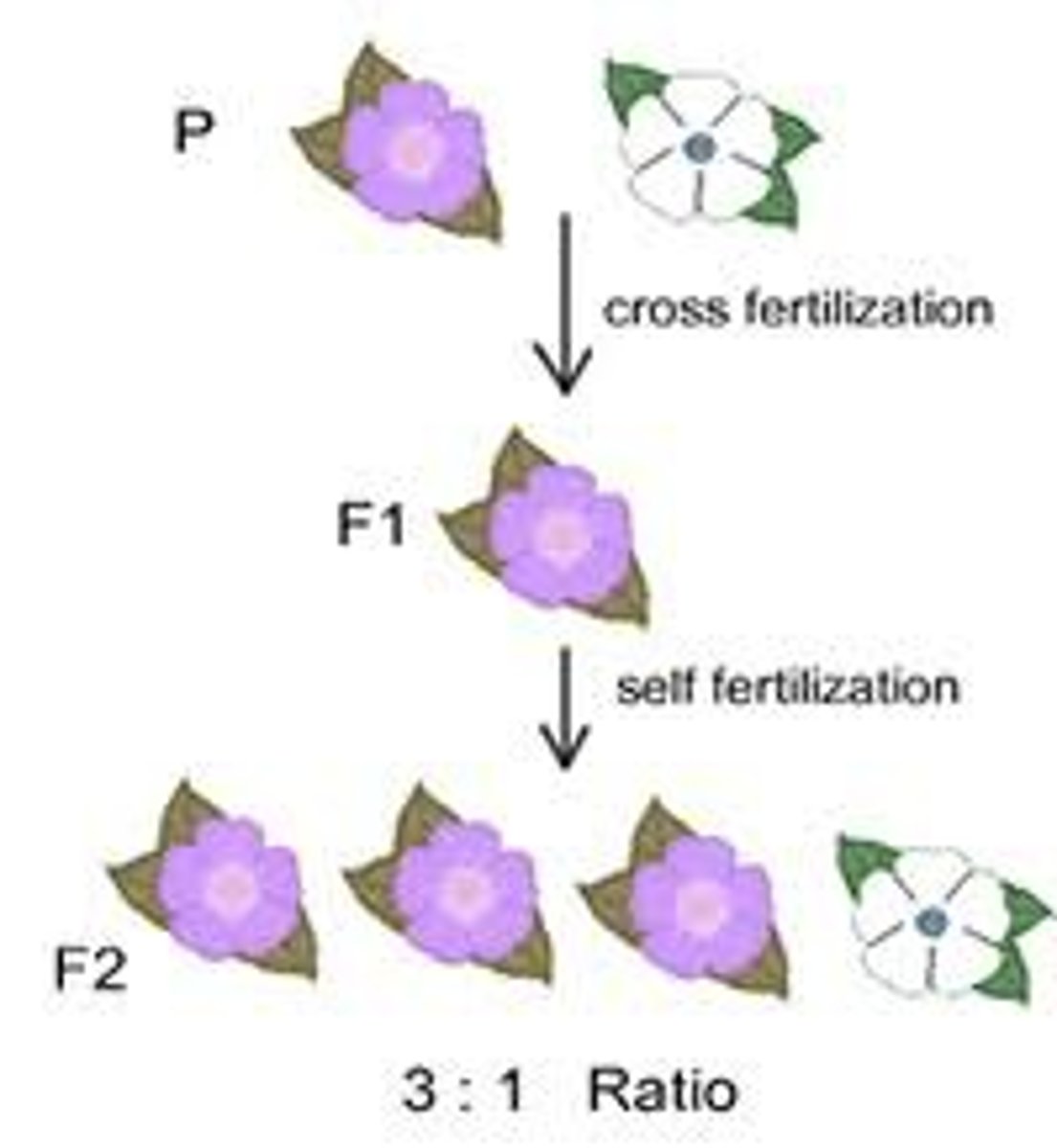
F1 generation
offspring from the first (P) cross
F2 generation
next generation after F1
Purebred
individuals that are genetically uniform
Principle of Dominance
the principle that if one allele is dominant and the other is recessive, the dominant allele is able to override its potential influence over the recessive allele
Dominant
stronger of two alleles; able to mask the other trait, represented by a capital letter
Recessive
the allele that is masked by the more dominant allele, represented by a lowercase letter
Homozygous
when both alleles of a gene pair are the same
Phenotype
the physical expression of the genotype
Principle of Segregation
