L4 aquired immunity
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
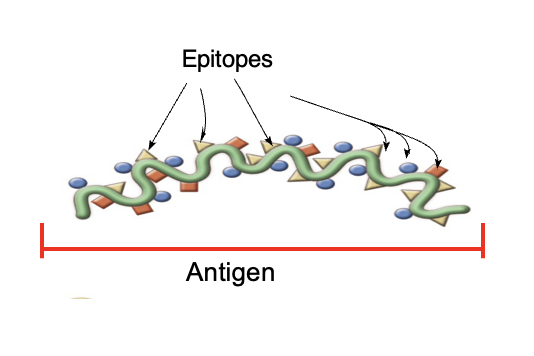
epitope
particular parts of antigen that is recognized by immune system
True or false: an antigen usually has many antigenic determinants or epitope
true
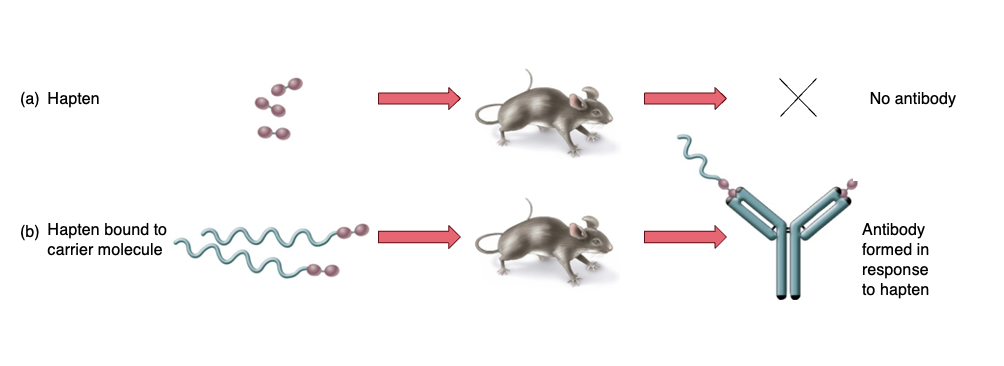
haptens
small foreign molecules that consist only a single determinant group
not immunogenic unless attached to a larger carrier
carrier grp contribute to size of the complex and enhances the orientation of antigen
Alloantigens
cell surface markers and molecules that occur in some members of the same species but not in others
determine blood groups and histocompatibility in transplantation → it’s the reason why transplant reject
superantigens
potent T cell stimulators - provoke an overwhelming (and often dangerously strong) immune response
can lead to toxic shock (ex. tampons)
Allergens
antigen that evoke allergic rxn
autoantigens
molecules on self tissues that sometimes will elicit an immune response due to failed tolerance
ex. autoimmune disease
APC cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
Bcells
T cells: site of maturation
thymus gland
T cells: immune surface markers
T cell receptor
CD molecules (like CD4 - helper; CD8 cytotoxic)
MHC1 receptors
T cells: Circulation in blood relative number compared to B
high number
T cells: receptors for antigen
T cell receptor (TCR)
T cells: distribution in lymphatic organs
paracortical site (interior to the follicles)
T cells: require antigen presented with MHC? (APC)
yes
T cells: effector cells
helper and cytotoxic T cells and memory cells
T cells: general function
regulate immune function
kill foreign and infected cells
synthesize cytokines
B cells: site of maturation
bone marrow
B cells:
B cells: immune surface markers
immunoglobulin MHCI and MHCII receptor
B cells: circulation in blood numbers compared to T cells
Low number
B cells: receptors for antigen
immunoglobulin D and M
B cells: distrubiton in lymphatic organs
cortex (in follicles)
B cells: require Antigen presented with MHC (APC)
no
B cells: effector cells
plasma cells and memory cells
B cells: general functions
produce antibodies to target, inactivate and neutralize antigen
T helper cells
primary receptor on T cells
function/important feature
CD4
function
activate other CD4 and CD8 (T cyt) cell
secrete IL2, TNF, interferon gamma
responsible for delayed hypersensitivity
interact with MHC II receptors
T helper cells 2
primary receptor on T cells
function/important feature
CD4
function
drives B cell proliferation
secrete IL4,5,6,10
can dampen TH1 activity
T reg
primary receptor on T cells
function/important feature
