44) Glomerular filtration
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
How is GFR regulated?
1) Renal autoregulation
-myogenic mechanism
-tubuloglomerular feedback
2) Neural regulation
3) Hormonal regulation
What is the myogenic mechanism?
1) Increase in systemic blood pressure (to blood vessels accessing nephron)
(*initial increase in GFR)
2) Increase in blood pressure pushes AGAINST those afferent blood vessels → stretches the blood vessel (kinda makes it dilate)
3) Smooth muscle instantly contracts afferent arteriole in response to stretching
4) maintains GFR (by “technically” decreasing the GFR; less blood flow; less filtration)
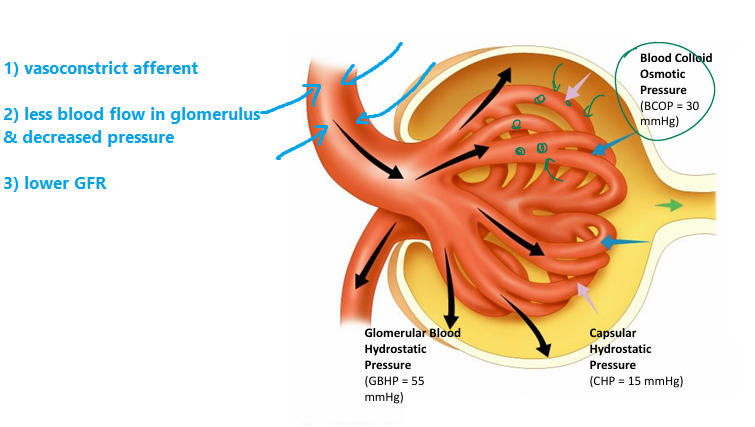
What is the tubuloglomerular feedback? (IMPORTANT)
(Increased solute concentration)
1) Macula densa senses: increased solute concentration (increased NaCl) in distal renal tubule
- means fluid upstream is flowing TOO FAST
→ no time to absorb stuff out upstream
(proximal renal tubule + nephron loop have less time for reabsorption)
→ aka GFR is too high
2) Macula densa cells signal:
→ release paracrine agents that INHIBIT nitric oxide (usually vasodilate)
→ vasoconstriction of AFFERENT arterioles
→ less blood flow; decreased glomerular pressure
→ less filtration
→ slows down GFR
—
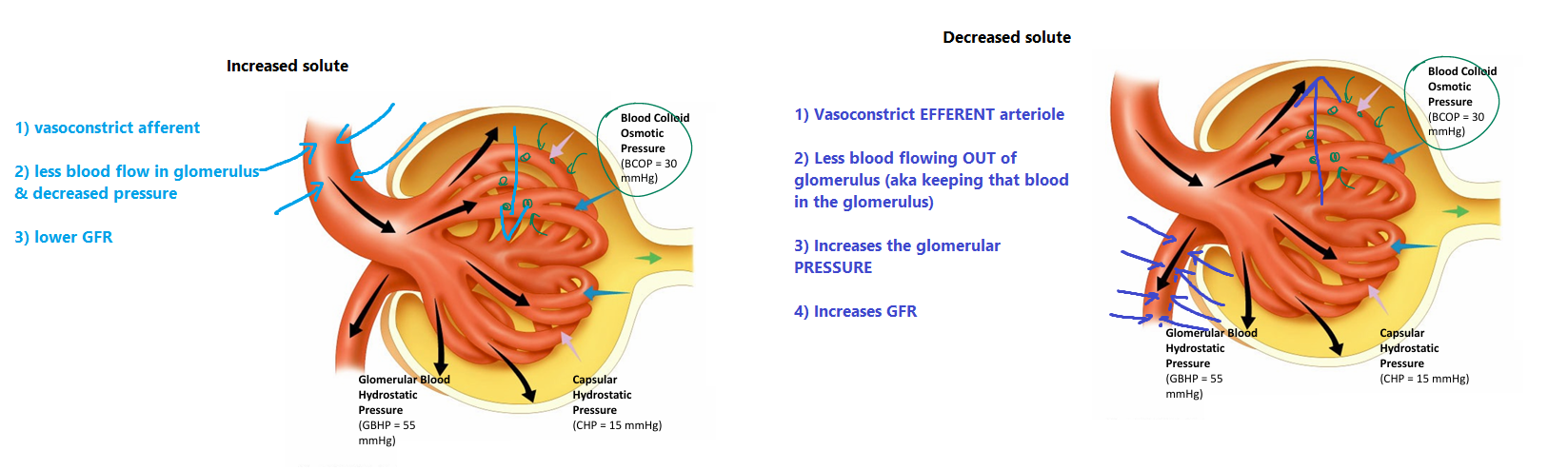
(Decreased solute concentration)
1) Macula densa senses: DECREASED solute concentration
- means fluid upstream is flowing TOO SLOW
→ everything is being absorbed upstream (greedy cells)
→ aka GFR is too LOW
2) Macula densa cells signal to:
i) Juxtaglomerular (JG) cells
→ secrete RENIN
→ activate ANG 2
→ vasoconstriction of EFFERENT ARTERIOLE
→ increases pressure in glomerulus
→ increased GFR
What is NEURAL REGULATION OF GFR?
