AP PSYCH - unit 3.2: developmental psychology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
developmental psychology studies how changes in our biology and social situations over our lifespan influence our development
what does developmental psychology study?
- chronological order of development
- themes across the lifespan
what are ways in which developmental psychology is studied?
- stability and change (traits persist, unchanging or changing as we age?)
- nature and nurture (genes or environment?)
- continuous and discontinuous stages of development (gradual development over time or development in stages?)
what are the thematic issues in developmental psychology? (3)
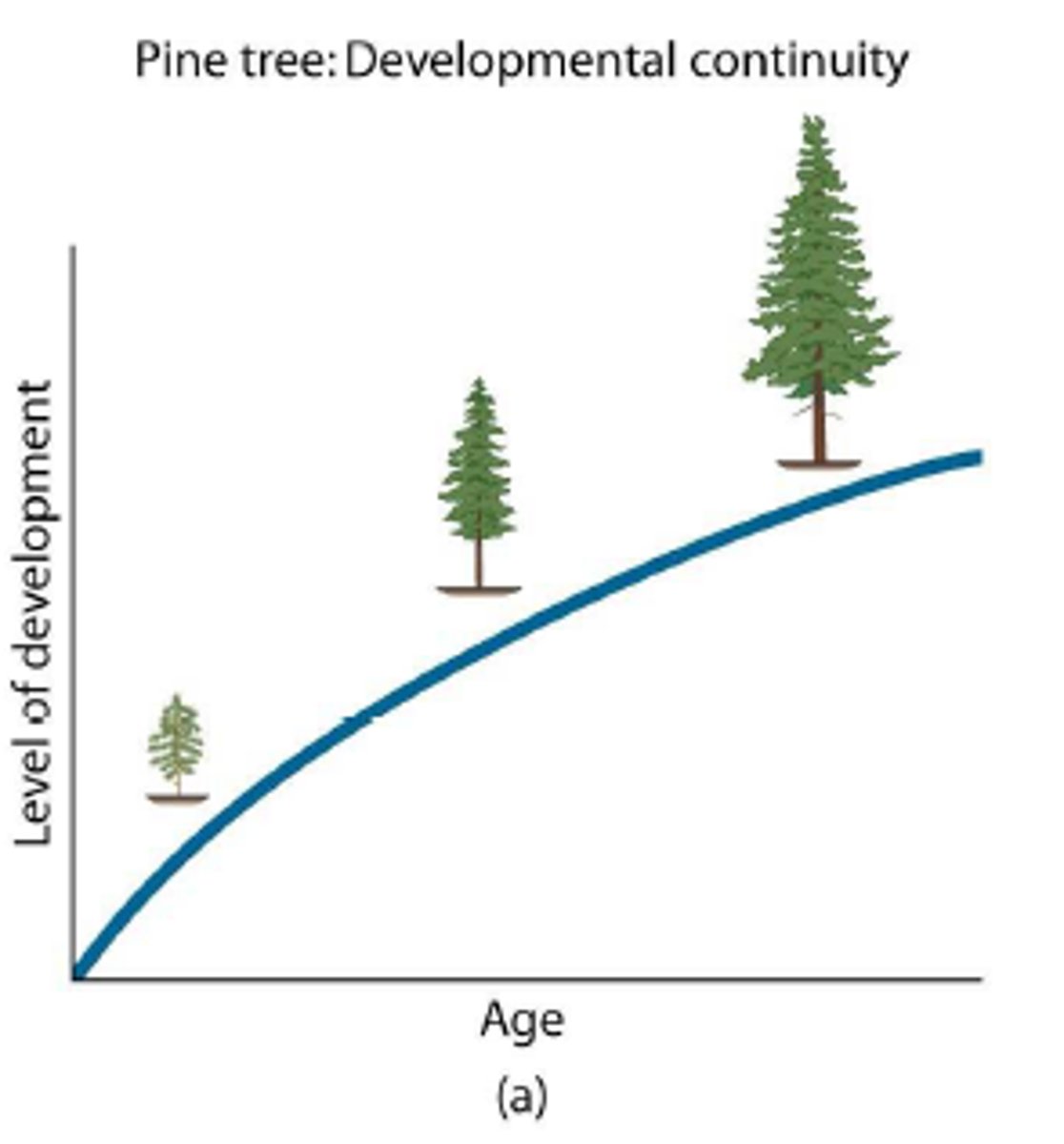
continuous development
development in a slow and continuous process
ex. baby sits up, crawls, stands, then walks
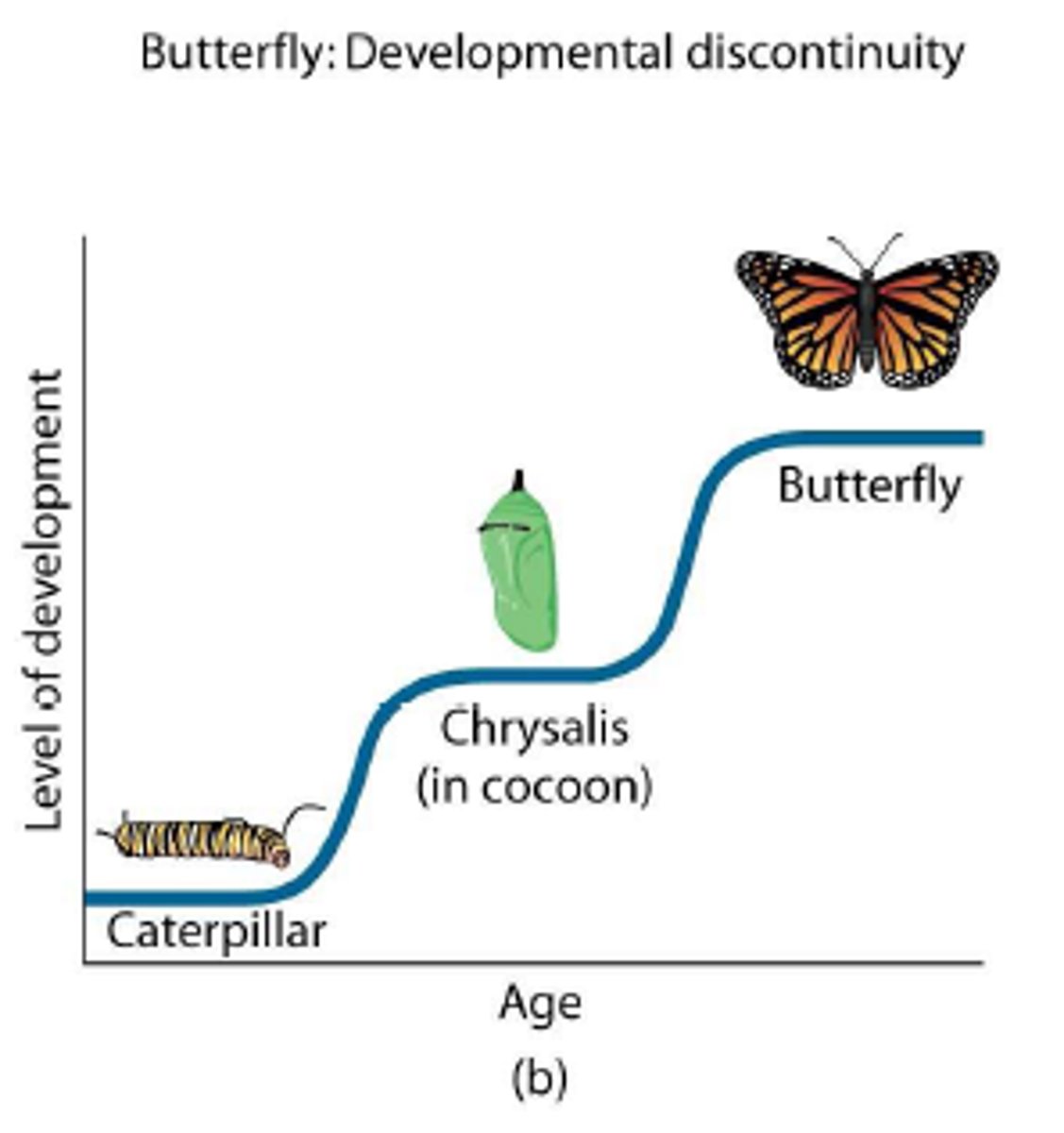
discontinuous development
idea that development takes place in district stages
ex. terrible 2s, adolescence, adulthood
cross-sectional studies
research when people of different ages are compared with one another
pro: can be completed quickly
con: different age groups are not always alike
longitudinal studies
research when the same people are studied over a long period
pro: detailed info about subjects
con: expensive and time-consuming
teratogens
agents that can harm the baby during prenatal development
ex. drugs, alcohol
fetal alcohol syndrome
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking
- low birth weight
- delays in physical and mental abilities
illness, mutations, hormones, the environment
besides teratogens, what else can impact prenatal development? (4)
reflexes
unlearned, organized involuntary responses that occur automatically in the presence of certain stimuli
- go away with time
grasping reflex
touch palm - close fist

