Lecture 31 Carbohydrate Structure and Function
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Sugars have many ________ attached.
alcohols
Alternative sugars such as sucralose have _________ attached instead of alcohols which makes them taste 300 times sweeter.
chlorides
_______ have the same molecular formula but different structure.
Isomers
_______ are isomers that differ at a new asymmetric carbon atom formed on ring closure.
Anomers
_______ differ at one of several asymmetric carbon atoms.
Epimers
_____________ have the same molecular formula but differ in the configuration of their atoms in space.
Stereoisomers
___________ are stereoisomers that are not superimposable on their mirror images. (only way to distinguish is polarized light)
Enantiomers
_____________ are one monomeric unit sugars (glucose)
Monosaccharides
________________ are 2-20 monosaccharides
Oligosaccharides
_______________ are more than 20 monosaccharides (glycogen)
Polysaccharides
_______________ are sugars linked to proteins or lipids
Glycoconjugates
______ have an oxygen double bond on the end. Most oxidized carbon is _-_.
Aldoses; C-1
_______ have an internal oxygen double bond. Most oxidized carbon is usually _-_.
Ketoses, C-2
_______ is a C-2 epimer of glucose. (OH is on opposite side of C-2)
Mannose
_________ is a C-4 epimer of glucose. (OH is on opposite side of C-4)
Galactose
________ is a ketose sugar that is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway.
Ribulose
________ is an important ketose sugar with 6 carbons
Fructose
Glucose is an ______ sugar
aldose
_____ anomers have an OH group on the bottom of the anomeric carbon in cyclized form
Alpha
____ anomers have an OH group on the top of the anomeric carbon in cyclized form
Beta
Most of our amino acids are _
L
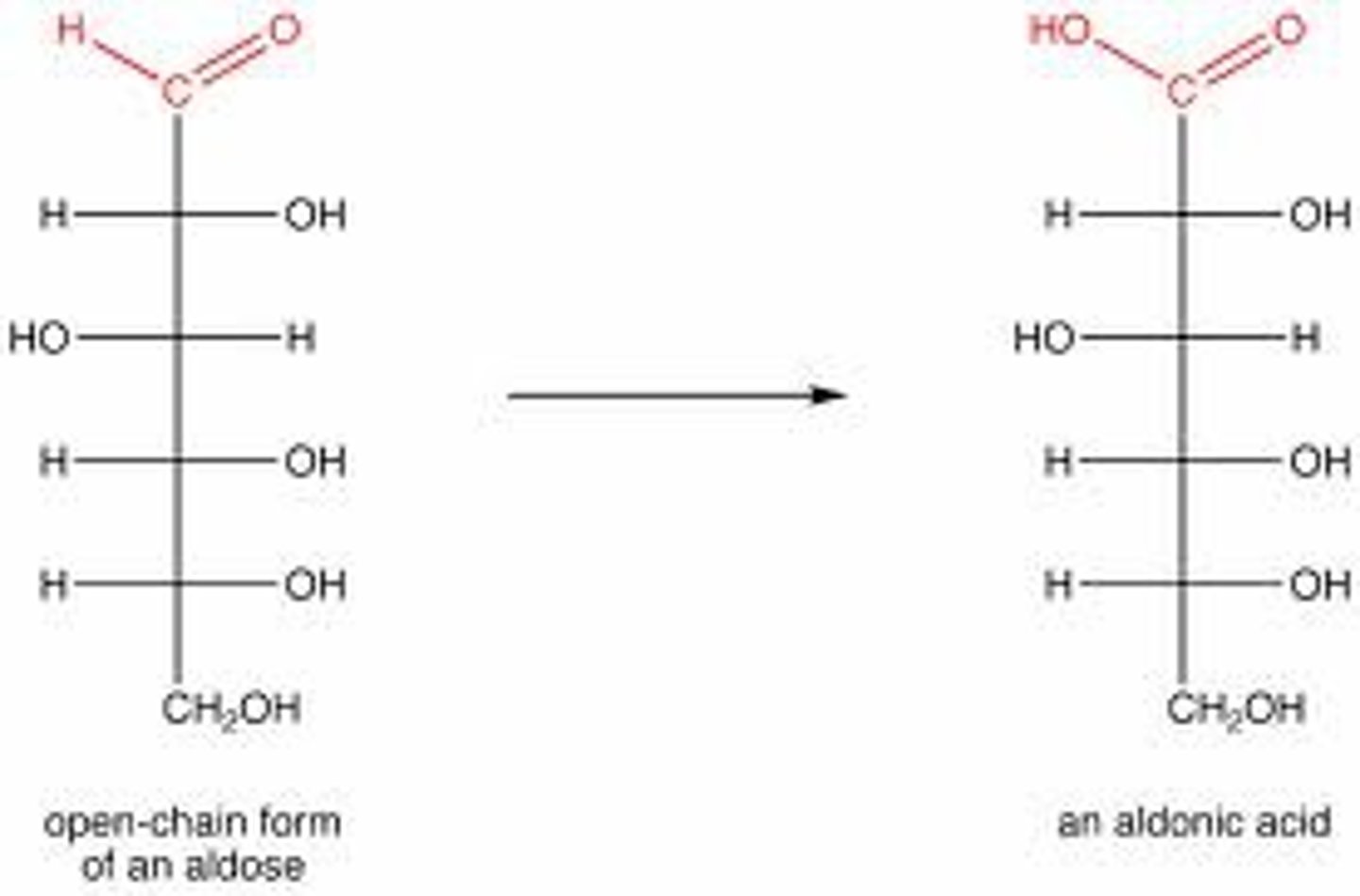
_______ _____: oxidation of (aldose) aldehyde group to a carboxylic acid
Aldonic acids
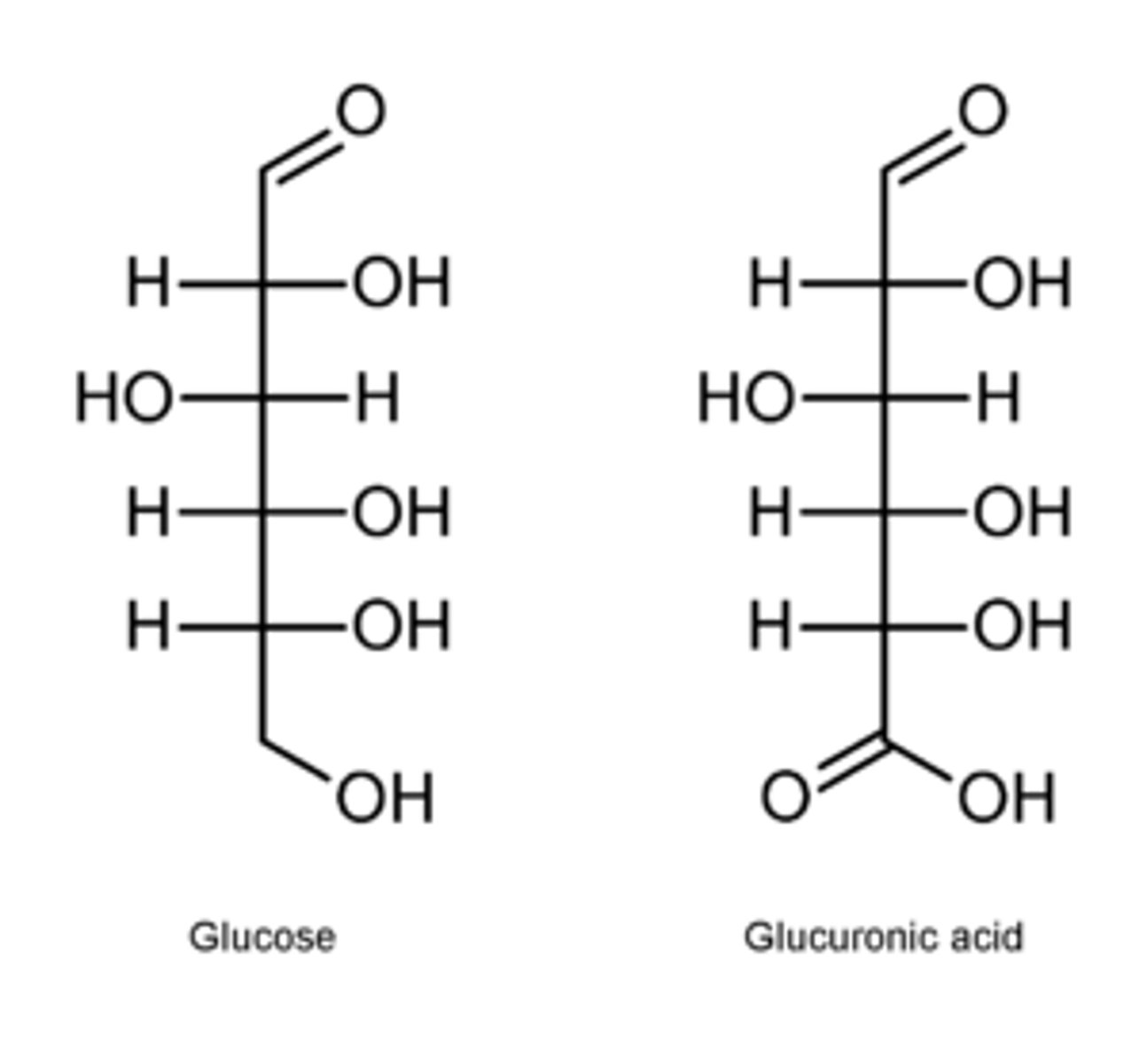
