Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards covering key concepts and vocabulary related to animal diversity, their development, and classification.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Multicellular Eukaryotes
Organisms that are composed of multiple cells and have a complex cellular structure where cells have a nucleus.
Heterotrophic
Organisms that obtain their food by ingesting other organisms or organic matter.
Collagen
A structural protein that helps hold animal cells together.
Which type of tissues are unique to animals?
Nervous and muscle tissue
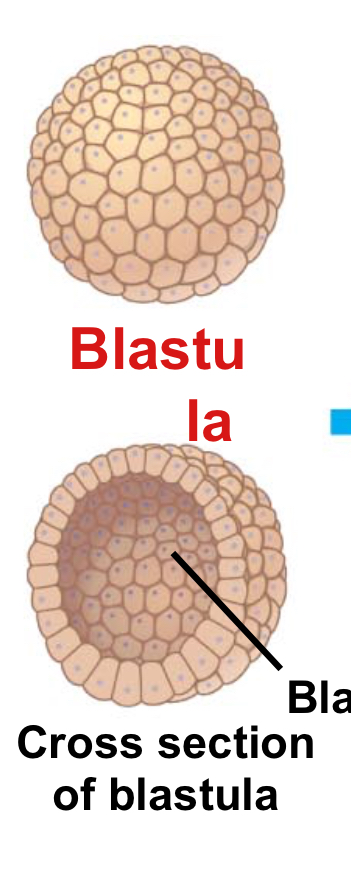
Blastula
An early stage of embryonic development that forms after the cleavage of the zygote.
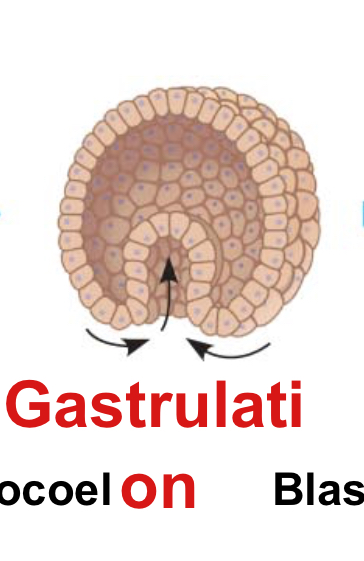
Gastrulation
The process where the blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, forming distinct layers of embryonic tissues.
Larva
A sexually immature stage of an animal that is morphologically distinct from the adult form.
What does larva eventually undergo?
Metamorphosis
Hox genes
A group of genes that regulate the body plan and development of animals.
What can the Hox family of genes produce?
A wide diversity of animal morphology
All animals share a:
Common ancestor
The common ancestor of living animals may have lived between:
675 and 875 million years ago
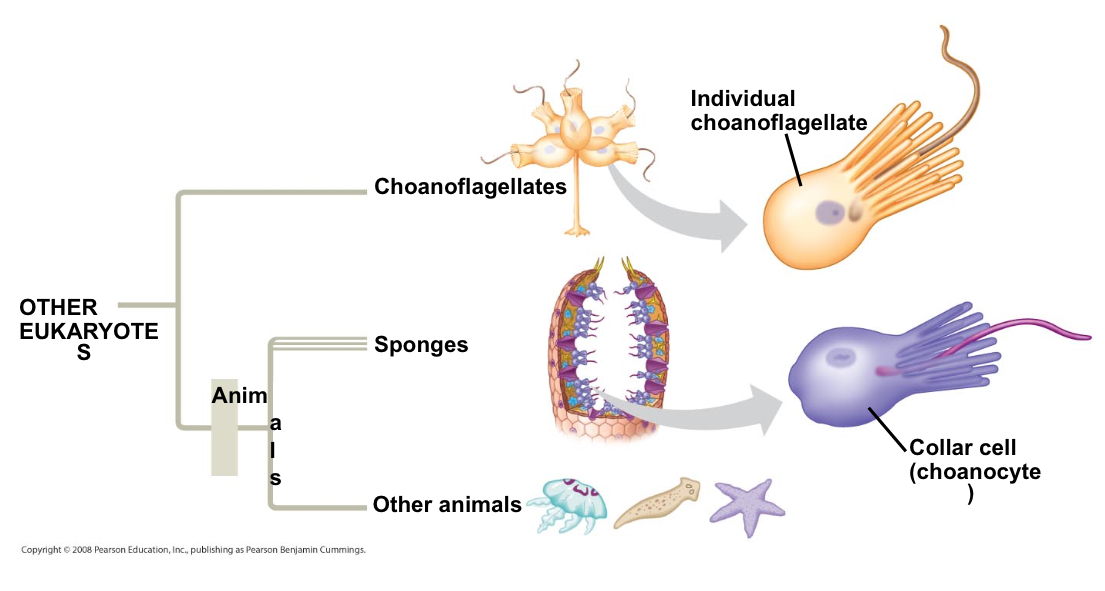
What are the closest living relatives of animals?