rooting reflex
stroke cheek - opens mouth
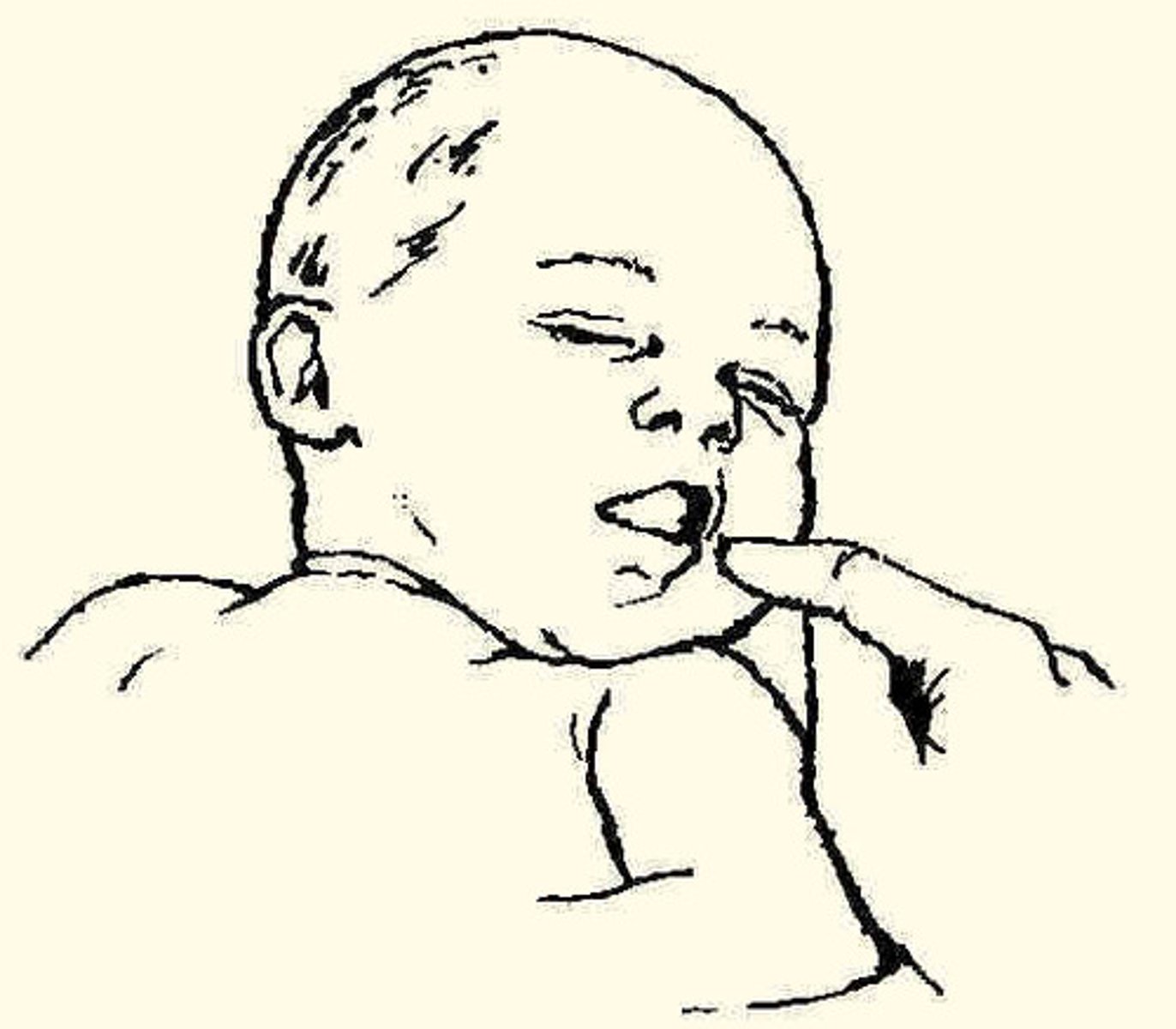
sucking reflex
touch mouth - sucks on object