______ _____: oxidation of primary alcohol group to carboxylic acid
Uronic acids
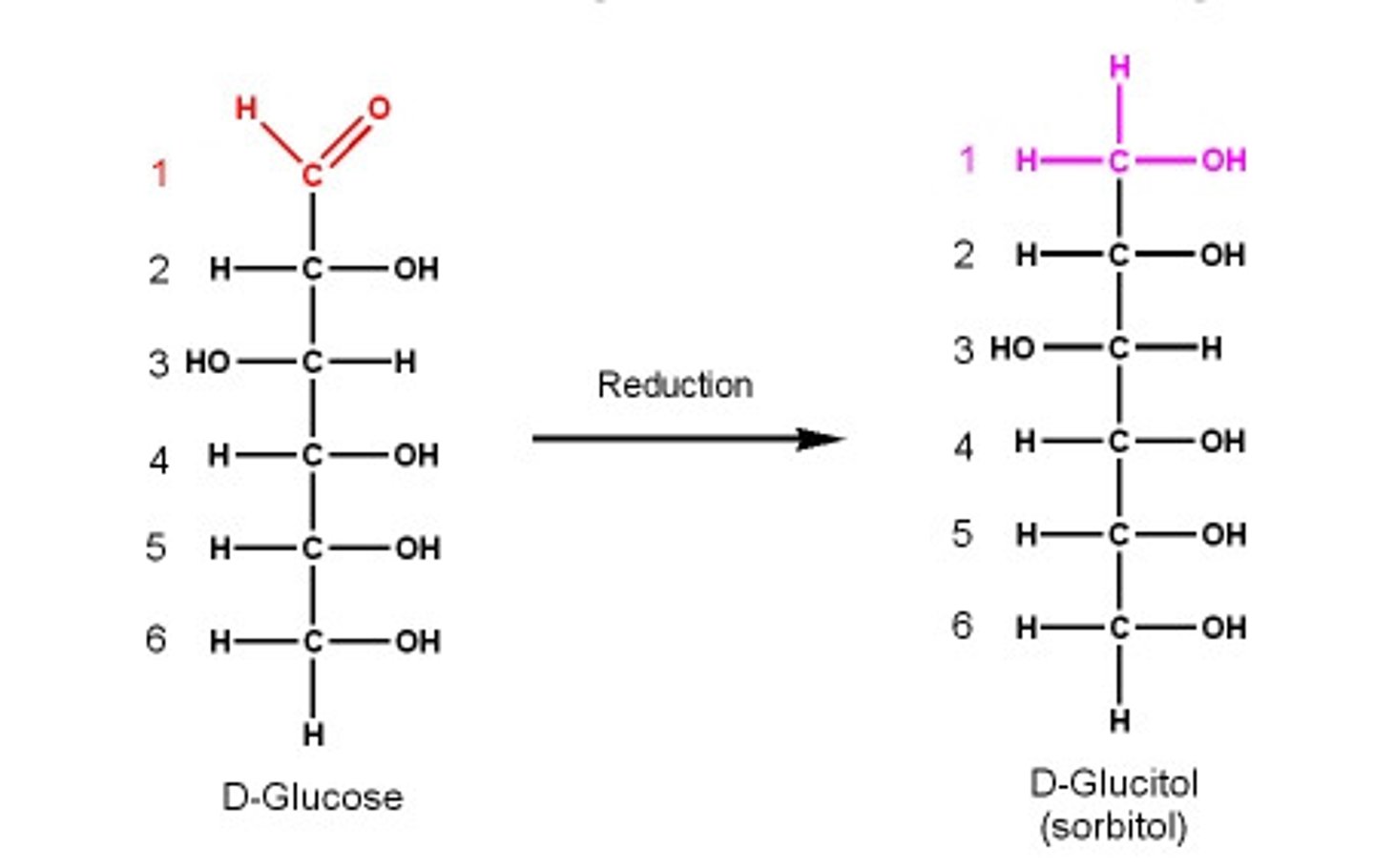
________: reduction of ketose and aldose aldehyde to hydroxyl
Alditols
_____ ______: OH group replaced by H
Deoxy sugars
_____ ______: one or more OH groups are replaced by an amino group
Amino sugars
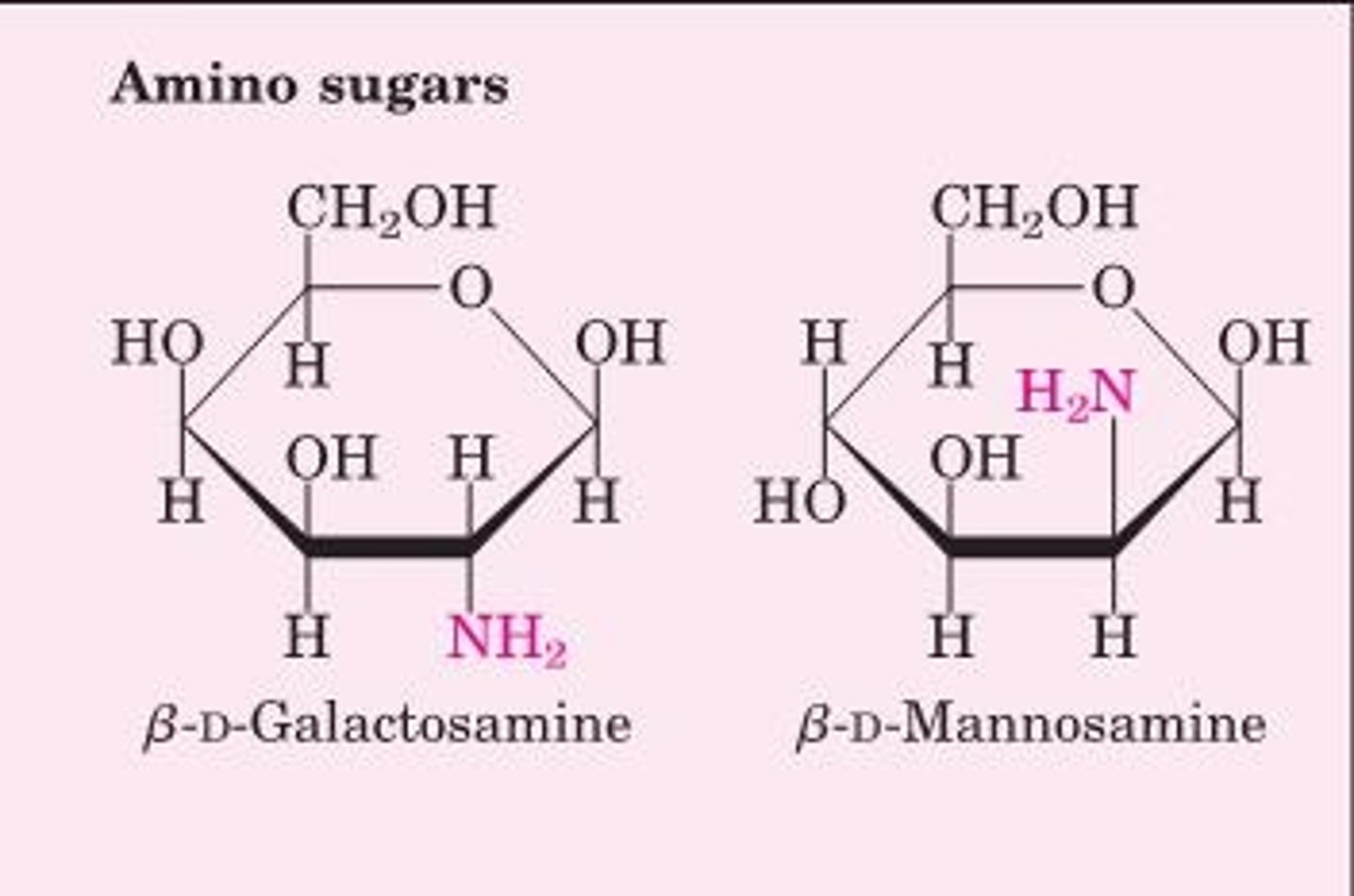
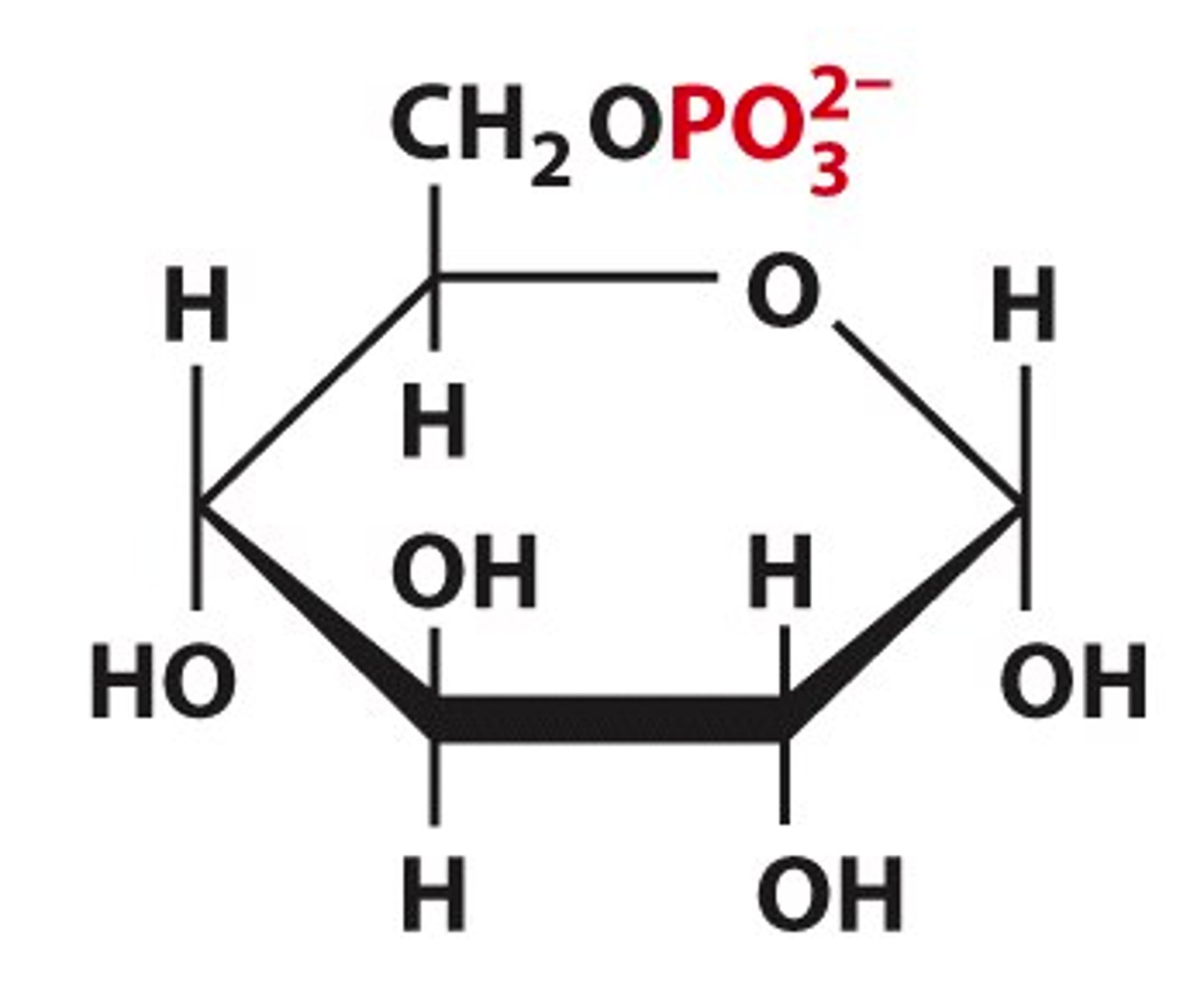
_____ _________: addition of phosphate to a hydroxyl group
Sugar phosphates
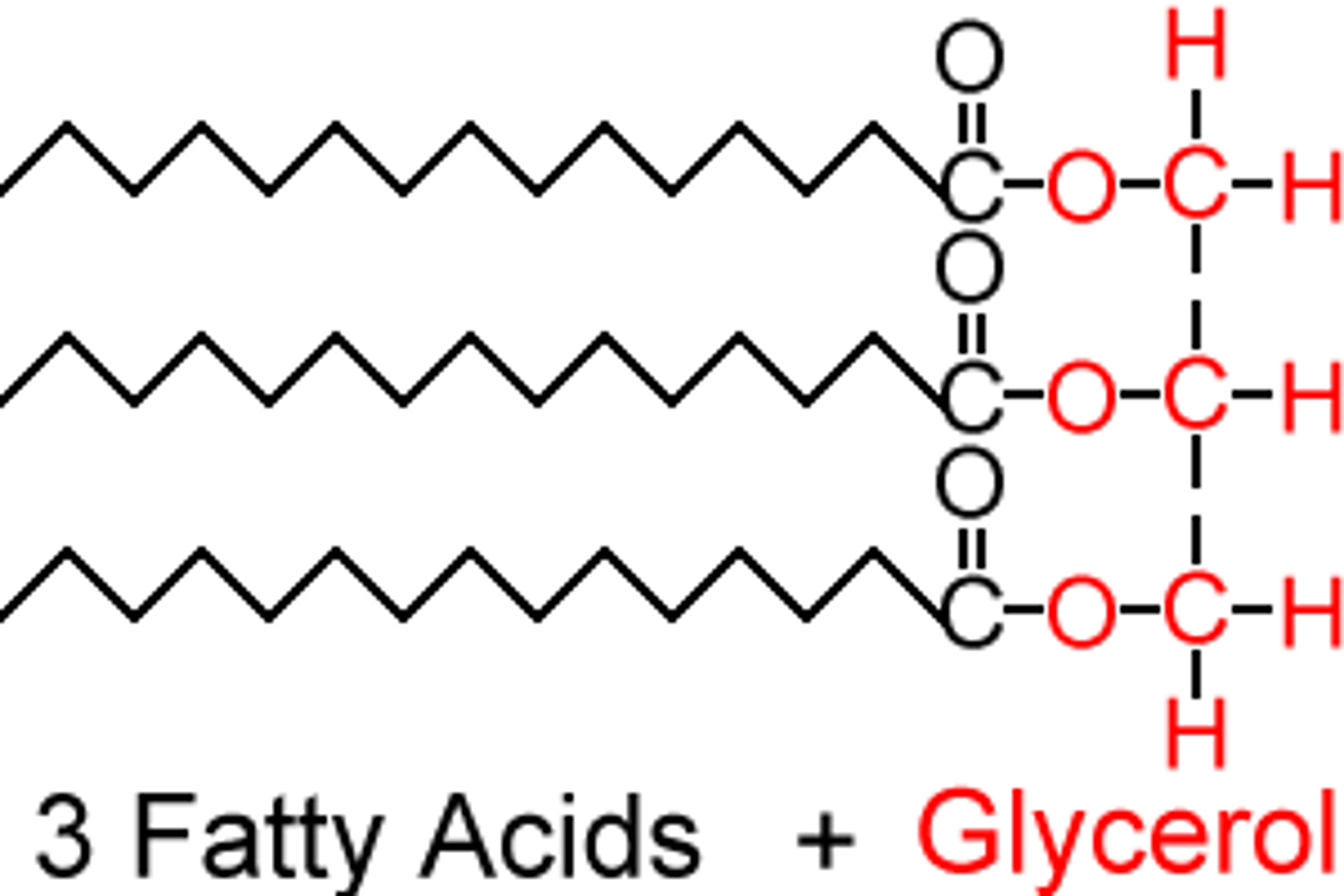
Glycerol is a _____ _______ where the carbonyl oxygen is reduced. Used in storage of fats in the form of triglycerides.