Choanoflagellates protists
In what era was the Cambrian Explsion?
Paleozoic Era (542 to 251 million years ago)
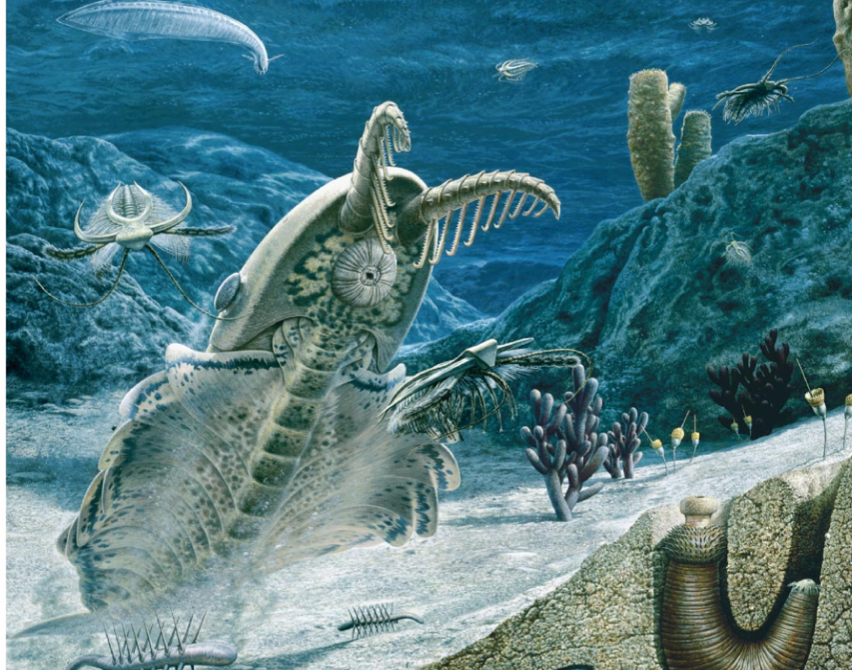

Cambrian Explosion
A period of rapid expansion of many major groups of living animals and early fossil appearance
How long ago was the Cambrian Explosion?
Approximately 535 to 525 million years ago
What are the hypotheses regarding the cause of the Cambrian explosion?
Predator-prey relations, rise in atmospheric oxygen, and Hox gene evolution
What happened to animal diversity during the Paleozoic Era?
Diversity continues to increase but was punctuated by mass extinctions
How long ago did animals began to make an impact on land?
By 460 million years ago
When did vertebrates make a transition to land?
By 360 million years ago
During the Mesozoic era, dinosaurs were:
The dominant terrestrial vertebrates
What emerged during the Mesozoic era?
The first mammals, along with coral reefs
How long ago was the Mesozoic Era?
252 to 65.5 million years ago
The beginning of the Cenozoic era followed:
Mass extinctions of both terrestrial and marine animals
What did the Cenozoic Era extinctions include?
The large, no flying dinosaurs and marine reptiles
What else diversified during the Cenozoic Era?
Modern mammal orders and insects
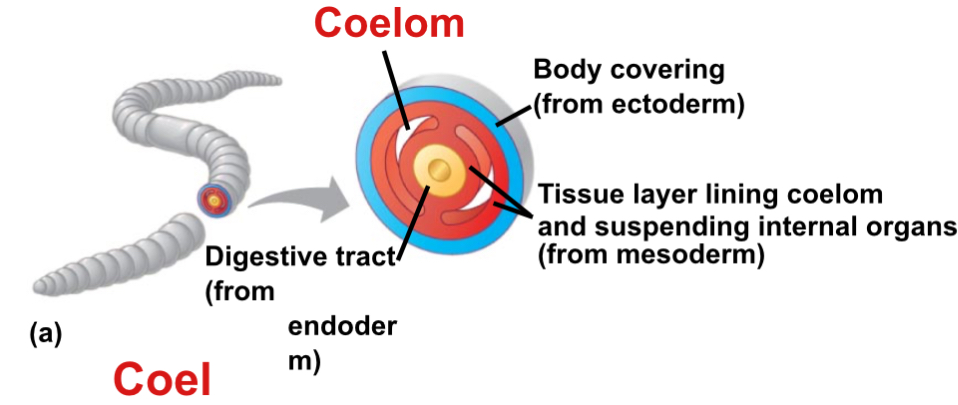
Coelom
A true body cavity that is derived from mesoderm in triploblastic organisms.
Protostome
An organism type where the blastopore becomes the mouth during development.
Deuterostome
An organism type where the blastopore becomes the anus during development.
Which type of phyla belongs to the clade deuterostomia?