babinski reflex
stroke foot - splays toes
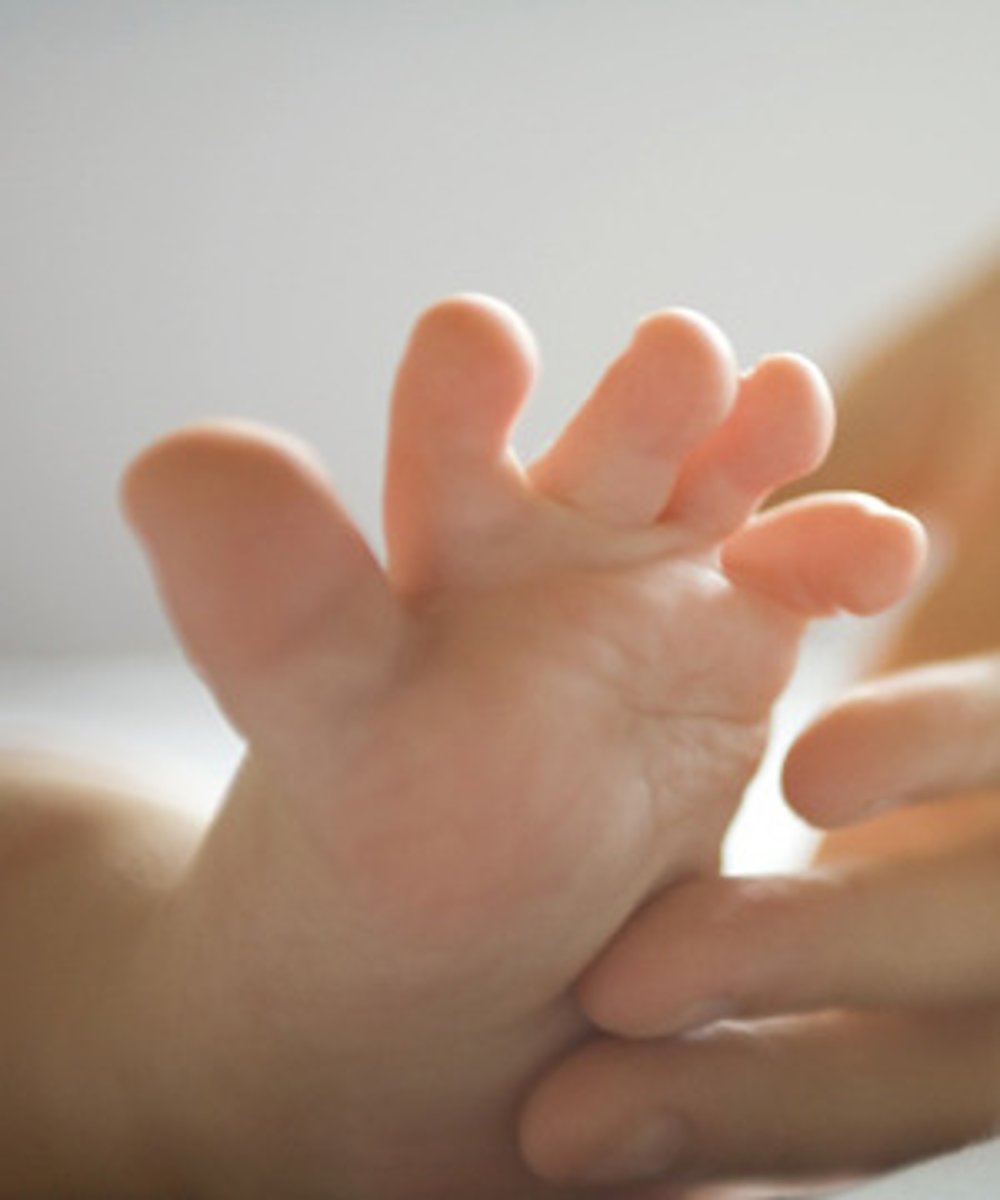

moro reflex (startle reflex)
sudden sound - throw out arms
gross motor skills
coordination on large body movements
ex. sitting (6 months), crawling (8 months), walking (1 year)

fine motor skills
coordination on small body movements
ex. pincer grasp

maturation
natural course of development, occurs no matter what; order of biological growth
ex. walking
maturing
the process of becoming an adult
- motor development is universal
- ages of development are at average ages
- physical maturation is genetics influenced by environment
what are the developmental norms of maturation?
critical period
period when certain experiences are required for development
ex. language for humans
imprinting
the process by which animals develop close bonds with the animal it first meets
ex. Konrad and his geese
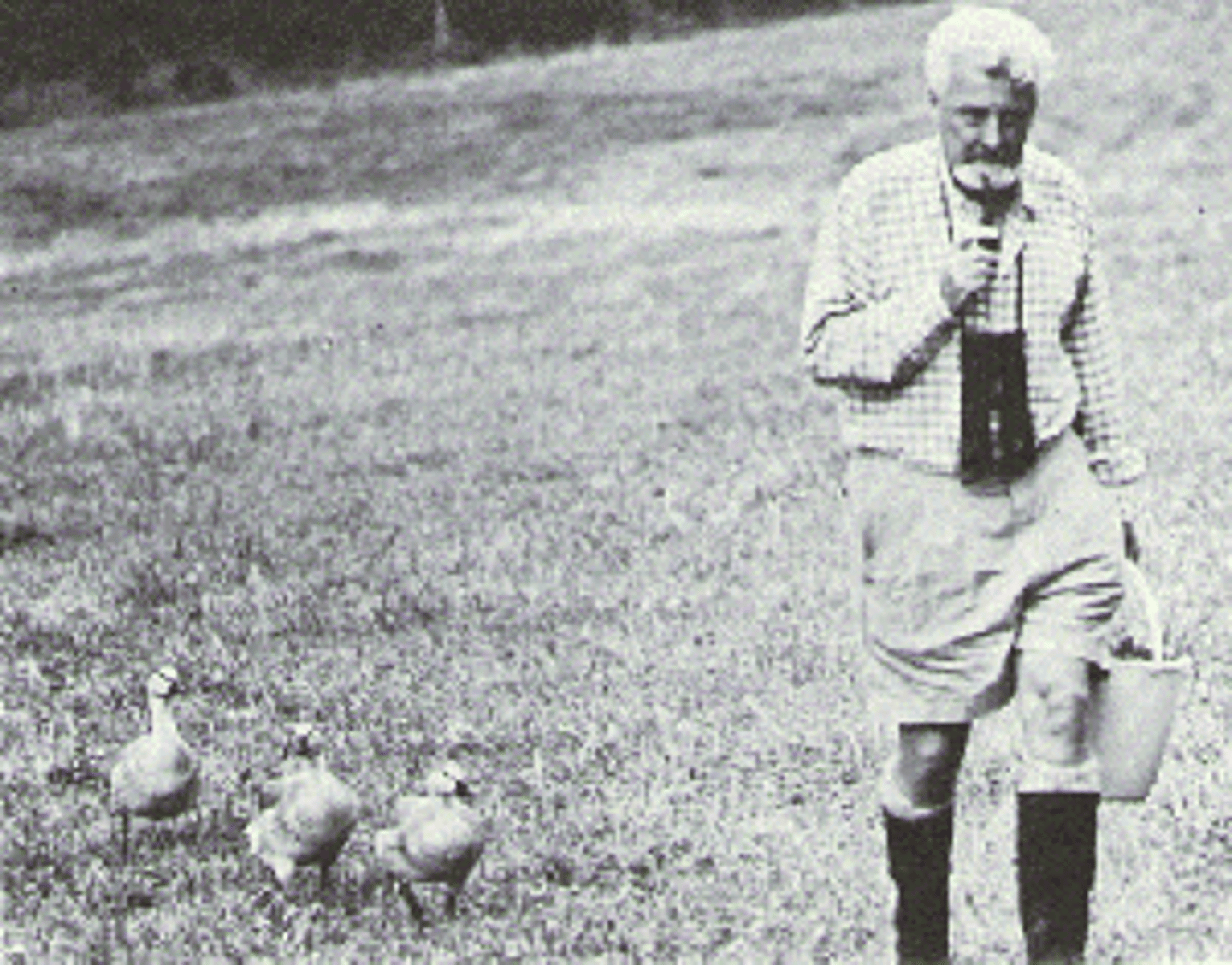