sugar alcohol
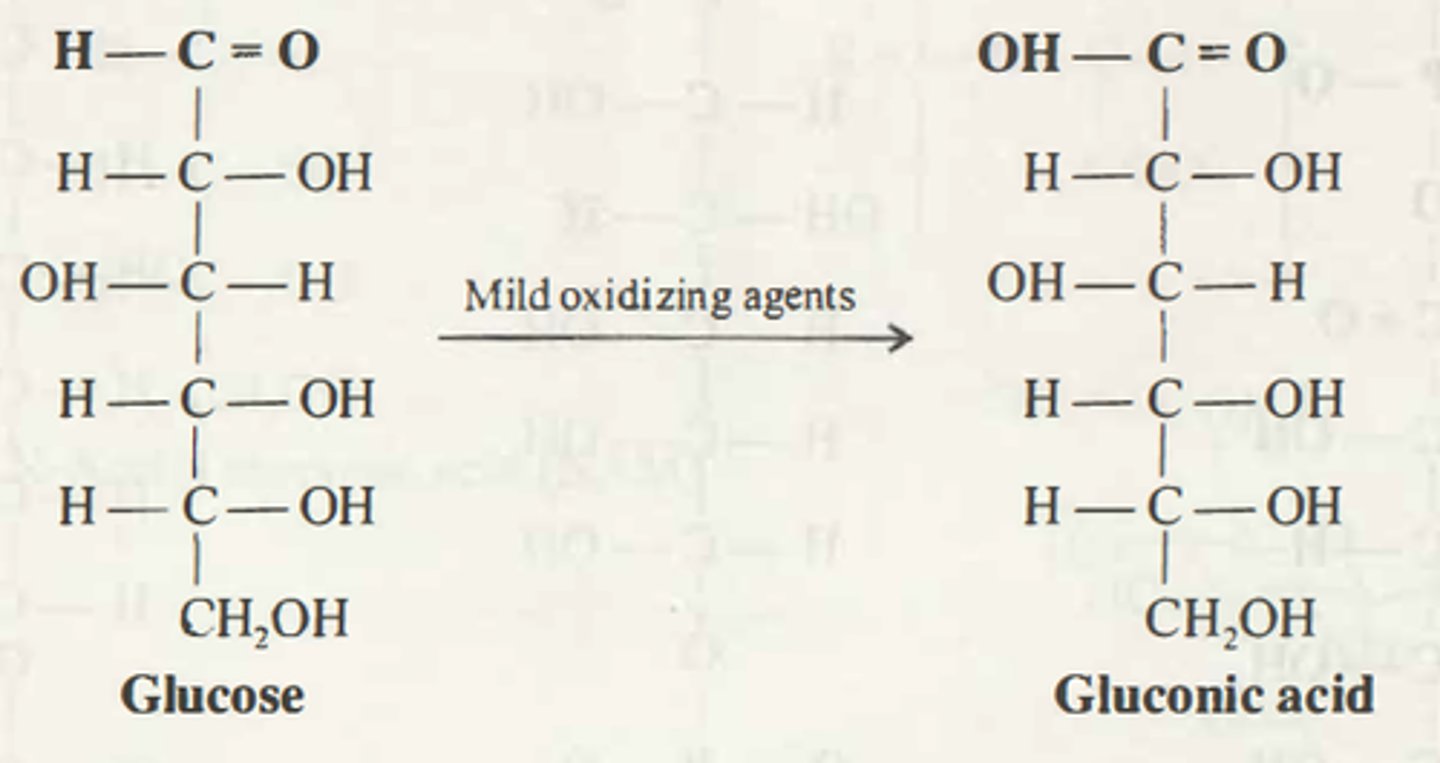
_____ _____ are carboxylic acids where C-1 is oxidized to yield an aldonic acid and the highest-numbered carbon is oxidized to an alduronic acid
Sugar acids
A __________ bond is a primary structural linkage in all polymers of monosaccharides
glycosidic
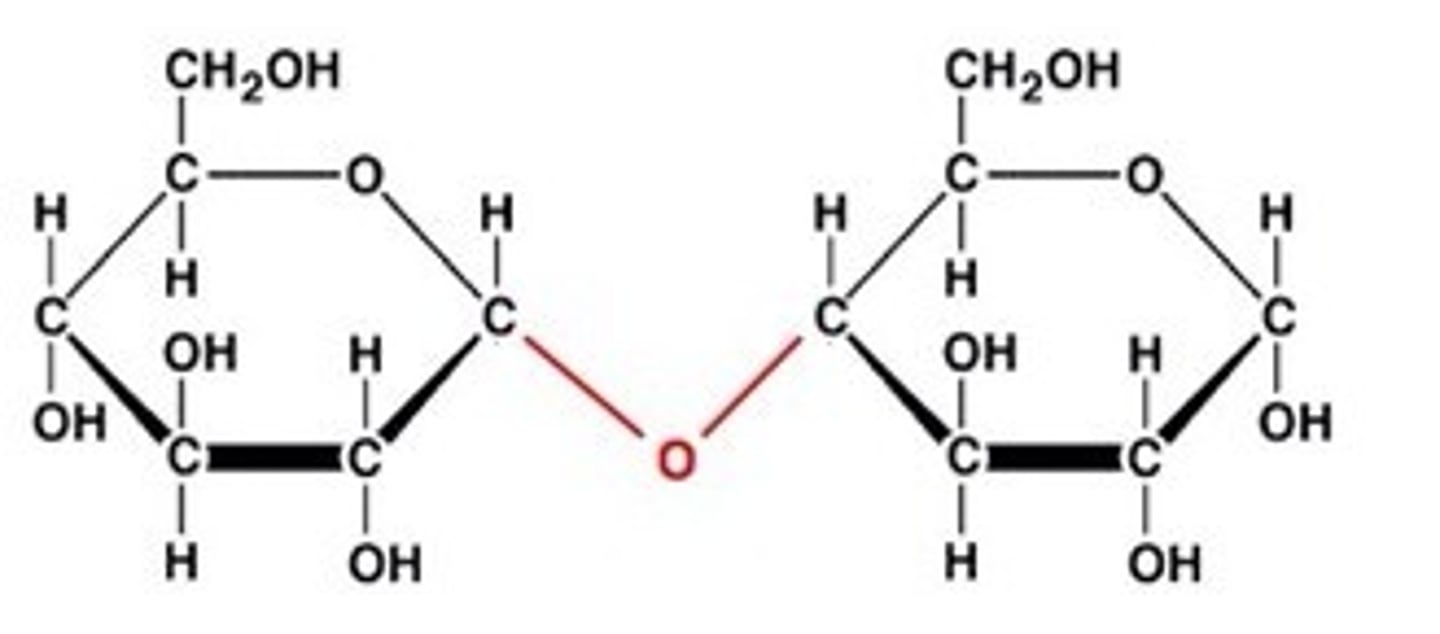
Glycosidic bonds form at the OH group of the ________ carbon.
anomeric
____ linkages form with an OH group on the top of the anomeric carbon of the first monosaccharide.
Beta (lactose)