two copies of a gene in a gene pair undergo segregation during the formation of sex cells
Principle of Independent Assortment
allele pairs separate independently during gamete formation and traits are passed on to offspring independently of one another
Punnett square
a tool used to predict the genotypes and/or phenotypes of the offspring and their expected ratios
Monohybrid cross
tracking one single trait
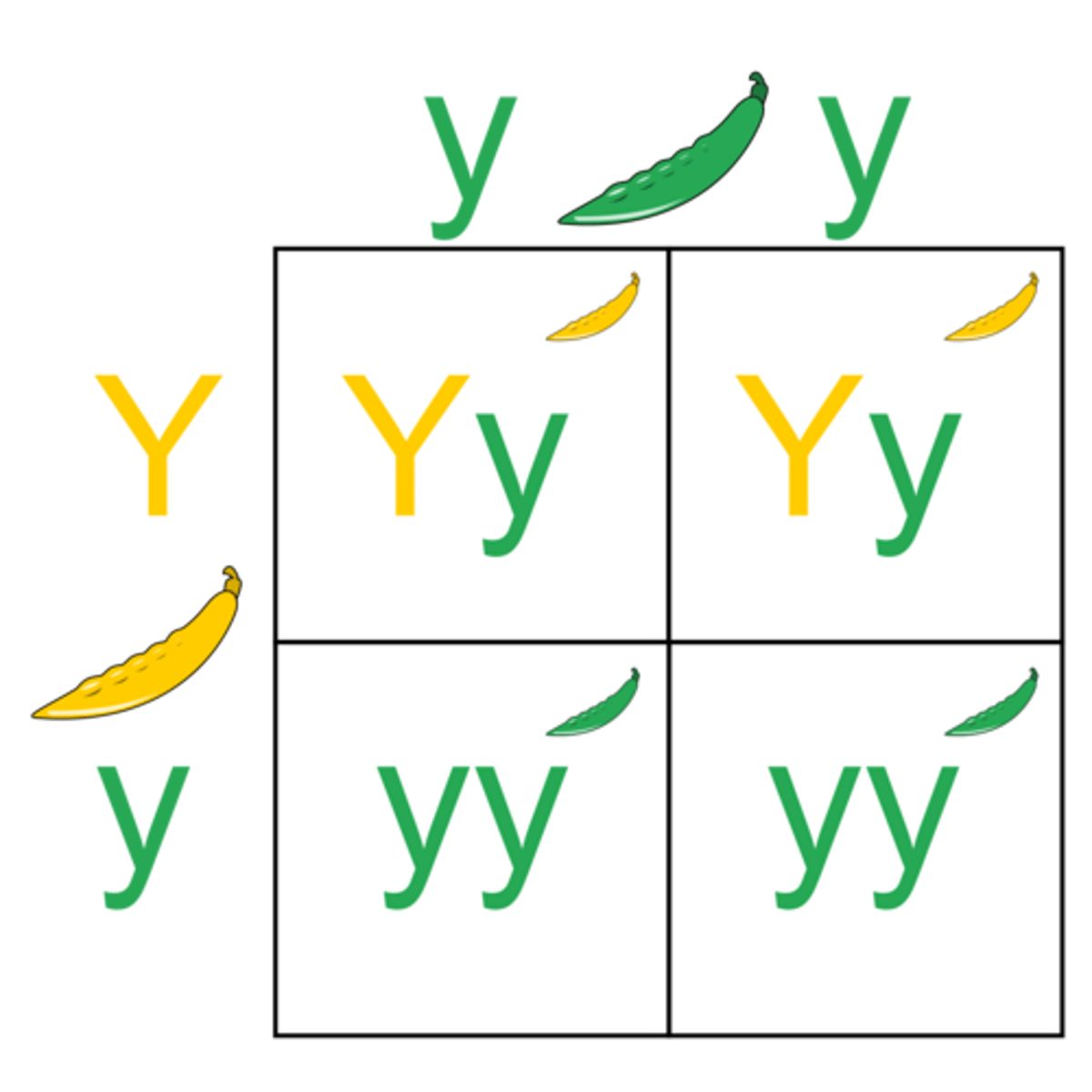
Gametes
the sex cells that carry alleles
Dihybrid crosses
crosses that involve two traits
Seed texture
an example of a gene
Round alleles
dominant alleles represented by R
Wrinkled alleles
recessive alleles represented by r
Monohybrid Crosses
A genetic cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits.
