Key Concepts in Ecology and Population Dynamics
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Population
Members of same species living in the same area
Community
A group of populations living in the same area
Ecosystem
Area where organisms in a community interact with their physical environment
Biosphere
Consists of all regions of earth containing living things
Habitat
Type of place where organism usually lives, including other organisms as well as physical, chemical environment
Competitive exclusion principle
When two species compete for the same resources (or occupy the same niche), one is likely to be more successful and the other will be eliminated
Predator
Organism that kills and eats another
Ecological/trophic efficiency
Describes energy proportion represented at one trophic level that is transferred to the next
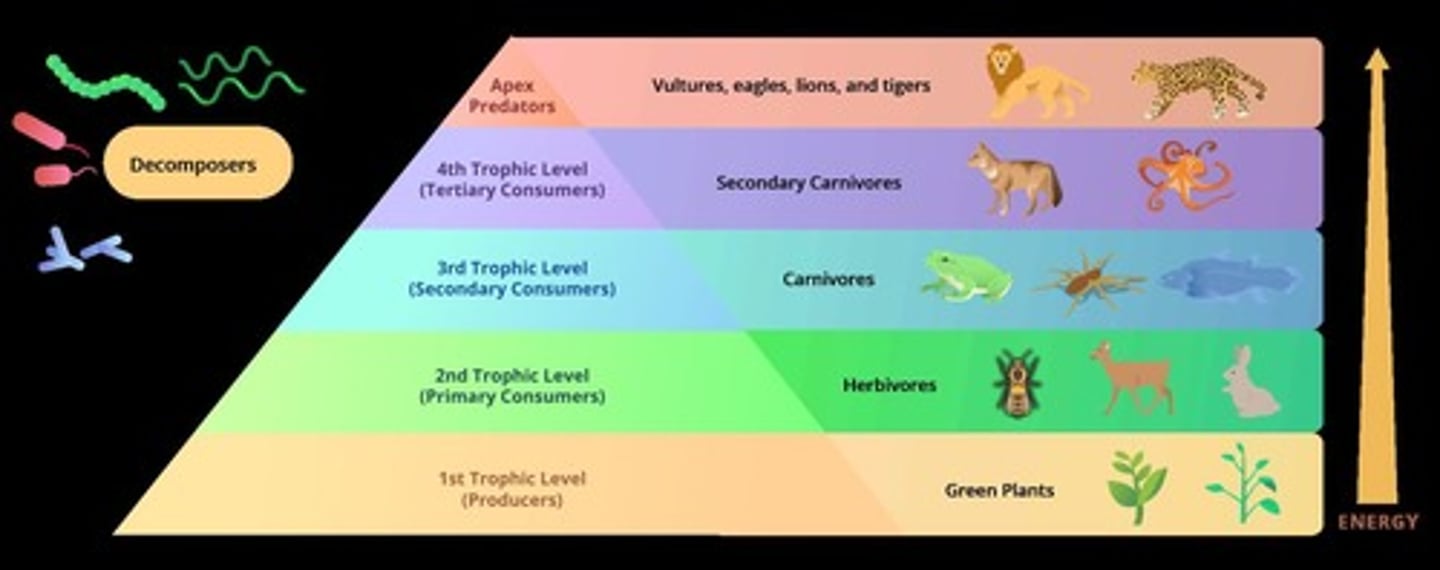
Trophic level
Energy, biomass, and quantity of organisms is highest at the 1º producer level and lowest at the 3º/4º consumer level
Type I Survivorship Curve
Most survive to middle age and die quicker after that

Type II Survivorship Curve
Length of survivorship is random
Type III Survivorship Curve
Most die young, and few survive to reproductive age and beyond
Energy transfer efficiency
On average, an efficiency of about 10% is transferred to the next trophic level
Energy loss
The remaining 90% is lost to metabolism, heat, & detrivores
Parasite
Organism that spends most of its life living on host and consuming nutrients from it
Herbivore
Organism that eats plants; herbivores have adapted to eating plants only by developing long intestinal tracts to fully absorb nutrients
Niche
Set of conditions & resources an organism needs and interactions it has with other species
Fundamental niche
Niche that an organism occupies when there are no competing species present
1º Producers
Autotrophs that convert sun energy into chemical energy [E.g., plants, cyanobacteria (organisms that can perform photosynthesis)]
1º Consumers
Herbivores that eat primary producers
2º Consumers
Primary carnivores that eat primary consumers
3º Consumers
Secondary carnivores that eat secondary consumers
Detritivores
Consumers that obtain energy by consuming detritus (dead matter consisting of leaves, animal remains, and waste products)
Realized niche
Smaller subset of the niche that species occupy when competition is present
Competition
Interaction between organisms that occurs when resources are limited, and multiple organisms requiring the same limited resources
Symbiosis
Interactions between two species
Mutualism (+/+)
Both organisms benefit [E.g., Nitrogen fixing bacteria & legumes, E.g., Bees pollinating flowers]
![<p>Both organisms benefit [E.g., Nitrogen fixing bacteria & legumes, E.g., Bees pollinating flowers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b197f8e8-3b37-4028-90f2-c6f8b5e0bad8.jpg)
Commensalism (+/o)
One benefits, other is unaffected [E.g., Remora & shark, E.g., Whale & barnacle]
Parasitism (+/-)
Benefits at the expense of the host [E.g., Virus & host cell - all viruses are parasites, E.g., Ticks feeding off cats]
Nitrogen Cycle
Describes how nitrogen moves from the environment to living organisms and from living organisms back into the environment.