the eyes have the most limited development, takes 1 year to fully develop
what part of the body has the most limited development?
infantile amnesia
the inability to remember events from early childhood
- earliest age of conscious memory is around 4 years old
the hippocampus is developing
why does infantile amnesia occur?
primary sex characteristics
the body structures that make sexual reproduction possible
ex. ovaries, testes
secondary sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics that develop during puberty
ex. body hair
menarche
first menstrual period
spermarche
first ejaculation
sex
the biological distinction between females and males
- determined by chromosomes and hormones; testosterones from testes for males and estrogen from ovaries for females
gender roles
socially constructed roles of males and females
- these change over time

- schemas
- assimilation and accommodation
- four stages of cognitive development
Piaget's cognitive theory of development is based on what key ideas? (3)
schemas
frameworks created by the brain to organize and understand information
- changes because of experiences
ex. A child sees dogs as animals that are furry and have four legs. When they see a cat for the first time, they call it a dog.
assimilation
when we add new information to a schema that we already know
ex. A child who knows that dogs are furry and have four legs sees a cat for the first time and calls it a dog.
accomodation
adjusting our current schemas to incorporate new information
ex. After calling a cat a dog, a child learns that cats are different from dogs (they meow, not bark). The child adjusts their schema to accommodate the new understanding that not all four-legged furry animals are dogs.
maturation (biological growth)
what does Piaget's theory of four stages of cognitive development believe that the force behind cognitive development is?
- sensorimotor stage (0-2)
- preoperational stage (2-7)
- concrete operational stage (7-12)
- formal operational stage (12+)
what are the four stages of cognitive development?
focused on exploration of the world
what is the focus in the sensorimotor stage?
- object permanence
- stranger anxiety
what occurs in the sensorimotor stage?
object permanence
in sensorimotor stage, the awareness that objects continue to exist even when not perceived
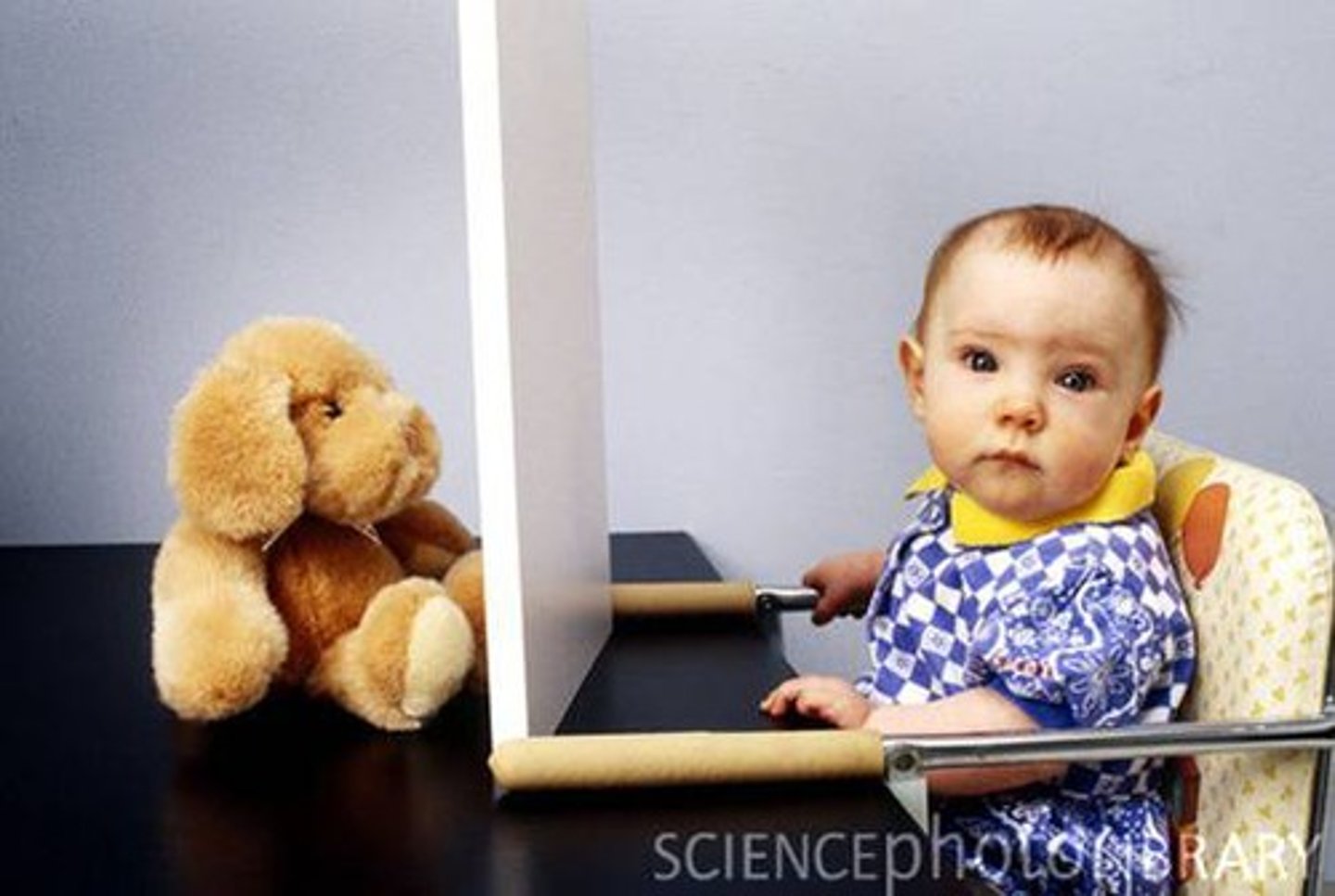