Genotypic Ratio
The ratio of different genotypes that can result from a genetic cross.
Phenotypic Ratio
The ratio of different phenotypes that can result from a genetic cross.
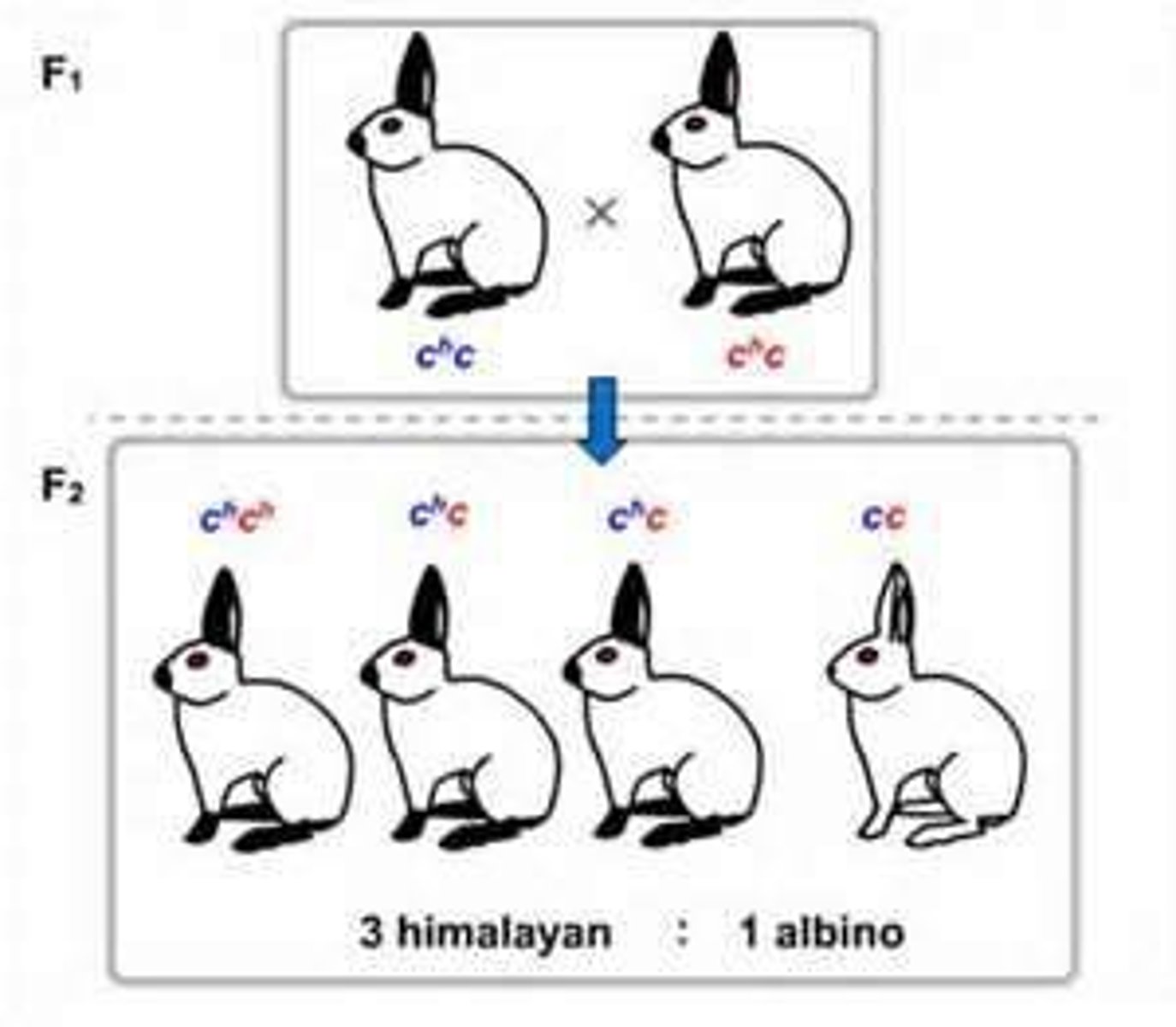
Probability in Genetics
The likelihood of a specific genotype or phenotype occurring in offspring.
Homozygous Dominant
An organism with two identical dominant alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
An organism with two different alleles for a trait.
Homozygous Recessive
An organism with two identical recessive alleles for a trait.
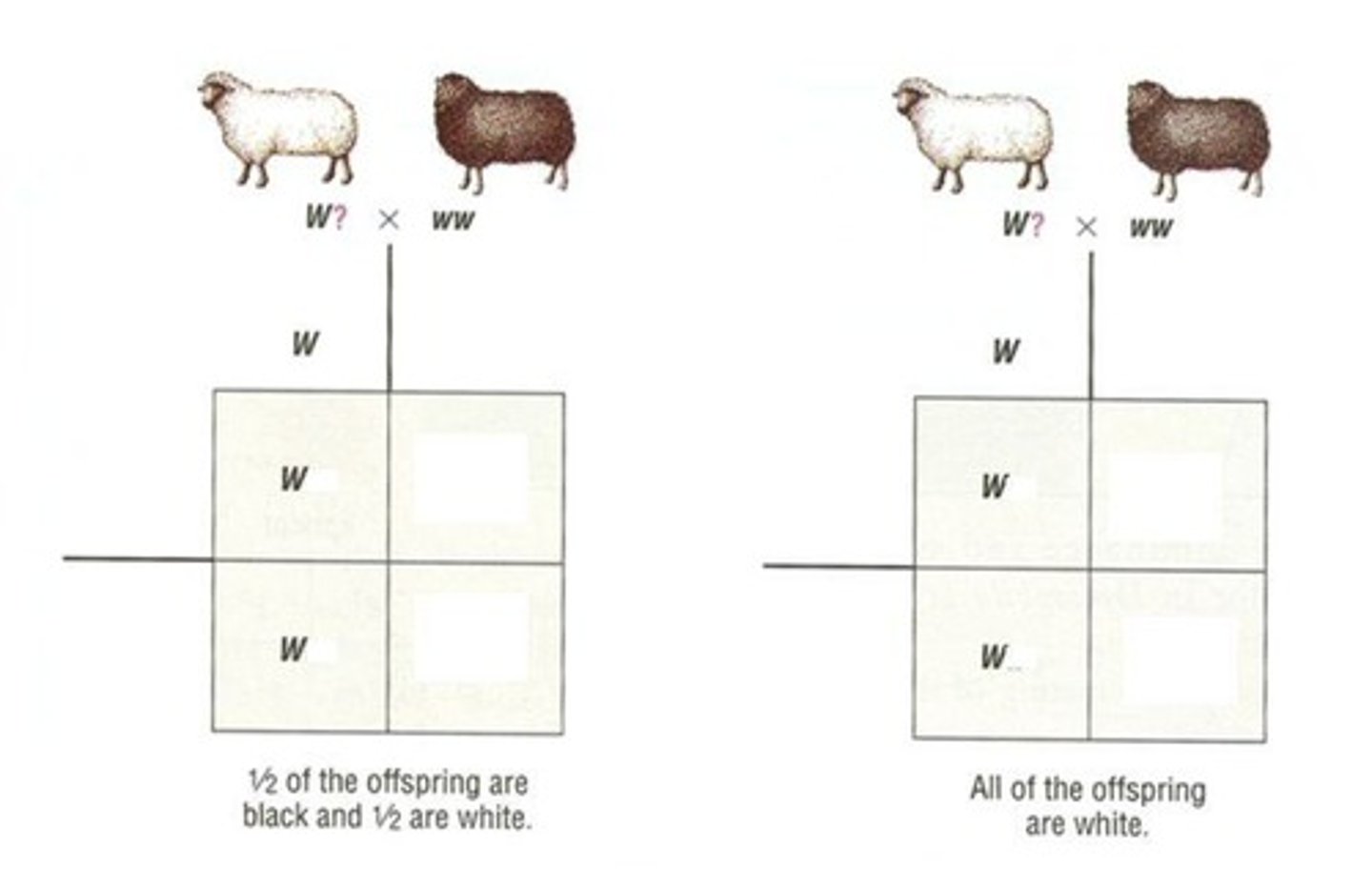
Test Cross
A mating between an individual of unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual.
