EXAM 5 BIOPSY
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
learning
the brain's ability to change in response to experience
memory
the brain's ability to store and access the learned effects of experiences
Henry Molaison/HM
an epileptic who had his medial (H.M.) - An temporal lobes removed in 1953
- Surgery removed most of the hippocampus and amygdala
- Had an almost total inability to form new long -term memories: Anterograde Amnesia
- Had an almost total inability to form new long -term memories: Anterograde Amnesia
anterograde amnesia
__________________ __________
an inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia
___________ ___________
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
hippocampus
amygdala
Henry Molaison an epileptic who had his medial (H.M.) temporal lobes removed in 1953
- Surgery removed most of the ________________and _______________ (struc.)
LTM
STM
H.M. was unable to form most types of ___________________, his______________was intact
digit span
The number of digits a person can remember.
- used as a measure of the capacity of STM
- H.M. could repeat digits provided the time between learning & recall was within the duration of STM
mirror drawing
incomplete pictures
implicit
H.M improves with practice on sensorimotor tasks (e.g. __________ ___________) and on a non sensorimotor task (e.g. ____________ ____________) - without recalling previous practice sessions
- __________/___________memory still in tact
classical conditioning
H.M. Readily "learns" responses through __________ _______________, but has no memory of conditioning trials
repetition priming tests
used to assess implicit memory; performance in identifying word fragments is improved when the words have been seen before
- incomplete picture test
implicit
Repetition-priming tests are used to assess __________ memory. One example is an Incomplete-Pictures Test
incomplete pictures test
Repetition-priming tests are used to assess implicit memory. One example is an _________ __________ _______
medial temporal
consolidation
3 Major Scientific Contributions of H.M.'s case
- ________ ____________ lobes are inv in memory
- STM, remote memory, and LTM are distinctly separate - H.M. is unable to move memories from STM to LTM, a problem with memory ________________
- Memory may exist but not be recalled - as when H.M. exhibits a skill he does not know he has learned (explicit vs. implicit)
implicit/procedural
__________ memory
Memories we don't deliberately remember or reflect on consciously
explicit/declarative
__________ memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
implicit
explicit
medial temporal lobe amnesia
H.M.'s ability to form __________, but not ___________, long -term memories is often seen in cases of ________ ___________ ________ _________
explicit
episodic
semantic
__________memories are divided into two categories:
- __________ memory (memories for the events of one's own life)
- Issues more common with this type of amnesia
- ___________ memory (memories for general facts or information)
episodic
__________ memory (memories for the events of one's own life)
- Issues more common with this
semantic
___________ memory (memories for general facts or information)
Hippocampus
Medial temporal cortex
_______________ & _________ _____________ ___________ (struc.)
spatial location & episodic memory
Perirhinal cortex
__________ ________(struc.)
- (part of medial temporal cortex)
- object recognition and Inferotemporal cortex together play a role in storing memories of visual input
Inferotemporal
(struc.)
Perirhinal cortex (part of medial temporal cortex) - object recognition and ________________ cortex together play a role in storing memories of visual input
amygdala
______________ (struc.)
role in memory for emotional significance for experiences (strengthens memories about emotional events that are stored by other structures)
prefrontal cortex
(struc.)
• Temporal order of events
- Those with damage to ___________ _________ have difficulties with tasks involving a series of responses
• Different part of *____________ __________ may mediate different types of working memory
- Some evidence from functional brain imaging studies
Cerebellum
_____________ (struc.)
Stores memories of learned sensorimotor skills (e.g., procedural memories & conditioned eye -blink response)
striatum
___________ (struc.)
Memories for consistent relationships between stimuli and responses (habit formation)
consolidation
engram
During _______________, the brain forms a more or less permanent physical representation of a memory.
