Chapter 7 The Nervous System and 8 Special Senses
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Contains: Spinal Cord and the Brain
Function: Command Center, Interprets incoming sensory information, Issues outgoing instructions
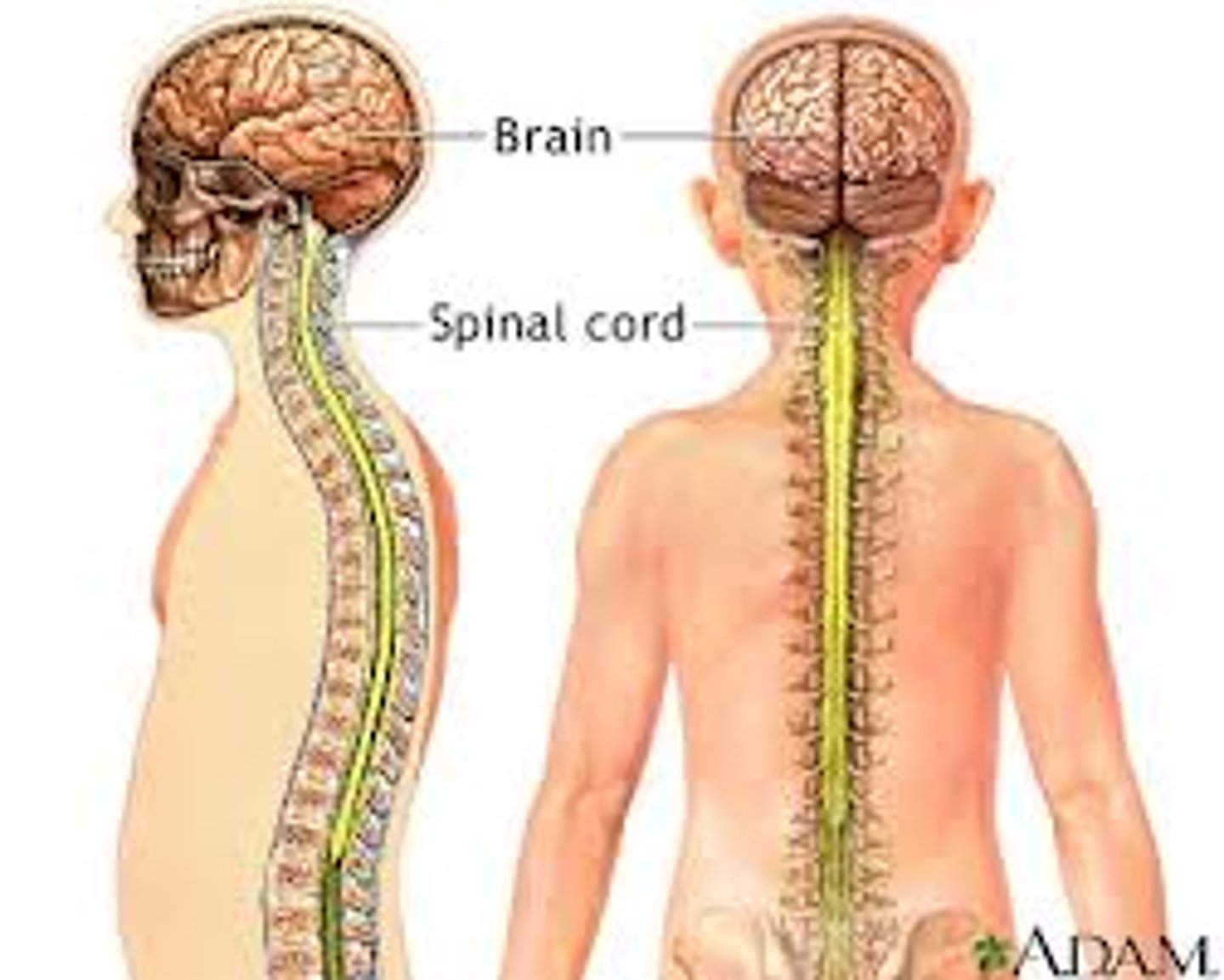
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Contains: Nerves extending from the brain and spinal cord
Functions: Serve as communication lines among lines among sensory organs, the brain and spinal cord, and glands or muscles.
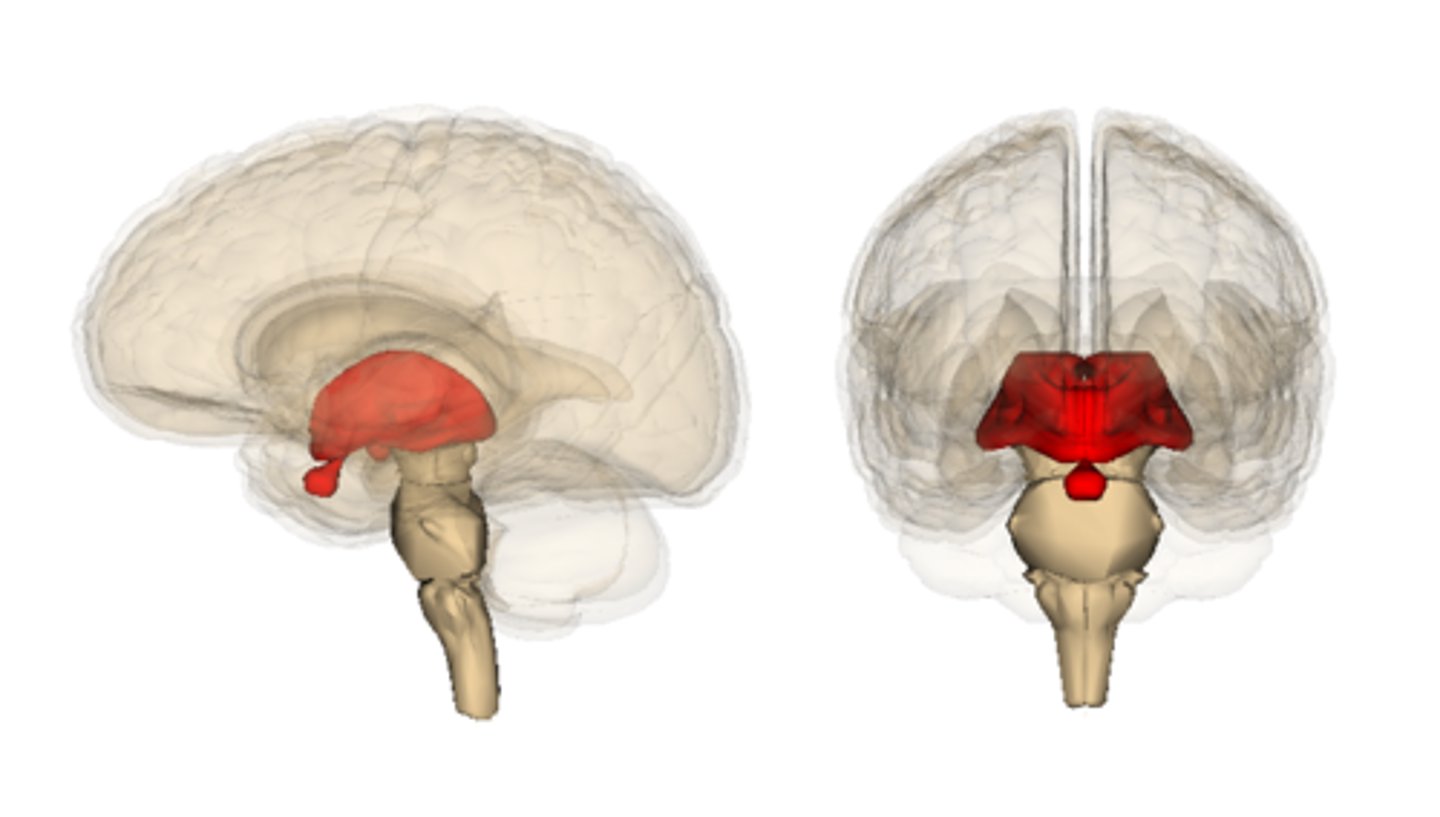
Diencephalon
-Sits on top of the brain stem
-Enclosed by central hemispheres
-Contains: Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
Hypothalamus
-Important autonomic nervous system
-Regulates body temperature
-Regulates water balance
-Regulates metabolism
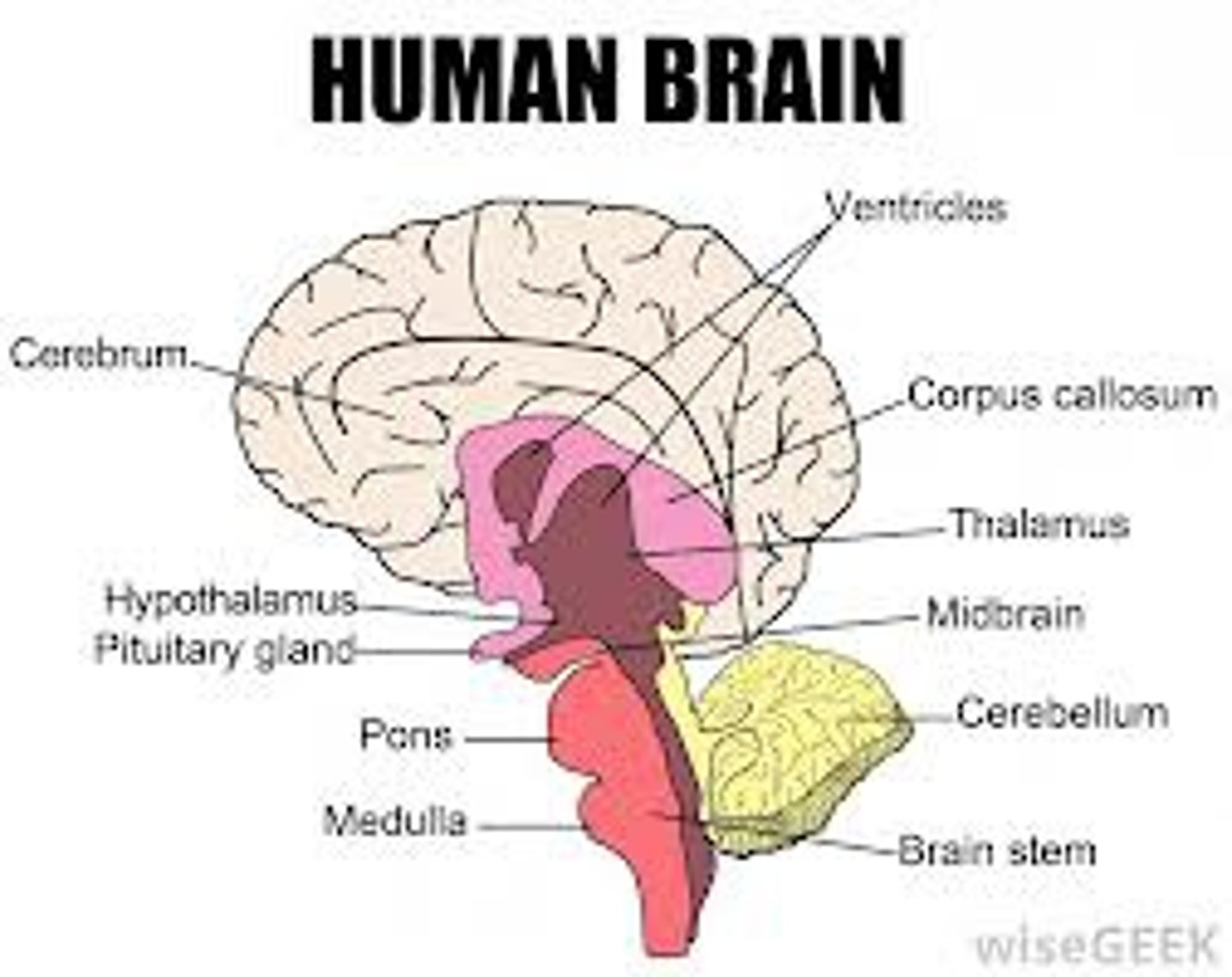