Multiple Alleles
A situation where a gene has more than two allelic forms.
Dominance Hierarchy
The ranking of alleles based on their dominance over others.
Incomplete Dominance
A genetic situation where a heterozygous organism shows a blending of traits.
Codominance
A genetic situation where both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism.
Expected Genotypic Ratio
The predicted ratio of genotypes in the offspring from a genetic cross.
Expected Phenotypic Ratio
The predicted ratio of phenotypes in the offspring from a genetic cross.
Blood Type O
Possible genotype is ii.
Parent Genotypes
If a boy has a blood type O and his sister has blood type AB, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of their parents?
Complementary Interaction
Occurs when 2 different genes interact to produce a phenotype that neither is able to produce by itself (ex. Chicken combs, squash shapes).
Pleiotropic Gene Action
Affects many different characteristics.
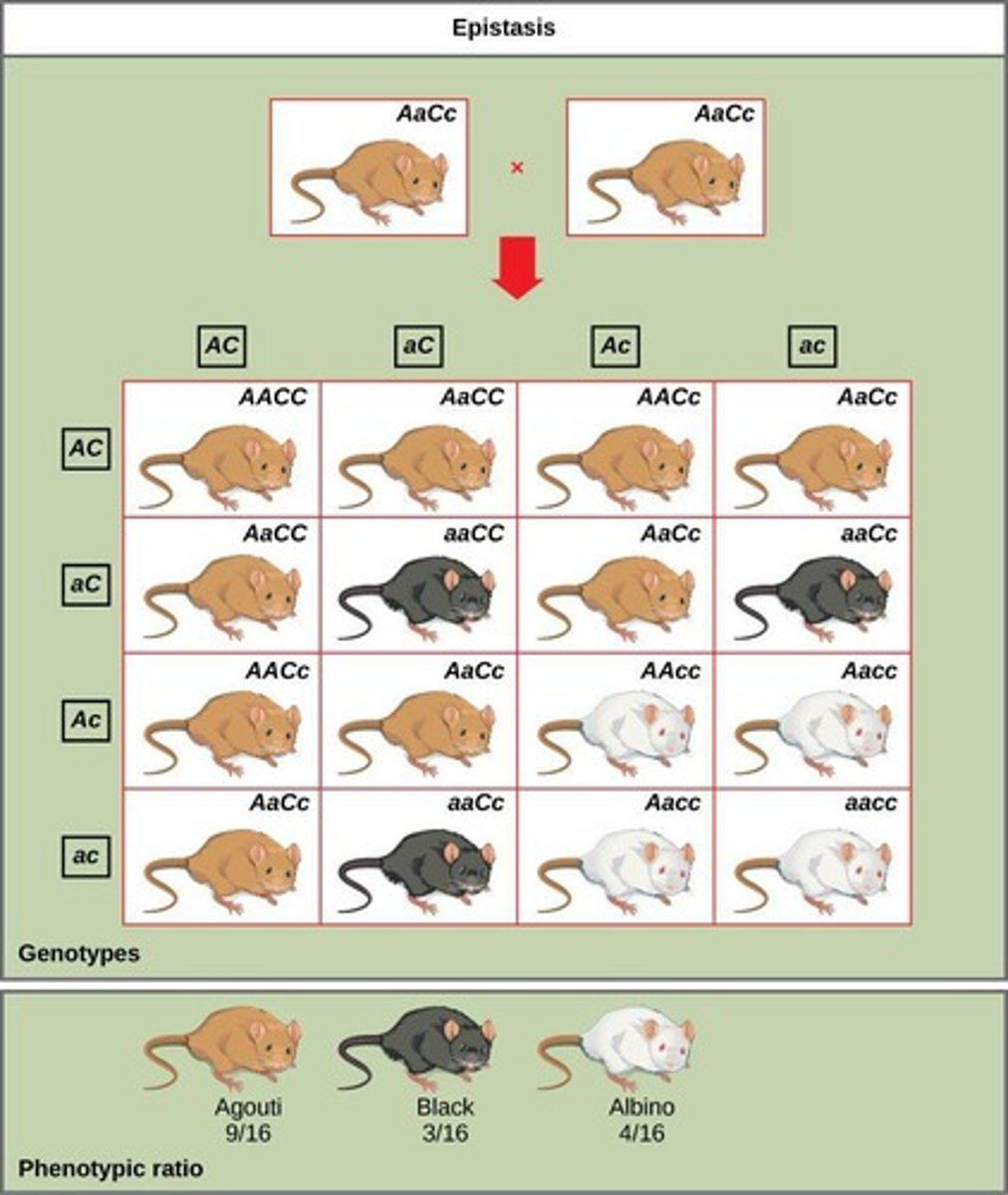
Epistasis
One gene interferes with the expression of another.