stranger anxiety
in sensorimotor stage, crying when an unfamiliar person approaches

use pretend play and mental symbols
what is the focus in the preoperational stage?
- pretend play
- animism
- centration
- egocentrism (lack theory of mind)
- conservation
- reversibility
what occurs in the preoperational stage?
pretend play
in preoperational stage, the playful use of ideas and symbols

animism
in preoperational stage, the belief that inanimate objects have feelings and act like they're alive
centration
in preoperational stage, focus on one aspect of a situation and exclude other parts
- "spotlight"

egocentrism
in preoperational stage, the difficulty of taking another's point of view
theory of mind
ability to understand that other people have their own thoughts and beliefs, different from our own
conservation
in preoperational stage, the principle that quantity remains the same despite changes in shape
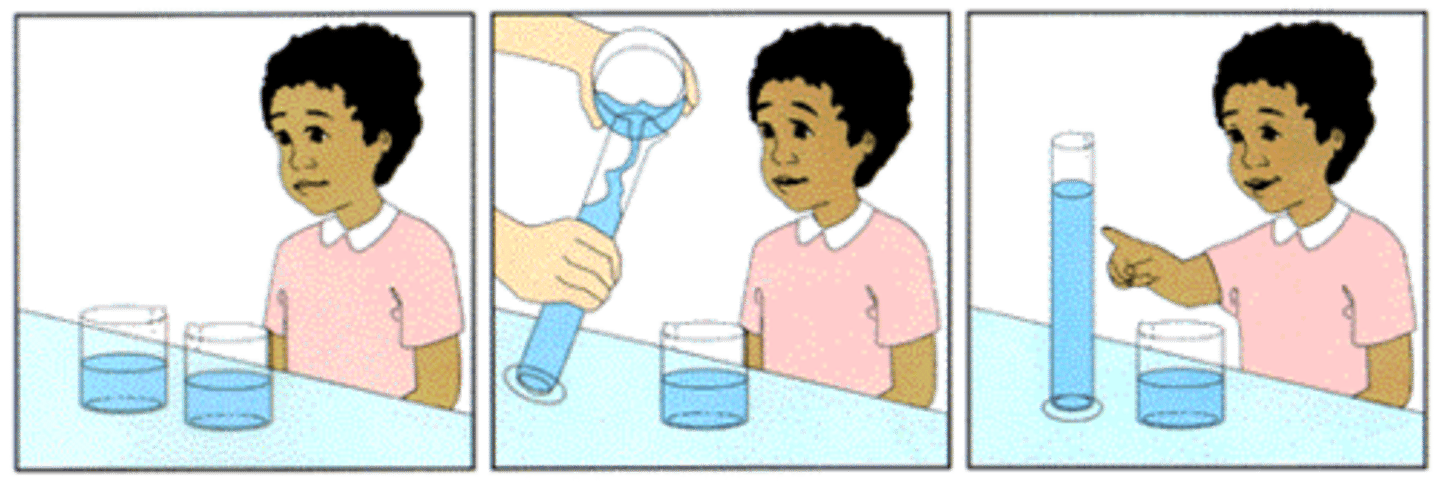

reversibility
in preoperational stage, understanding that things can be reversed

use operational thinking, classification, and can think logically in concrete context
what is the focus in the concrete operational stage?
- logical thought: thinking logically about concrete situations
what occurs in the concrete operational stage?
use abstract and idealist thoughts, hypothetical-deductive reasoning
what is the focus in the formal operational stage?
- hypotheticals
- moral reasoning
- planning for future
- metacognition
what occurs in the formal operational stage?
hypotheticals
in formal operational stage, possible outcomes and consequences; "what if" questions

metacognition
in formal operational stage, the ability to think about how you think
- awareness of strengths and weaknesses and how to use or change them