- Resulting in an ___________(memory trace): physical basis for memory (change in brain that stores memory)
engram/memory trace
__________/____________ ________
physical basis for memory (change in brain that stores memory)
Retrieval
prefrontal
__________: the process of accessing stored memories.
• The ___________ area is believed to direct the search strategy required for retrieval.
Reconsolidation
__________________: the return of an engram to stable long-term storage after it has been temporarily made unstable during process of recall.
glutamate
_____________ required both for consolidation & retrieval
Consolidation
retrieval
glutamate require for ____________ & ___________
Hebb rule
_______ ______: If the axon of a presynaptic neuron is active while the postsynaptic neuron is firing (co-occurrence), the synapse will be strengthened.
- "cells that fire together wire together!"
- Changes in synaptic efficiency are the basis of LTM
synaptic efficiency
according to hebb rule, Changes in ________ ____________ are the basis of LTM
Long term potentiation/LTP
_______ _______ _________________: increase in synaptic strength that occurs when presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons are both activated (co-occurrence).
- Synapses are effectively made stronger by repeated stimulation
Hippocampus
where is LTP studied :
- dentate gyrus
- CA1 subfield
- CA2 subfield
- CA3 subfield
- CA4 subfield
of ____________
drug
_______
chemical compounds administered to produce a desired change in the body
psychopharmacology
________________
study of how drugs affect the nervous system and behavior
psychoactive
_________________ drugs influence subjective experience (mood and thoughts) and behavior by acting on the nervous system
- also used to manage neuropsychological illness
drug administration
route of admin influxes the rate at which and the degree to which the drug reaches its site of action
ingestion
injection
inhalation
absorbtion
4 drug administrations
ingestion/oral route
(drug administration)
- easy, relatively safe, most common
- most complex; more barriers to cross
- absorption via digestive tract is unpredictable (influenced by food)
inhalation./tobacco, anesthetics, marijuana
(drug administration)
- absorbed through capillaries in lungs
- difficult to regulate doses
- damage to lung tissue
injection
(drug administration)
- bypass digestive tract
- subcutaneously (SC): under the skin
- intramuscularly (M) into large muscles
- intravenously (IV) into veins, drug deliver directly to the brain
- effects strong, fast, predictable
- difficult to counteract effects
subcutaneously/SC`
drug administration via injection
- under skin
intramuscularly/IM
drug administration via injection
- into large muscles
intravenously/IV
drug administration via injection
- into veins, drug deliver directly to the brain
- effects strong, fast, predictable
- difficult to counteract effects
absorbtion
(drug administration)
- __________ through mucous membranes
- nose, mouth, rectum
- membranes can be easily damaged
BBB/blood brain barrier
In order for a psychoactive drug to have an effect, it must get to the brain - it must pass through the ______ _________ __________
liver
elimination
- action of most drugs terminated by enzymes in the _______
- Small amounts may also be excreted in urine, sweat, feces, breath, and mother's milk
drug metabolism
converting active drugs to non-active forms (drug unable to pass th5rough lipid cell membrane)
- Small amounts may also be excreted in urine, sweat, feces, breath, and mother's milk
small
uncharged
Drugs developed for the brain must be ______& ______________or they must be structurally similar to a substance that already has an active transporter that allows it to pass the BBB
astrocyte feet
capillaries in the brain have tight junctions and are covered with __________ _______. These properties pr4event materials from moving in and out easily
endothelial
small, uncharged molecules are able to pass through the ____________ membrane
tight junctions
capillaries in the body have few _______ ____________ materials can move in and out quite easily
synaptic transmission
Drugs can alter chemical processes at any of seven major stages of _______ ____________
• Increasing/decreasing the synthesis of NTs.
• Destroy degrading enzymes or causing vesicles to leak.
• Increasing release of NT or blocking release
• Blocking inhibitory effect of autoreceptor or activate autoreceptor.
• Blocking the breakdown into inactive chemical.
