Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Plants originated from
Green algae about 470 Million years ago
About 425 million years ago
Traits of facilitating life on land appeared
What are the three structure of plant
Reproductive structure
Photosynthetic branches
Structure that anchor the plant to the soil
What are three types of plants
Nonvascular plants
Seedless vascular plants
Seed plants
What is the function of plants
Supply oxygen, food sources and habitat for many other terrestrial organism
The closest relative of plant
Green algae called Charophytes
What are some evidence that algae is plants’ ancestor?
multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic autotrophs
have cellulose in their cell walls and chloroplasts containing chlorophyll a and b
Morphological and Molecular evidence of Plant and green algae shared ancestor
Cellulose-synthesizing membrane proteins are arranged in rings, rather than linear sets
Structure of flagellated sperm
Sequence similarities in nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial DNA
Sporopollenin
a polymer that prevents zygotes form drying out present on charophytes and plants
Helps to resist harsh environment
Charophytes moving from ocean to land will
Benefit: unfiltered sunlight, more plentiful CO2 and nutrient rich soil
Challenges: Scarcity of water and lack of structural support against gravity
Embryophytes
Plants with embryo
dependency of the embryo on the parent
Derived Trait of Charophyte from plants
Alternation of generation
Walled spores produced by sporangia
Apical meristems
Derived Trait of plant: What is alteration of generation?
The process which the life cycle of plants alternate between two generations of multicellular organism
Gametophyte and sporophyte
Gametophyte
Multicellular haploid produces haploid gametes (sperm and egg) by Mitosis
Sporophyte
Multicellular diploid produces haploid spores by Meiosis
Spores develop into
Gametophyte
Fertilized egg develop into
Sporophytes
Diploid Embryo is retained within
The tissue of the female gametophyte
How the nutrients are transferred with embryophytes?
From parent to embryo through placenta transfer cells
Derived Trait of plant: Sporangia
Organ in the plant that produces spores
Derived Trait of plant: Apical Meristem
Located at the tip of the root and shoot for the cell division
The cell divide continuously enabling elongation of roots an shoots for better resource acquisition
Derived Trait of plant: Cuticle
Waxy covering the epidermis
Derived Trait of plant: Stomata
Specialized cell that allow for gas exchange between the outside air and the plant
Early plants lacked
True toots and leaves making absorption challanging
The fossil suggests that 420 million yeas ago
symbiotic associations with fungi (mycorrhizae) may have helped plants without roots to colonize land
when did the first plant spore appear
470 million years ago
Vascular tissue
Cells join into tube s for the transport of water and nutrients
Vascular plants
Plants with complex vascular system
Non vascular plant
Lack of an extensive transport system
Bryophytes
name of non vascular plants such as liverworts, mosses and hornwarts
not a monophyletic group
Seedless vascular plants
Have extensive vascular transport system but does not produce seeds
Seedless vascular plants divided into two clades
Lycophytes
Monilophytes
Lycophytes
Club mosses and their relatives
Monilophytes
Fern and their relatives
The majority of living plants are
Seed vascular plants
What is seed?
Embryo packed within a supply of nutrients inside a protective coat
What are the two group of seen plants?
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Gymnosperm
Produce seed that are enclosed (naked)
Angiosperm
Produce seed that develop inside chambers that originate with flowers
90% of living plant species
Bryophytes
Nonwoody herbaceous plants
What are some examples of bryophytes?
Liverwort
Mosses
Hornwort
Which cycle is dominant for bryophytes?
Haploid gametophytes are dominant in all bryophytes
Bryophytes: Protonema
mass of green, branched and one cell thick filament spore of moss
Bryophytes: How does moss develops gametophyte?
Protonema absorbs water and nutrients and form buds that develop into gametophyte
Why most of the bryophyte does not get taller?