the environment
what did Vygotsky emphasize in cognitive development of children?
scaffolding
learners complete small, manageable steps to learn more difficult information
ex. A teacher helps a student solve a math problem by guiding them step-by-step at first. As the student gains understanding, the teacher gradually reduces help until the student can solve similar problems independently.
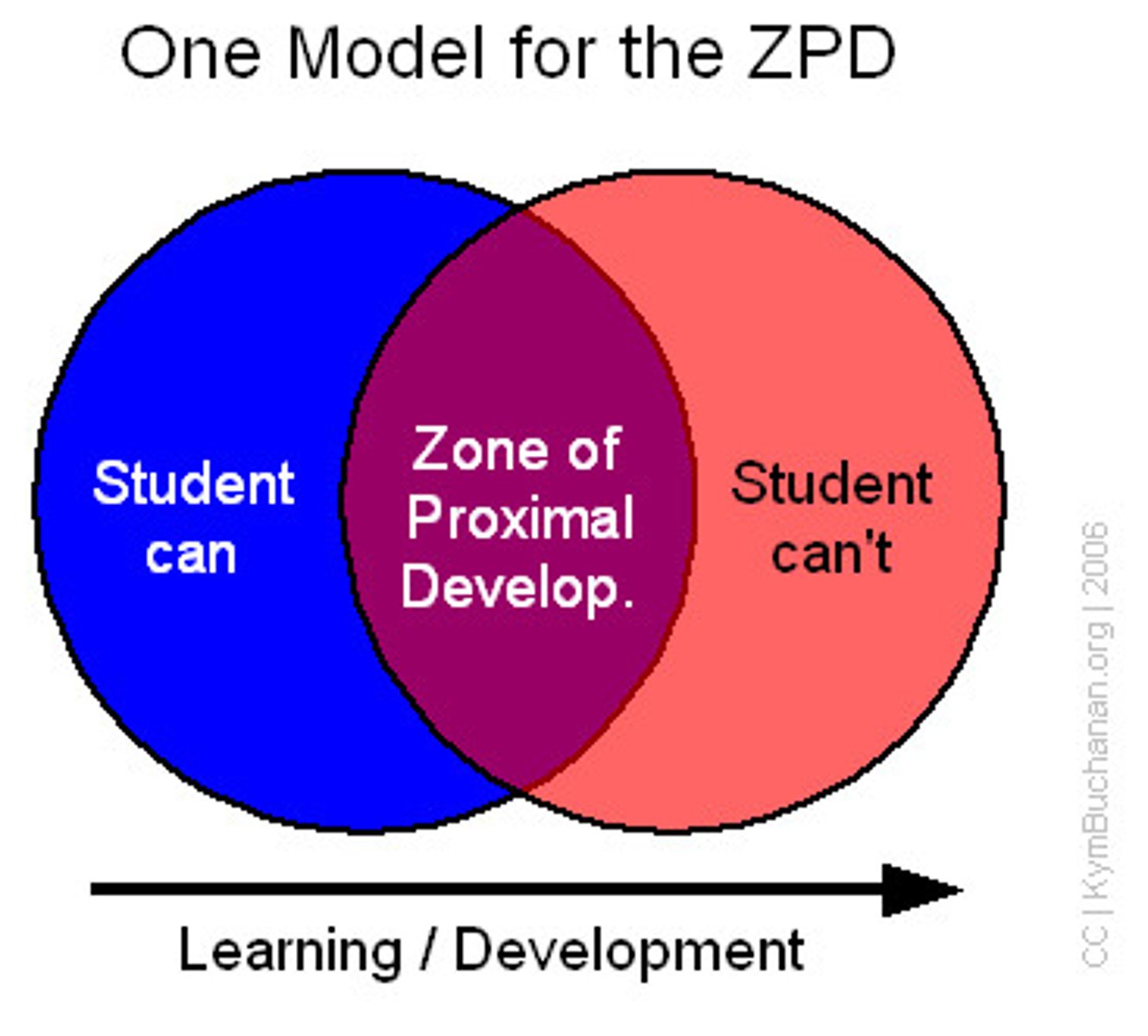
zone of proximal development (ZPD)
the gap between what a child can do and what they cannot do
- where the sweet spot of learning occurs
- needs scaffolding
crystallized intelligence
the ability to retain and use knowledge that was acquired through experiences and prior learning
- increases with age
ex. An older adult uses their knowledge of vocabulary and world history to win a trivia game.
fluid intelligence
the ability to learn new things, reaction times, abstract thinking and quick problem solving
- decreases with age
ex. A young adult quickly solves a new type of puzzle they've never seen before by identifying patterns and thinking logically.
dementia
loss of cognitive function that results in emotional and behavioral changes
ex. Alzheimer's
- authoritarian
- permissive
- authoritative
- negligent
what are Baumrind's parenting styles? (4)
how responsive and how demanding parents are
- parenting is a mix of each with a focus on one
what two traits does Baumrind's parenting styles combine?
authoritatian
parenting style with set rules and expected obedience
- children lack independence and make poor decisions; low self-esteem
ex. A parent tells their child, "Because I said so," when the child asks why they have a strict 8 PM bedtime, and does not allow discussion or input.
permissive
parenting style with few rules and few demands
- children become assertive and impulsive; high self-esteem
ex. A parent lets their child stay up as late as they want, watch any show, and eat candy for dinner without setting rules or consequences.
authoritative
parenting style with set rules and open discussion
- children become self-reliant and have high competence; high self-esteem and initiative
ex. A parent sets a 9 PM bedtime but explains the reason and listens to their child's input, adjusting slightly when appropriate.
negligent
parenting style that is fully uninvolved
ex. A parent is rarely home, doesn't ask about their child's day, and provides little guidance, attention, or emotional support.
authoritative parenting style
what is the best parenting style?
adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
traumatic events that occur in childhood that impacts development
ex. physical/mental abuse, growing up during war
- physical/mental health problems
- criminality
- lower intelligence scores
- reduced brain development
what are the results of ACEs on development? (4)
attachment
an emotional bond with another person
Freud's cupboard theory found that infants become attached to those who provide nourishment; attachment is survival
what did Sigmund Freud's cupboard theory state?
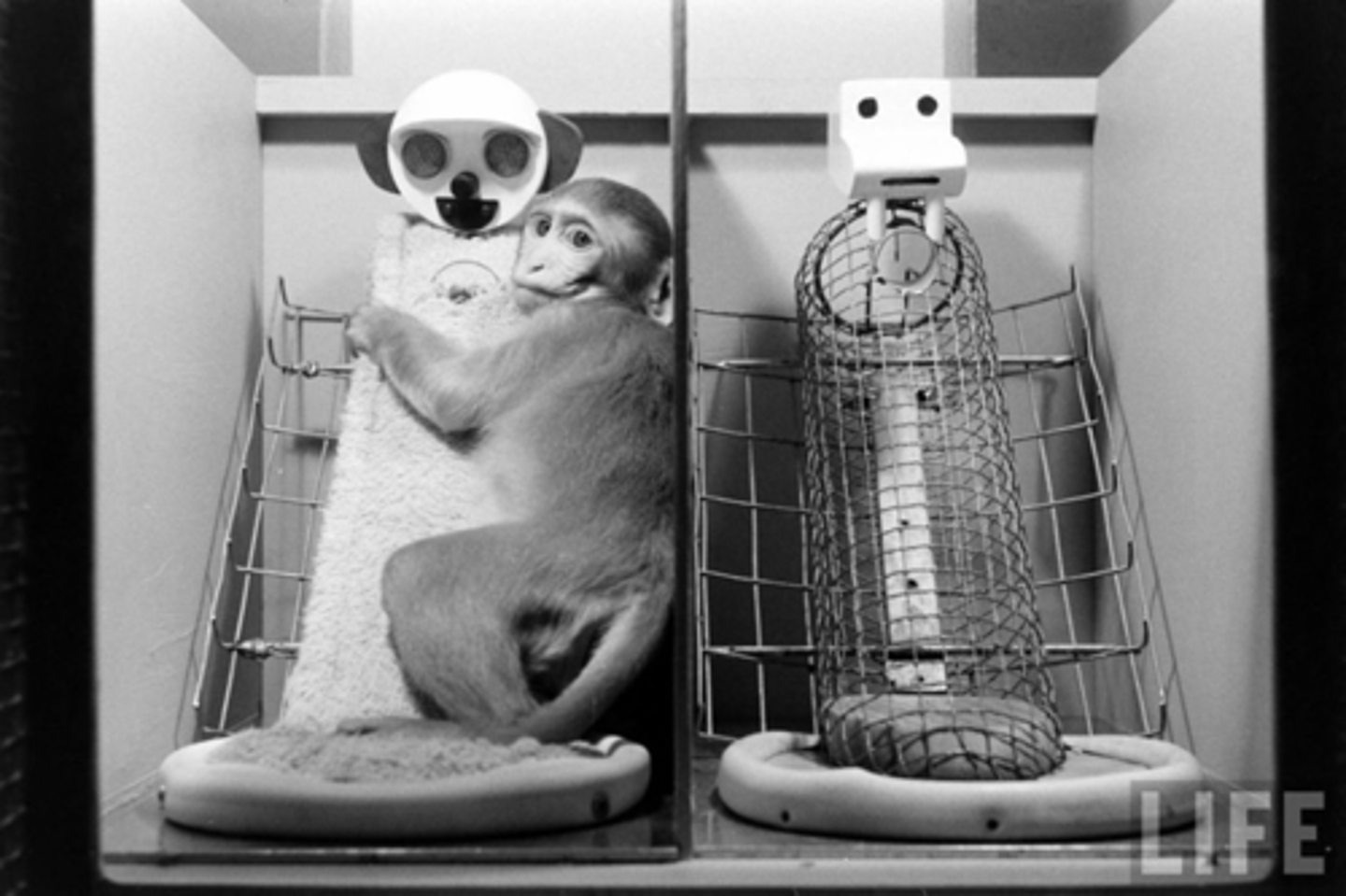
the infant monkeys preferred contact with the soft cloth mother over the bottle wire monkey; found that physical contact was important to form attachment and contact comfort is more important than feeding
what did Harry Harlow's monkey experiment find?