• Directly stimulating or blocking postsynaptic receptors
agonist
amphetamine
cocaine
example of ___________
- ____________ and ___________ block the reuptake of dopamine and promotes the release of dopamine
antagonist
chlorpromazine
example of _____________
- _____________occupies the dopamine site on the D2 receptor, preventing receptor activation
MAO inhibitor
______ ____________ inhibits the breakdown of serotonin so that more is available for release
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors/SSRIs
_________ __________ __________ _________ block transporter protein for serotonin reuptake so that serotonin stay in synaptic clefts longer
opiates
- analgesia or pain relief
- hypnotic or sleep inducting
- euphoria or strong feelings of happiness
- morphine, heroin
- similar to endorphins
morphine
- opiate used to treat the pain of wounds, surgery, and cancer
heroin
- synthesized from morphine
- opiate
- produces intensely pleasurable effects
- crosses the BBB easily and rapidly
- user may be unaware of the drugs purity
- tolerance develops rapidly, increasing the chance of overdose
endorphins
opioid
dopamine
______________
- endogenous opiates
- produce pain relief by stimulating ________ receptors
- produce additional positive effects by indirectly stimulating _________ pathways
learned tolderance
_________ ______________ develops between tolerance and the environment in which it develops
- drug taken in different setting are more likely to result in an overdose
depressants
_____________ are dugs that reduce central nervous system activity, causing
- sedation; anxiety reduction, hypnotic effects
- alcohol is most commonly used and abused
alcohol
___________ is most commonly used and abused depressant
- low doses: stimulant, by turning off cortical inhibition, reducing social constraints and anxiety