1) you get shot/hemmorage + big decrease in blood pressure
2) increased sympathetic activation
3) vasoconstriction of branches renal artery
4) vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole
5) less blood flow to glomerulus → decrease GFR
6) intention to reduce water loss in urine
*TLDR: vasoconstrict to limit blood flow going to renal
(we want to keep our fluid especially if we’re bleeding out)
What is hormonal regulation of GFR? (ANP)
(ANP)
- released from atrial cells when stretched (increased BV and pressure)
- RELAXES glomerular mesangial cells
→ increases GBHP (glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure) → increase GFR
What is hormonal regulation of GFR? (ANG 2)
(ANG2)
- SYSTEMIC vasoconstriction
→ increases systemic blood pressure BUT also increases VASCULAR RESISTANCE
→ increased vascular resistance = less blood flow to the glomerulus
= decreased GFR (think of afferent arterioles being vasoconstricted)
—
However, there is ALSO vasoconstriction of EFFERENT ARTERIOLE
(ANG 2 constricts efferent more than afferent)
→ increases GBHP
→ helps maintain OR restore GFR, despite decreased renal blood flow
—
*Key points:
- although systemic vasoconstriction tends to reduce GFR,
VC of efferent arteriole has greater impact
which counteracts drop in GBHP, in turn, maintaining GFR
TLDR:
1) GFR too high = fluid/solutes pass through renal tubule TOO QUICKLY = not enough reabsorption → need to slow down GFR
2) GFR to too slow = too much REABSOPRTION → impairs excretion of waste products → need to INCREASE GFR
How can we keep GFR within normal limits?
Adjust:
1) diameter (vasoconstrict) afferent & efferent arterioles
2) glomerular capillary surface area for filtration
(adjust contractility of mesangial cells)
→ hormones act on mesangial cells → icnreases space b/w fingers (podocytes’s pedicils)
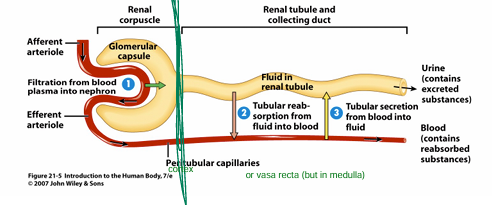
What are the components of the nephron?
1) Renal corpuscle = filters blood
2) Renal tubule = transports filtered fluid + alters composition via absorption & secretion
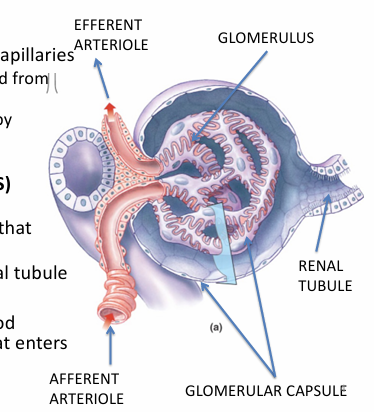
Describe the renal corpuscle
1) Glomerulus = fenestrated capillaries
- blood comes in via AFFERENT arteriole
- blood EXITS via EFFERENT arteriole
2) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
- double wall structure that receives filtrate +
- continuous w/ renal tubule
What is the HISTOLOGY of bowman’s capsule? (1/2)
What is the HISTOLOGY of renal tubule? (3/4)
What is the HITOLOGY of the collecting tubule?
