Biology- Photosynthesis, Chlorophyll, and Chromatography
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
light
rays are invisible (only seen when they hit something)
composed of all of the colors of the visible spectrum (ROYGBRIV)
we don’t see all the colors because they are all absorbed
what we see is reflected to our eyes
the ______ around us is white ______
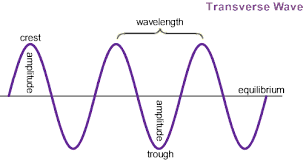
when it hits a prism, the light separates and the other colors are seen traveling in waves
red is the longest wave length, violet is the shortest
sunsets
reds are most commonly seen because pollution doesn’t let short waves through
light wavelengths
light and sound travel in waves (each sound level and each color has a specific wave)
in light, the colors of the spectrum vary in length and height
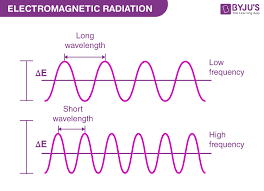
frequency
the number of waves that pass a certain point
more short waves can pass a certain point in less time than one long wave
longest wavelength = lowest frequency and energy
shortest wavelength = highest frequency and energy
refraction
when white light splits
photosynthesis
plants need energy 24/7
happens continuously (night too)
divided into 2 parts:
light reaction (will not take place without the presence of light)
dark reaction (can take place without the presence of light)
chloroplasts
most prominent membranes of the plastid family of organelles
plastids present in all living plant cells, each cell type having its own characteristic complement
all plastids share certain tendencies
all plastids in a particular plant species contain multiple copies of the same relatively small genome
each is enclosed by an envelope composed of 2 membranes
characteristics and functions of chloroplasts
carry out their energy inter converisons by chemiosmotic mechanisms like mitochondria
chloroplasts are larger but organized on the same principles
have a highly permeable over membrane; much less permeable inner membrane, where membrane transports proteins are embedded; and a narrow intermembrane space (all of these form the chloroplast envelope)
inner membrane surrounds a large space (stroma) which is like the mitochondrial matrix and contains metabolic enzymes (RNA, a special set of ribosomes, chloroplast DNA)
difference in organization of chloroplast and mitochondria
inner membrane doesn’t have cristae and doesn’t contain ETC
ETC chains, photosynthesis light capturing systems, and ATP synthase are all in the Thylakoid membrane that forms a set of flattened disclike sacs (thylakoids)
chlorophyll
green because green light is reflected to our eyes, other colors are absorbed (absorbs energy of red and blue wavelengths)
word comes from Greek words for “green leaves”
acts as a photoreceptor
has 5 different pigments
photoreceptor
perceives light energy and aids in the biochemical process
chlorophyll a
pigment found in all higher plants (not algae or moss)
most vital pigment in photosynthesis
some algae, cyanobacteria, and anaerobic phototrophs have chlorophyll a
strong rate of absorption
absorbs violet-blue and orange-red
reflections blue-green
chlorophyll b
seen in green algae and plants
accessory pigment that aids chlorophyll a
absorbs orange-red light
reflects yellow-green
why leaves turn in the fall
colder, less daytime, less sun = less light, less photosynthesis = leaves change
when it is colder, the leaves’ veins close and less nutrients and water is absorbed. thus, chlorophyll is broken down and cartinoids show
similar to when veggies turn color when ripe
leaves are dead and stopped growing
photosynthesis part one
takes place in the thylakoids
light energy is required
2 steps:
photosystem one and photosystem two
differ in what they oxidize and what they reduce
photosystem I and II
photons from the sun enter the chloroplasts and travel to the thylakoids
photons hit the chlorophyll and excite chlorophyll electrons
excited electrons give off energy. some of the energy is captured to be used in photosynthesis and some is lost (eventually captured to be used to make ATP). electrons are captured by special proteins that must pass the electrons to other proteins until they reach the stroma
electron transport chain in the stroma (outside) in the thylakoid lumen (inside)
with each step of the ETC, electrons lose energy. energy is used to form ATP
at the bottom of the ETC, electrons find NADP and H2O (water comes from the plant’s vacuole)
splits H2O and H bonds with NADP to form NADPH*
oxygen is released into the atmosphere (another oxygen must be released to make O2 for us to breathe (H2O needs to be split twice)
*NADPH is just a protein carrier that stores the energy and doesn’t use it
photolysis
when water is split and oxygen is released, electrons from this process are given back to chlorophyll to make up for the electrons that were lost at the beginning
cuticle and epidermis
(leaf)
the outer layers of the leaf and protect it from dying
chloroplasts
found in the mesophyll cells and are where photosynthesis occurs
(leaf)
stomata
(leaf)
pores where gas is exchanged; opened and closed by the guard cells located in the leaf surface
xylem and phloem
“veins and arteries” of the leaf that carry water and nutrients throughout
xylem
upward (leaf)
phloem
downward (leaf)
light independent reaction
called the Calvin cycle
must go around 6 times to make one molecule of glucose (6CO2 + 6H2O —-—> C6H12O6 + 6O2)
uses carbon dioxide
takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast
divided into three parts: fixation, reduction, regeneration
Calvin Cycle
CO2 enters the stroma
Fixation:
CO2 (with one C) finds a compound called RuBp. which has 5 carbons
forms a 6 carbon compound (unstable)
6 carbon compound splits into 2 compounds called PGA (with 3 carbon each)
Reduction:
PGA molecules pick up ATP and H (H comes from the NADPH that was formed during the light reaction)
PGA bonds with H to become PGAL*
ATP enters the stroma and drops off energy —> ADP
ADP goes back to the light reaction to find another P to make ATP again
Regeneration:
2 PGALs now ——> one drops out of the cycle and the other is used to make glucose by continuing the cycle and releasing energy (another ATP changes to ADP)
PGAL will become RUBp to start the reaction over
*reduction because it involves the gain of electrons by 3 carbon PGAs
carbon fixation
fixing a carbon from CO2 to another compound
ok
label the chloroplast
chromotography things
paper is polar
solvent- nonpolar-moves up the paper
pigments- nonpolar- dissolves in the solvent