Lack of rigid support of tissues
Lack of vascular tissue for long distance transport
Bryophytes: Rhizoids
Root like structure that anchor gametophyte to the substrate
Does not absorb water or minerals
Bryophytes gametophyte: Gametangia
Produces gametes in plants, algae, ferns
Bryophytes gametophyte: Archegonia/ archegonium
Female gametangia
Produce single non-motile egg
Bryophytes gametophyte: Antheridia
Male gametangia
produce many motile sperms
How does the Bryophytes sperm move?
Flagellated sperm will swim to the egg through a film of water in response to chemical attraction
Bryophytes gametophyte: What happens to the fertile egg?
As an embryo it will be retained within the archegonium
Bryophytes gametophyte: Reproduction, Sexual or asexual?
Can be produced sexually but it is limited by the water availability and the proximity of male and female gametophytes
Asexual production is frequent
Bryophytes sporophyte
It depends on the gametophyte and are attached to them
Bryophytes sporophyte three major parts consist of
Foot: Absorbs nutrients from the gametophytes
Seta (stalk): conducts nutrients to the sporangium
Capsule: AKA sporangium which it produces spores by meiosis
How the spores re dispersed?
the peristome at the top of the capsule disperses the spores when conditions are dry
Liverwort characteristics
The name comes from their liver shaped gametophyte

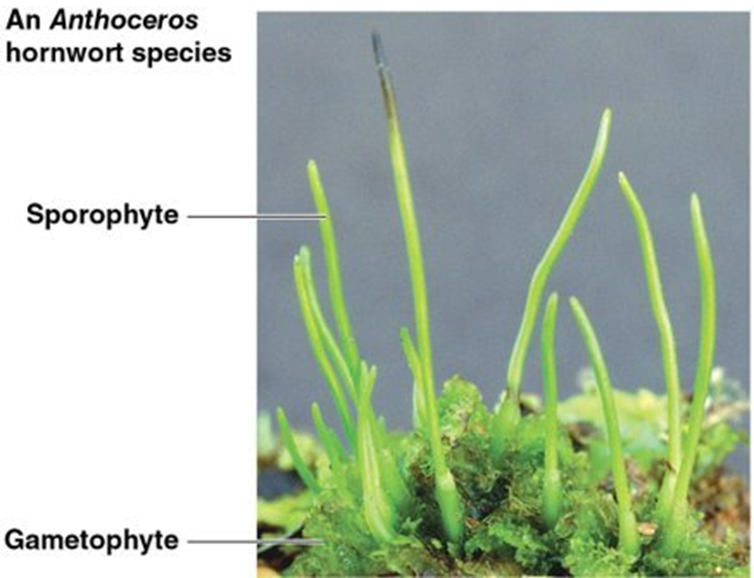
Hornwort characterisitcs
long horn shaped sporophyte
spores are released when horn split open
Form symbioses with nitrogen fixing bacteria
Mosses characteristics
Sporophyte visible to the naked eye
photosynthetic when are young
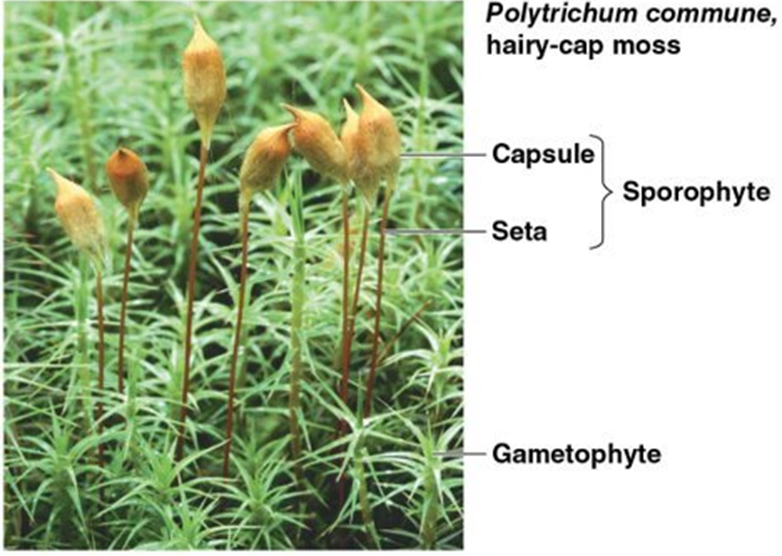

What moss is important ecological and economically?
