algae and marine plants
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
seaweed and stuff
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
why are algae not considered to be plants?
they do not have leaves, stems, or roots
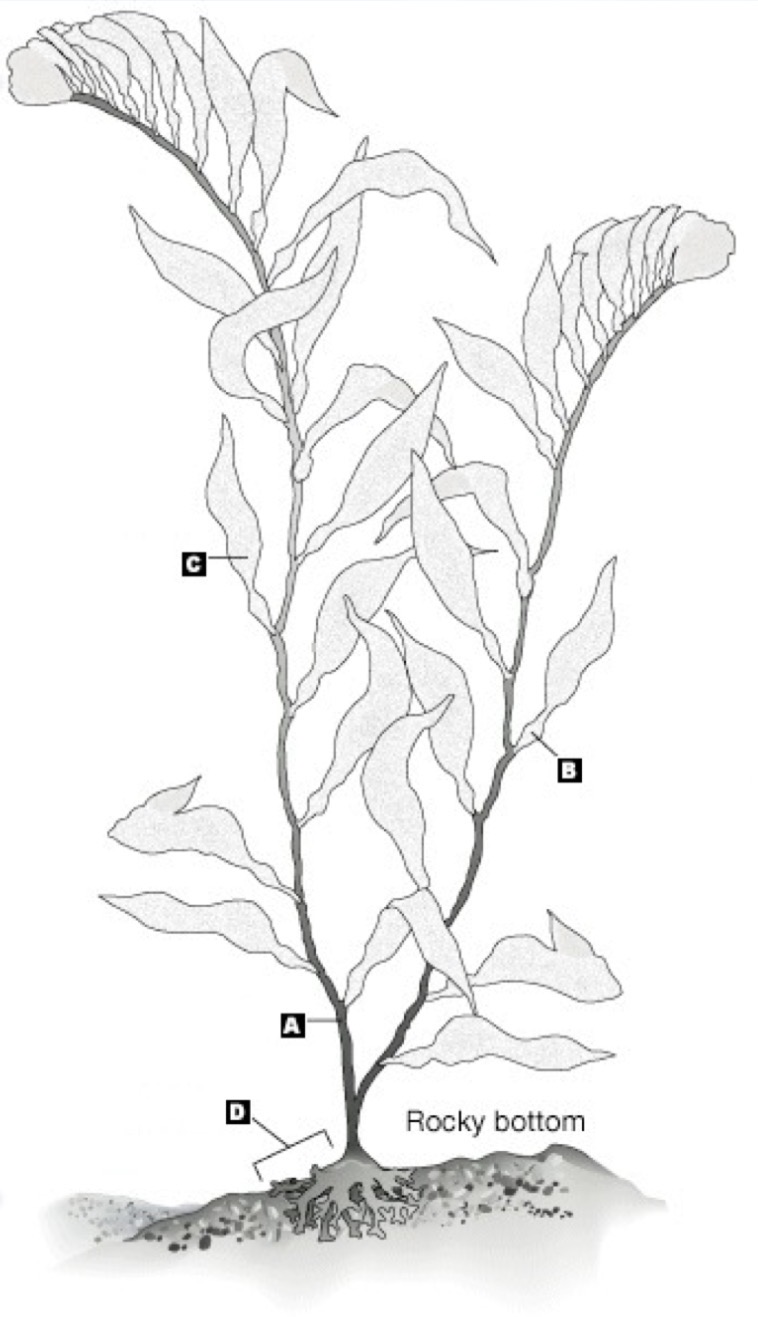
a
stipe

b
pneumatocyst
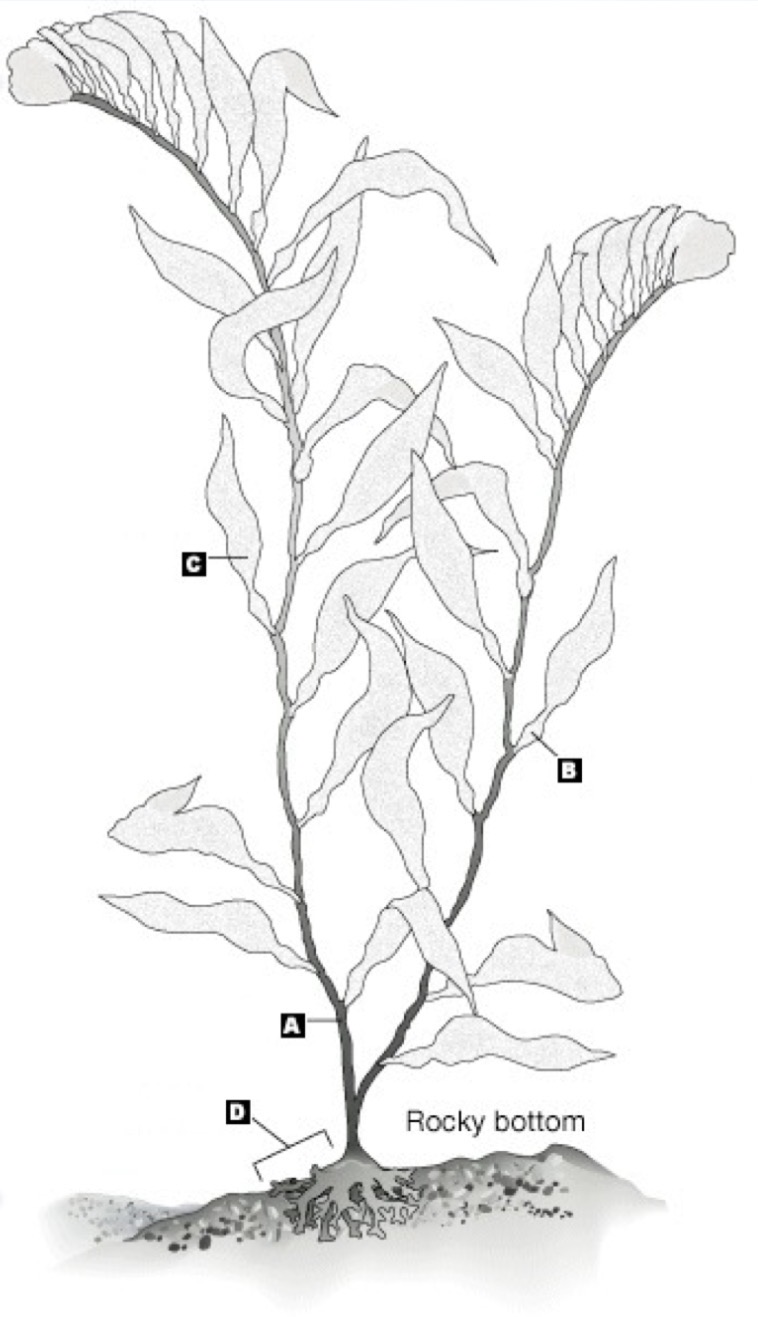
c
blade
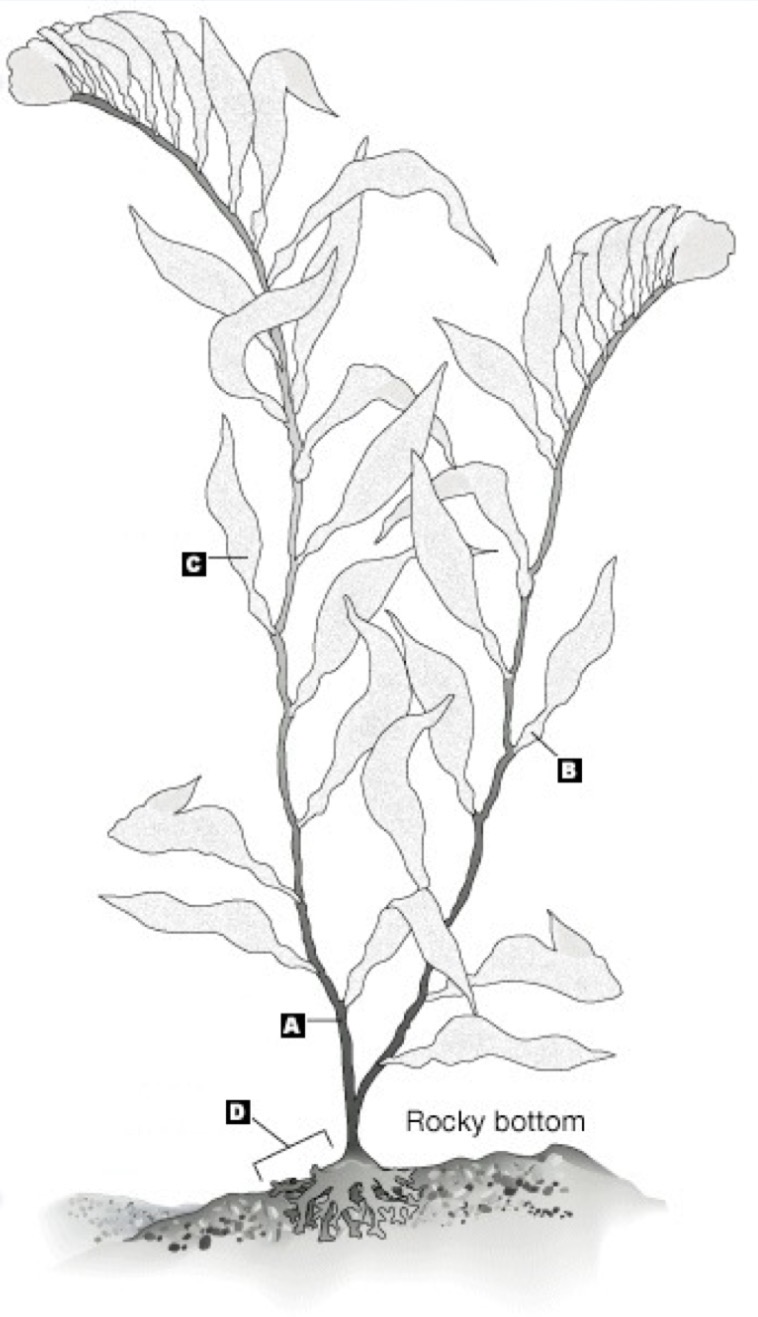
d
holdfast
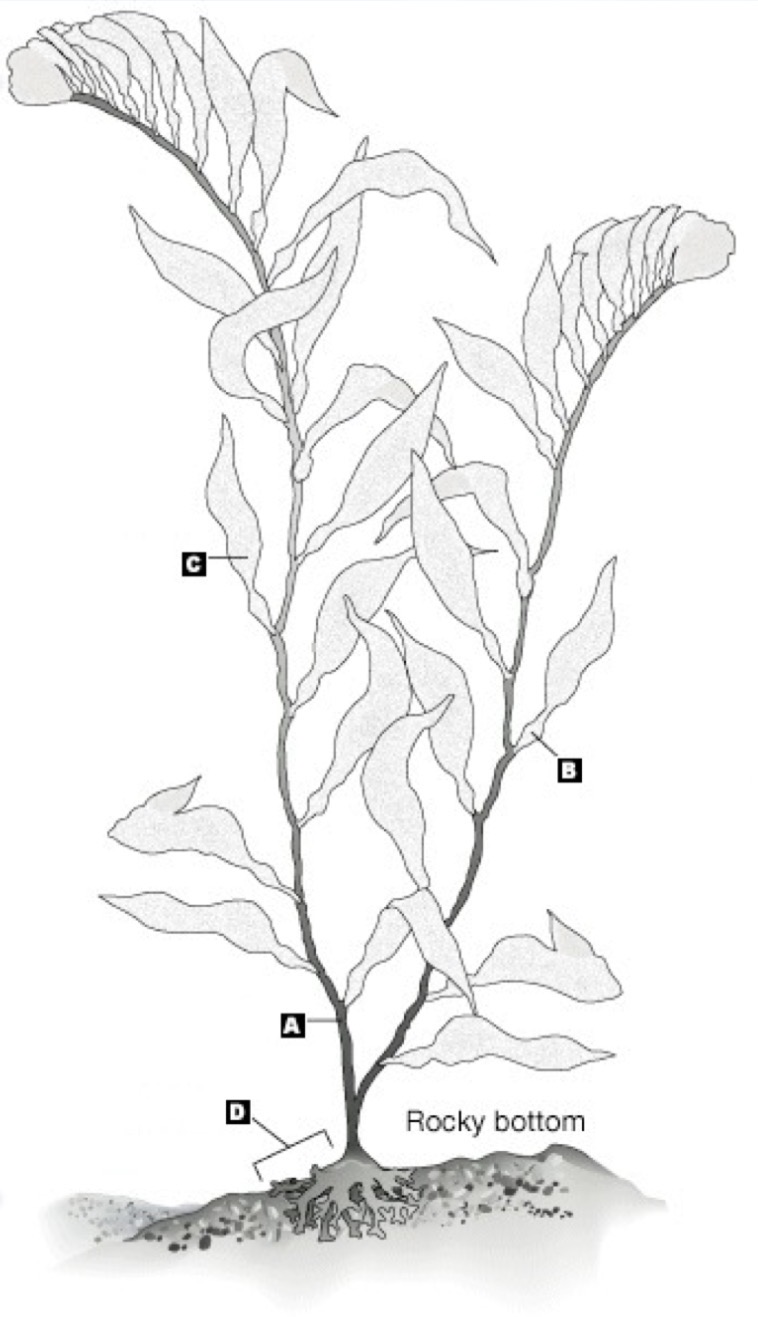
the entire thing
thallus
green algae
a vital food source, produce a significant portion of the world’s oxygen, and are closely related to plants
brown algae
have a unique pigment called fucoxanthin, which gives them their color and aids in photosynthesis
red algae
have the ability to thrive in deep water thanks to pigments like phycoerythin, their lack of flagella, and their unique cellular features like pit connections
human uses for green algae
