AP PSYCH DISORDERS AND TREATMENTS
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
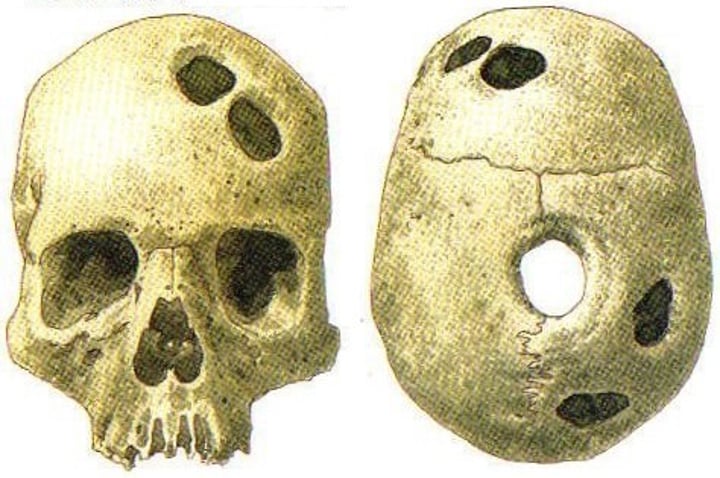
Trephining
practice in which holes were drilled into the skull in an attempt to release evil spirits
Deinstitutionalization
moving people with psychological or developmental disabilities from highly structured institutions to home- or community-based settings

Psychotherapy
treatment involving psychological techniques; consists of interactions between a trained therapist and someone seeking to overcome psychological difficulties or achieve personal growth

free association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing

dream analysis
the therapist interprets the symbolic meaning of the client's dreams

manifest content
the remembered story line of a dream

latent content
the underlying meaning of a dream

Resistance
in psychoanalysis, the blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material
Transference
in psychoanalysis, the patient's transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships (such as love or hatred for a parent)

insight therapies
therapies that aim to improve psychological functioning by increasing a person's awareness of underlying motives and defenses

humanistic therapies
therapies that emphasize the development of human potential and the belief that human nature is basically positive

Roger's Client-Centered Therapy
help clients take responsibility for themselves; unconditional positive regard; non-directive

unconditional positive regard
an attitude of total acceptance toward another person

active listening
Empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy.
Gestalt therapy
therapy that aims to integrate different and sometimes opposing aspects of personality into a unified sense of self

Behaviorist therapies
aimed at changing disordered behavior without concern for the original causes; uses basic learning techniques to modify maladaptive behavior patterns by substituting new responses to given stimuli for undesirable ones

counterconditioning
a behavior therapy procedure that uses classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors; includes exposure therapies and aversive conditioning
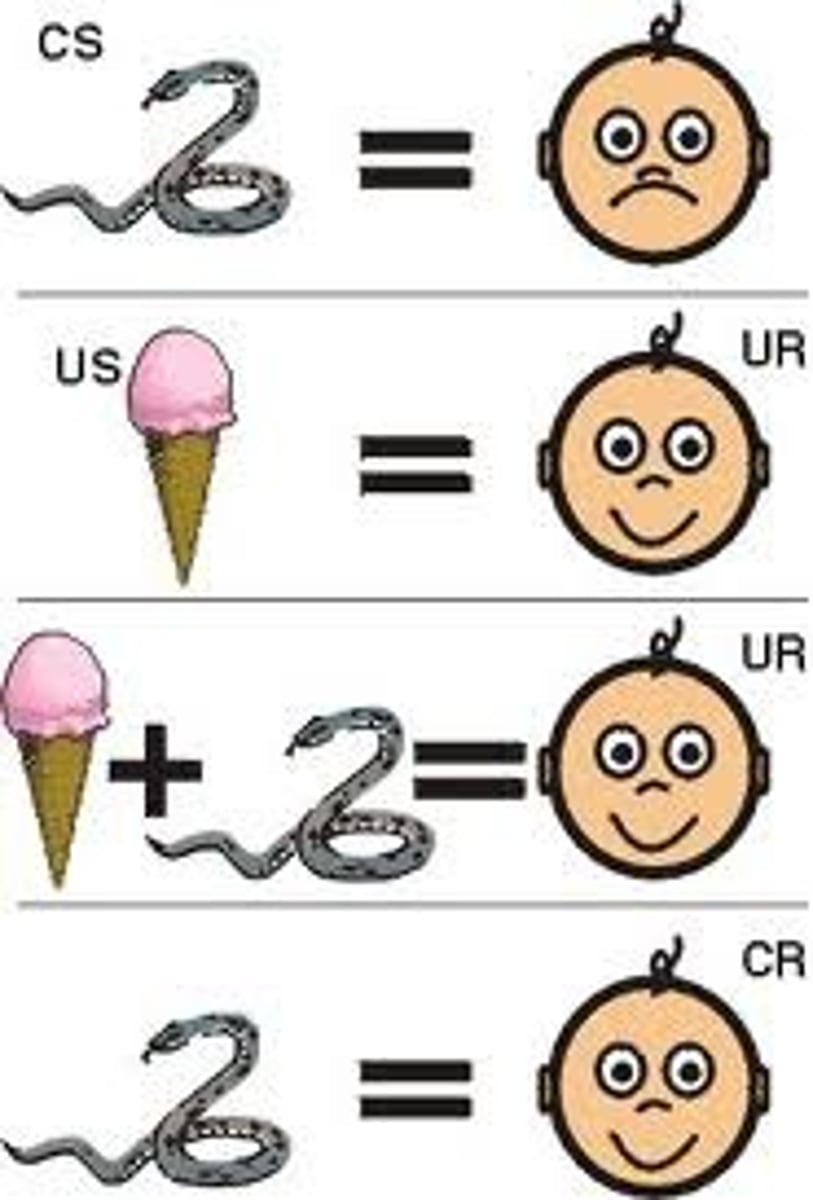
systematic desensitization
A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. Commonly used to treat phobias.