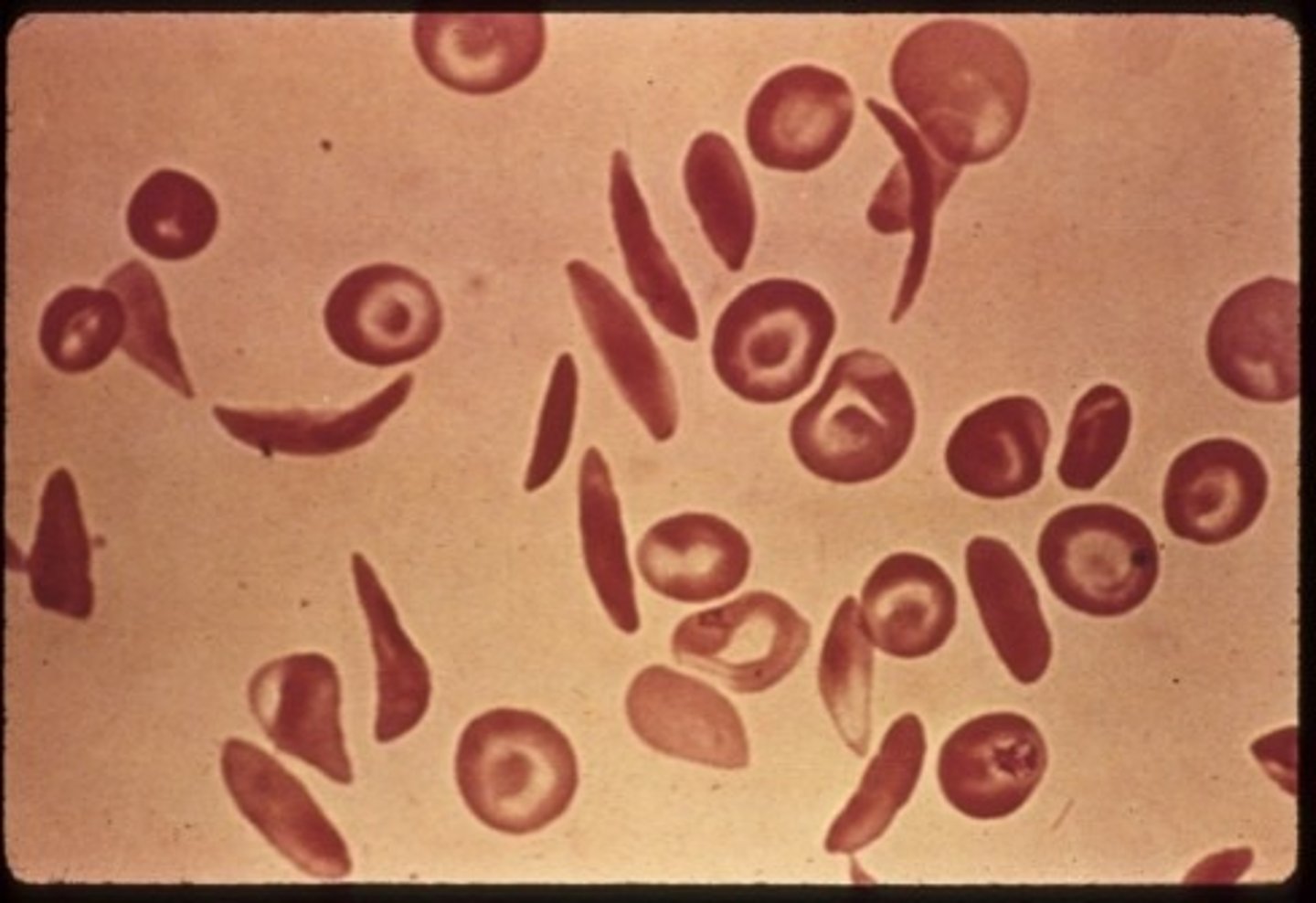
Pleiotropy Example
Sickle-cell anemia is caused by a pleiotropic gene.
Sickle-Cell Anemia Effects
The mutated gene causes hemoglobin to be abnormally shaped, leading to sickle-shaped red blood cells that cannot deliver oxygen.
Polygenic Inheritance
Assume there are two gene pairs to determine the color of an offspring's eyes.
Sex Determination
In many species, the most obvious difference in phenotype between individuals is their sex.
Sex Chromosomes
There are two chromosomes involved in the determination of sex of most animals.