- high doses: produces sedative and hypnotic effects, impairing cognitive and motor functioning
glutamate
GABA
alcohol affects several NTM systems
- inhibits __________
- acts at alcohol receptor, part of the ________ receptor complex; it increases binding of (most prevalent inhibitory transmitter) to the receptor
- combined effect is sedation, anxiety reduction, muscled relaxation, and inhibition of cognitive and motor skills
delirium tremens/DTs
withdrawal from alcohol
- hallucinations, delusions, confusion, rapid heartbeat, seizures and in extreme cases possible death
stimulants
_________ activate or increase CNS activity to produce arousal, increased alertness, and elevated mood
- cocaine
- amphetamines and methamphetamines
cocaine
- produces euphoria, decreased appetite, increases alertness, relieves fatigue
- blocks the reuptake of dopamine and serotonin at synapses, enhancing their effect
- users have executive function deficits that involve the prefrontal cortex
amphetamines
methamphetamines
________________ and __________________
- most widely misused
- produce euphoria and increase confidence and concentration
- increase the release of norepinephrine and dopamine
- long term use may damage dopamine neurons in the nigrostriatal pathways increasing risk of developing Parkinson's disease
nigrostriatal
Parkinsons
long term use of Amphetamines and methamphetamines may damage dopamine neurons in the ___________ pathways increasing risk of developing _________________ disease
nicotine
_________ is the primary psychoactive and addictive agent in tobacco
- stimulates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- PNS, activates muscles and may causes twitching
- CNS, produces increased alertness and faster response to stimulation