anxiety hierarchy
constructed by patient in which feared situations are arranged from least to most anxiety provoking; used to set sequence for therapy
flooding
a treatment for phobias in which clients are exposed repeatedly and intensively to a feared object and made to see that it is actually harmless
aversive conditioning
a type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior (such as drinking alcohol)

token economy
an operant conditioning procedure in which people earn a token of some sort for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for various privileges or treats

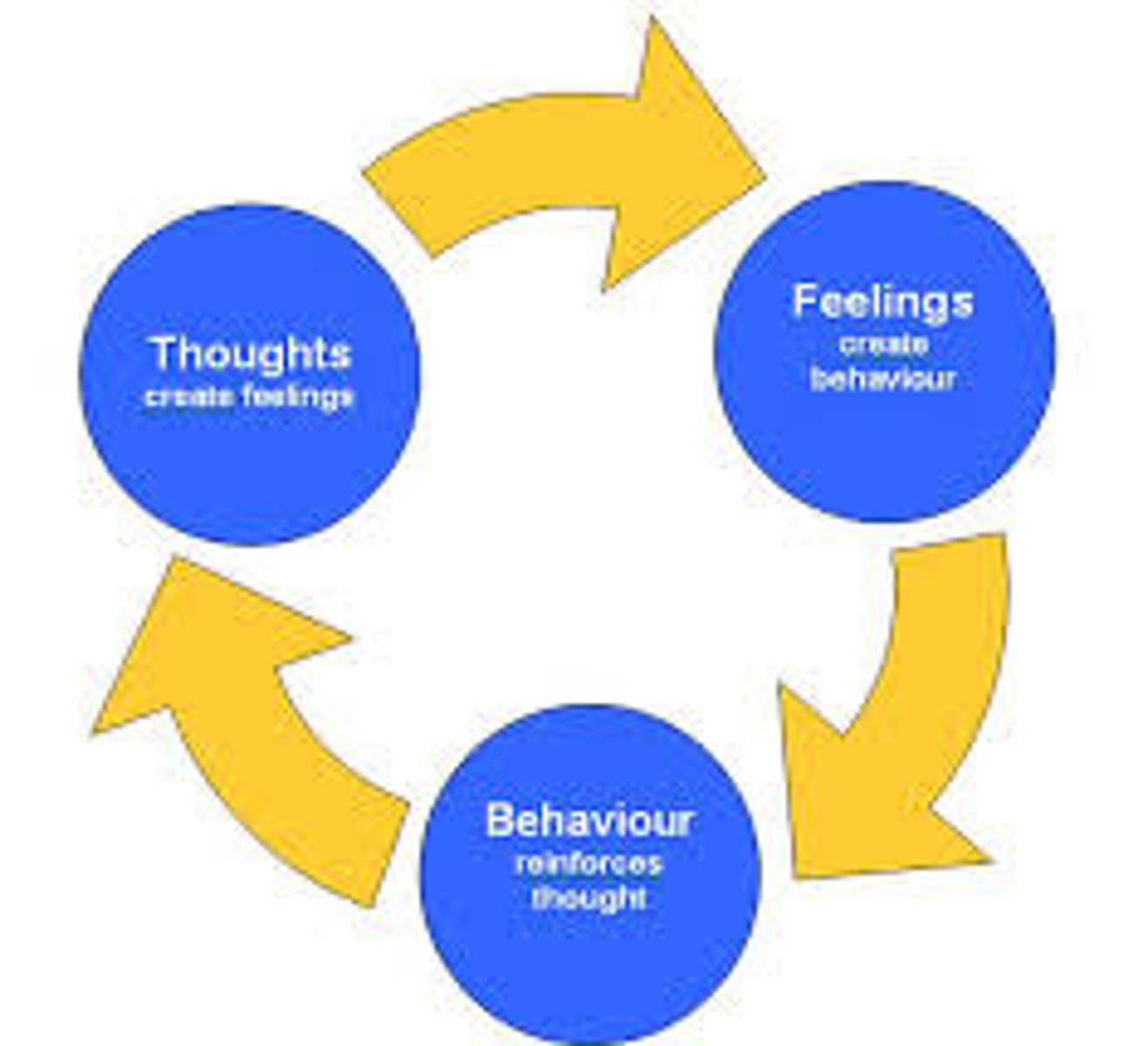
cognitive therapies
therapy that teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking and acting; based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions
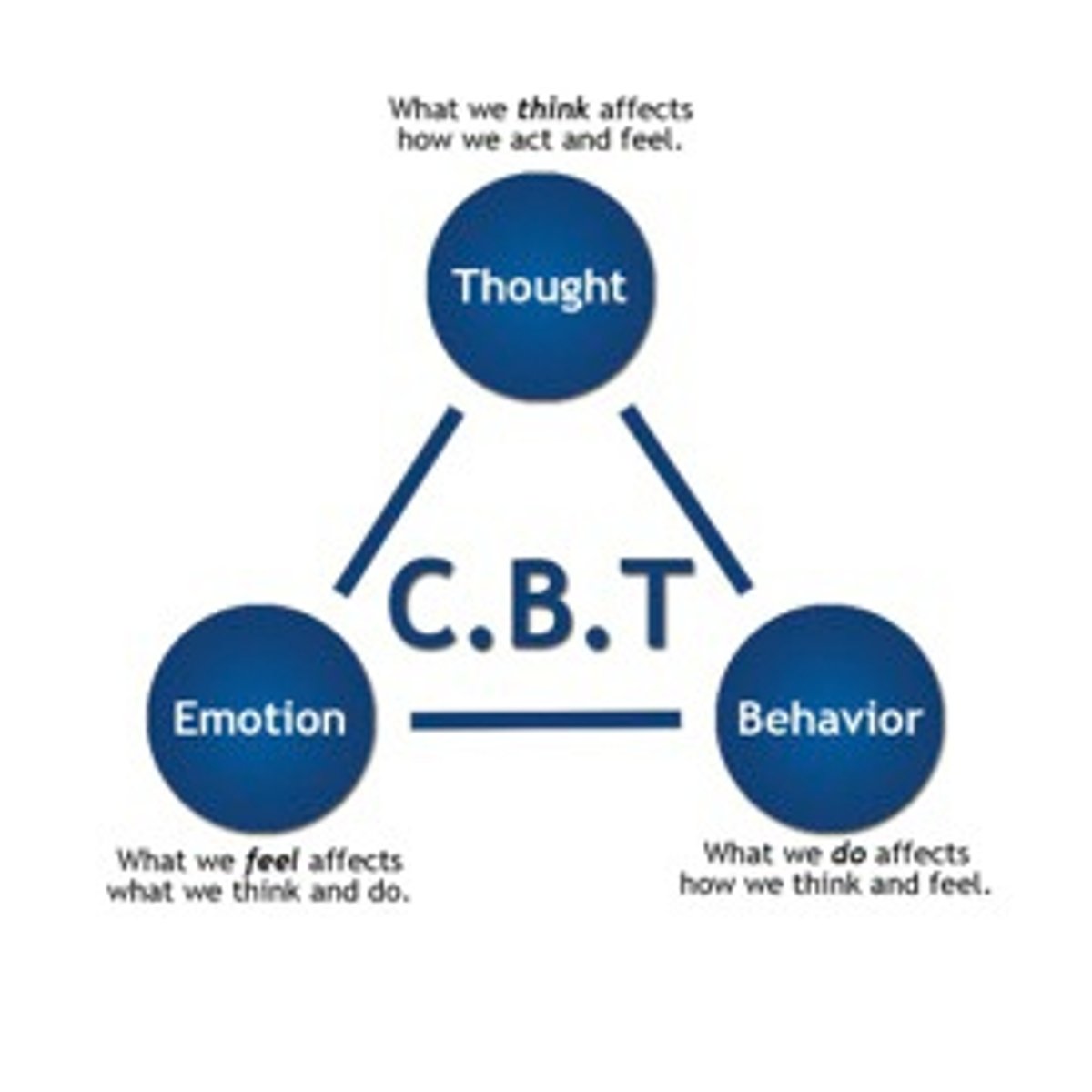
cognitive behavioral therapy
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
Ellis' Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
attempts to restructure a person's belief system into a more realistic, rational, and logical set of views

Group therapies
Therapist led small groups that are cheaper and help people see others with similar problems.