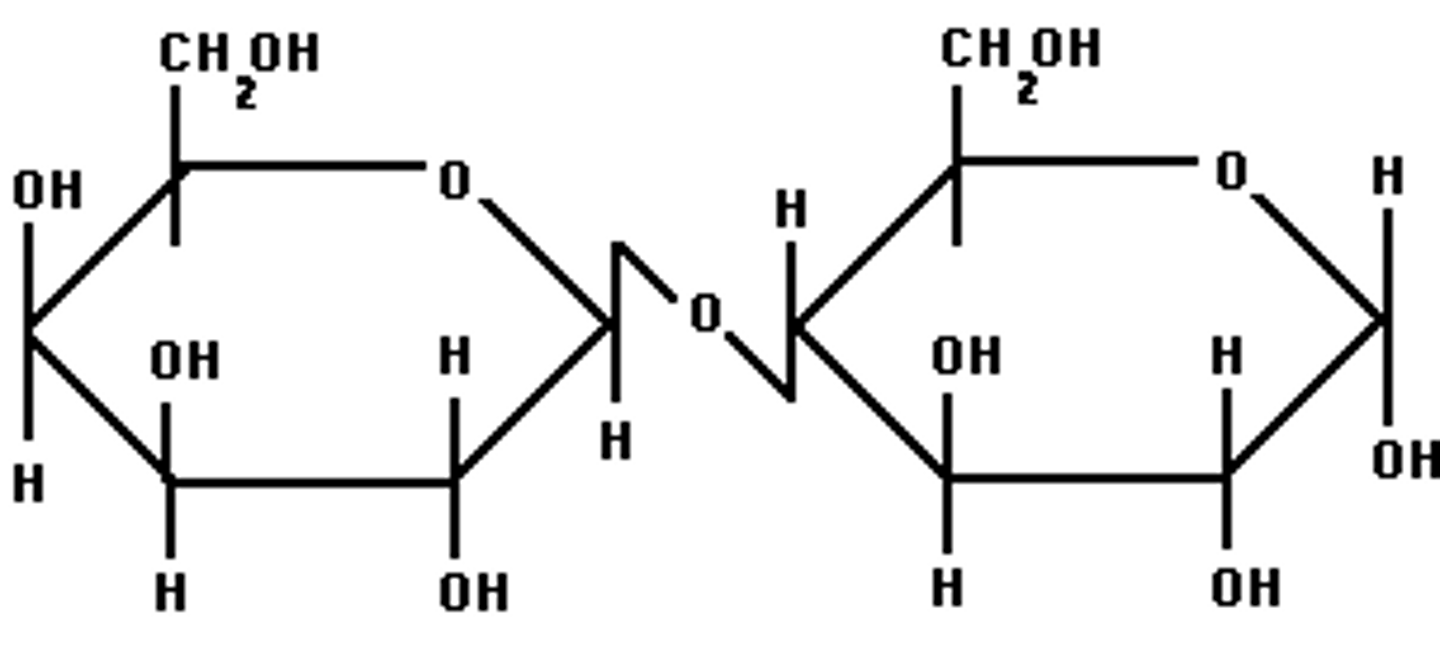
_____ linkages form with an OH group on the bottom of the anomeric carbon of the first monosaccharide.
Alpha (sucrose)
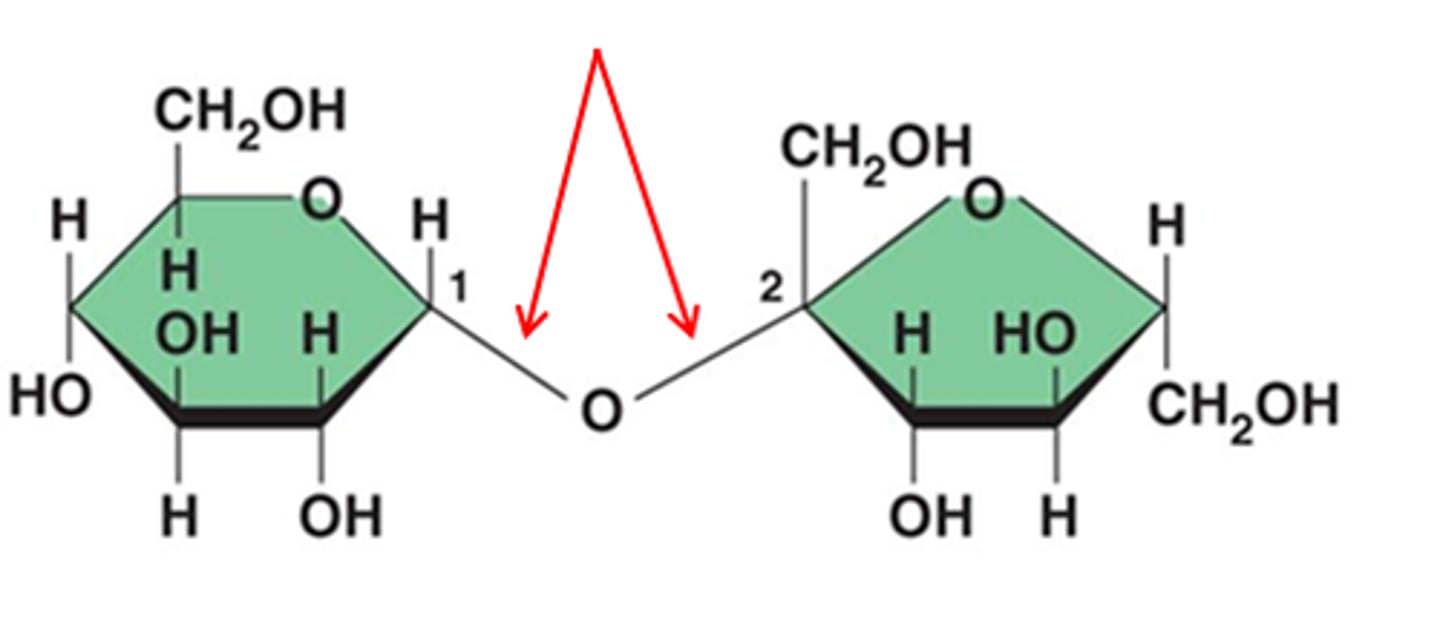
A ________ sugar is still able to open up at the anomeric carbon. (OH on anomeric carbon is not bound to another monosaccharide)
reducing
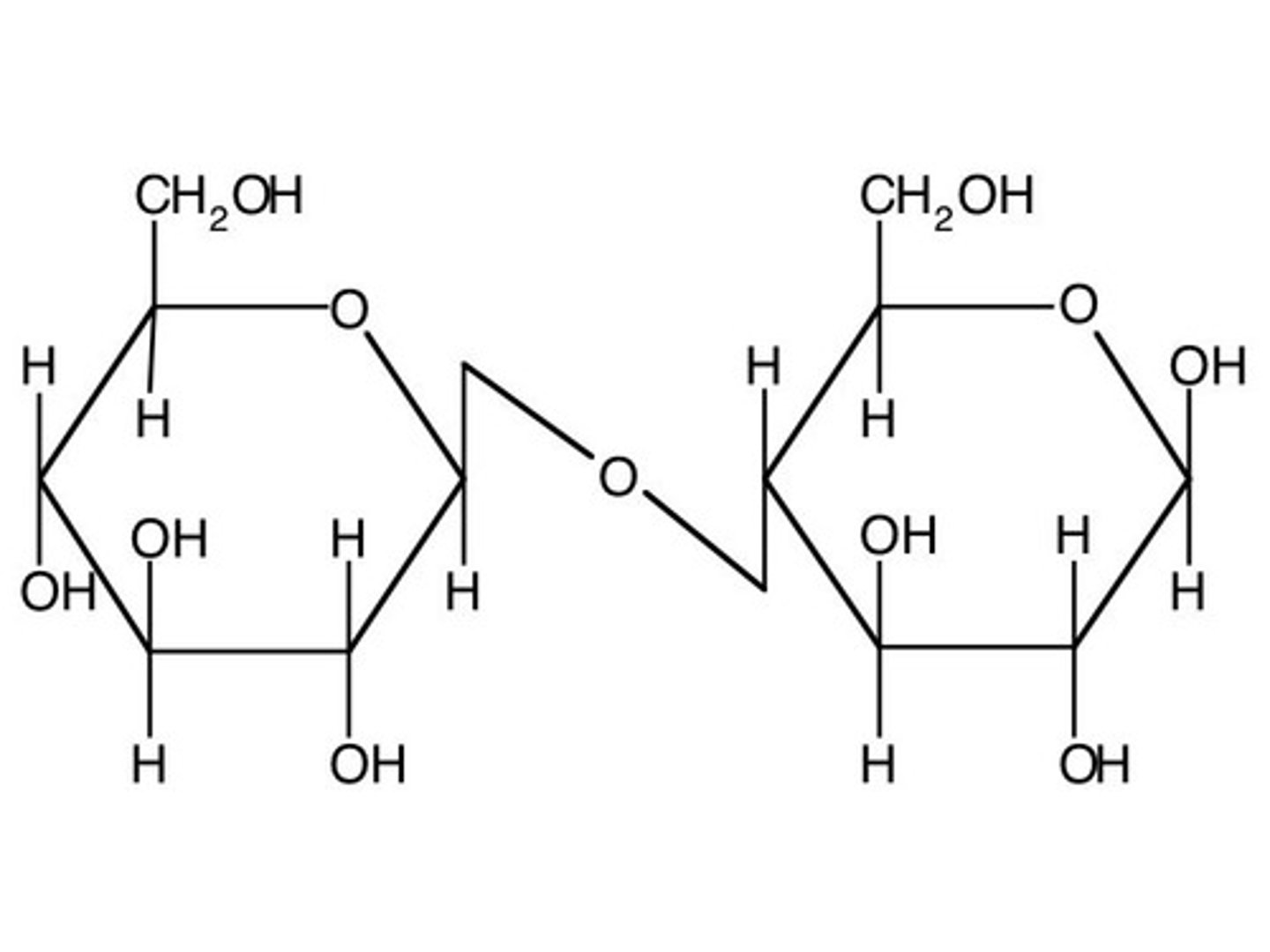
A ___-________ sugar is not able to open up at the anomeric carbon because it is bound to another monosaccharide.