involve in development of immune tolerance
suppression of pathological immune responses, inflammation, autoimmunity (“reduce excess immune reaction”)
T cytotoxic cell
primary receptor on T cells
function/important feature
CD8
Function
lysis target foreign cell
destruction of cancer cells, virus infected cells
graft rejection
requires MHCI for function may have some regulatory function
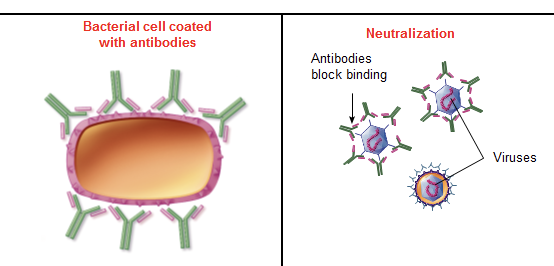
neutralization
antibody react w/ surface molecules of bacteria/viruses → prevent them from attaching to surfaces or cell receptor
also can neutralize enzymes or toxin involved in disease pathogenesis
ex. covid - vaccine create Ab attach to spike protein of covid
bacteria and virus needs to attach, without they can’t enter cell
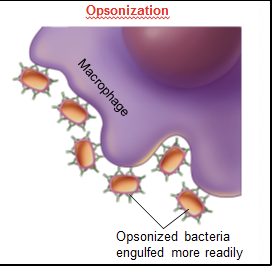
Opsonization
coating microorganisms or other particles w/ specific antibodies → recognized by phagocytes → engulfed/destroyed
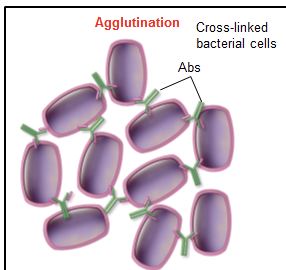
agglutination
crosslinking cells or particles with antibody into large clumps
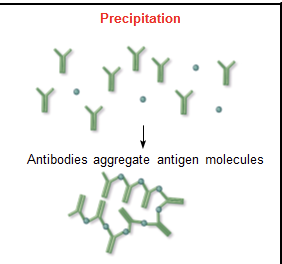
precipitation
aggregation of soluble or finely particulate antigen with antibody
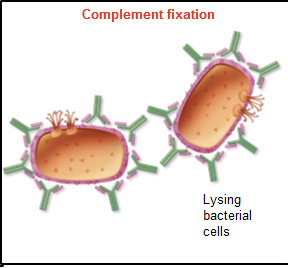
complement fixation
activate of classical complement pathway → result in specific rupturing of cells and some viruses
IgG
shape
function
prevalance
monomer → 2 antigen binding
function
long term immunity
neutralize toxins and viruses
produced in plasma cells by primary response; in memory cells via secondary response (memory antibody)
prevalance
MOST prevalent (80% in total antibody serum)
IgA
shape
function
prevalance
monomer circulates in blood → 2 antigen binding
dimers in mucous and serous secretion → 4 antigen binding
type
secretory antibody
Prevalence in serum
13%
IgM
shape
function
prevalance
5 monomers (pentamers) → 10 antigen binding sites
function
produced at first response to antigen
can serve as b cell receptor
prevalence and size
6%
biggest
IgD
shape
function
prevalance
monomers → 2 antigen binding site
Function
serve as receptor on B cells for antigen recognition
Prevalence
0.001%
IgE
shape
function
prevalance
monomers → 2 antigen binding sites
function:
antibody of allergy; reactions against parasitic worm infection
prevalence
0.002%
which immunoglobulin classes cross placenta?
IgG only
which immunoglobulin classes fixes complement
IgG and IgM
what does each immunoglobulin classes binds to
G
phagocytes
A
epithelial cells - cuz involve with mucous memory
M
NA
E
NA
D
mast cells and basophils - cuz involve with allergy
average life in serum
G - longest
23 days
A
6
M
5
E
3
D
2.5
another name for secondary response of antibody
anamnestic response