psychopharmacology
the use of drugs to control or relieve the symptoms of psychological disorders
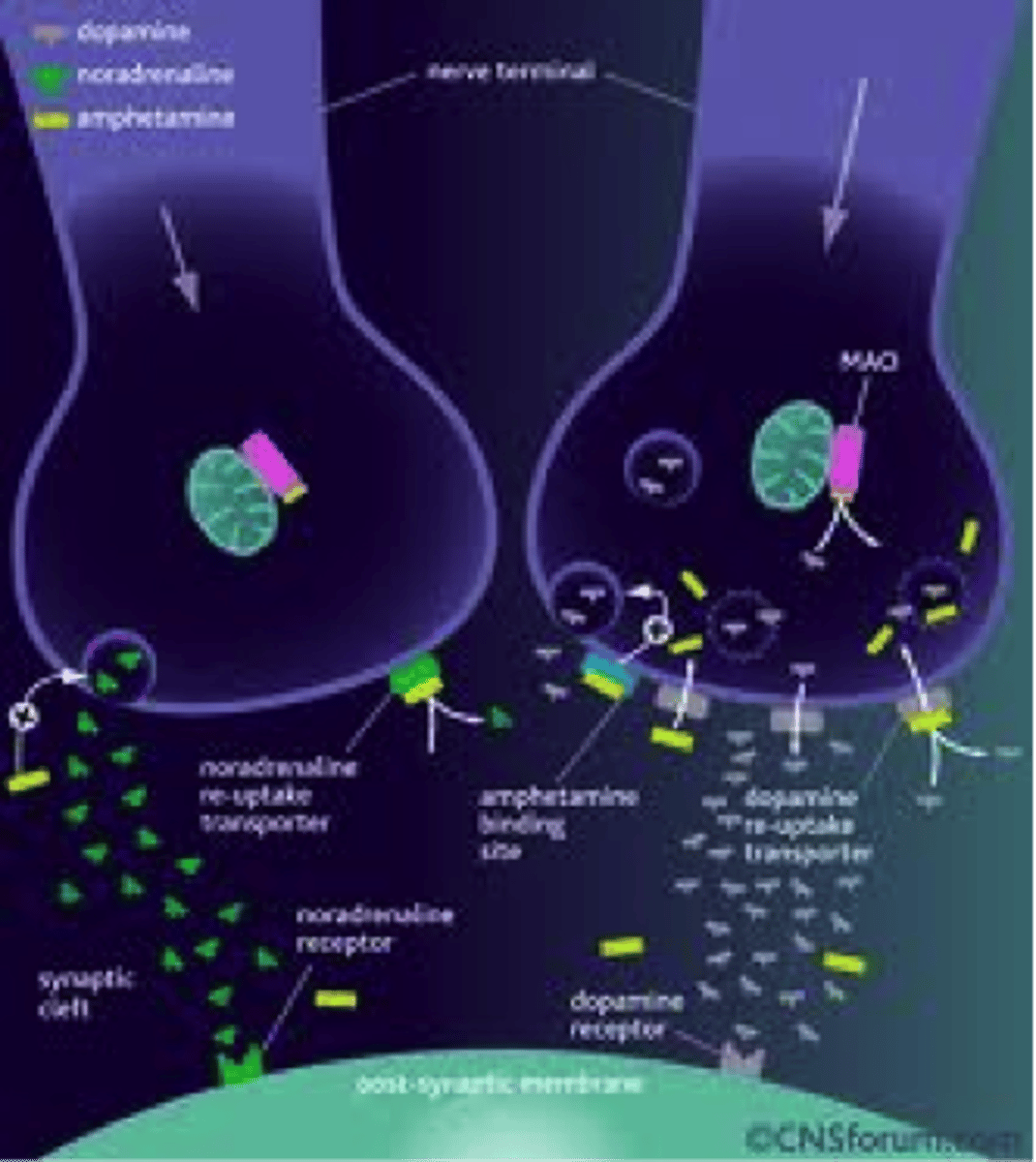
antipsychotic drugs
medications that are used to treat schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders,
Antidepressants
drugs that combat depression by affecting the levels or activity of neurotransmitters in the brain (Act slow)
antianxiety drugs
drugs used to treat and calm anxiety reactions, typically minor tranquilizers, act fast

electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
Catharsis
the process of releasing, and thereby providing relief from, strong or repressed emotions.

Insane
not sane

DSM
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders

Agoraphobia
fear or avoidance of situations, such as crowds or wide open places, where one has felt loss of control and panic

Social Phobia
a disorder that involves an irrational fear of being publicly humiliated or embarrassed

GAD
generalized anxiety disorder
Anxiety Disorder
a condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control

Somatoform Disorders
disorders characterized by physical symptoms for which no known physical cause exists

dissociative disorders
disorders in which conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings

fugue state
a sudden loss of memory or change in identity, often in response to an overwhelmingly stressful situation

Affective disorders
Emotional disorders that are characterized by changes in mood.