conducted experiments to investigate if parenting attachment impacts child's later formation of attachment; found that maternal sensitivity to the infant's needs were important to develop mater attachments
what was the significance of Mary Ainsworth's strange situation experiment in the 1970s?
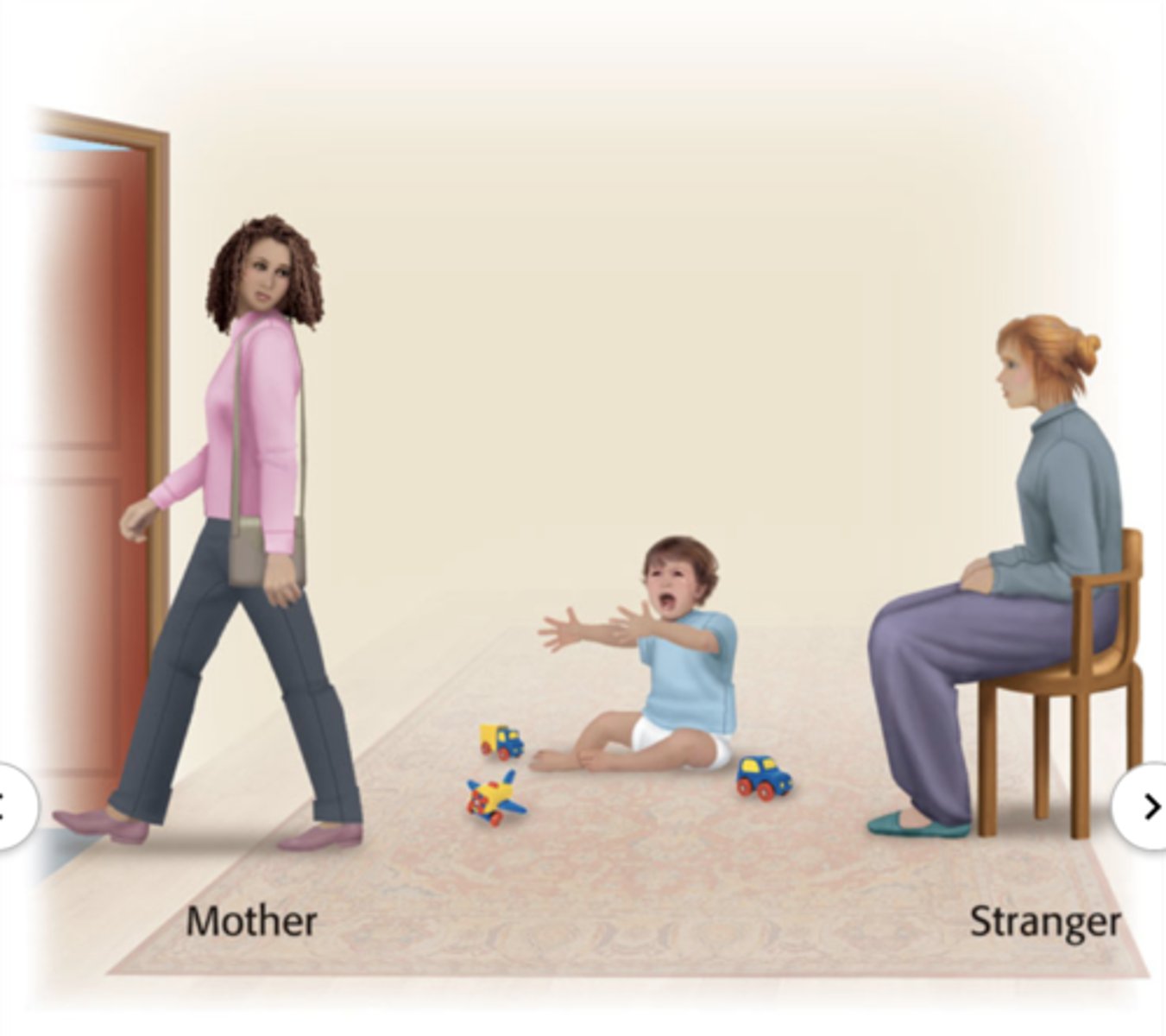
secure attachment
attachment style where the caregiver consistently responds
children develop healthy relationships, trust, and self-esteem
secure attachment
what attachment style is this?
A toddler explores a new room but regularly checks back with their parent. When the parent leaves, the child is upset but calms down quickly when they return.
anxious attachment
insecure attachment style where the caregiver inconsistently responds
children become needy and have low self-esteem
anxious attachment
what attachment style is this?
A child clings to their parent and is very distressed when the parent leaves. When the parent returns, the child is not easily comforted and may seem both clingy and upset.
avoidant attachment
insecure attachment style where the caregiver has an emotionally distant response
children avoid getting close to others and have difficulty maintaining relationships later on in life
avoidant attachment
what attachment style is this?
A child shows little reaction when their parent leaves the room and avoids seeking comfort when the parent returns, preferring to play independently.
disorganized attachment
insecure attachment style where the caregiver has a confusing mixed response
children develop to crave relationships but avoid them and become confrontational
disorganized attachment
what attachment style is this?
A child approaches their parent when they return but then freezes or suddenly backs away, showing confusion and fear.
temperament
a person's inborn emotional reactivity and intensity
- impacts attachment
identity
one's sense of self
during adolescence
when is the focus on finding identity?
exploration - options to explore for whom they can become
commitment - committing to options
what are the parts that make up finding one's identity?
diffusion, moratorium, foreclosure, achievement
what are the four states of Marcia's identity theory?
identity diffusion
low exploration and low commitment
- no commitment, no exploration, no idea who they are
ex. "I don't know and I don't care what I'm supposed to do with my life"
identity moratorium
high exploration and low commitment
- actively seeking an identity, no commitment
ex. "I'm thinking about what I should do"
identity foreclosure
low exploration and high commitment
- premature commitment with no exploration
ex. "I've made a choice without thinking; I'll be a lawyer because my parents said so"
identity achievement
high exploration and high commitment
- explored options, made identity commitments
ex. "I thought about it and I now know what I should do with my life"
parallel play
activity in which children play side by side without interacting
- turns into pretend play