Chordates and some other
Ecydsozoans
A bilaterian clade that sheds their exoskeleton
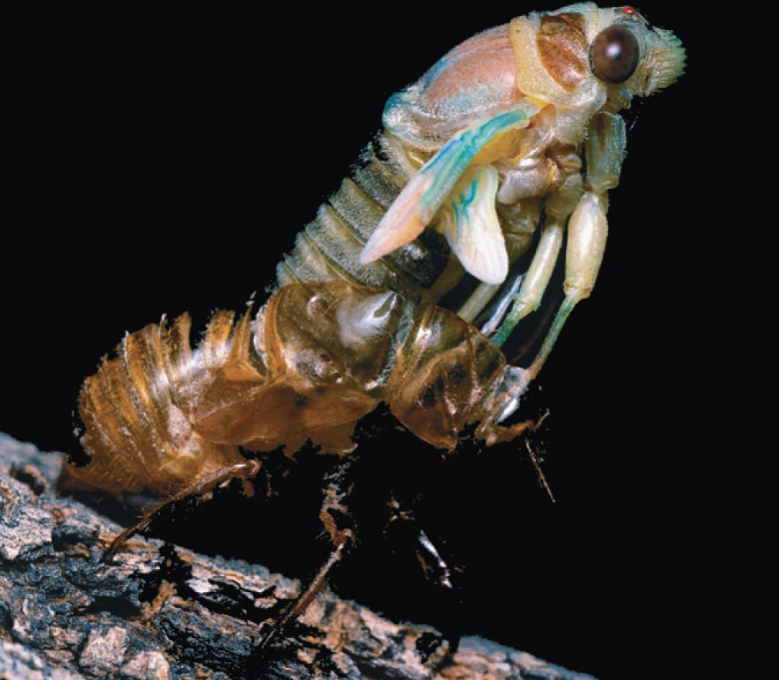

Ecdysis
The process of shedding an exoskeleton, common in certain animal groups.
Diploblastic
Animals that have two germ layers: ectoderm and endoderm.
Triploblastic
Animals that have three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
Ectoderm
The germ layer covering the embryo’s surface
Endoderm
The innermost germ layer
Cephalization
The evolution of a head where sensory organs and nervous tissues are concentrated.
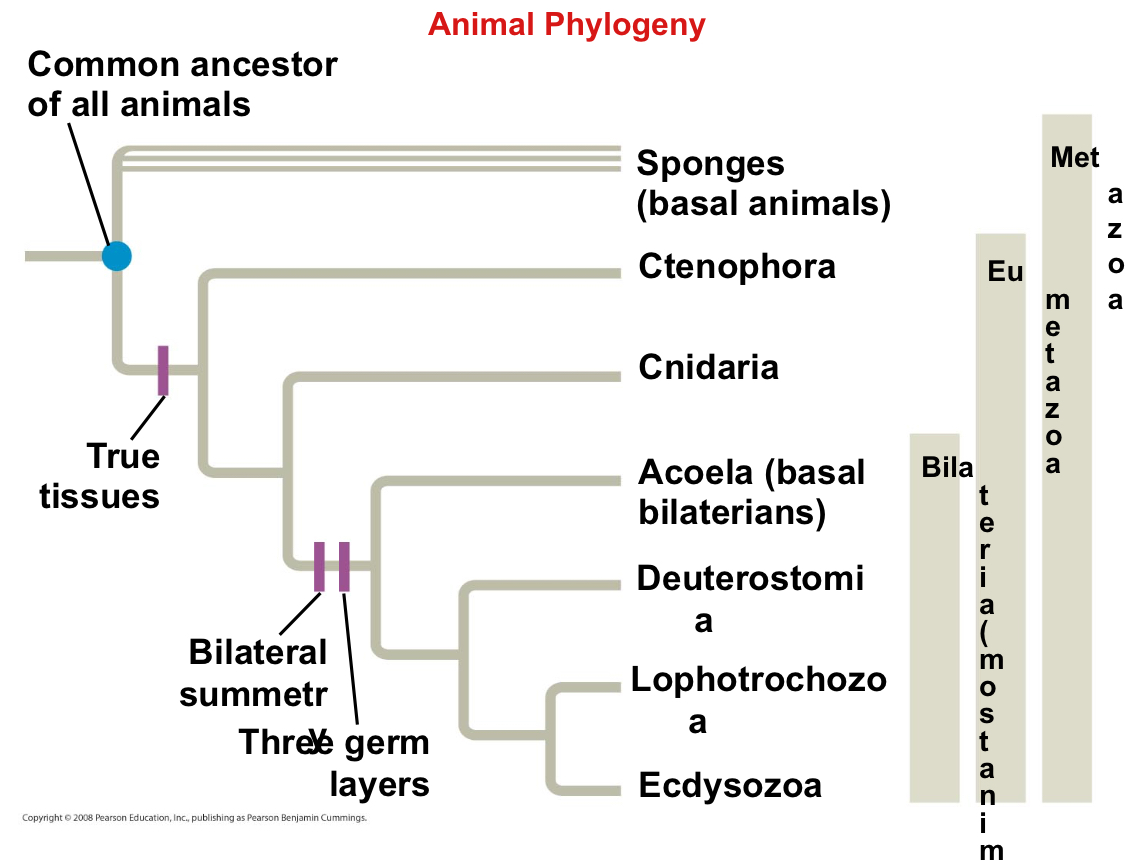
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history and relationships among groups of organisms.