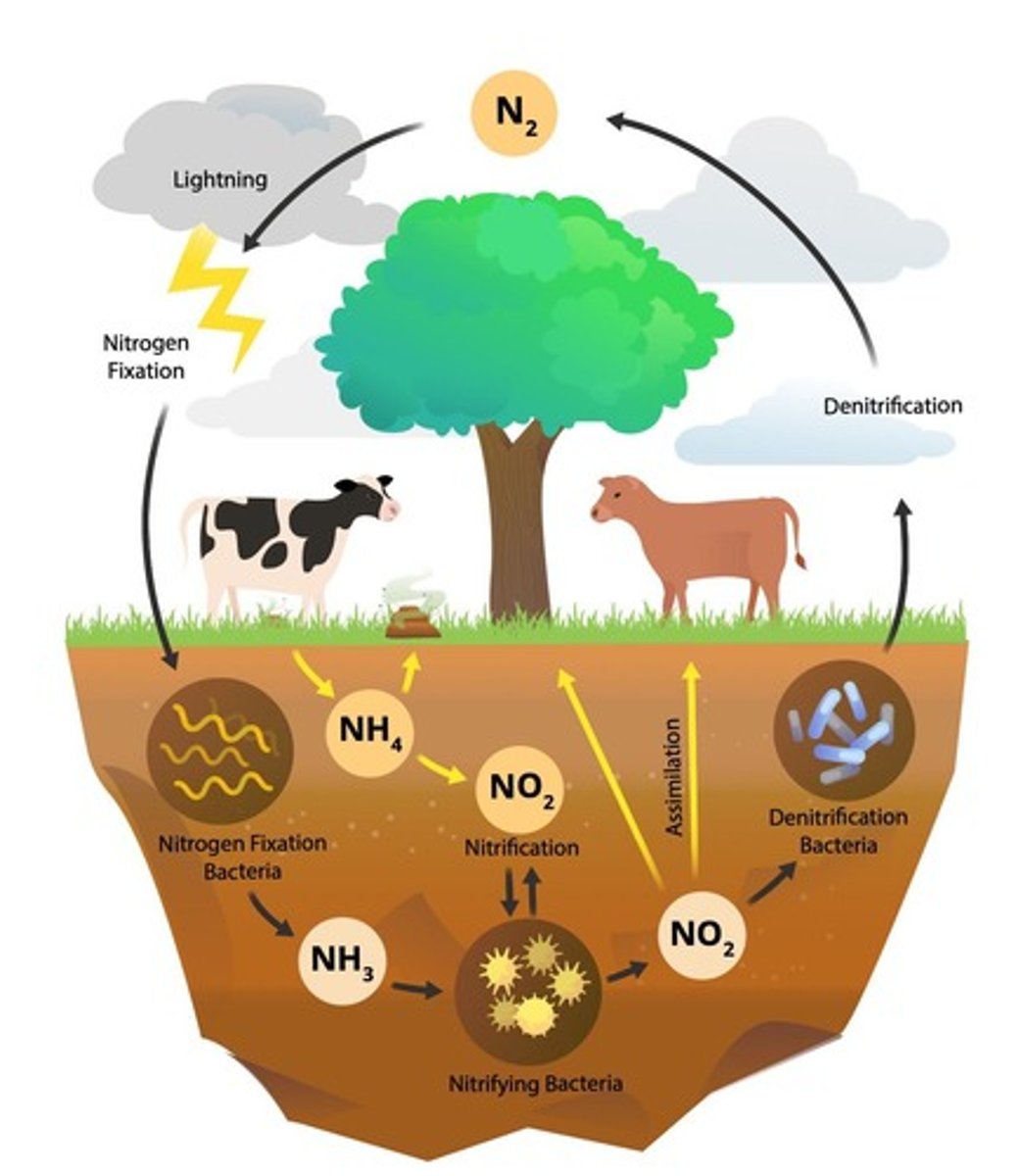
Fixation
Nitrogen must go through 'fixation' to be converted from its environmental form to a form usable by organisms.
Denitrification
Nitrogen must go through denitrification to be converted from the form used by organisms to the form that exists in the environment.
Biological magnification
As one organism eats another, toxins become more concentrated at higher trophic levels.
Eutrophication
Process where water becomes enriched with excess nutrients and biomass.
Succession
Change in composition of ecological community over time.
1º succession
Occurs on substrates that never previously supported living things (E.g., lichen growing on a rock previously devoid of life).
2º succession
Occurs where communities were entirely/partially destroyed by damaging event (E.g., forest regrowing after wildfire).
Pioneer species
First to colonize a newly exposed habitat; they are usually opportunistic, can tolerate harsh conditions, grow fast, and produce progeny rapidly.
Tropical grasslands
Characterized by high temperature, uneven seasonal rainfall, and scattered trees.
Tropical rain forest
Most diverse biome with high humidity and heavy rainfall.
Savannas
Grasslands with scattered trees and a seasonal occurrence of drought and fire.
Temperate grasslands
Regions with low precipitation, temperature fluctuations, and large mammals grazing.
North American prairie
A type of temperate grassland characterized by large mammals grazing.
Deserts
Regions with very little rainfall, extreme temperatures, and minimal vegetation.
Chaparral
A biome along California coastline with wet winters and dry summers.
Taigas
Cold forests with long cold winters and moderate precipitation.
Tundras
Cold regions with permafrost and minimal vegetation.
Temperate deciduous forests
Forests where large deciduous trees shed leaves during winter.
Vertical stratification
The layering of different plant species in a habitat, often seen in forests.
Detritivorous bacteria
Bacteria that decompose organic matter and can deplete oxygen in aquatic environments.
Realized niche:
Smaller subset of the niche that species occupy when competition is present