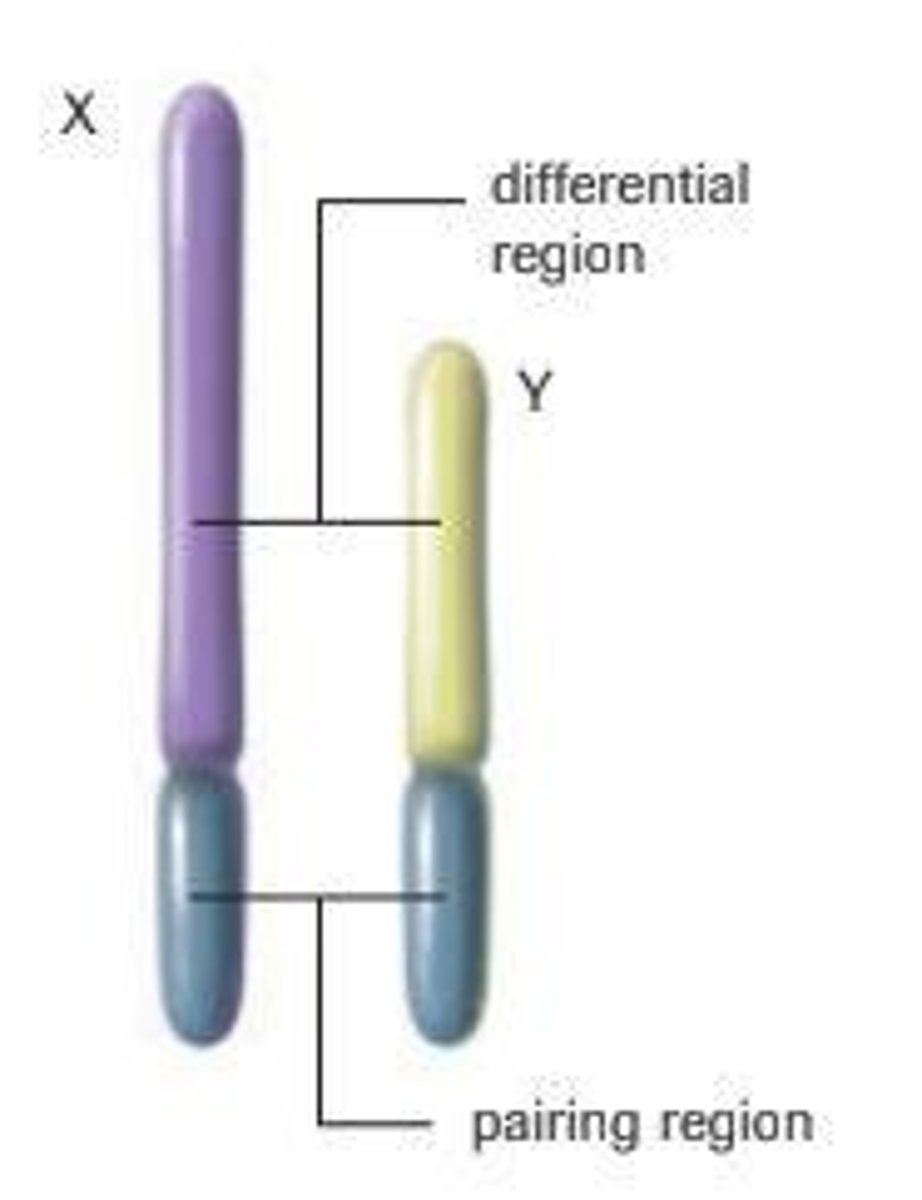
Autosomes
Any other chromosome not involved in sex determination is called an autosome.
Human Chromosomes
Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes.
Female Chromosomes
XX
Male Chromosomes
XY
Gamete Contribution
Females can produce eggs carrying only an X chromosome, while males produce sperm carrying either an X or a Y chromosome.
Sex Linkage
Genes for sex-linked traits are carried on the X chromosome but not on the Y chromosome.
Y Chromosome
The Y chromosome does not carry genes that have counterparts on the X chromosome.
Male Gene Expression
In a male, the gene on the X chromosome is expressed whether it is dominant or recessive.
Female Gene Expression
In a female, she must have two recessive alleles to have the recessive phenotype.
Thomas Hunt Morgan
Geneticist who discovered a mutant white-eyed male fly among his hundreds of red-eyed flies.
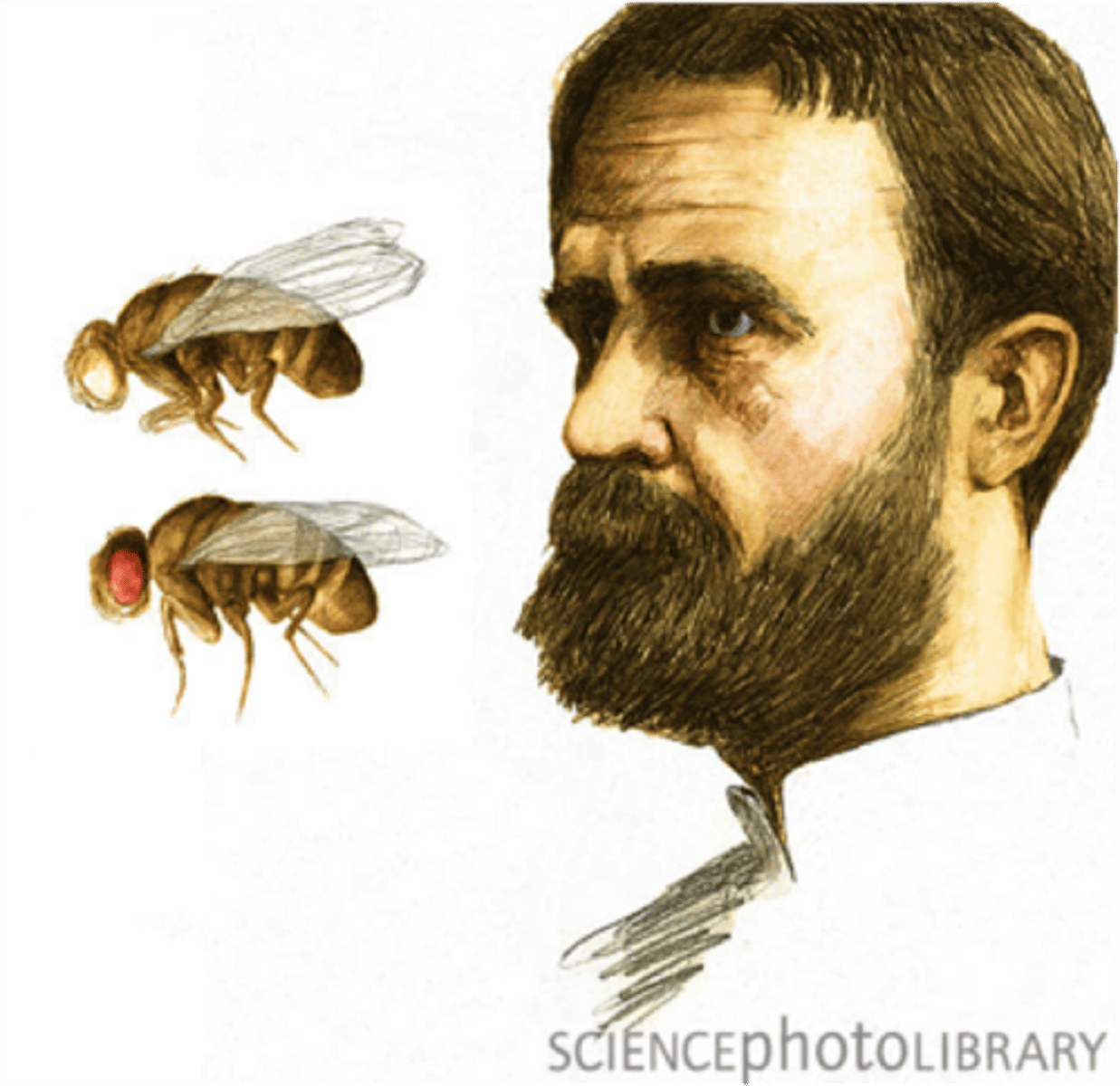

Eye Colour Gene
Morgan concluded that the gene controlling eye-colour was carried on the X-chromosome.