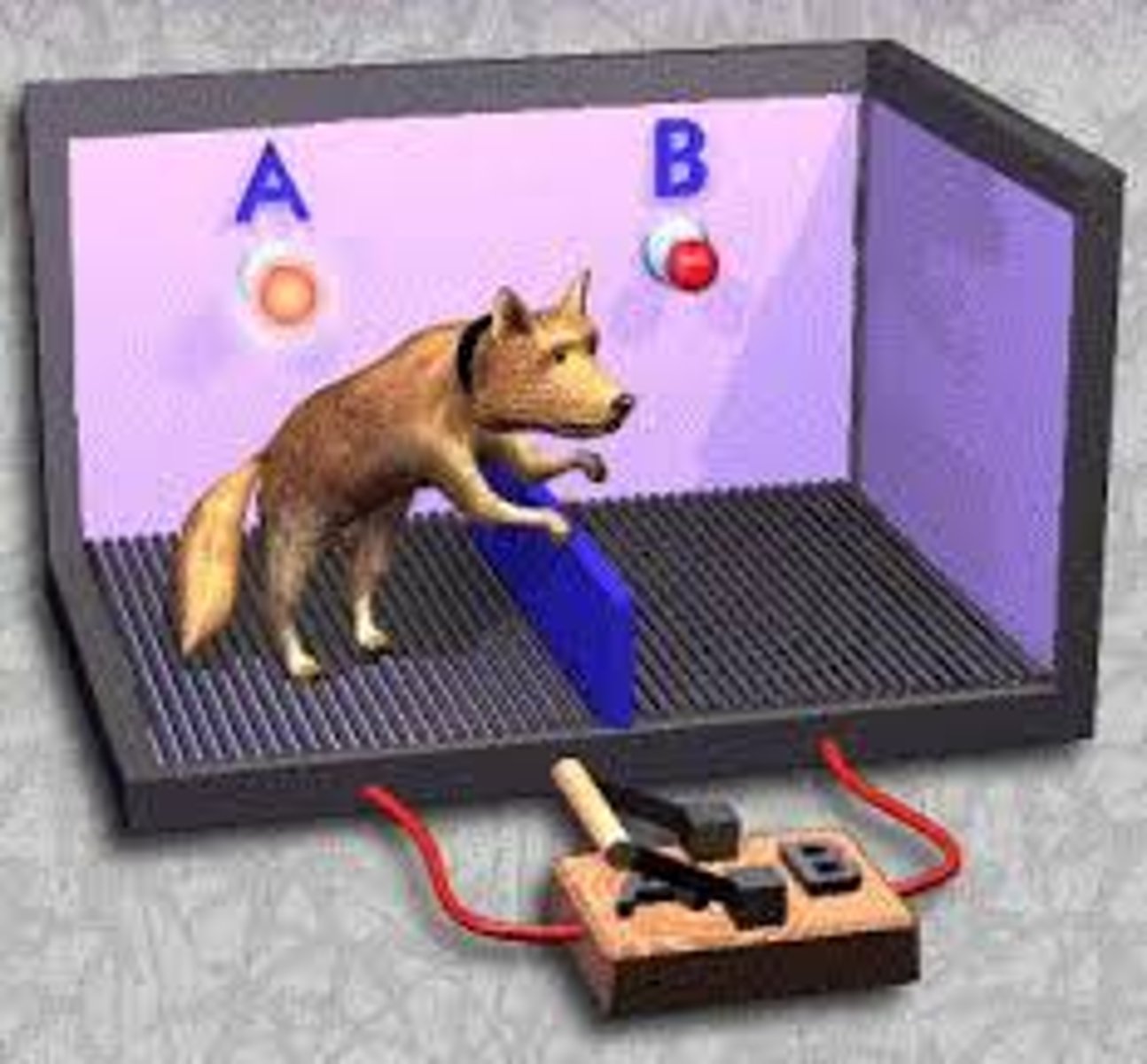
Learned Helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events
Delusions of persecution
the belief that the person is being deliberately interfered with, discriminated against, plotted against, or threatened

Delusions of Grandeur
A false belief that one is a famous person or a powerful or important person who has some great knowledge, ability, or authority.

Hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
Schizophrenia
a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions

waxy flexibility
feature of catatonic schizophrenia in which people rigidly maintain the body position or posture in which they are placed by others
Dopamine Hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity
tardive dyskinesia
involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; a possible neurotoxic side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs that target certain dopamine receptors
Personality Disorders
psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning

Rosenhan Study
study in which healthy individuals were admitted into mental hospitals after saying they were hearing voices. Once in, they acted normally and still were not labeled as impostors.

catatonia
a state of unresponsiveness to one's outside environment, usually including muscle rigidity, staring, and inability to communicate

positive symptoms of schizophrenia
delusions and hallucinations
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
the absence of appropriate behaviors (expressionless faces, rigid bodies)

abnormal behavior
behavior that is deviant, maladaptive, or personally distressful over a relatively long period of time

psychological disorder
Pattern of behavioral and psychological symptoms that causes significant personal distress, impairs ability to function in one or more important areas of life, or both

DSM-V
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, describes specific symptoms and diagnostic guidlines for different psychological disorders

Insanity Defense
Affirmative defense by excuse in a criminal case, arguing that the defendant is not responsible for his actions due to an episodic or persistent psychiatric illness at the time of the crime

Confidentiality
the act of holding information in confidence, not to be released to unauthorized individuals

David Rosenhan
did study in which healthy patients were admitted to psychiatric hospitals and diagnoses with schizophrenia; showed that once you are diagnosed with a disorder, the label, even when behavior indicates otherwise, is hard to overcome in a mental health setting. Thud experiment