Thalamus
The brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem, it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
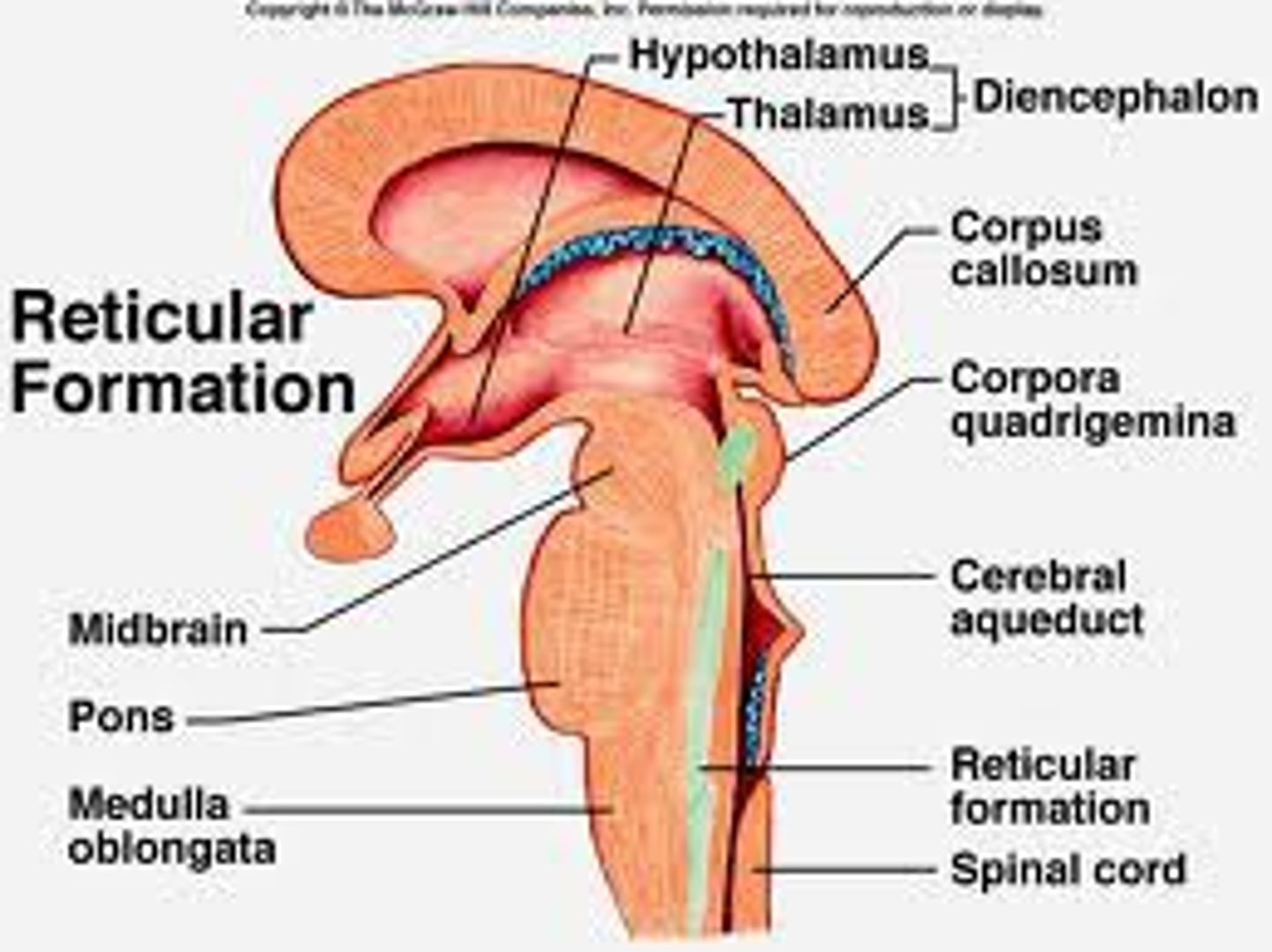
Brain Stem
-Attaches to the spinal cord
-Parts of the brain stem:
-Midbrain
-Pons
-Medulla oblongata
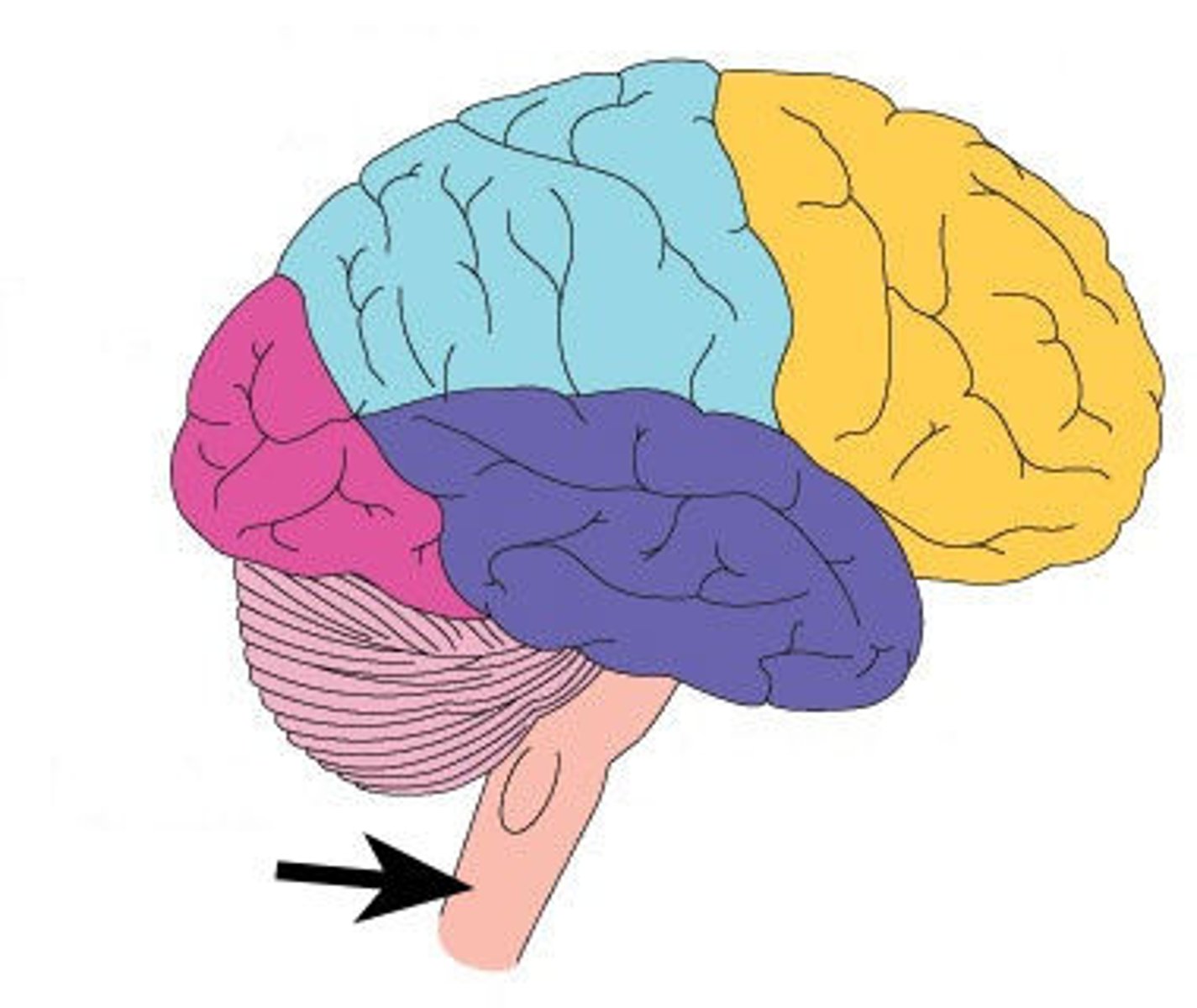
Pons
the part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus. Involved in the control of breathing
medulla oblongata
The most inferior part of the brain stem that merges into the spinal cord
Contains import centers that control:
-Heart rate
-Blood pressure
-Breathing
-Swallowing
-Vomiting
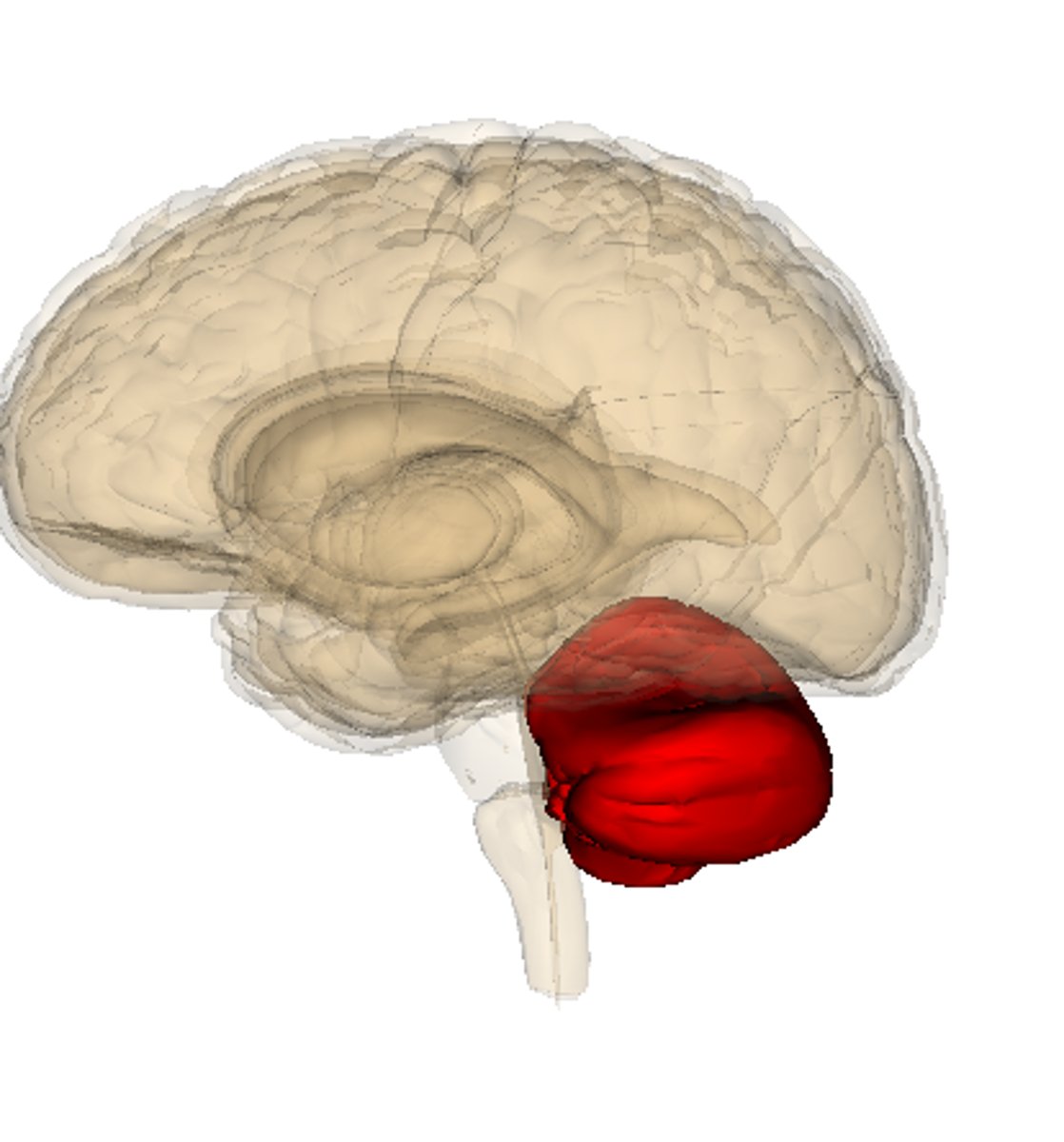
Cerebellum
-Two hemispheres with convoluted surfaces
-Controls balance
-Provides precise timing for skeletal muscle activity and coordination of body movements
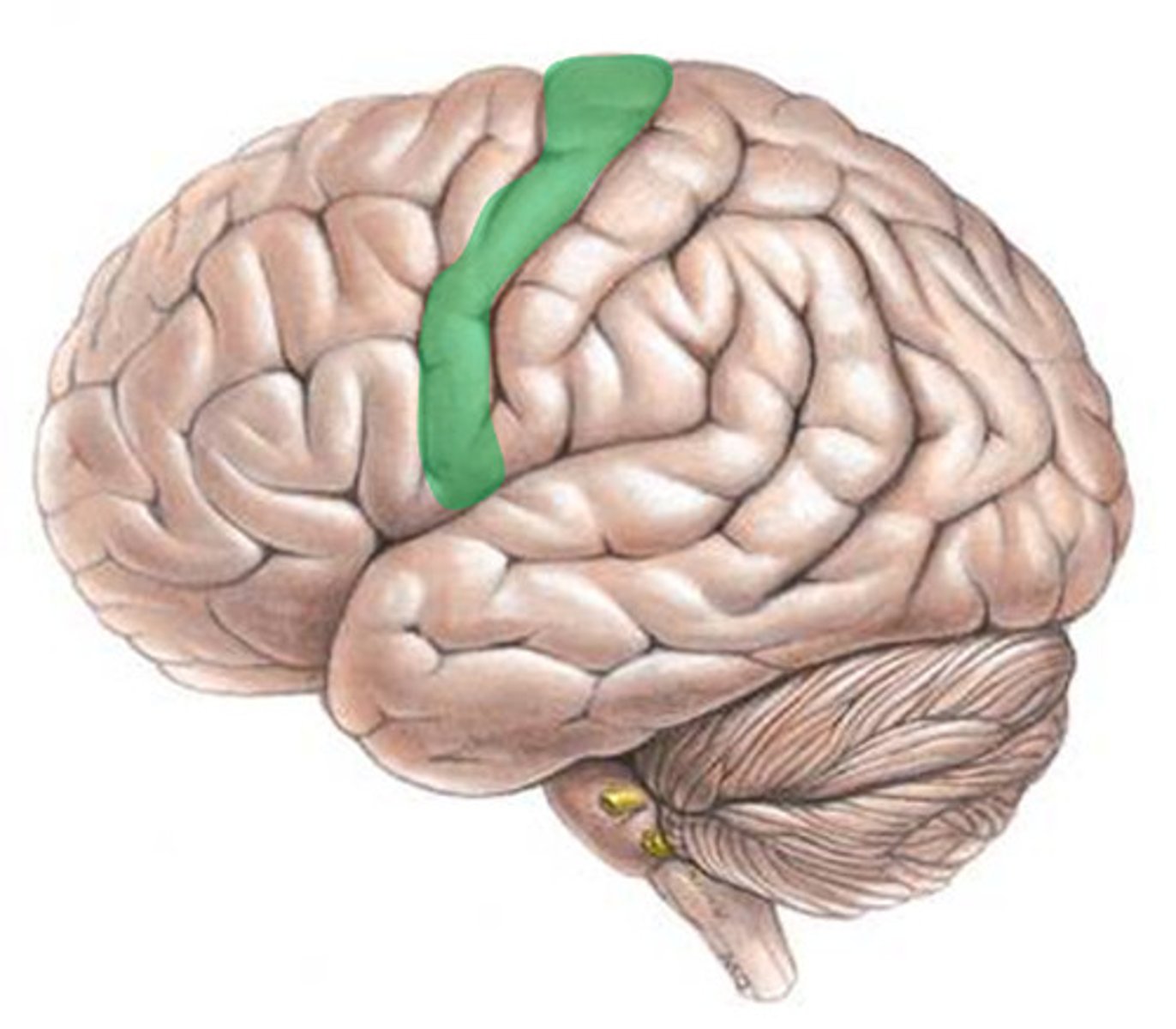