non-reducing
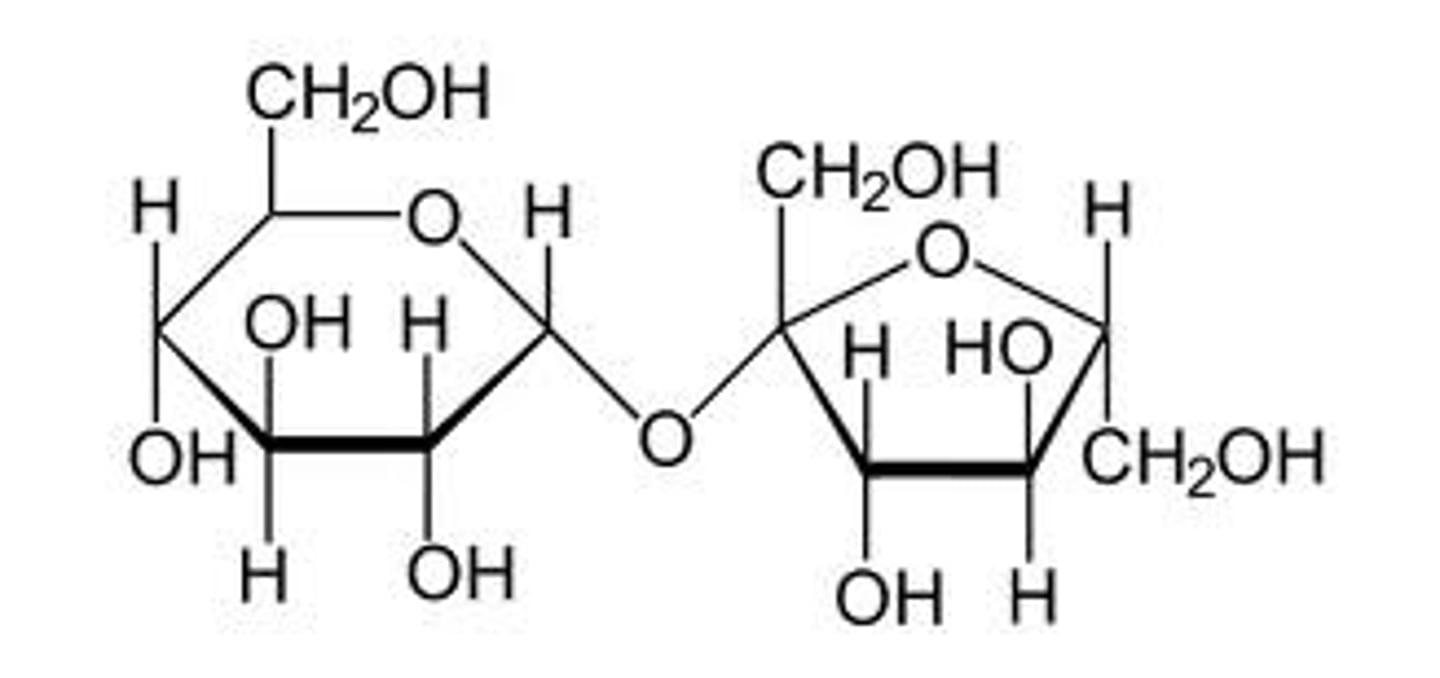
Disaccharide structure is written starting with the ___-________ end at the left.
non-reducing
In order to be a reducing sugar, both ________ carbons cannot be bound to one another.
anomeric
___________ are homopolysaccharides containing only one type of monosaccharide. (glycogen)
Homoglycans
_____________ are heteropolysaccharides containing residues of more than one type of monosaccharide.
Heteroglycans
Glycoconjugates include _____________, ______________, and _____________.