Medical/Biological Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Explains mental disorders as issues with physical structures of body/brain
Psychodynamic Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Abnormal behavior is result of conflicts/repressions of the unconscious mind
Humanistic Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Abnormal behavior is result of conscious experiences and how the individual perceives themselves
Cognitive Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Psychologically ill behaviors are result of irrational thought
Behavioral Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Psychological disorders are learned and a direct result of our environment
Socio-cultural Perspective Cause of Abnormal Behavior
Focuses on how societal influences and pressures lead to psychologically ill behaviors
neurodevelopmental disorder
Any disorder that impairs growth and development of the brain and/or the central nervous system

neurocognitive disorders
acquired disorders marked by cognitive deficits, general term describing decreased mental function due to a medical disease other than a psychiatric illness

ADHD (Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) (neurodevelopmental disorder)
a chronic mental illness that involves difficulty in sustaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) (neurodevelopmental disorder)
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by significant deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviors

Alzheimer's disease (neurodevelopmental disorder)
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
delirium (neurodevelopmental disorder)
Abrupt changes in brain that cause mental confusion or emotional disruption

Schizophrenia (psychotic disorder)
a psychological disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, and/or diminished, inappropriate emotional expression
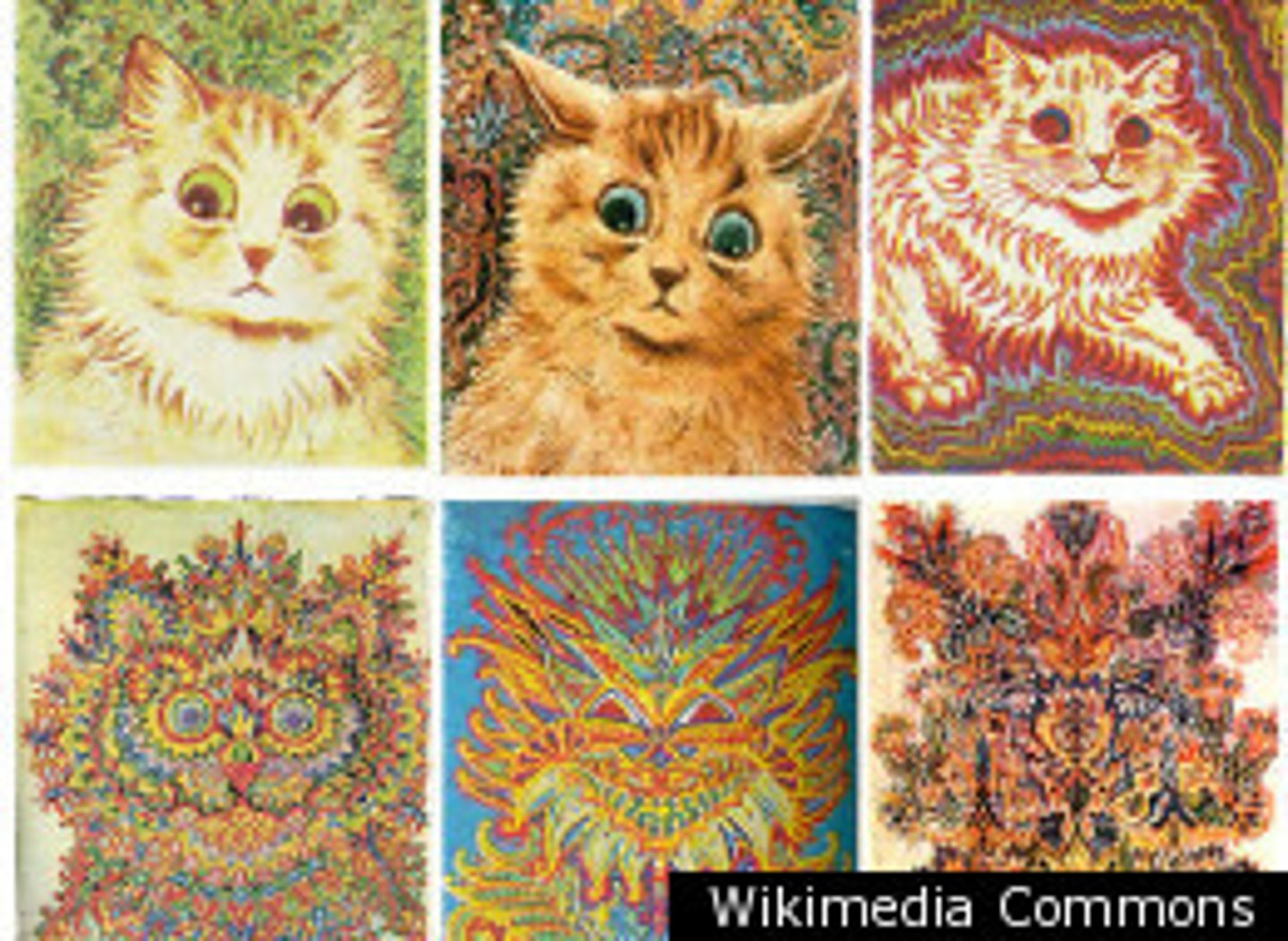

Hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
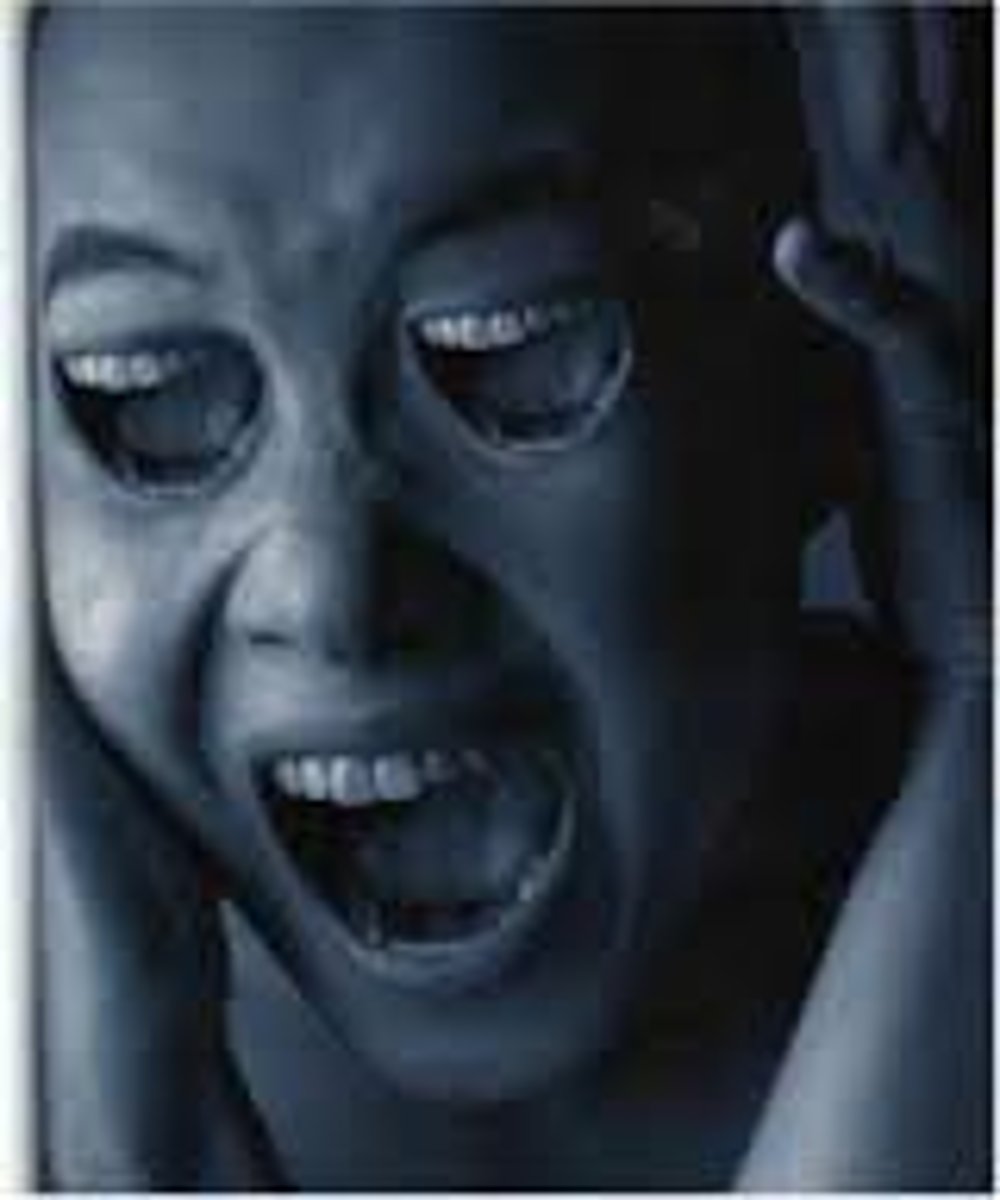

Delusions
false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders

catatonia
Abnormality of movement and behavior arising from a disturbed mental state. It may involve repetitive or purposeless overactivity, or resistance to movement.

bipolar disorder
A mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania.

manic episode
a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state

rapid cycling
4 or more episodes of acute mania within 1 year
Hypomania
A mild manic state in which the individual seems infectiously merry, extremely talkative, charming, and tireless.