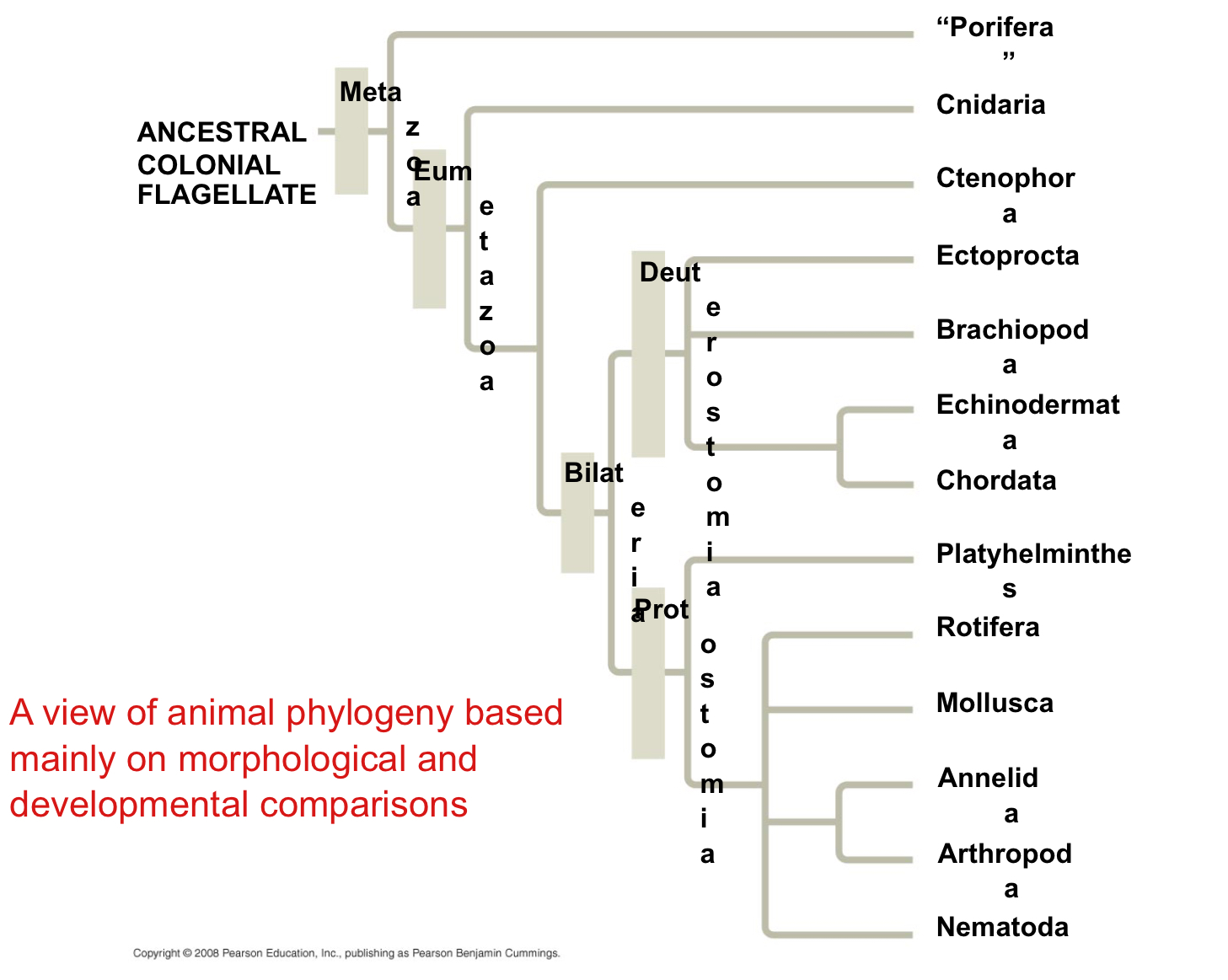
What is a hypothesis of animal phylogeny?