taken as nutritional supplements and is in bio-fuels
human uses for brown algae
produces alginic acid, which is used as a stiffening agent for pastry fillings, instant puddings, salad dressing, milk shakes, whipped cream, ice cream, adhesives, explosives, and lotions
human uses for red algae
sushi “seaweed”, cheese, yogurt, laxatives, and has many uses in medicine
seagrasses are most closely related to what type of common land plant?
lilies, orchids, and ginger
in what general type of environment are seagrasses found?
shallow, coastal marine environments
what likes to eat seagrass?
manatees, green sea turtles, and dugongs
what purpose does arenchyme serve?
allow for flotation
what are the 4 main types of mangroves?
red mangrove, black mangrove, white mangrove, and buttonwood
where are mangroves found?
along tropical shores with limited wave action, subtle slope, and high rate of sedimentation
what ecological roles do mangrove forests play?
protect the coast from storms, provide a nursery for juvenile marine life, help filter sediment which keeps water near coral reefs clear, and remove carbon dioxide from the environment
how do mangroves maintain proper salt balance?
black mangroves have salt glands and salt is concentrated in old leaves that are shed in others
how does algae reproduces asexually
fragmentation, when the thallus can break up into smaller pieces which can then grow into new algae, and spore formation, when haploids spores are the result of meiosis from sporangium and diploid spores are produced by sporophytes
how does algae reproduce sexually
gametophytes produce gametes which fuse to form diploid cells
how do sea grasses reproduce
sexually and asexually by spreading through seeds and cloning themselves
how do mangroves reproduce
pollination of flowers which occurs via wind of bees; they release buoyant seeds that can drift in the water and stay buoyant for up to 100 days; they also produce propagules which are embryonic plants that grow on the parent plant and they fall from the parent tree and drift in currents
how might an increase in pollution affect the primary producers in the ocean? (claim)
an increase in pollution might lead to algal blooms, reduced sunlight, and direct toxicity
how might an increase in pollution affect the primary producers in the ocean? (evidence)
excess nutrients can cause rapid growth of algae, microplastics on the surface block sunlight, and pollutants inhibit photosynthesis
how might an increase in pollution affect the primary producers in the ocean? (reasoning)
algal blooms consume so much oxygen they produce dead zones, sunlight cannot reach the producers, and growth will be reduced