1) Capsular epithelium (outer wall) = simple squamous epithelium
2) Visceral epithelium (water hoses) = MODIFIED simple squamous epithelium = podocytes
3) renal tubule = simple cuboidal or simple squamous epithelium
5) simple cuboidal epithelim
Discuss Podocytes in more depth.
*Note: podocytes are part of bowmans capsule - specifically visceral epithelium (water hoses)
Podocytes contain PEDICELS (like fingers overlapping)
- increased overlap = less filtrate going through
- less overlap = more filtrate going through
What are mesangial cells?
located in spaces b/w glomerular capillaries (aka inside the hose)
- phagocytic activity
- modified smooth muscle
- alters capillary surface area → helps w/ glomerular filtration rate
(contracts/relaxes due to vasoactive agents)
What is the FILTRATION MEMBRANE?
1) Fenestrated glomerular capillary endothelium
= large pores
- YES: plasma components
- NO: blood cells + platelets
2) Basement membrane (basal lamina)
= negative charge BM
- NO: large negative proteins
3) Podocyte layer
= small filtration slits
- NO: small proteins (ex. albumin)
Filtered subtances that pass through the filtration membrane form the __.
This typically includes: __.
1) Filtrate / tubular fluid
2) salt, water, sugar,amino acids, ions, urea, creatinine
What consists of the RENAL TUBULE?
1) Proximal convoluted tubule = (renal cortex)
2) Nephron loop (of Henle) = extends into renal medulla
3) Distal convoluted tubule = (renal cortex)
What are the functions of the renal tubule (more tomorrow i think)
1) Tubular reabsorption = takeup the useful shit (glucose, AA, water)
2) Tubular secretion = throw out ions/wastes not filtered @ glomerulus
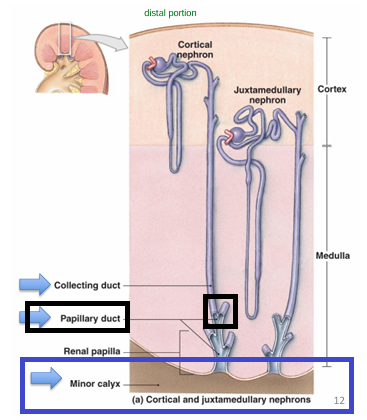
Discuss the COLLECTING SYSTEM
All nephrons have their own COLLECTING DUCT
→ many collecting duct drains tubular fluid to PAPPILARY DUCT
→ papillary duct to MINOR CALYX → major → renal pelvis → ureter
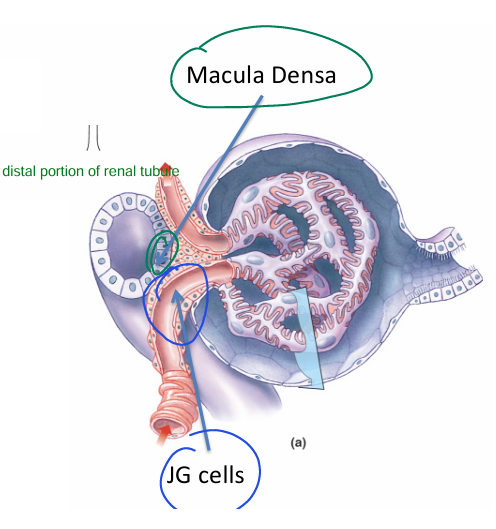
What are the specialized cells within the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
2) Macula DENSA cells = final part of ascending loop of henle
- detects alterations in NaCl concentration in distal convoluted tubule
→ signals to JG cells if we need to change anything (GFR)A
1) Juxtaglomerular cells (JG) = modified smooth muscle cells for AFFERENT ARTERIOLE
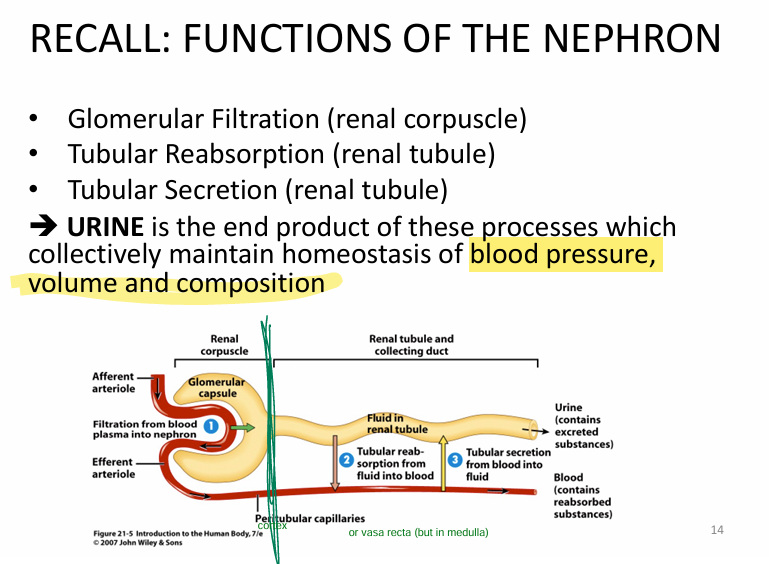
What is the takeaway function of the nephron?