- teratogenic effects (disturbs normal development of fetus)
- high levels of drug craving
marijuana
agonist
anandamide
________________
- psychoactive effects from thc
- thc is an __________ at g protein-linked receptors (CB1) used by endogeneous cannabinoid NTM (____________)
- high doses can impair STM and motor functions, distorted sensations, and paranoia
- linked between adolescent use and development of schizophrenia
- several therapeutic effects: suppresses nausea & vomiting, blocks seizures, reduces anxiety & multiple sclerosis symptoms
tolerance
decreased sensitivity to a drug as a consequence of exposure
- shift in the dose-response curve to the right
cross tolerance
- response to a novel drug is reduced because of trolerance developed in response to a related drug
- suggests that the 2 drugs affect a common nervous system target
- example Barbiturates (Amytal) and benzodiazepines (Valium) affect the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA
metabolic
functional
two categories of changes underlie drug rolerance
__________ & ____________
metabolic
drug tolerance that results fron changes that reduce the amont of drug getting to its cites of action (target cells)
functional
- drug tolerance that results from changes that reduce the responsiveness at the site of action
- fewer receptors; decreases efficiency of binding at receptors; receptors less responsive
withdrawal
- seen when drug use is terminated
- symptoms are the opposite of the drugs effects
- body has made changes to compensate for drugs presence- functions normally with the drug present
- severity varies with drug and pattern of use
drug addiction
- use drugs despite adverse effects
- is not the same as physical dependence
- preventing withdrawal symptoms is not the main motivating factor