Primary motor area
-Located anterior to the central sulcus in the frontal lobe
-Allows us to consciously move skeletal muscles
-Motor neurons for pyramidal tract (corticospinal), which descends to spinal cord
-Motor homunculus is a spatial map
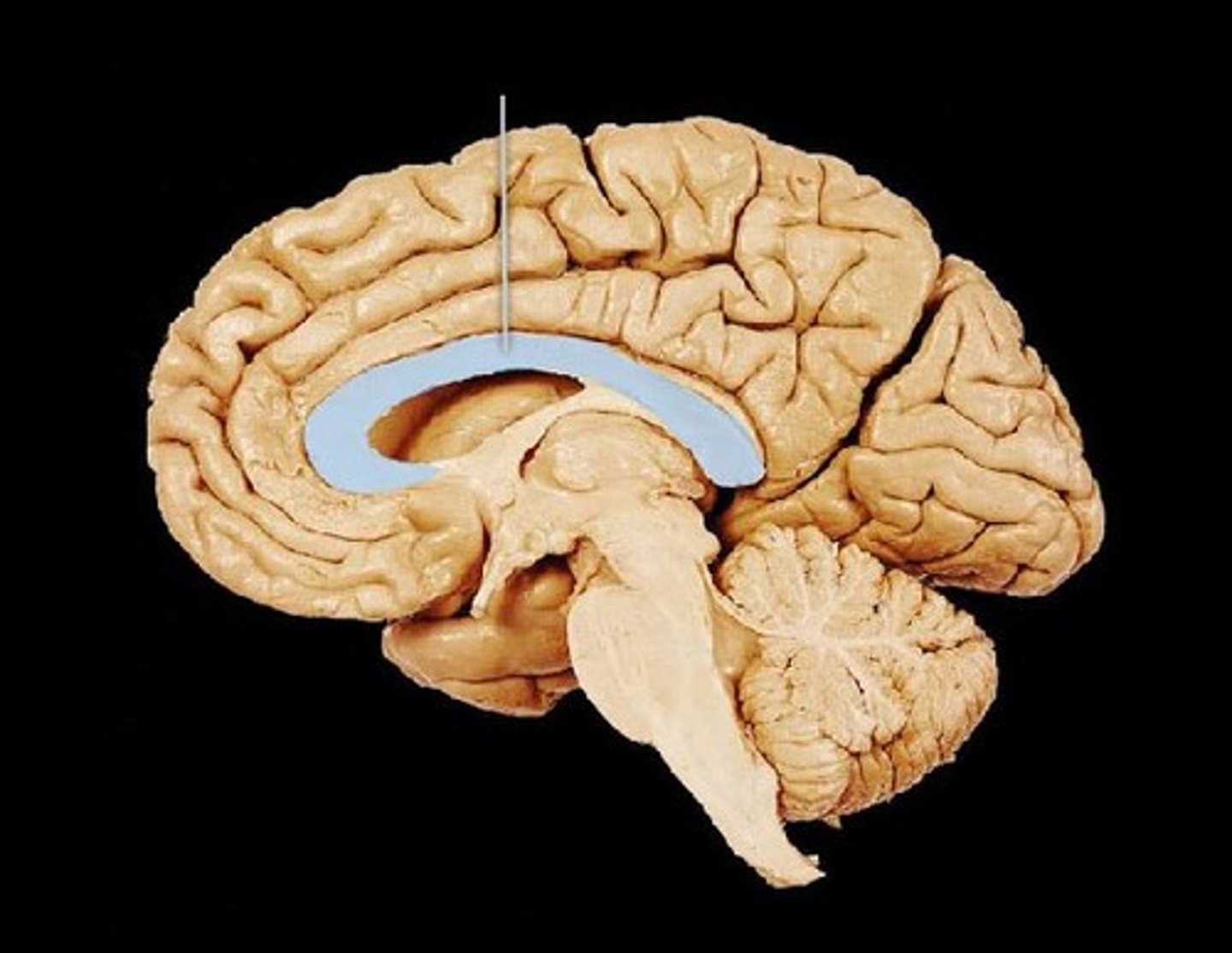
corpus callosum
connects brain hemispheres
autonomic nervous system
-Involuntary
- Controls smooth and cardiac muscles and glands
-Parasympathetic and Sympathetic
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
-Fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
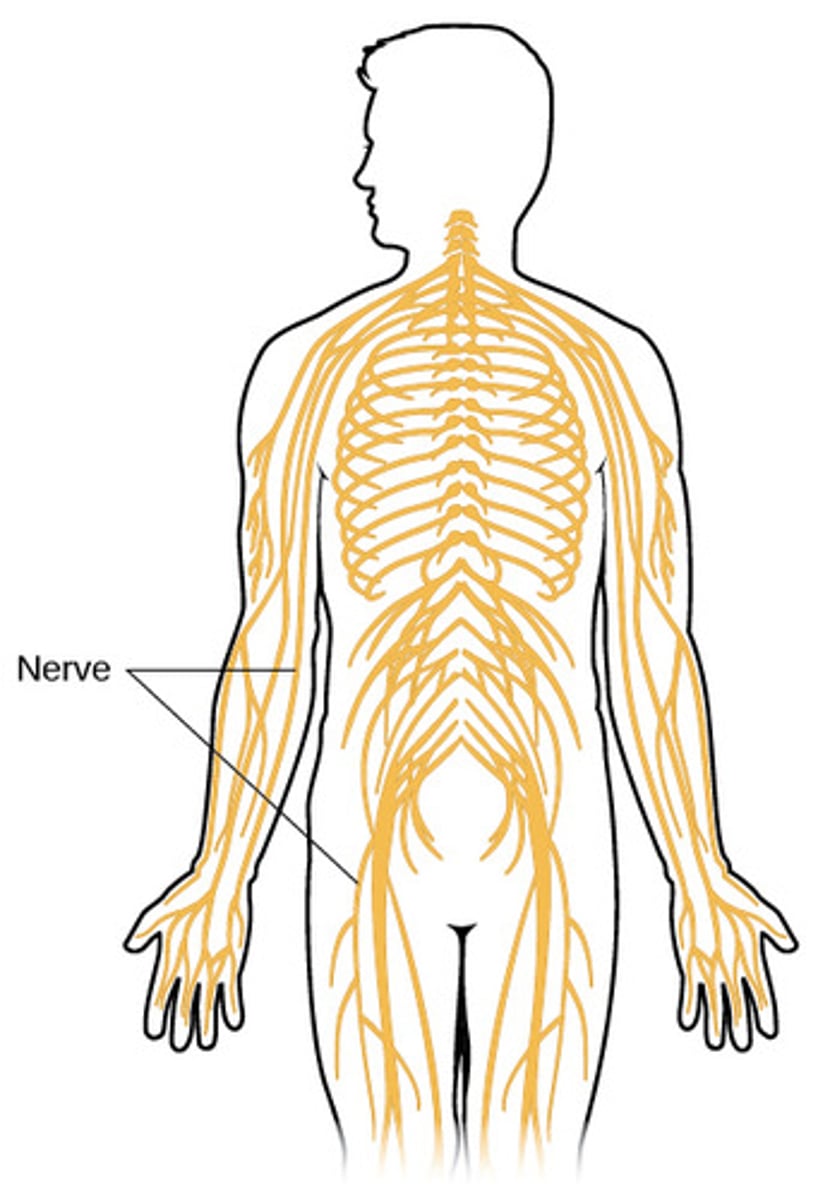
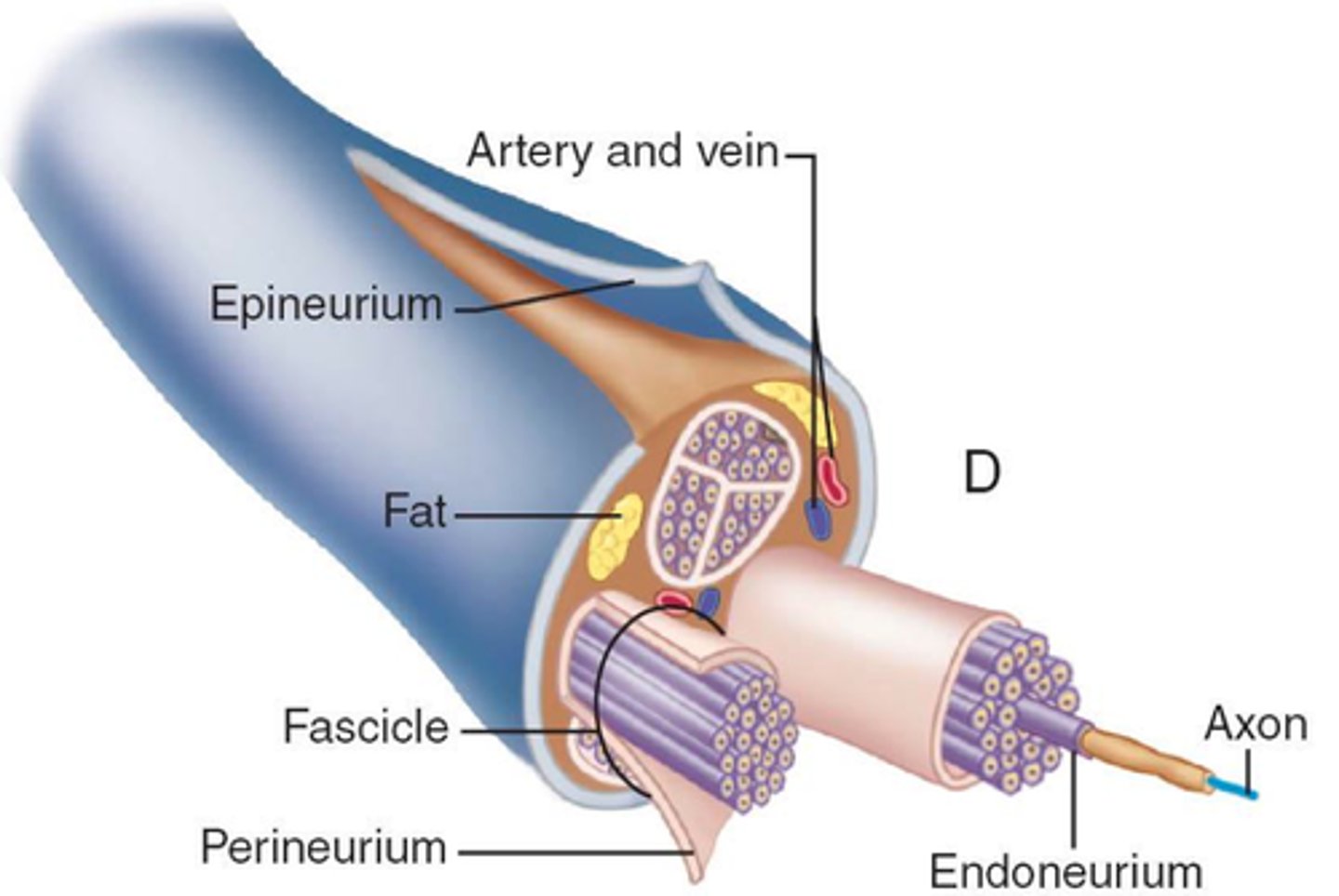
Nerves
bundles of neurons found outside the central nervous system
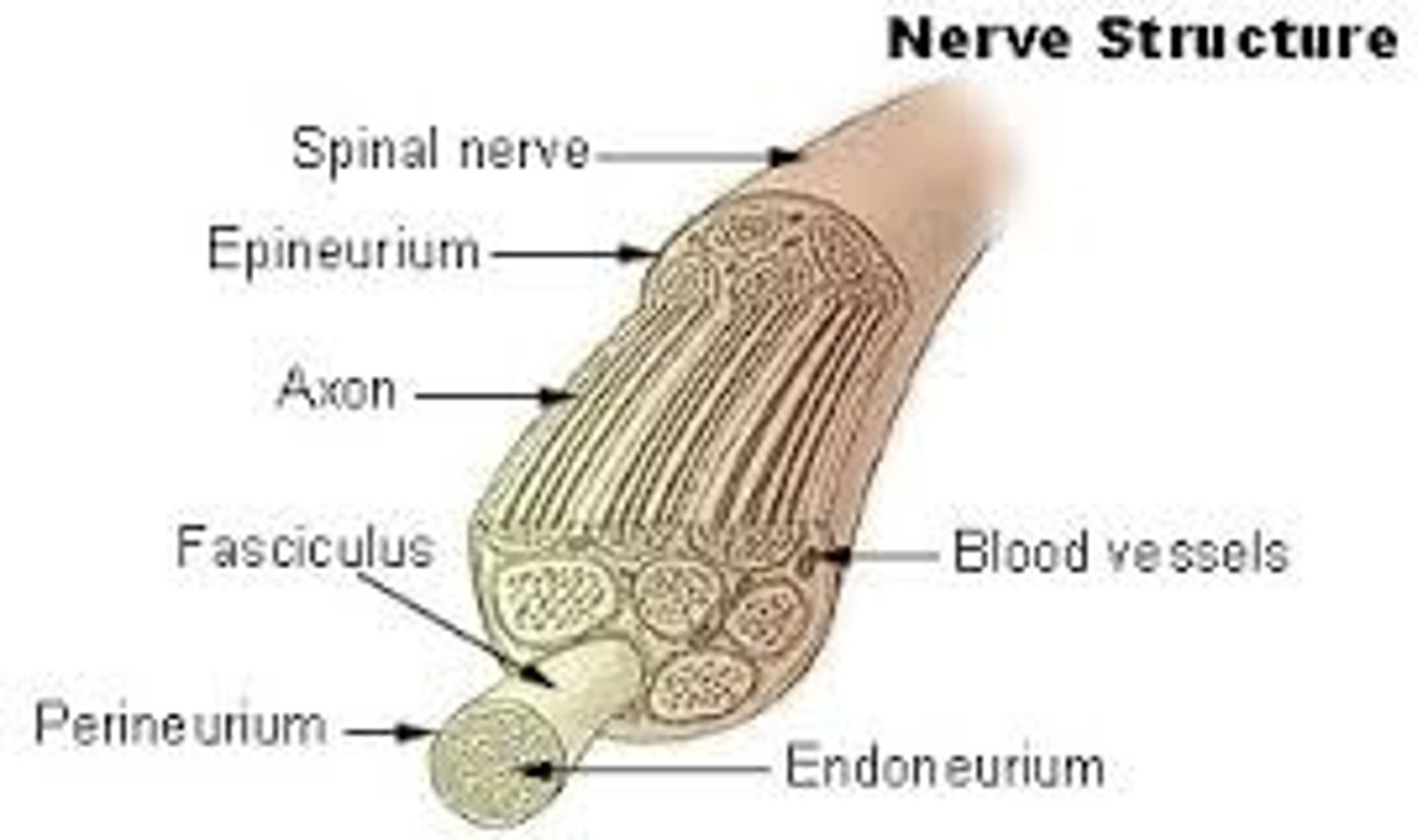
Endoneurium
A connective tissue sheath that surrounds each fiber
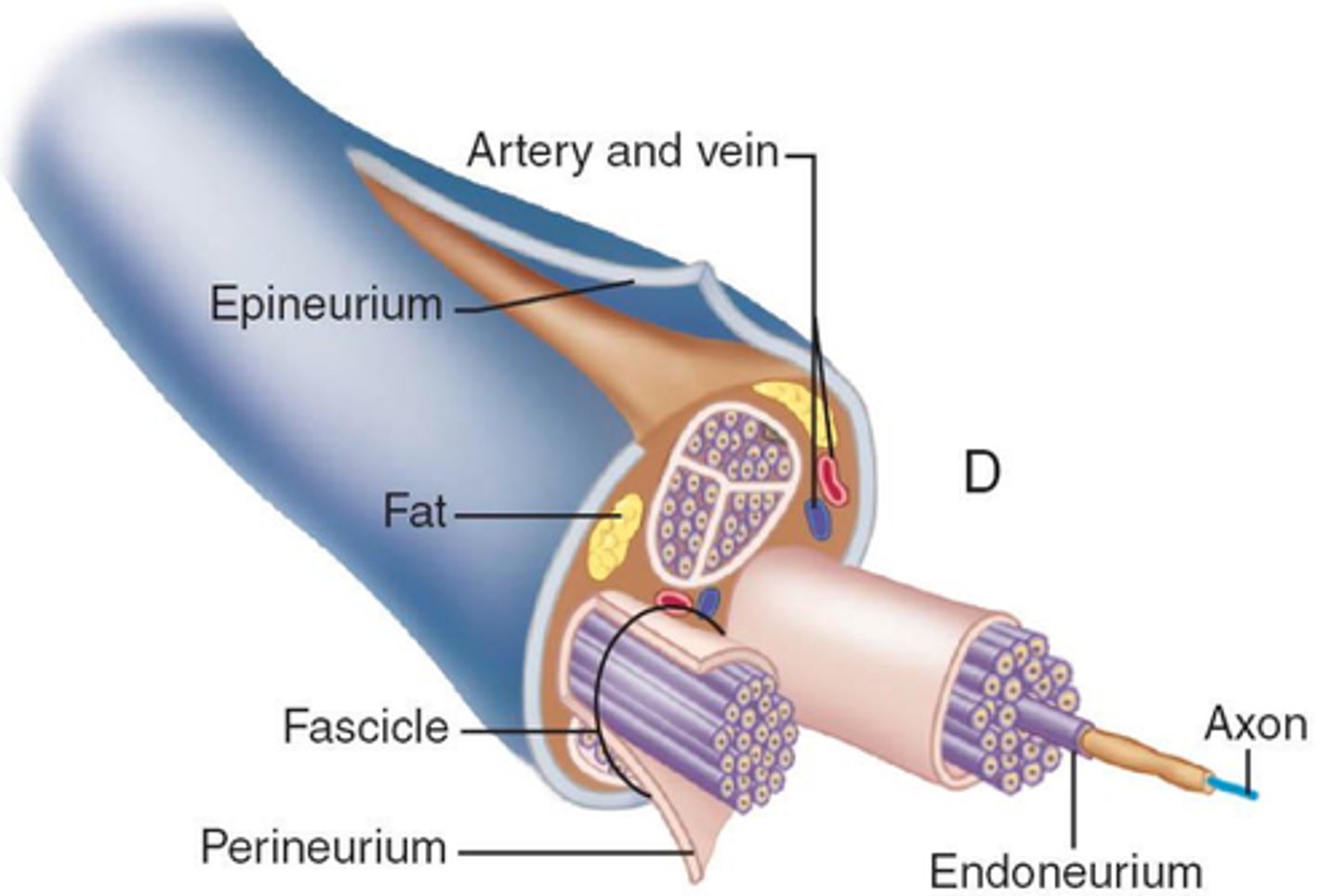