proteoglycans; peptidoglycans; glycoproteins
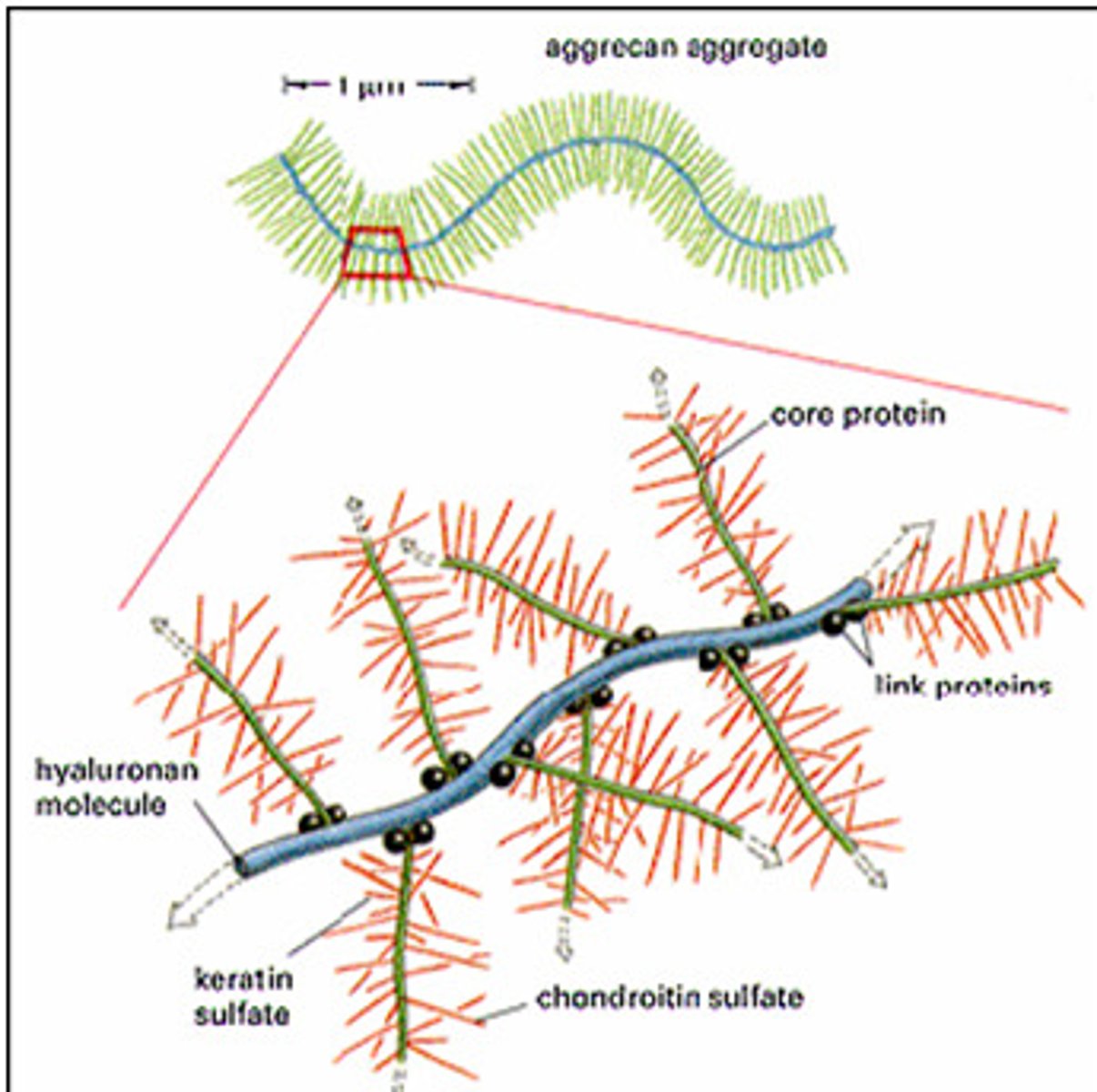
_____________ are glycosaminoglycan-protein complexes. A core molecule has branches of core proteins which is attached to smaller branches of oligosaccharides. (hydrophilic because of sugar residues, present in hyaluronic acid)
Proteoglycans
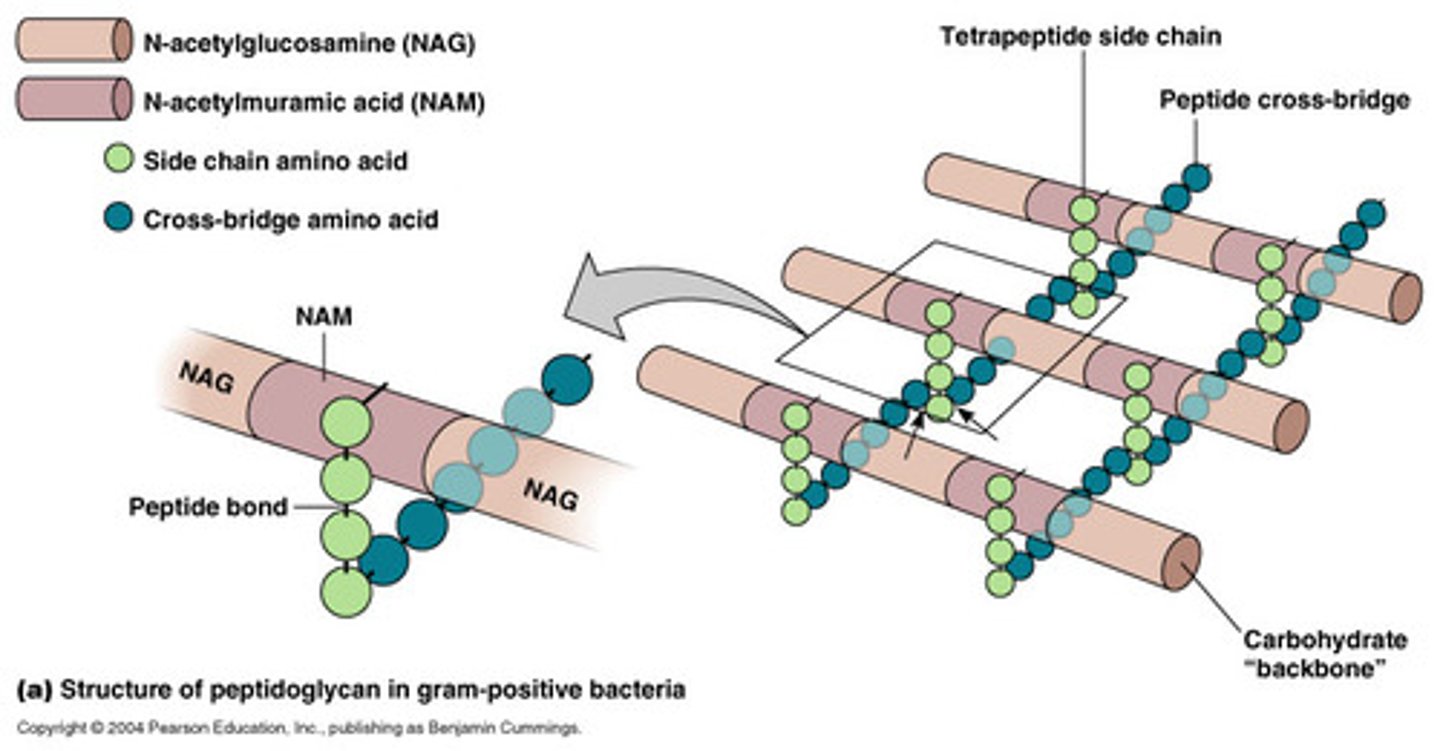
______________ are heteroglycan chains linked to peptides. Major component of bacterial cell wall.
Peptidoglycans
_____________ are proteins that contain covalently-bound oligosaccharides which exhibit great variability.
Glycoproteins
The addition of one or more oligosaccharide chains (glycosylations) affects a protein's ________ __________ which, in turn, affects the __________ __________.
physical properties; biological properties
Glycoproteins are important in the specificity of _____ ________ and ________.
blood proteins; antigens