- not restricted to drugs (food, gambling, internet, sex)
contingent drug tolerance
before and after design shows that tolerance only develops to drug effects that are experienced
• Rats given alcohol one hour before or after convulsive amygdala stimulation
• Test trial: both groups given alcohol before convulsive stimulation
• Results: alcohol no longer prevented seizures in the
conditioned drug tolerance
maximal tolerance effects that are seen in the envinronment in which a drug is usually taken (drug predictive stimuli)
- Pavlovian conditioning trial
exteroceptive
interoceptive
conditioned stimuli
conditioned compensatory responses
___________________ (external or public) cues or _________________(internal or private) cues associated with drug-taking become _____________ _____________ (CS) that elicit ___________________ ________________ ________________ (CR):
• Physiological responses opposite to the effects of a drug (body prepares for drug), thought to be elicited by stimuli regularly associated with experiencing drug effects
• produce tolerance prior to drug use or withdrawal in the absence of the drug
pleasure centers
brain circuitry exists that reinforces behavior
- many species will work for stimulation in brain ________ _________
olds milner
skinner
_______& ___________(1954) placed rats in a _______box that allowed self-stimulation of the brain by pressing a lever.
• Rats may press lever thousands of times/hr stimulating the release of dopamine in nucleus accumbens.
• Addictive substances increase dopamine activity in certain areas of the brain, reinforcing drug use
dopamine
nucleus accumbens.
old and milner
- Rats may press lever thousands of times/hr stimulating the release of ___________ in ___________ _______________
mesotelencephalic dopamine system
Dopaminergic neurons projecting from two midbrain areas to the telencephalon