Common Sex-Linked Disorders
Common sex linked disorders include hemophilia, colour-blindness, and muscular dystrophy.
Sex-Linked Gene Symbols
X and Y will be used to symbolize the gene; same letters are NOT used.
Superscripts in Sex-Linked Genes
Superscripts (capital and lower-case letters) are used only on the X chromosome.
Product Rule
The probability that two or more independent events will occur is equal to the product of their respective probabilities.
Independent Events
Independent events are those in which the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of another.
Heterozygous Parents
If the parents are both heterozygous for the tongue curling trait, what are the chances that they will produce a boy who cannot curl his tongue upwards?
Dihybrid Crosses
In addition to his monohybrid crosses, Mendel performed dihybrid crosses of plants with two different pairs of contrasting alleles.
Self-fertilization
The process by which F1 plants produce an F2 generation of seeds with various phenotypes.
Phenotypes
Observable traits of an organism, such as round yellow or wrinkled green seeds.
Independent assortment
The principle that genes governing different traits segregate independently during gamete formation.
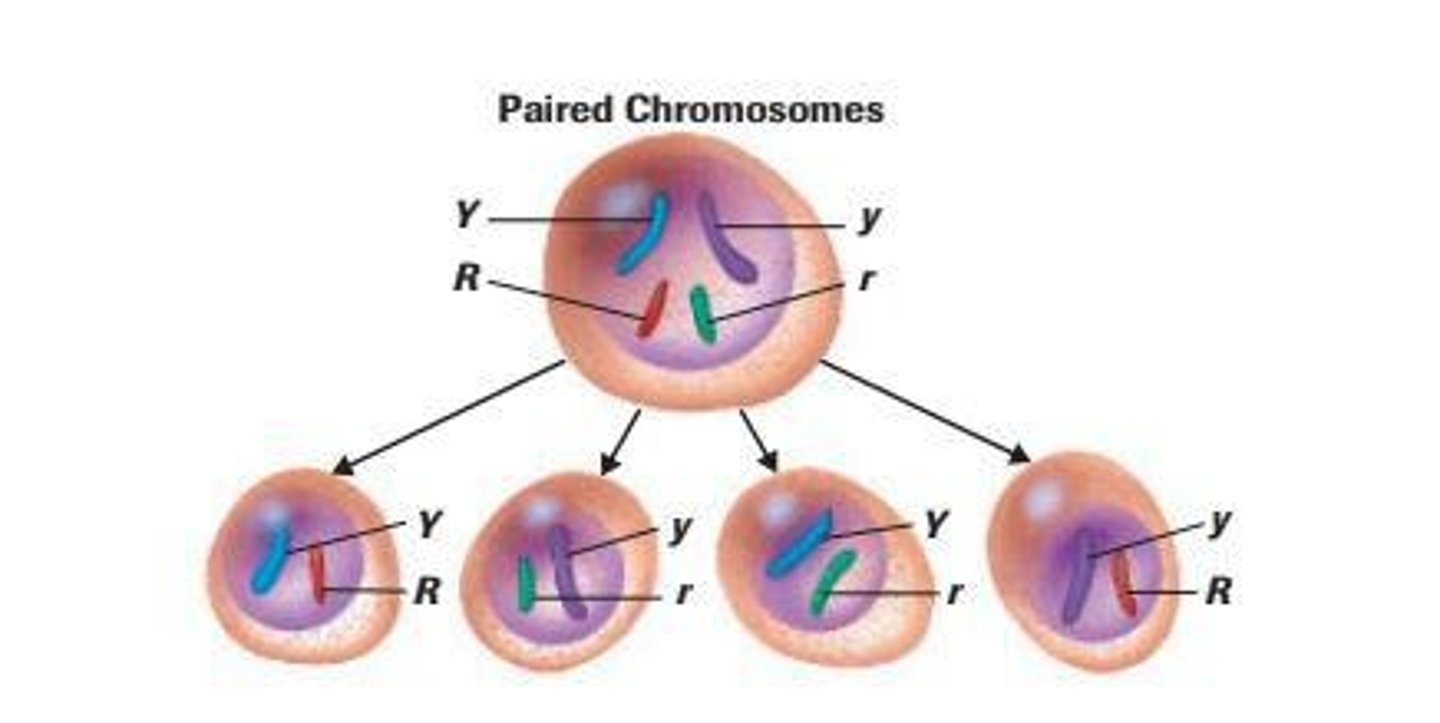
Dihybrid
An organism that is heterozygous for two traits.