It’s based mainly on morphological and developmental comparisons
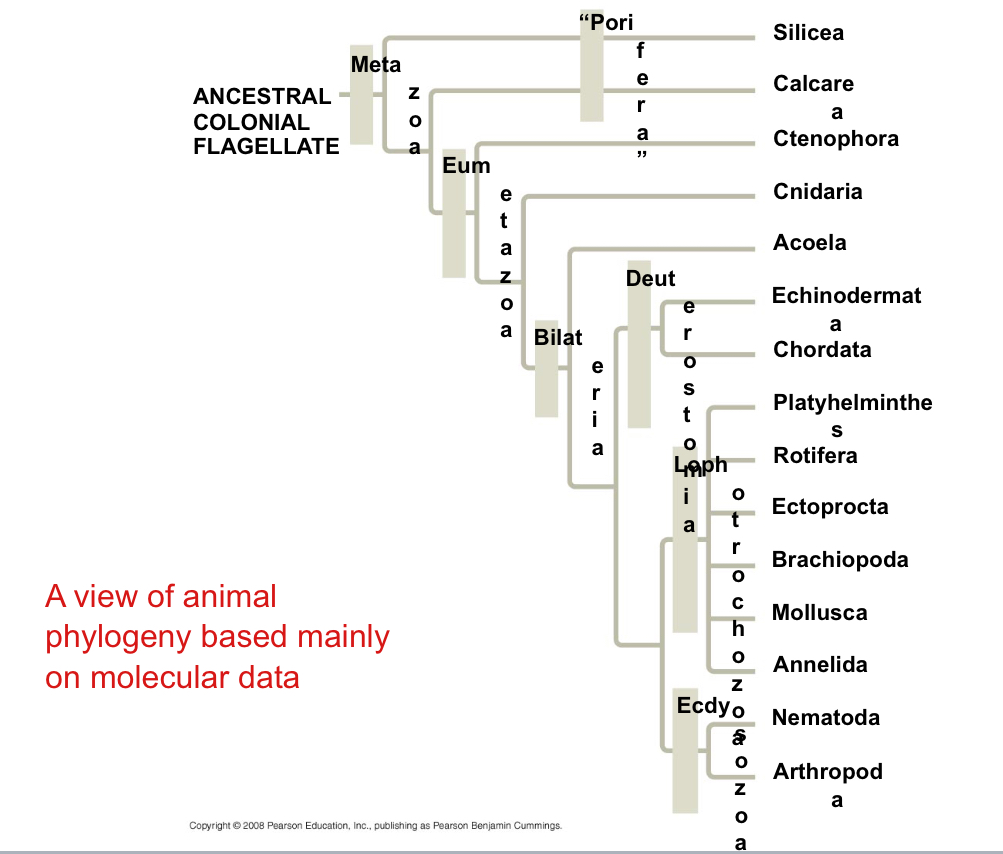
What is another hypothesis of an animal phylogeny?
Based mainly on molecular data
Body plan
A set of morphological and developmental traits used to categorize animals
Grade
A group whose members share key biological features
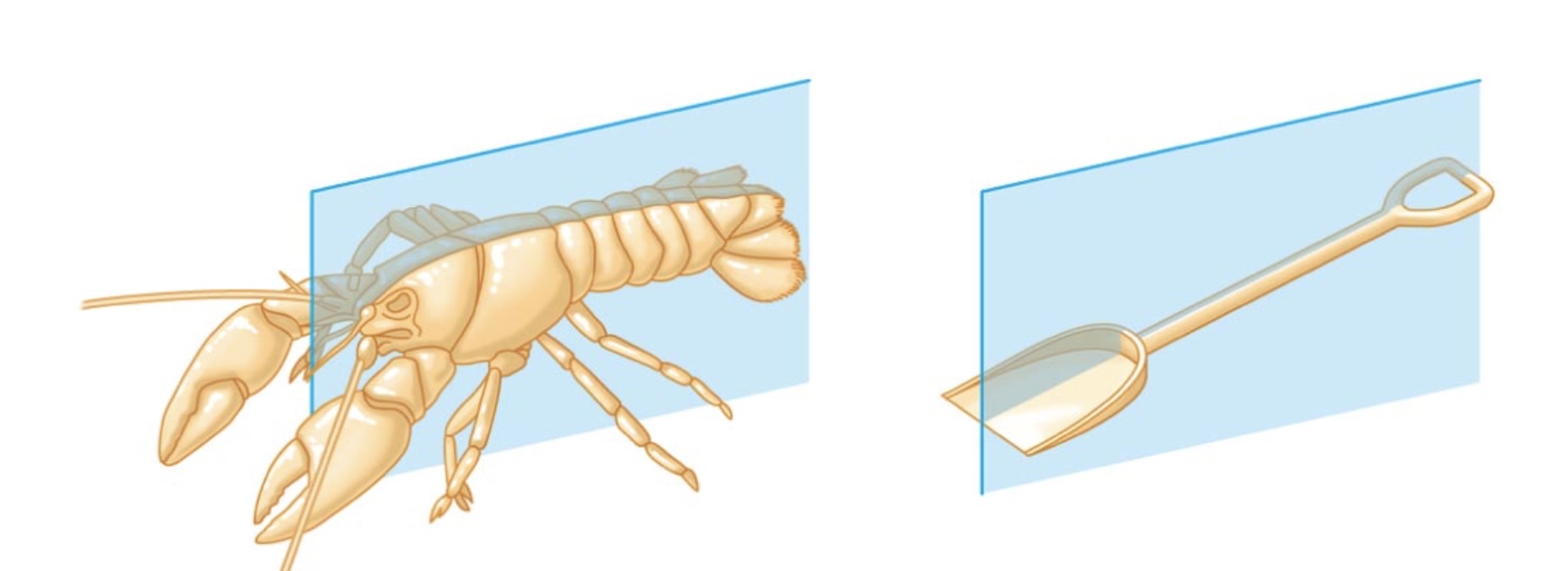
Bilateral symmetry
A body plan in which the left and right sides of the organism are mirror images.