adolescent egocentrism
heightened self-consciousness and self-absorption during adolescence
- characterized by: imaginary audience and personal fable
imaginary audience
adolescents' belief that they are the focus of everyone else's attention and concern
- everyone is constantly watching and judging which makes adolescents easily embarrassed
ex. A teenager gets a small pimple and feels like everyone at school will notice and judge them for it.

personal fable
adolescents' belief that they are so special, unique, and invincible
- think that their parents can't understand their problems and leads to increased risk-taking
ex. A teenager believes that no one could possibly understand their heartbreak because their feelings are uniquely intense and special.

social clock
shared (cultural) expectation of age-appropriate behavior
ex. when to get married, have kids, etc.

the ecological systems theory explored how different environments influence children's social development
what did Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory explore?
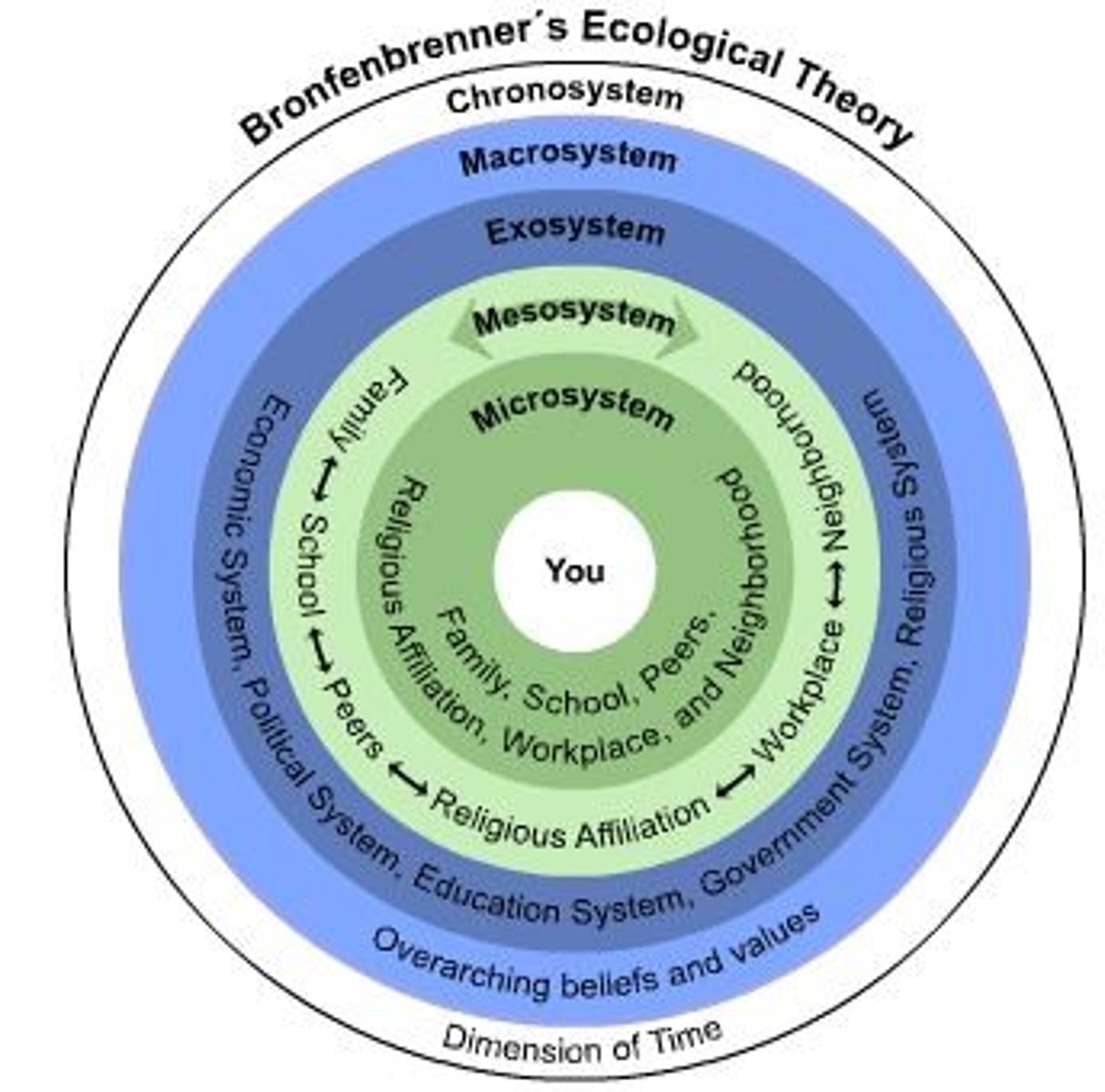
microsystem
in ecological systems theory, the innermost level of the environment, consisting of groups with direct contact with the child
- most influential
ex. A child's relationship with their parents, teachers, and classmates at school.