It is commonly lived in moist forest and wetland
Also inhabits extremely cold, hot and dry environment
It rehydrates after complete desiccation
IT HELPS TO RETAIN NITRON IN SOILS
What is PEAT?
Decayed organic material (moss)
It is used as source of fuel
Peatland characteristics
With low temperature, pH and oxygen level, it inhibits decay of moss and other organism
is can preserve corpses for thousands of years
Peatland fact with Earth
3% of earth land is covered with peatland but it contains 1/3 of world’s soil carbon
overharvest will cause global warming
what makes the plant to grow taller?
The vascular tissue allow plants to grow tall
What is one of the difference between bryophyte and vascular plant SPOROPHYTE?
Vascular plant sporophyte lives independently from the gametophyte from it nutrient supply where bryophyte sporophyte depend from gametophyte
Vascular plants Are characterized by:
Life cycle with dominant sporophytes
Transport in vascular tissue called xylem and phloem
Well developed root and leaves
Sporophylls: Spore bearing leaves
Seedless Vascular life cycle
Sporophyte are larger and complex
Fern: Leafy part is sporophyte and the gametophyte are tiny plant growing bellow the soil surface
Vascular Tissue: Xylem
Conducts most of the water and minerals through TRACHEIDS
Dead at functional maturity
Vascular Tissue: Tracheids
Water conducting long tapered cell that conducts water in the plant
Vascular Tissue: Lignin
When xylem cell is at functional maturity it dies and releases complex organic polymer that are deposited in the cell wall of the plants which it makes them rigid.
Vascular Tissue: Phloem
Arranged in tube for transport of organic materials such as sugar
Cells are alive at functional maturity
Function of Vascular Tissue
Structural support
Long distance transport needed for the plant to grow tall
Function of Root
Organs that anchor vascular plants into the ground and absorb water and nutrient from the soil
It resembles the stem tissue of earlier vascular plants
Function of Leaves
Increase surface area for light capture
Conduct most of the photosynthesis in plants
Type of Leaves: Microphylls
small
spine shaped
single vein
found only in lycophytes
Type of Leaves: Megaphylls
large leaves
highly branched vascular system
found in all plant groups
Sporophylls
Leaves with sporangia attached
Sporophylls of angiosperm are called
Carpels and stamens
Homosporous
Most of the seedless vascular plants
One type of sporophyll and sporangium
Produce one type of spore: becomes bisexual gametophyte
Heterosporous
All seed plants and some seedless plants
two types of sporophylls with different sporangia
Produces different spore types
either male or female spores
Megasporophylls
Megasporangia→produce large megaspores→ female gametophyte
Microsporophylls
Microsporangia→ produce small microspores→ male gametophyte
Phylum Lycophyta (lycophytes)
seedless vascular plants clade
club mosses, spike mosses, quillwort
Phylum monilophyta (monilophytes)
Seedless vascular plants clade
fern, horsetails, whisk fern and its relative
Lycophytes characteristics
Grow in diverse habitat
some have photosynthetic gametophyte
sporophyte with both leafy upright stem and ground hugging root forming stem
spikemoses and quillwort: heterosporous
Clubmosses: Homosporous
Not true mosses
Monilophytes: Fern
Most species are homosporous and have spring like device for spore disposal
Large megasporophylls
Monilophytes: Horsetails
bisexual gametophyte
have separate fertile and vegetative stem
Horsetail sporophytes have jointed stems with rings of small leaves or branches
Monilophytes: Whisk Ferns and its family
all are homosporous: bisexual gametophyte
Three fused sporangia form a yellow knob on the end of each stem
Monilophytes Characteristics
Most widespread seedless vascular plant
Most diverse in tropic
Most closely related with seed plant than lycophytes
When did lycophytes, horsetails, and ferns formed?
During Devonian and Carboniferous period