Perineurium
wraps groups of fibers bound into a fascicle

Epineurium
binds groups of fascicles
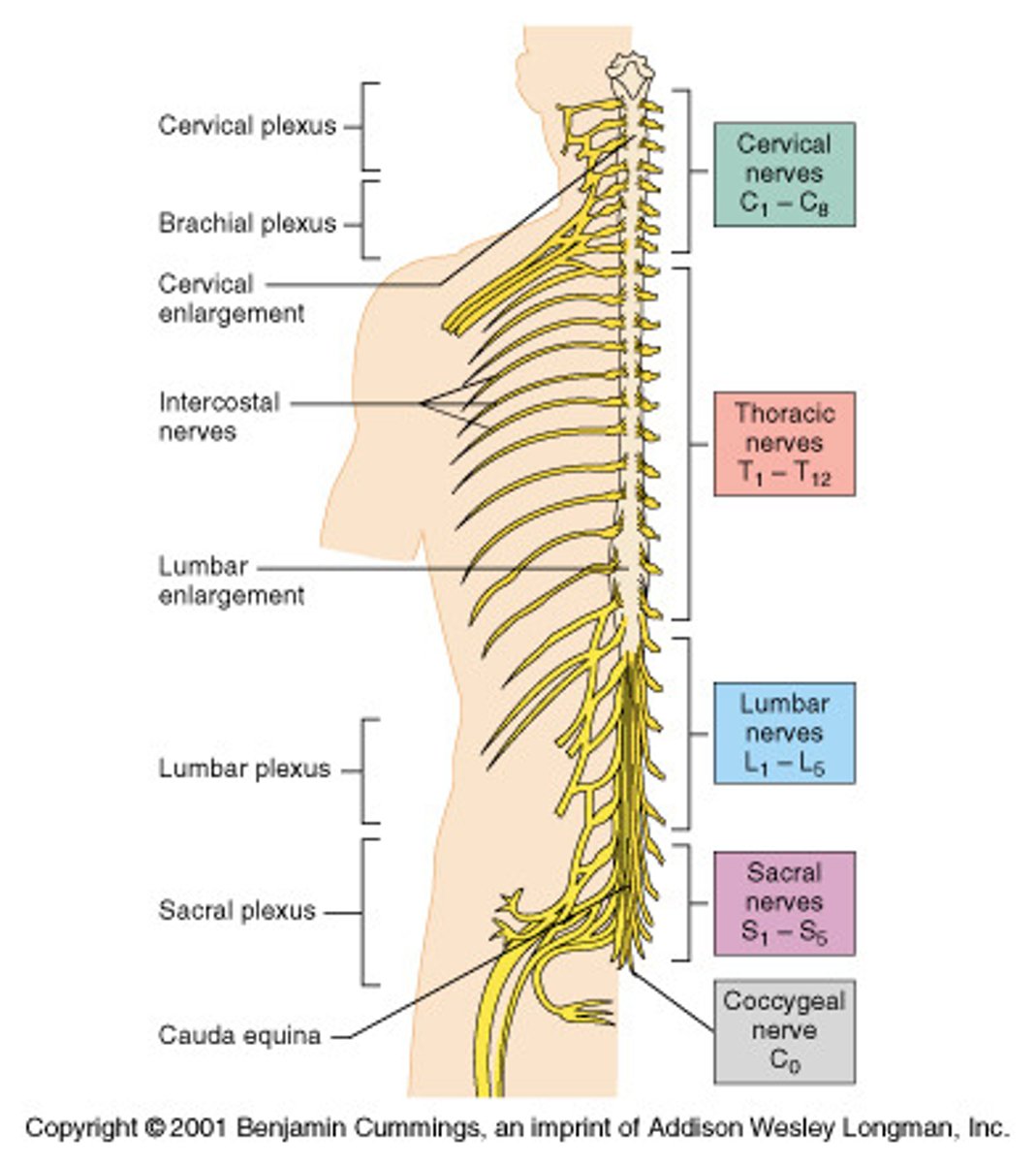
Spinal Nerves
-31 Pairs
-Formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord
-Named for the region of the spinal cord from which they arise -Spinal nerves divide soon after leaving the spinal cord into a --Dorsal ramus and a ventral ramus
Ramus
branch of a spinal nerve; contains both motor and sensory fibers
Dorsal Rami
serve the skin and muscles of the posterior trunk
Ventral Rami
(T1-T12) form the intercostal nerves that supply muscles and skin of the ribs and trunk
Ventral Rami (except T1-T12)
form a complex of networks (plexus) for the anterior
Cranial Nerves
-12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
-Only the pair of vagus nerves extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities
-Most are mixed nerves, but three are sensory only:
Optic
Olfactory
Vestibulocochlear
Plexus
-Networks of nerves serving motor and sensory needs of the limbs
-Form from ventral rami of spinal nerves in the cervical, lumbar, and sacral regions
-Four plexuses:
Cervical
Brachial
Lumbar
Sacral
Ventral vs dorsal root of spinal cord
The dorsal root of the spinal cord carries sensory information to the central nervous system, while the ventral root transmits motor commands from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.
Parasympathetic (cholinergic) fibers
they release acetycholine
Sympathetic Postganglionic (adrenergic) fibers
they release norepinephrine
Preganglionic
axons of both divisions release acetylcholine
Sympathetic Division
-Response to unusual stimulus when emotionally or physically stressed or threatened
-Fight or Flight response
-Remembers as the "E" division
Exercise
Excitement
Emergency
Embarrassment
Parasympathetic Division
-Conserves energy
-Rest and digest
-Maintains daily necessary body functions
-The "D" Division:
Digestion
Defecation (pooping)
Diuresis (urinating)
Conjunctiva
-Membrane that lines the eyelids and eyeball
-Connects with the transparent cornea
-Secretes mucus to lubricate the eye and keep it moist
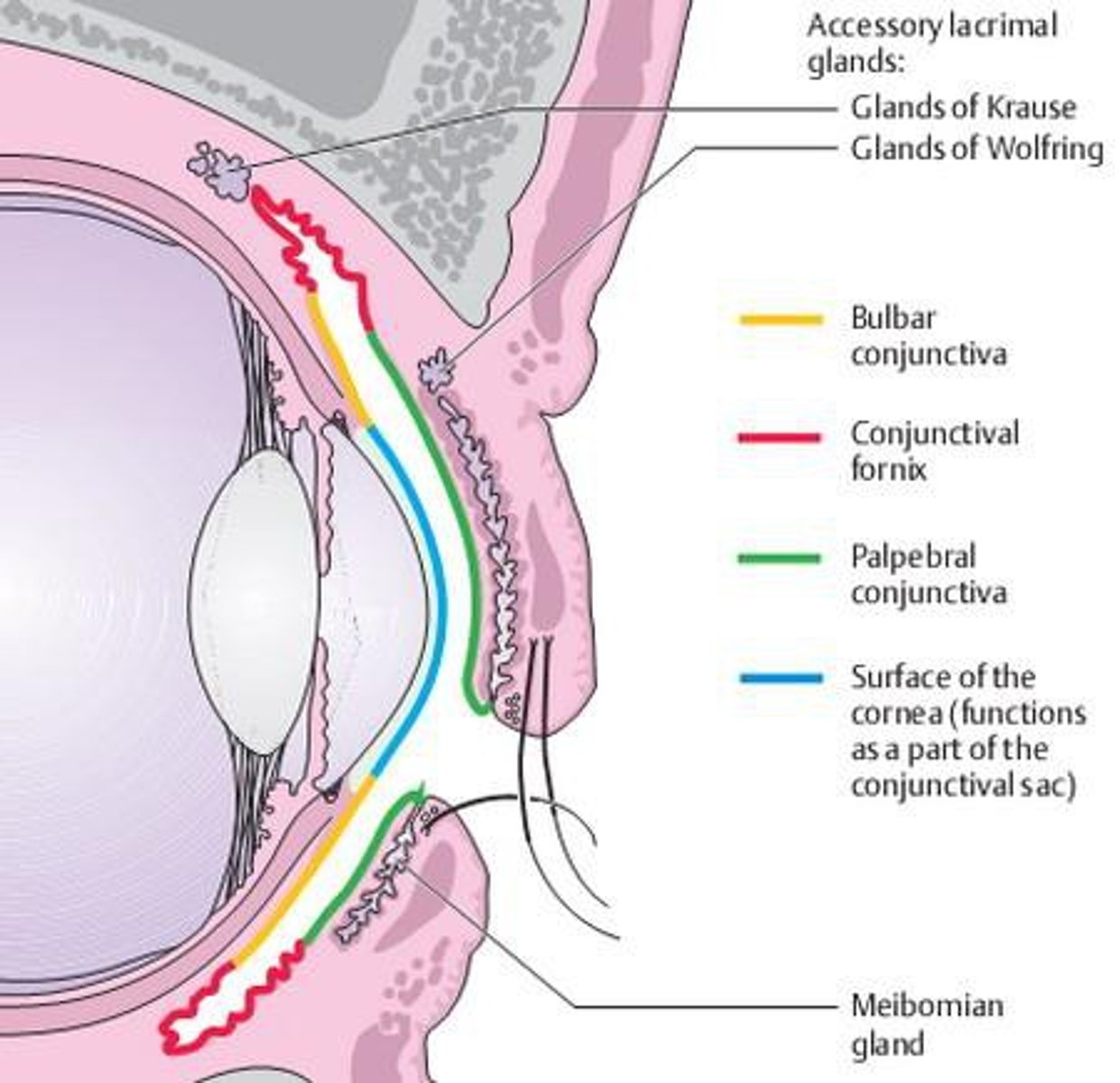
Lacrimal Gland
-Produces lacrimal fluid (tears)
-Situated on the lateral end of each eye
-Tears drain across the eye into the lacrimal canaliculi, then the lacrimal sac, and into the nasolacrimal duct, which empties into the nasal cavity
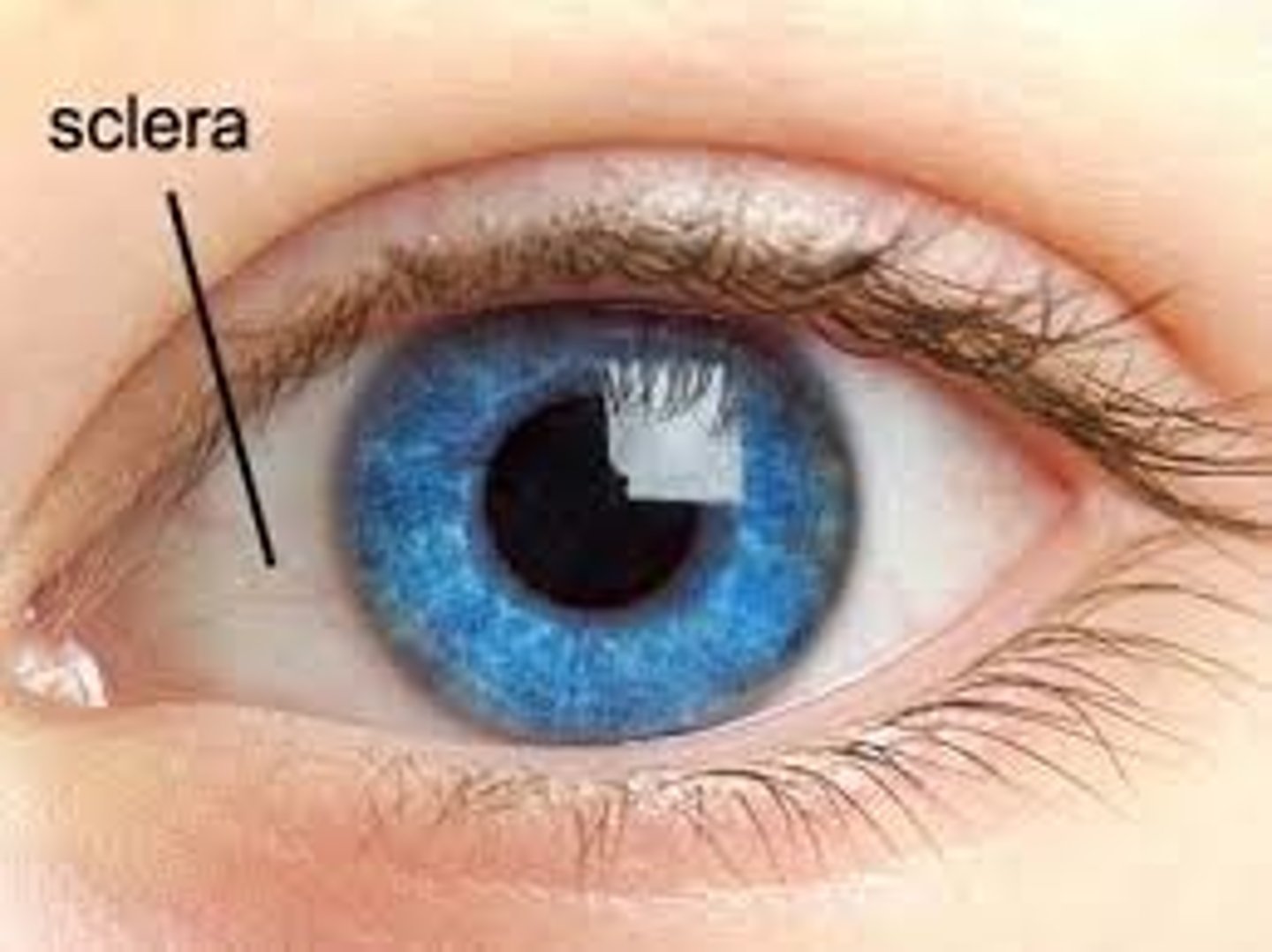
Sclera
-White part of the eye
-Seen anteriorly as the "white of the eye"
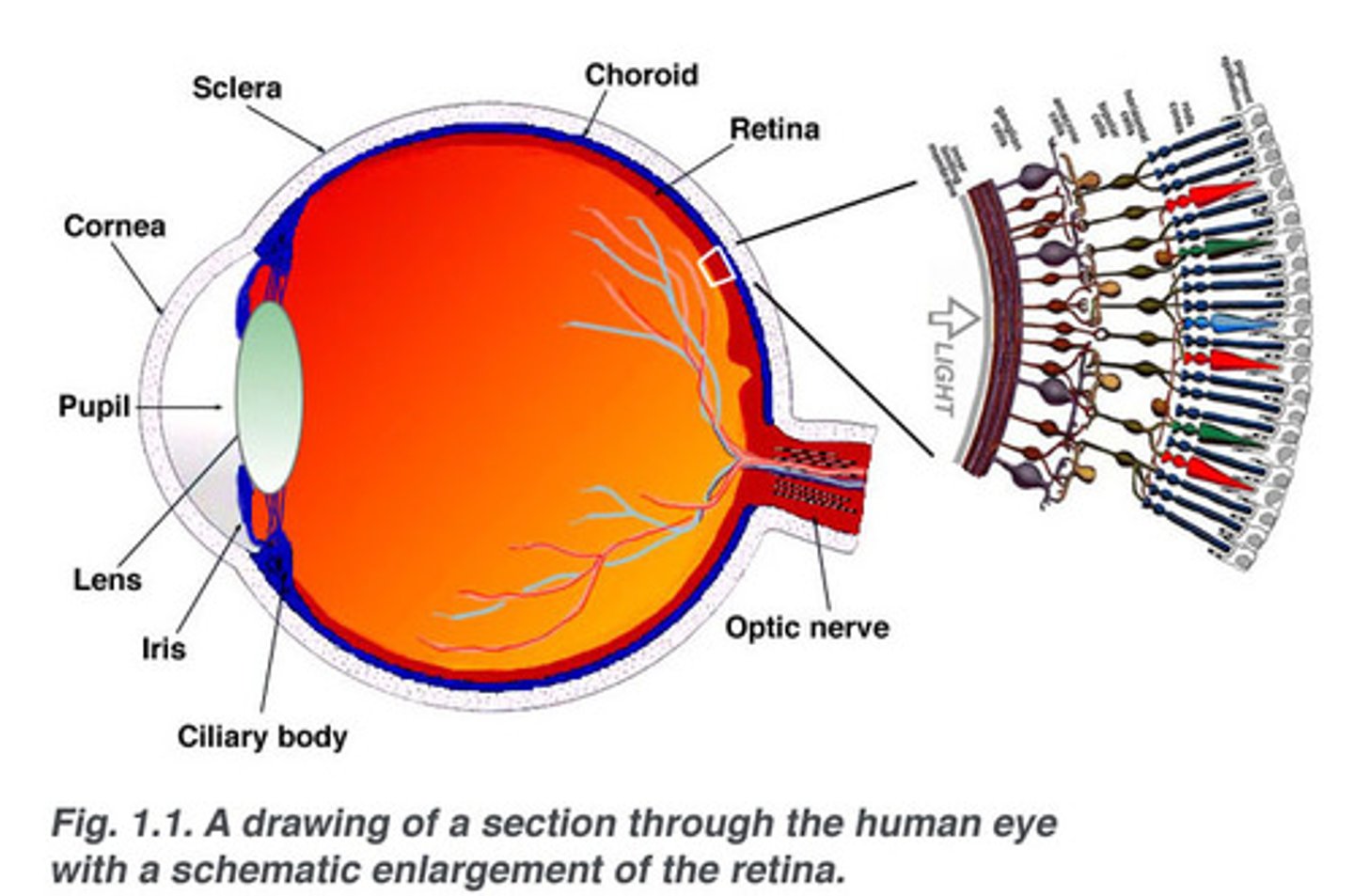
Retina