- nigrostriatal pathway
- Mesocorticolimbic pathway ***
nigrostriatal
___________ pathway of Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System
- Substantia nigra neurons projecting to the dorsal striatum (degenerates in Parkinson's disease)
Substantia nigra
dorsal striatum
nigrostriatal pathway of Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System
- __________ _______ neurons projecting to the ________ _________ (degenerates in Parkinson's disease)
parkinsons disease
Substantia nigra neurons projecting to dorsal striatum (degenerates in __________ ___________)
Mesocorticolimbic
__________________________ pathway
-Ventral tegmental area neurons projecting to cortical and limbic sites, including the nucleus accumbens (the major "reward" pathway for ICSS, natural rewards, & addictive drugs)
Ventral tegmental
cortical limbic
nucleus accumbens
Mesocorticolimbic pathway
- ___________ _____________ area neurons projecting to ________ and ________ sites, including the _____________ _______________(the major "reward" pathway for ICSS, natural rewards, & addictive drugs)
nucleus accumbens
the major "reward" pathway for ICSS, natural rewards, & addictive drugs
Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System
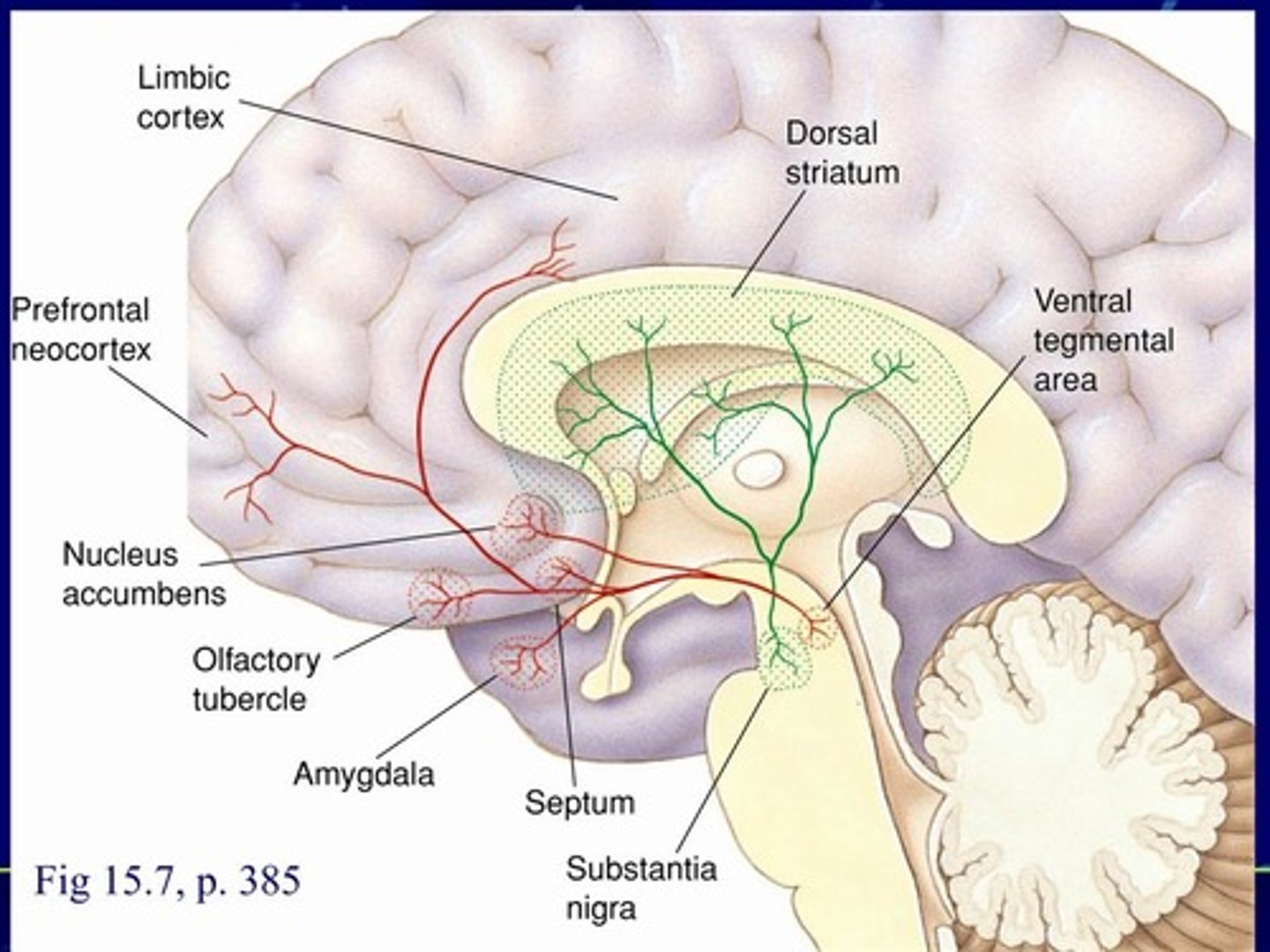
Nigrostriatal
Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System
green
___________ pathway
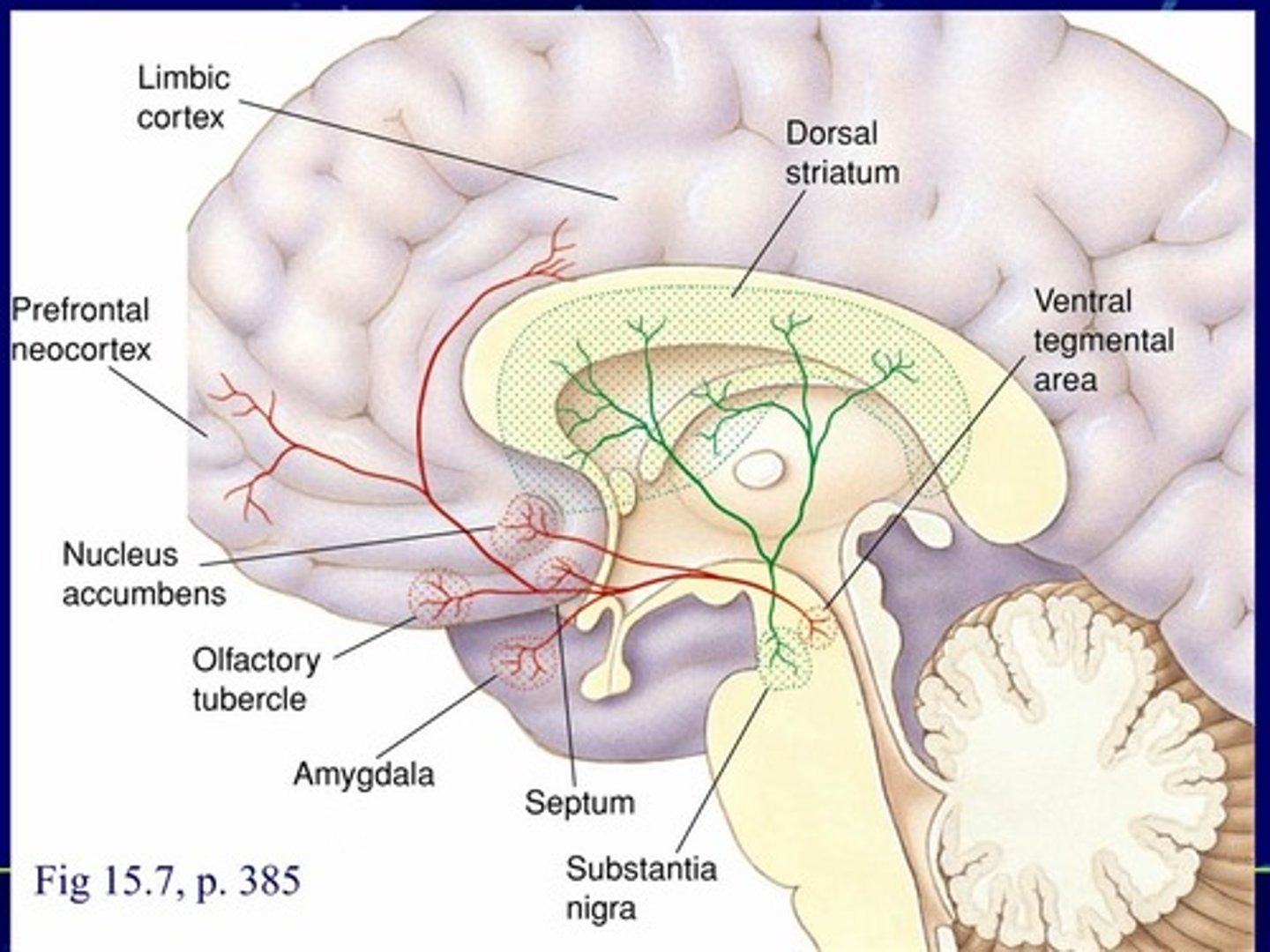
mesocorticolimbic
Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System
red
___________ pathway
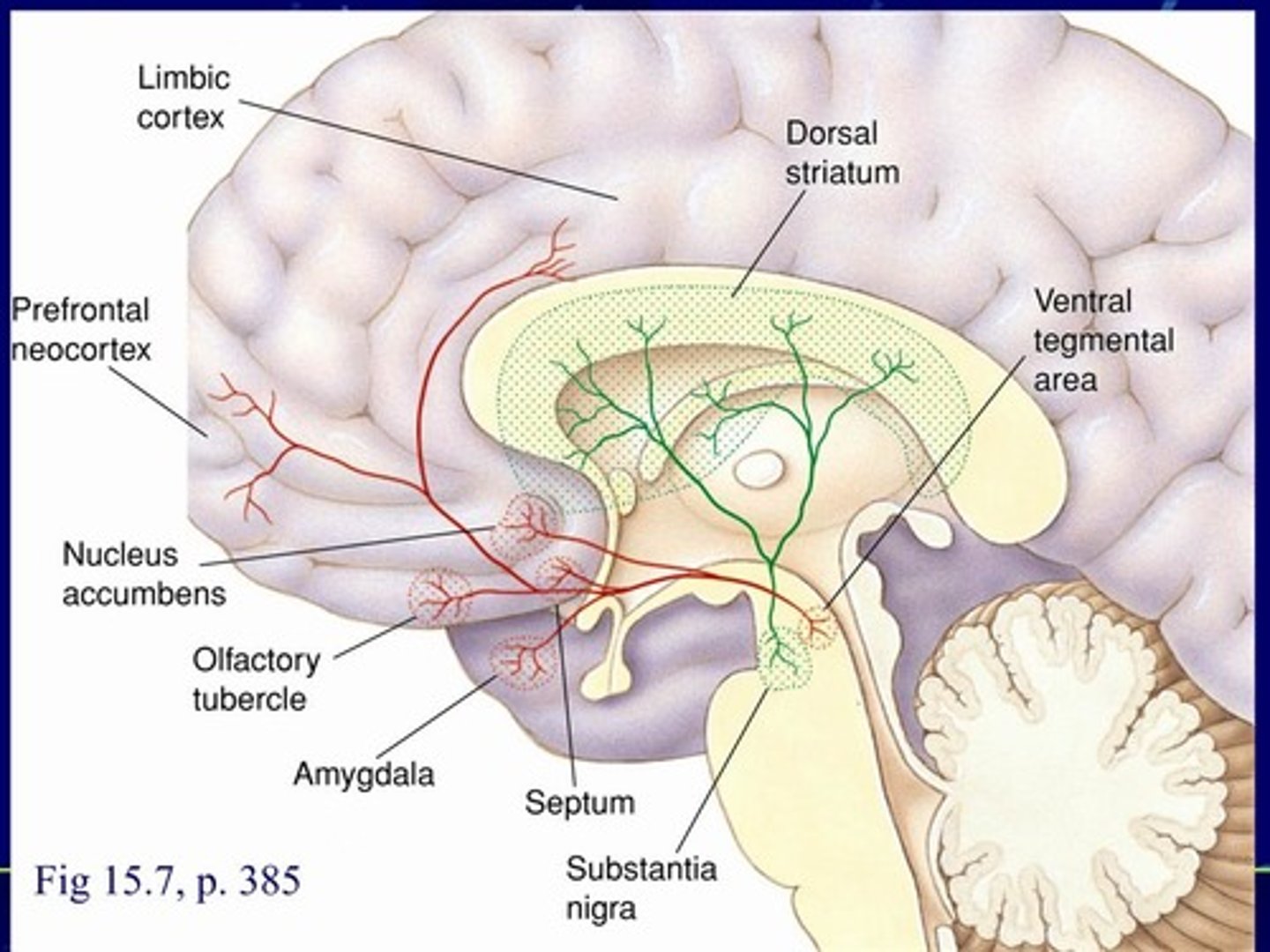
dopamine
Nucleus Accumbens
• Almost all abused drugs stimulate ___________ release in the __________ ______________
- small subcortical area rich in dopamine receptors (responsible for feelings of pleasure)