Animals with bilateral symmetry have:
A dorsal (top), a ventral (bottom) side and anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends
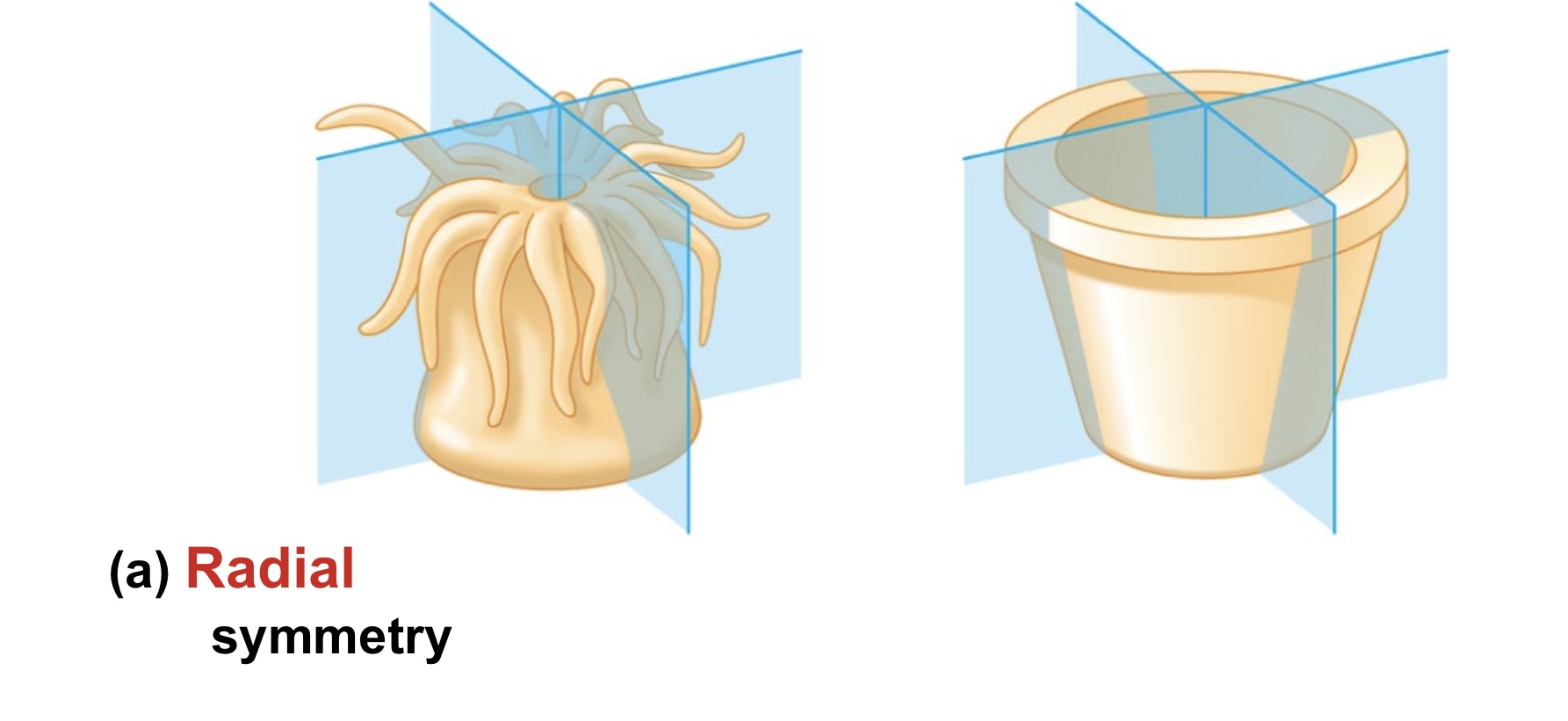
Radial symmetry
A body plan in which body parts are arranged around a central axis.

Lophophore
A feeding structure found in some groups of lophotrochozoans.