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict the genotypes of offspring from parental genotypes.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual, represented by alleles.
Albinism
A recessive trait characterized by the absence of normal pigment levels.
Pedigree chart
A diagram that shows the inheritance of a trait across generations.
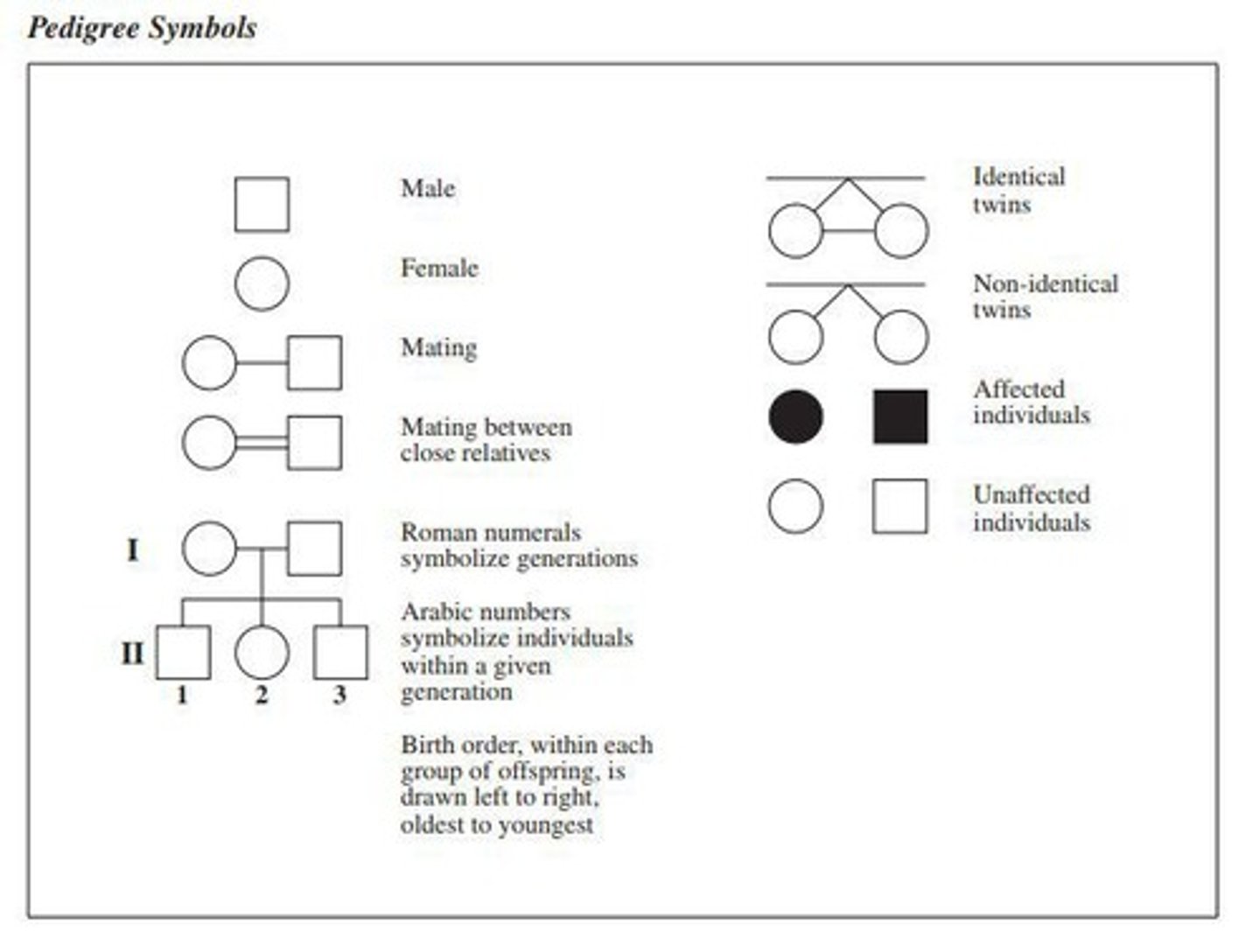
Autosomal dominant
A pattern of inheritance where only one copy of a dominant allele is needed for the trait to manifest.
Autosomal recessive
A pattern of inheritance where two copies of a recessive allele are needed for the trait to manifest.
Sex-linked dominant
A pattern of inheritance where a dominant allele is located on a sex chromosome.
Sex-linked recessive
A pattern of inheritance where a recessive allele is located on a sex chromosome.
Polydactyly
An autosomal dominant trait characterized by extra fingers or toes.
PKU
Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disorder that affects metabolism.
Linked genes
Genes that are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together.
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Crossover frequency
The percentage of recombinant offspring resulting from crossing over between genes.
Gene mapping
The process of determining the order and relative distances of genes on a chromosome.
Recombination frequency
The proportion of offspring that exhibit new combinations of traits due to crossing over.
Unlinked genes
Genes that assort independently because they are located on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome.
Drosophila
A genus of small flies, commonly used in genetic research.