The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
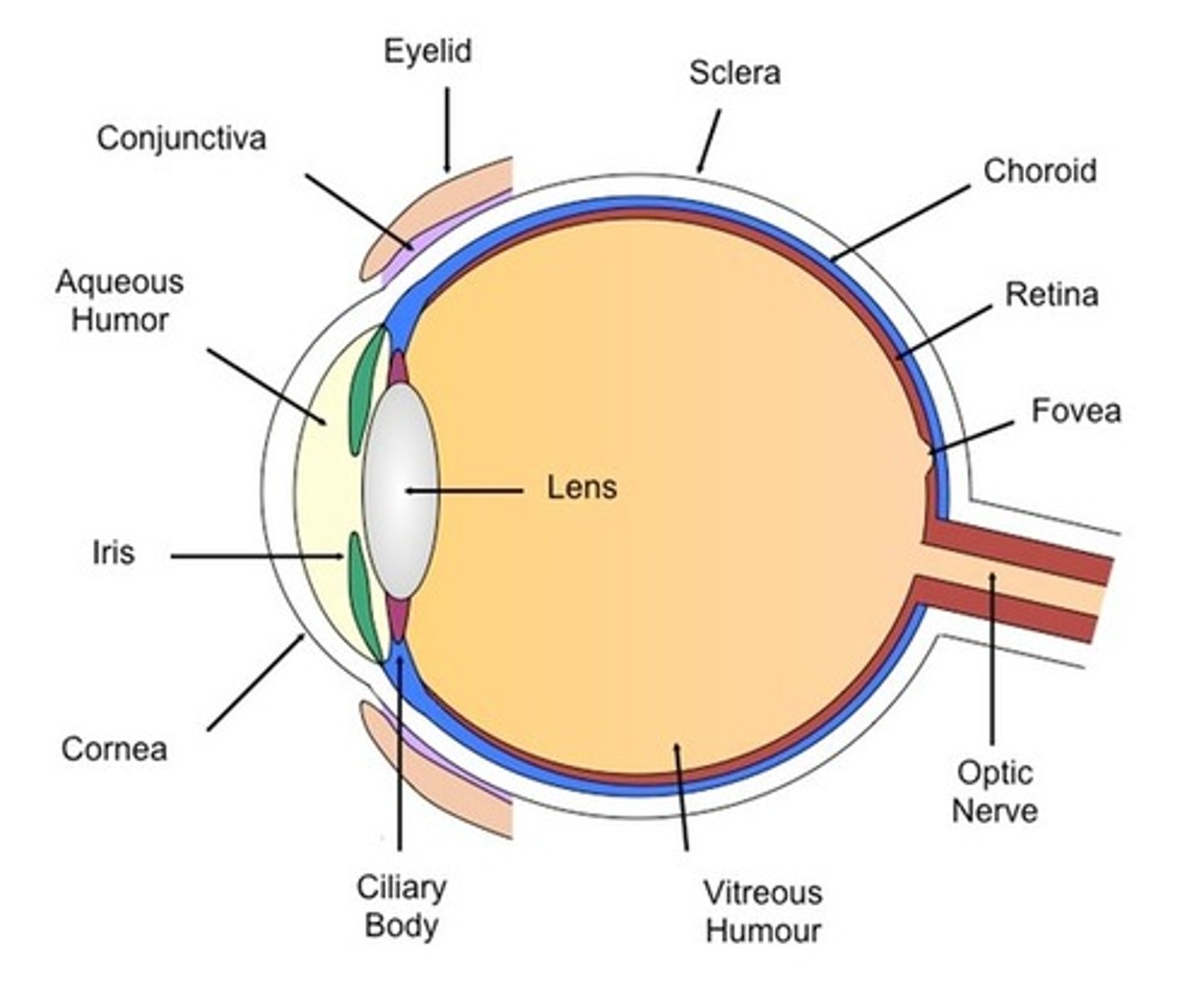
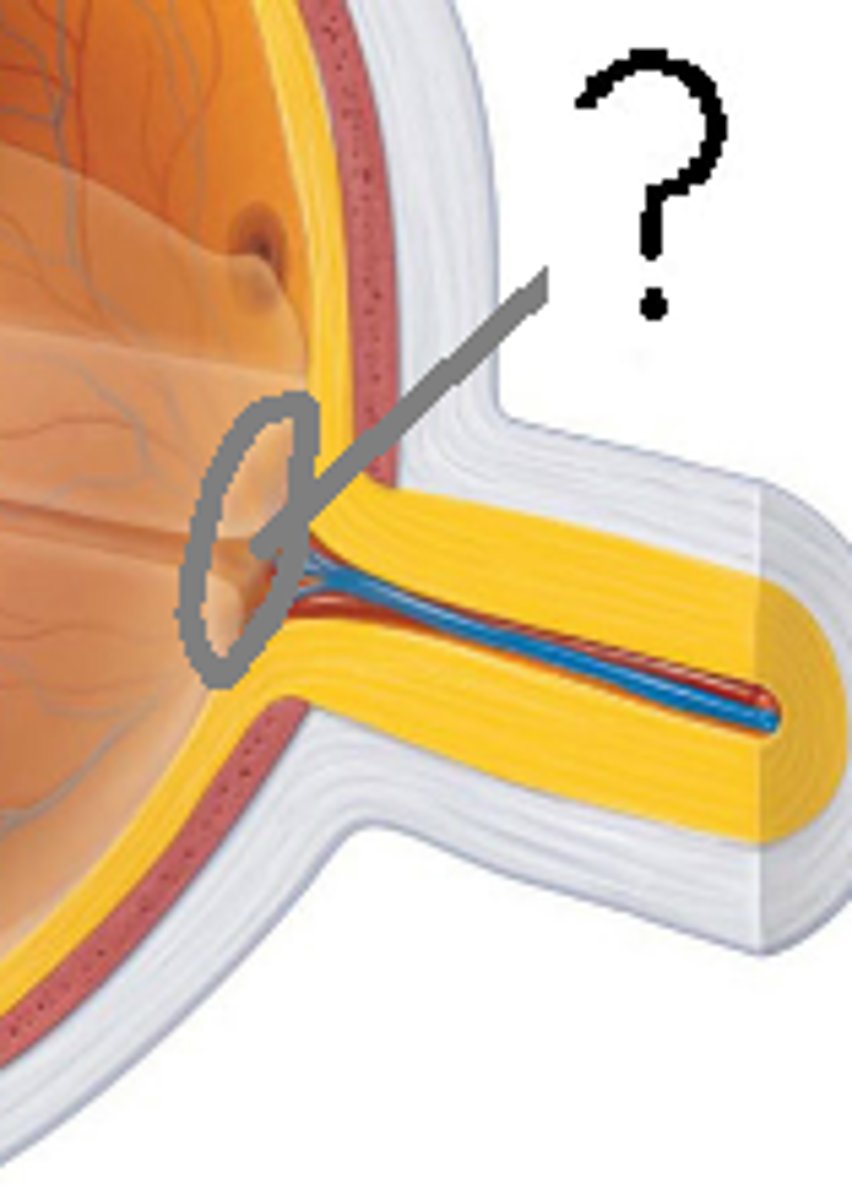
Optic Disc
-Blind spot
-Where the optic nerve exits the eye
-Cannot see images focused on the optic disc
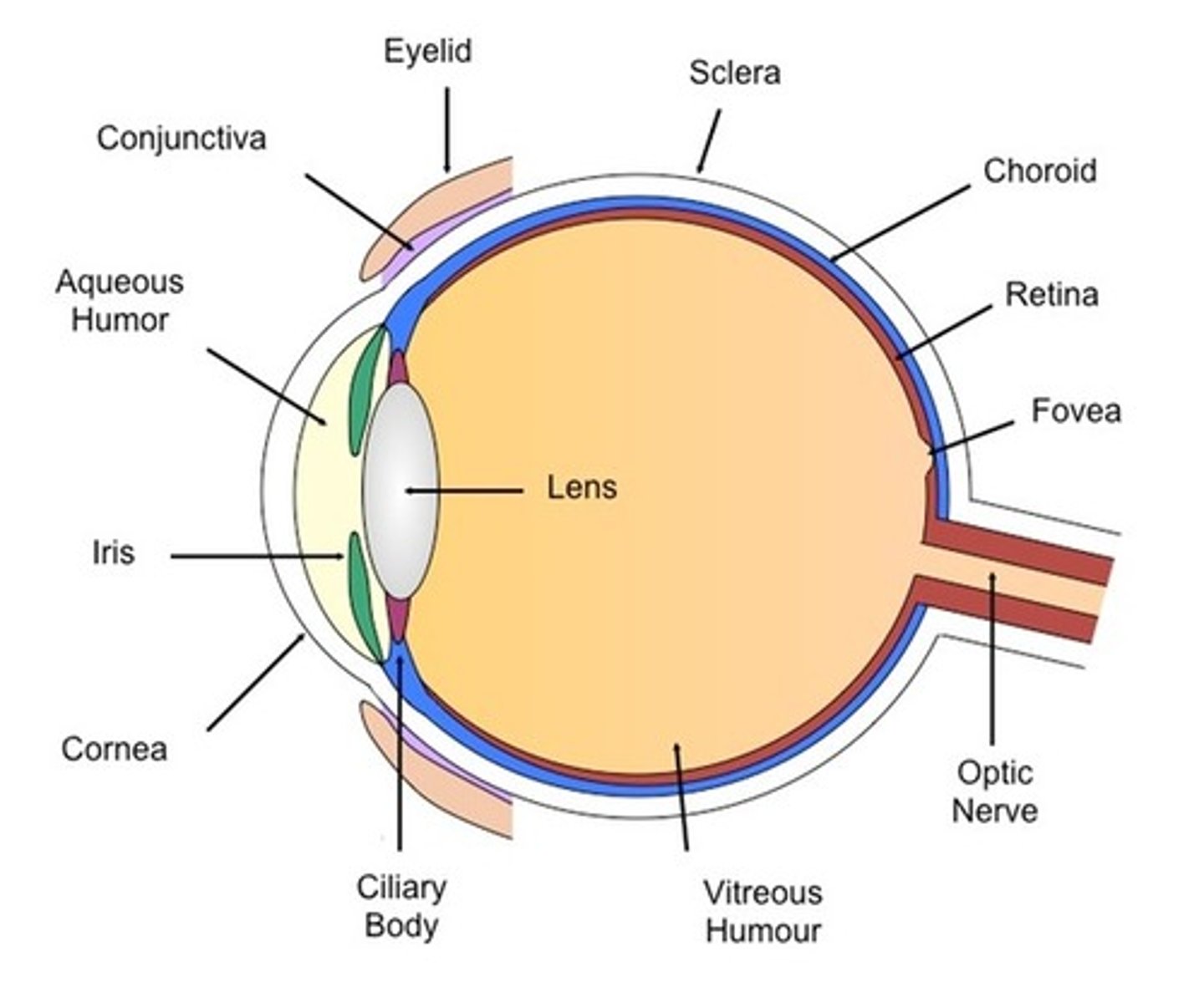
Lens
a flexible, elastic, transparent structure in the eye that changes its shape to focus light on the retina
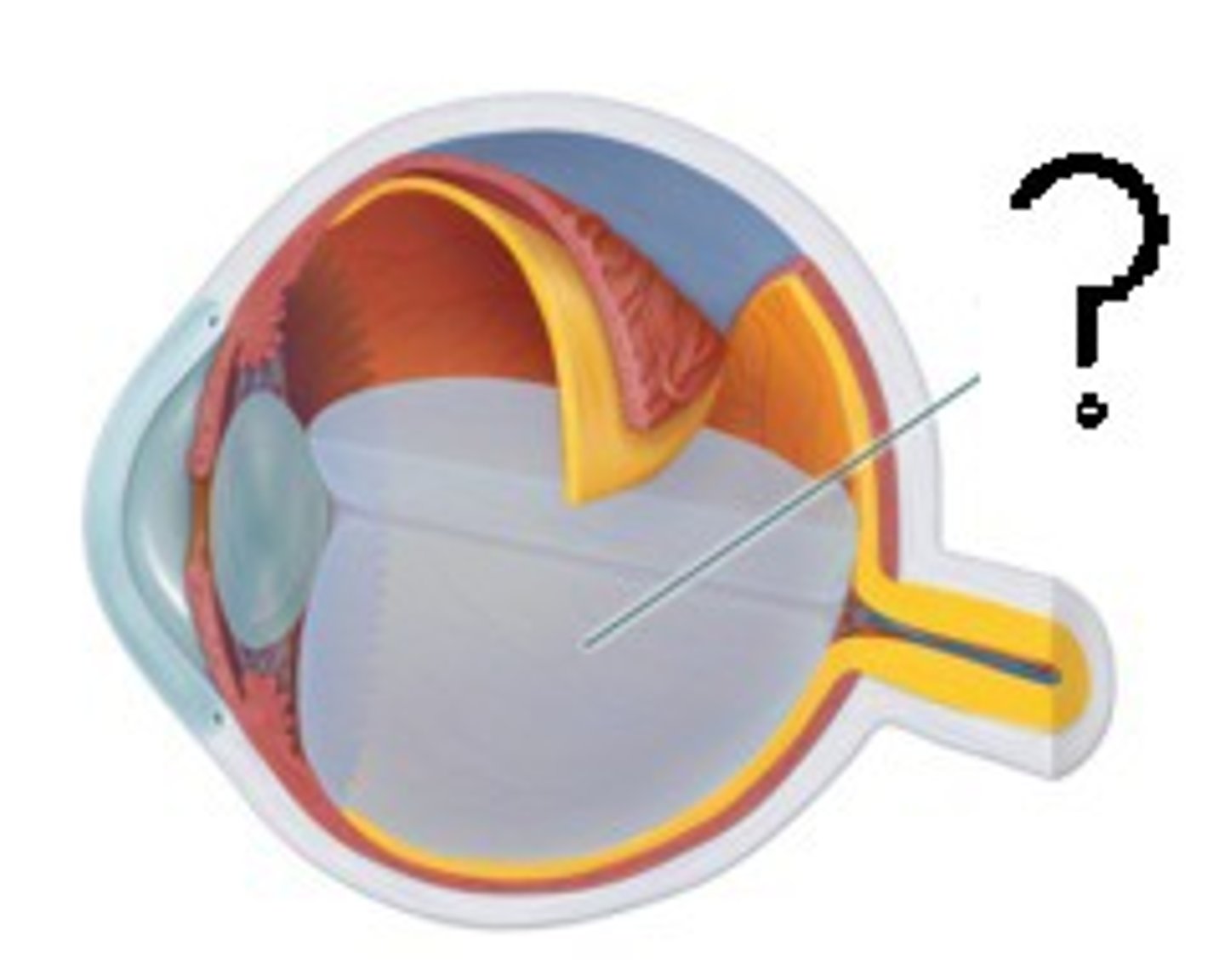
Vitreous Humor
-Gel-like substance posterior to the lens
-Prevents the eye from collapsing
-Helps maintain intraocular pressure
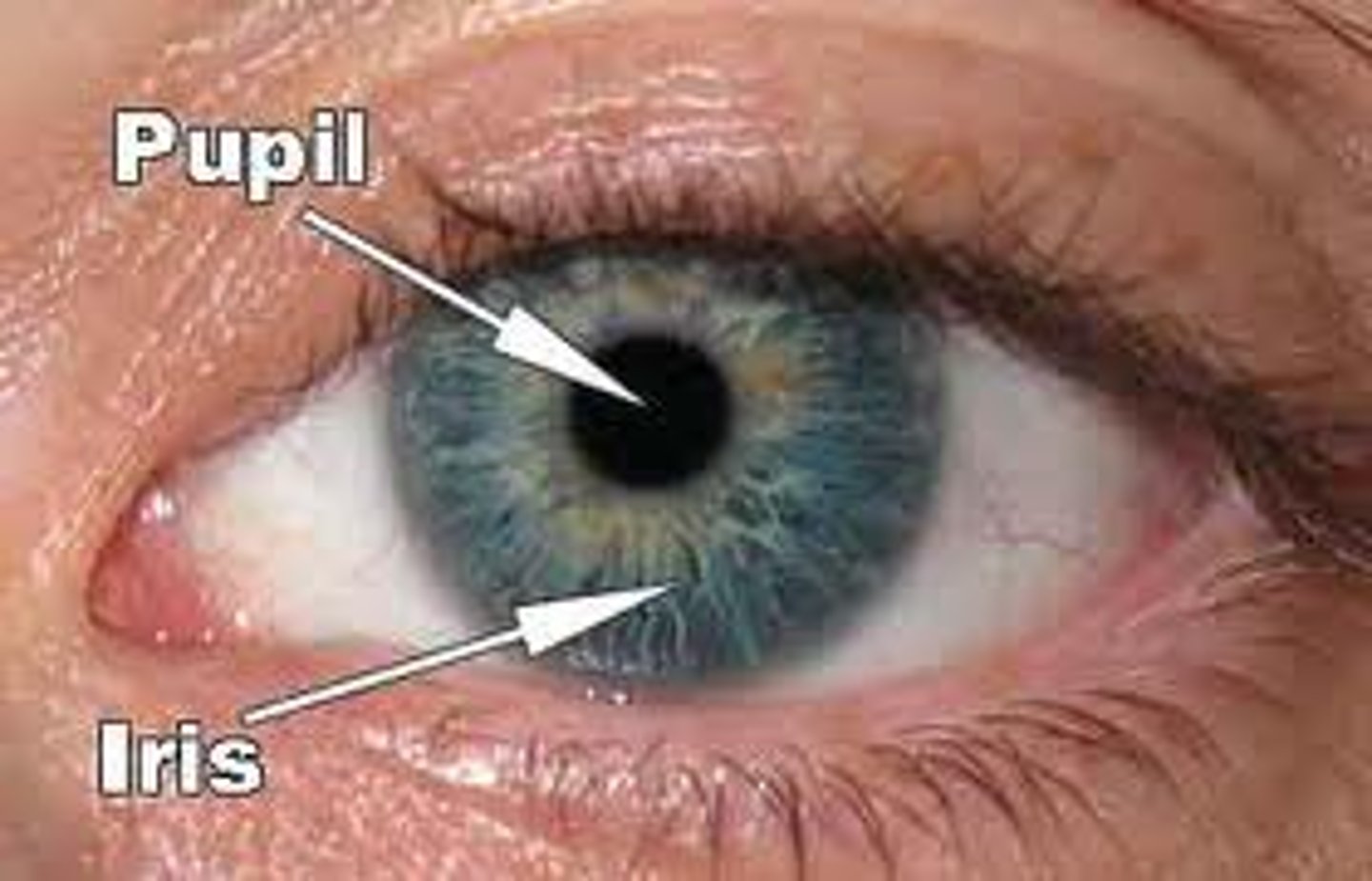
Pupil
-The adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
Rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray; necessary for peripheral and night vision, when cones don't respond
Cones
Detects the color and works best in bright light .