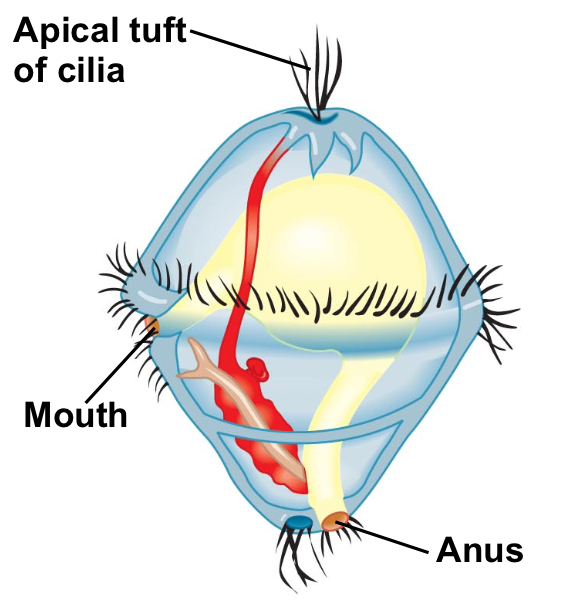
Trochophore larva
A distinct development larval stage exhibited by several protostome animal groups.
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer that develops into muscles and several other organs.
Archenteron
The developing digestive tube that forms during gastrulation.
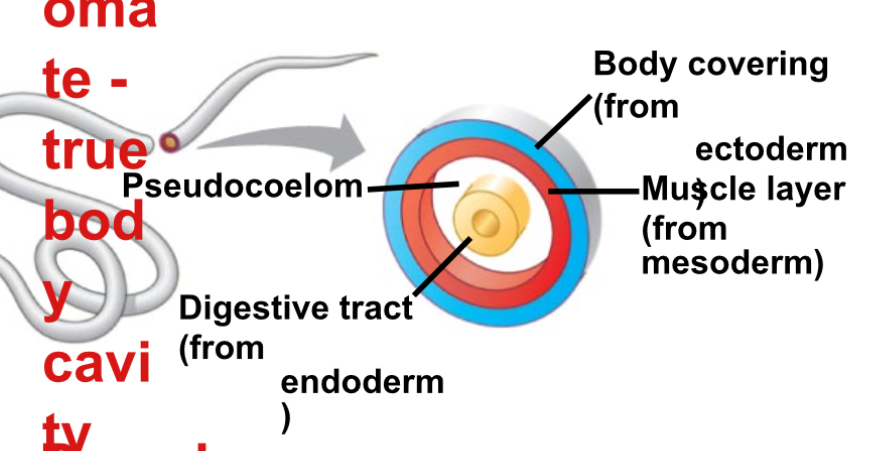
Coelomates
Animals that posses a true coelom
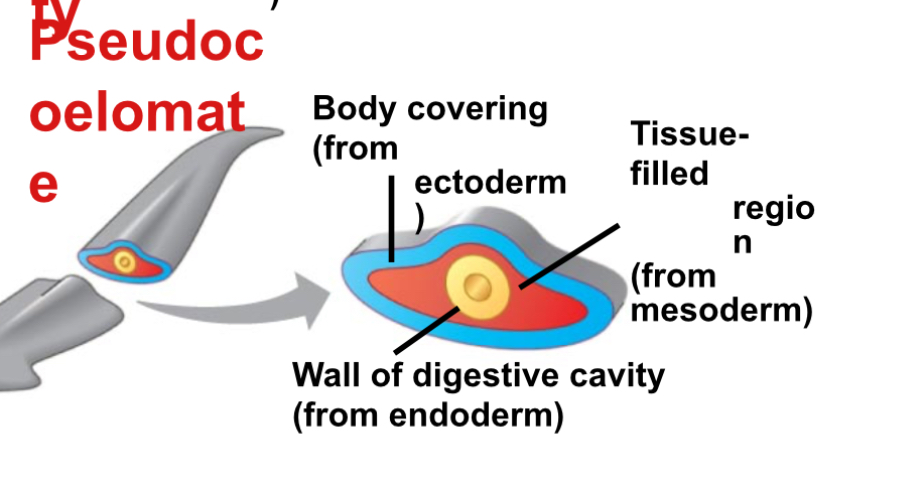
Pseudocoelomate
A triploblastic animal that possess a pseudocoelom
Pseudocoelom
A body cavity derived from both mesoderm and endoderm
Acoelomate
Triploblastic animals that lack a body cavity
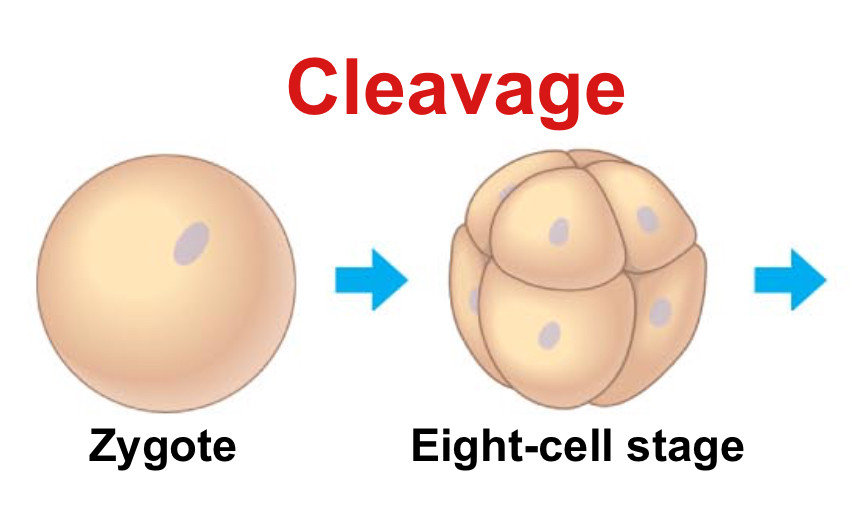
Cleavage
The process of cell division that occurs after fertilization of the egg.
