3.3.12 Polymers
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The study of polymers is extended to include condensation polymers. The ways in which condensation polymers are formed are studied, together with their properties and typical uses. Problems associated with the reuse or disposal of both addition and condensation polymers are considered.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Condensation polymers are formed by reactions between what? What polymers does each form?
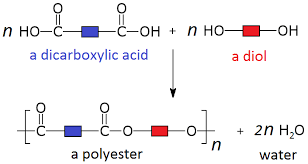
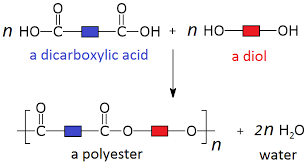
dicarboxylic acids and diols = Polyester
dicarboxylic acids and diamines = Polyesters
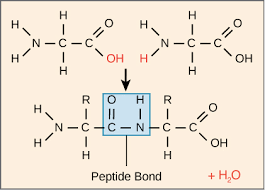
amino acids. = Polypeptides
Condensation polymer
A polymer that is formed when monomers join together, eliminating a small molecule such as water (or HCl) in the process.
Reactions between dicarboxylic acids and diols make polyesters.
The carboxyl groups of dicarboxylic acid can react with the -OH groups of diols to form ester links.
A water molecule is lost each time an ester link is formed. Therefore, this is a condensation reaction.
What bonding is in the polymer chains
There are permanent dipole-dipole attractions between the polymer chains in polyesters due to the the polar C=O bonds in the ester linkage.
Therefore, there are greater forces of attraction between the polymer chains in polyesters compared to the weak van der Waals forces between addition polymer chains.
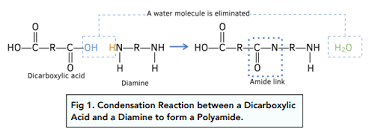
Reactions between Dicarboxylic acids + diamines make polyamides.
Diamine molecules have amine groups (R-NH2) at either end of their molecules.
The amine and carboxylic acid groups react to form amide links between the molecules.
Water is removed from the reaction.
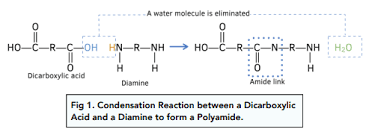
What bonds are present in polyamides?
There are H−bonds between the polymer chains in polyamides due to the presence of C=O bonds and N−H bonds.
This means there are greater forces of attraction between the polymer chains in polyamides compared to the weak van der Waals forces between addition polymer chains.
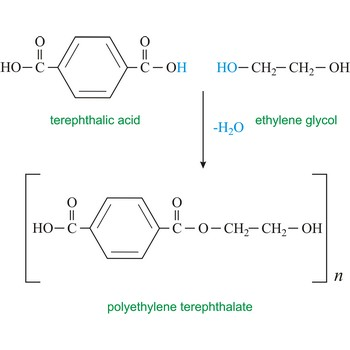
Is PET a polyester or polyamide
Polyester
What is PET used for
Terylene is used to make plastic bottles (and similar plastic products) and is recycable.
1.) What is the structure of the polymer PET
2.) What is the monomer of the polymer PET
Is Nylon 6,6 a polyester and polyamide
Polyamide
1.) Monomers of nylon 6,6
2.) Polymer structure of nylon 6,6
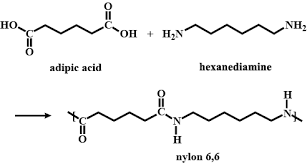
What is nylon used for?
• Nylon is used to make fabrics, ropes, and medical prosthetics.
Is Kevlar a polyester or polyamide?
Polyamide
1.) Structure of polymer Kevlar
2.)Monomers of kevlar
Monomer 1: a dicarboxylic acid, benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid.
Monomer 2: a diamine, 1,4-diaminobenzene.