Urine = end product
→ maintain homeostasis of BP, blood volume, composition
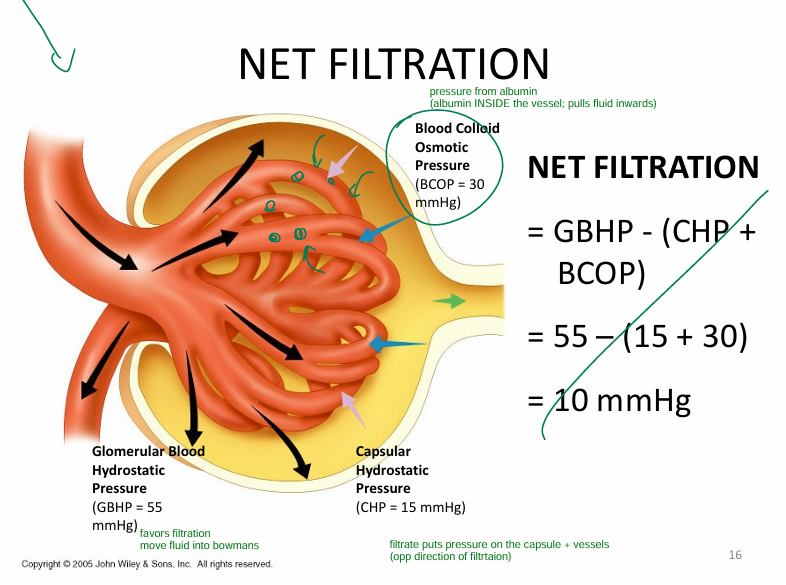
What is glomerular filtration rate dependent on? (i.e., the 3 pressures)
1) glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP)
→ fluid into bowman’s capsule
2) capsular hydrostatic pressure (goes against GBHP)
3) blood colloid osmotic pressures (goes against GBHP)
- fluid reabsorbed due to albumin
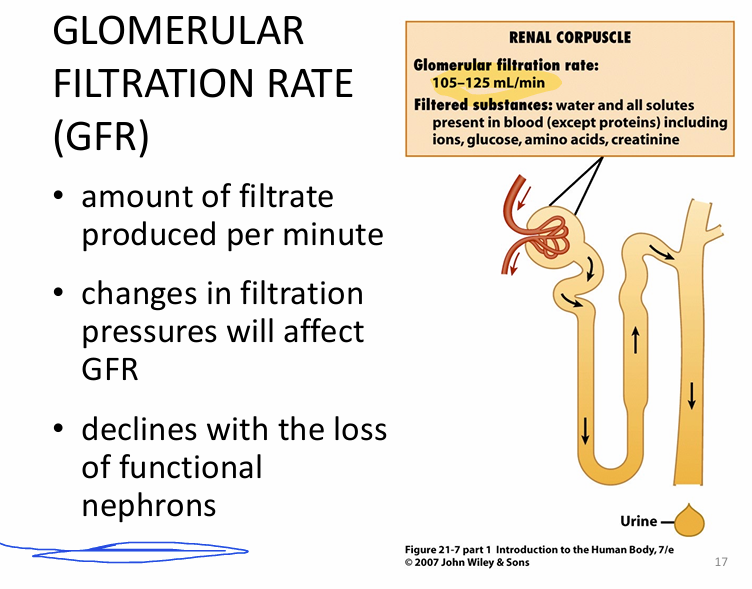
*Extra notes:
- glomerular filtration rate = 105-125mL/min
-GFR declines w/ LOSS of nephrons