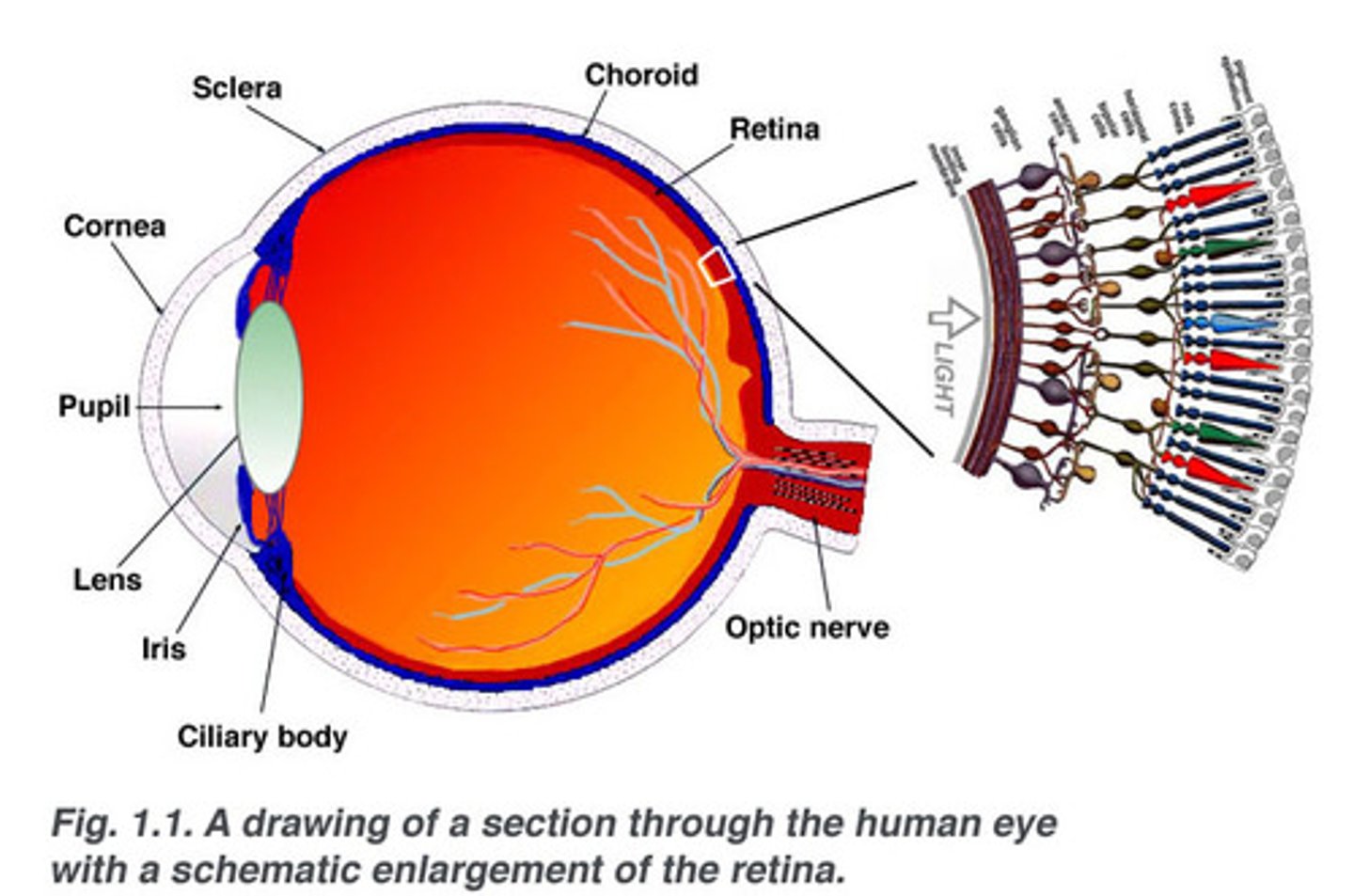
Ciliary body
Structure surrounding the lens that connects the choroid and iris. It contains ciliary muscles, which control the shape of the lens, and it secretes aqueous humor.
Accommodation
The eyes ability to adjust the shape of the lens to focus on objects at different distances
Order and which light passes through eye structures
Light enters through the cornea, passes through the pupil, is focused by the lens onto the retina, and is detected by sensory neurons in the photoreceptors
Hair cells (in ear)
long tufts of stereocilia on top surface, once basilar membrane vibrates, stereocilia swap back and forth within endolymph - causes opening of ion channels
vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
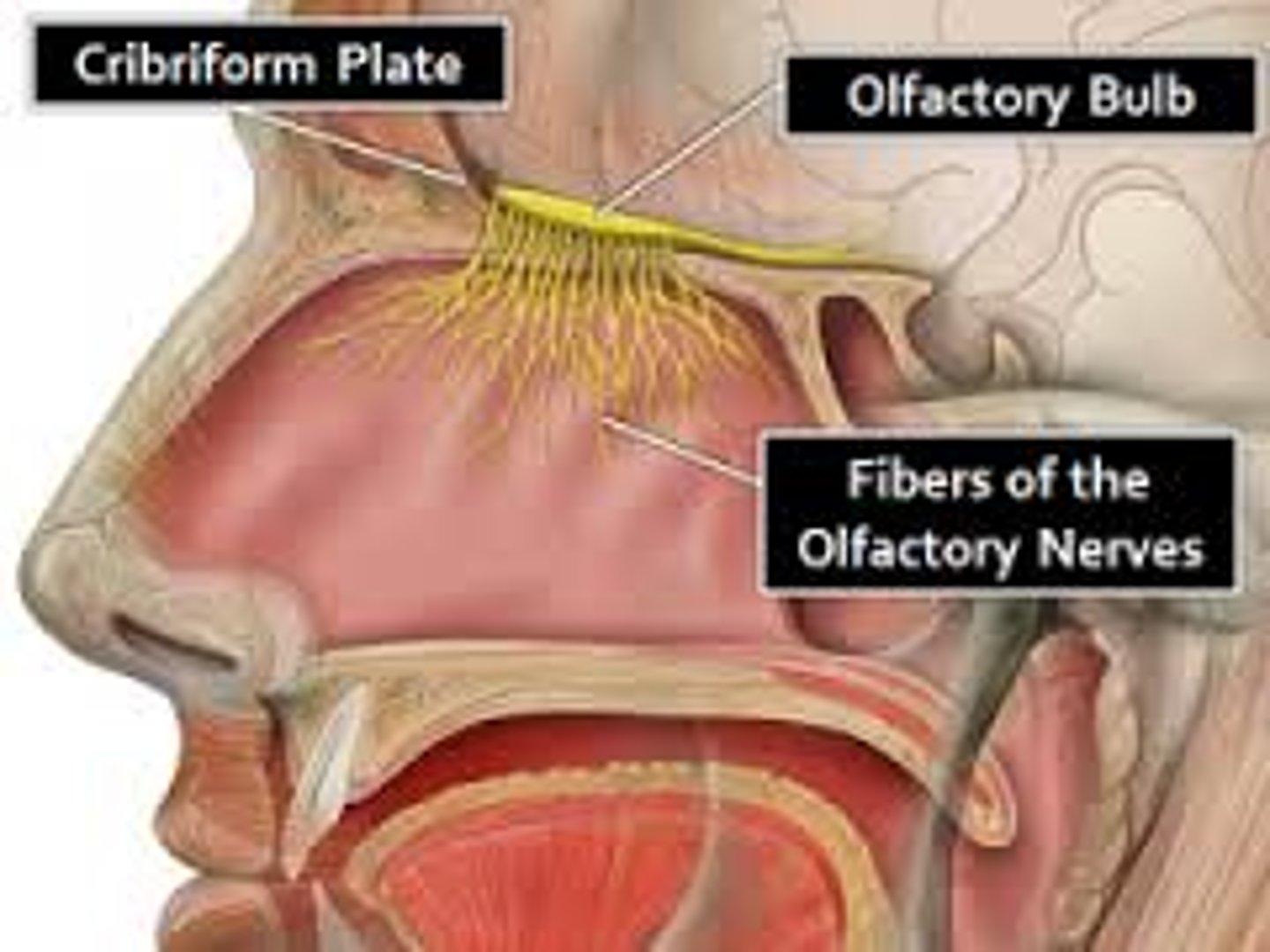
Olfactory receptors
-chemoreceptors in the upper nasal cavity that respond to odor chemicals
-In the roof of the nasal cavity
Five taste sensations
-Sweet receptors respond to sugars, saccharine, some into amino acids
-Sour receptors respond to H+ ions or acids
-Bitter receptors respond to alkaloids
-Salty receptors respond to metal ions
-Umami receptors respond to amino acid glutamate or the beefy taste of meat