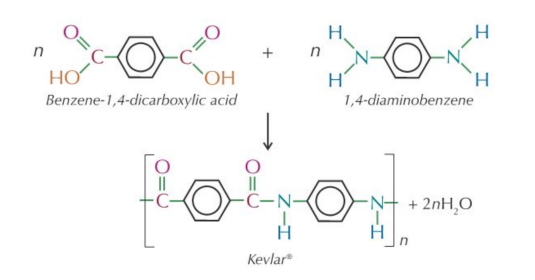
What is Kevlar used for
Kevlar is used to make bullet-proof vests (because it’s strong, stable and also fire resistant).
What is the structure of amino acids
Amino acids contain an amine functional group and a carboxylic acid functional group.
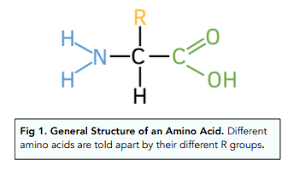
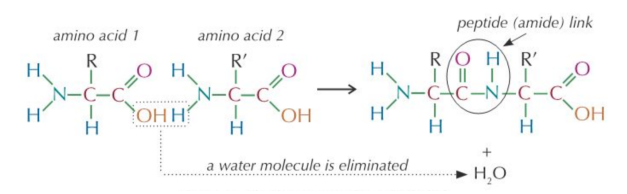
What do polyamides form from amino acids?
Polypeptides
Write the Formation of polypeptide from two amino acids molecule
What determines the biodegradability of polymers
It depends on the types of intermolecular forces within the polymer chains:
If a polymer has no polar bonds, it is non-biodegradable.
If a polymer contains polar bonds, it can undergo hydrolysis by acid or base, allowing it to break down.
Newly developed synthetic polymers called Photodegradable polymers, are biogradable. Explain why?
Photodegradable polymers break down when exposed to UV light.
Are polyesters/amides biodegradable, why?
Polyesters and polyamides can be broken down by hydrolysis. This means they are biodegradable.
How are polyalkenes formed?
Polymers formed through addition polymerisation (Addition polymers are produced when alkene molecules combine through an addition reaction) are known as polyalkenes.
What is the structure of polyalkenes
The main chain of a polyalkene consists of carbon atoms connected by strong covalent bonds.
Describe the key properties of polyalkenes
Polyalkenes are chemically inert and non-biodegradable.
Why are they inert and non-biodegradable
Since addition polymers lack polar bonds, they are inert and non-biodegradable.
Why is this bad?
They are inert and non-biodegradable, making them resistant to breakdown in natural environments.
Two types of hydrolysis
Acid and Base
Acid hydrolysis of polyesters
Acid Hydrolysis: When treated with dilute acids, polyesters revert to their original dicarboxylic acids and diols.
Base hydrolysis of polyesters
Base Hydrolysis: With dilute alkalis, polyesters break down to produce dicarboxylic acid salts and diols.
Acid Hydrolysis of polyamides
When polyamides are hydrolysed with dilute acids, they yield dicarboxylic acid and diamine salts.
Base Hydrolysis of polyamides
Base Hydrolysis: With dilute alkalis, polyamides break down into dicarboxylic acid salts and diamines.
Why are polyalkenes hard to dispose
Polyalkenes are chemically inert and NON-biodegradable (they cannot be
hydrolysed)This is because they’re saturated and have no bond polarity.
This means their disposal is a considerable problem, they remain in the environment almost forever.
This is the stuff a lot of plastic bags are made from.
+tives of disposal in landfill
- Does not produce toxic gases. - Most cost-effective |
-tives of disposal in landfill
- Limited space in landfills. - Toxins from decomposing waste can contaminate water supplies. - Releases methane (CH4). |
+tives of Incineration
- Saves money on transport costs. - Reduces the amount of waste sent to landfill. |
-tives of Incineration
- Produces toxic gases (CO, HCl, HCN). - Contributes to global warming. - More expensive than landfill. |
+tives of recycling
- Conserves crude oil supplies. - Reduces the amount of waste sent to landfill. - Produces less CO₂ than incineration. |
-tives of recycling
- Collecting, sorting, and processing plastic is more expensive than landfill or incineration. - Plastic can be contaminated during recycling. |