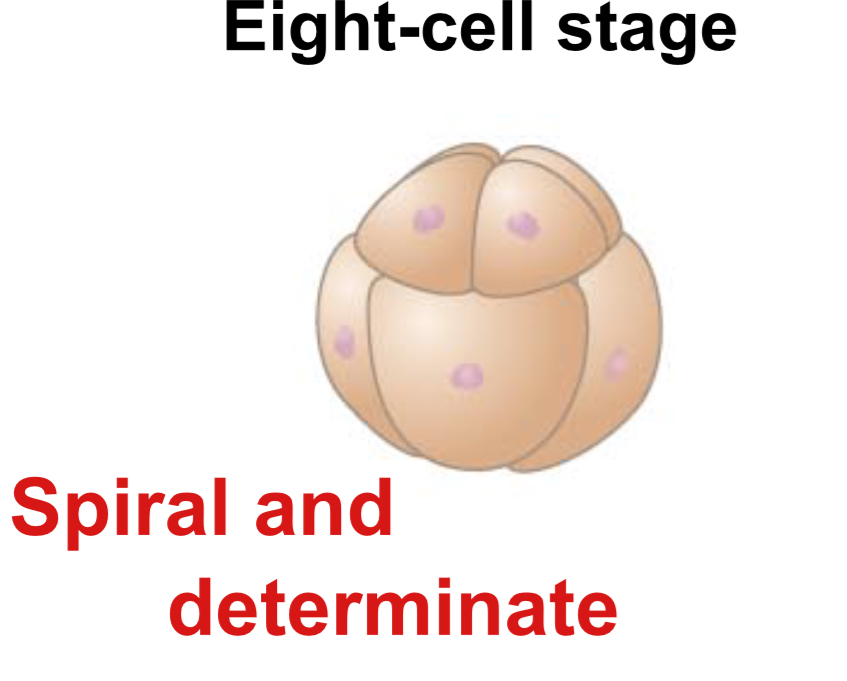
In protostome development, cleavage is:
Spiral and determinate
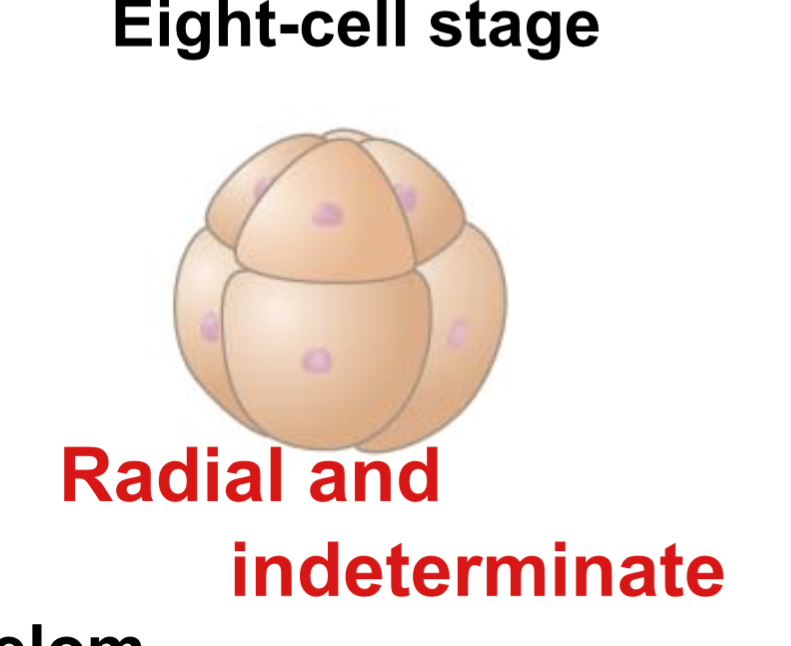
In deuterostome development, cleavage is:
Radial and indeterminate
What occurs in each cell with indeterminate cleavage?
The cell retains the capacity to develop into a complete embryo
What does indeterminate cleavage make possible?
Identical twins and embryonic stem cells
Eumetazoa
A clade of animal (eumetazoans) with true tissues
Bilaterians
Animal phyla that belong to the clade Bilateria