cyclothymic disorder
a disorder marked by numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms and mild depressive symptoms. Not extreme enough to be biplar 1 or 2.
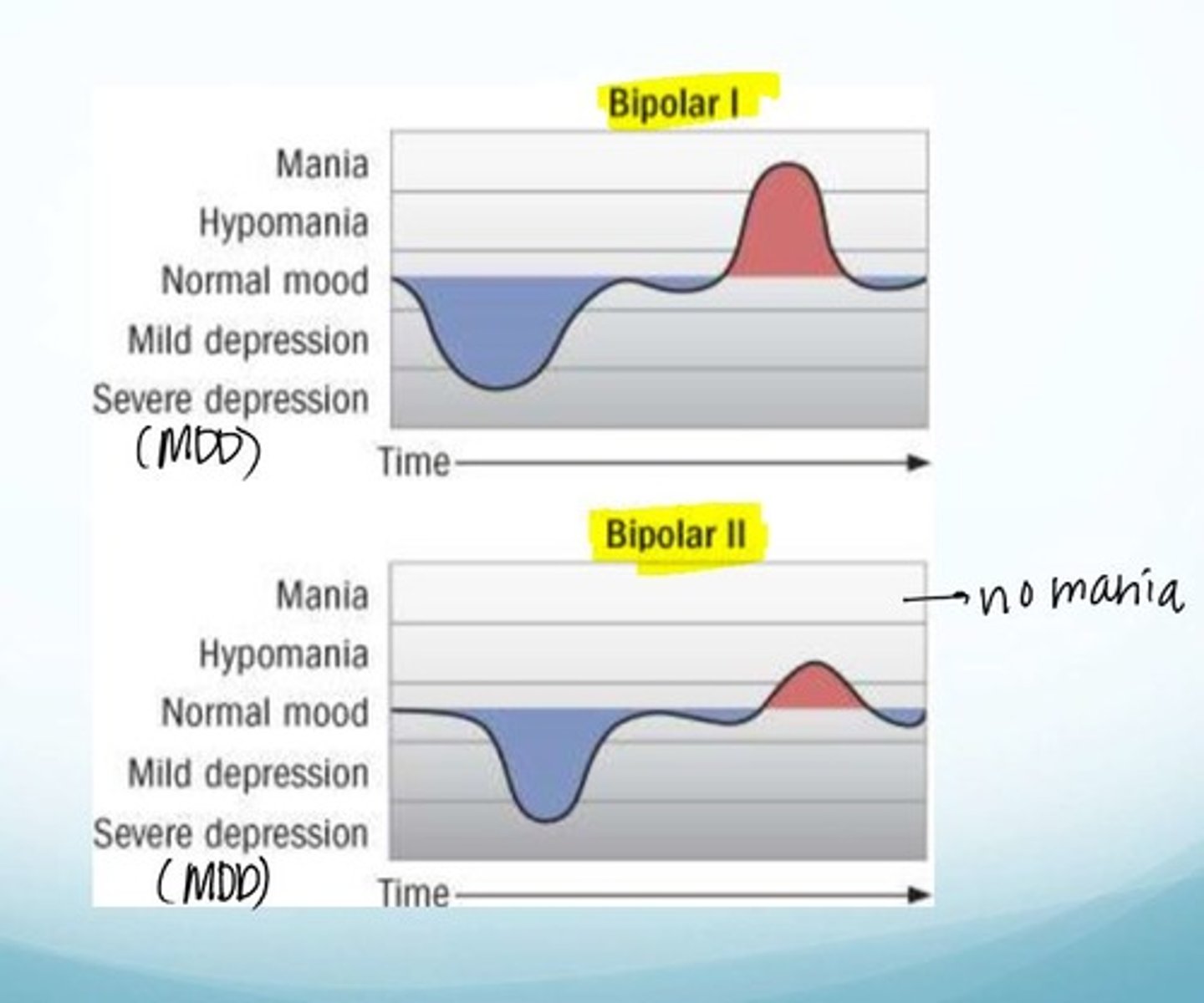
Bipolar 1 vs Bipolar 2
1 - manic episodes, depressive episodes common but not required for diagnosis
2 - hypomanic episodes, >1 major depressive episoes required
Major Depression
Mood disorder characterized by prolonged feelings of worthlessness and guilt, the disruption of normal eating habits, sleep disturbances, a general slowing of behavior, and frequent thoughts of suicide. Treat symptoms

seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
a mood disorder caused by the body's reaction to low levels of sunlight in the winter months

Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
Mood disorder involving persistently depressed mood, with low self-esteem, withdrawal, pessimism, or despair, present for at least 2 years, with no absence of symptoms for more than 2 months. Often less sever than major depressive disorder
premenstrual dysphoric disorder
a disorder marked by repeated episodes of significant depression and related symptoms during the week before menstruation

anxiety disorders
A class of disorders marked by feelings of excessive apprehension and anxiety.

Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) (Anxiety Disorder)
Sever ongoing anxiety that interferes with daily activities
panic disorder (Anxiety Disorder)
An anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Rapidly escalates and intensifies

phobic disorder (Anxiety Disorder)
marked by a persistent and irrational fear of an object or situation that presents no realistic danger

Agorophobia
fear of open spaces

Social Phobia
a disorder that involves an irrational fear of being publicly humiliated or embarrassed

Selective Mutism (SM) (Anxiety Disorder)
Failure to speak in social situations, even though individual speaks in other situations, mainly seen in children

OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder)
an anxiety disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts and/or actions

Obsessions
persistent ideas, thoughts, or impulses that are unwanted and inappropriate, causing marked distress

Compulsions
Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that are performed to prevent or reduce anxiety.

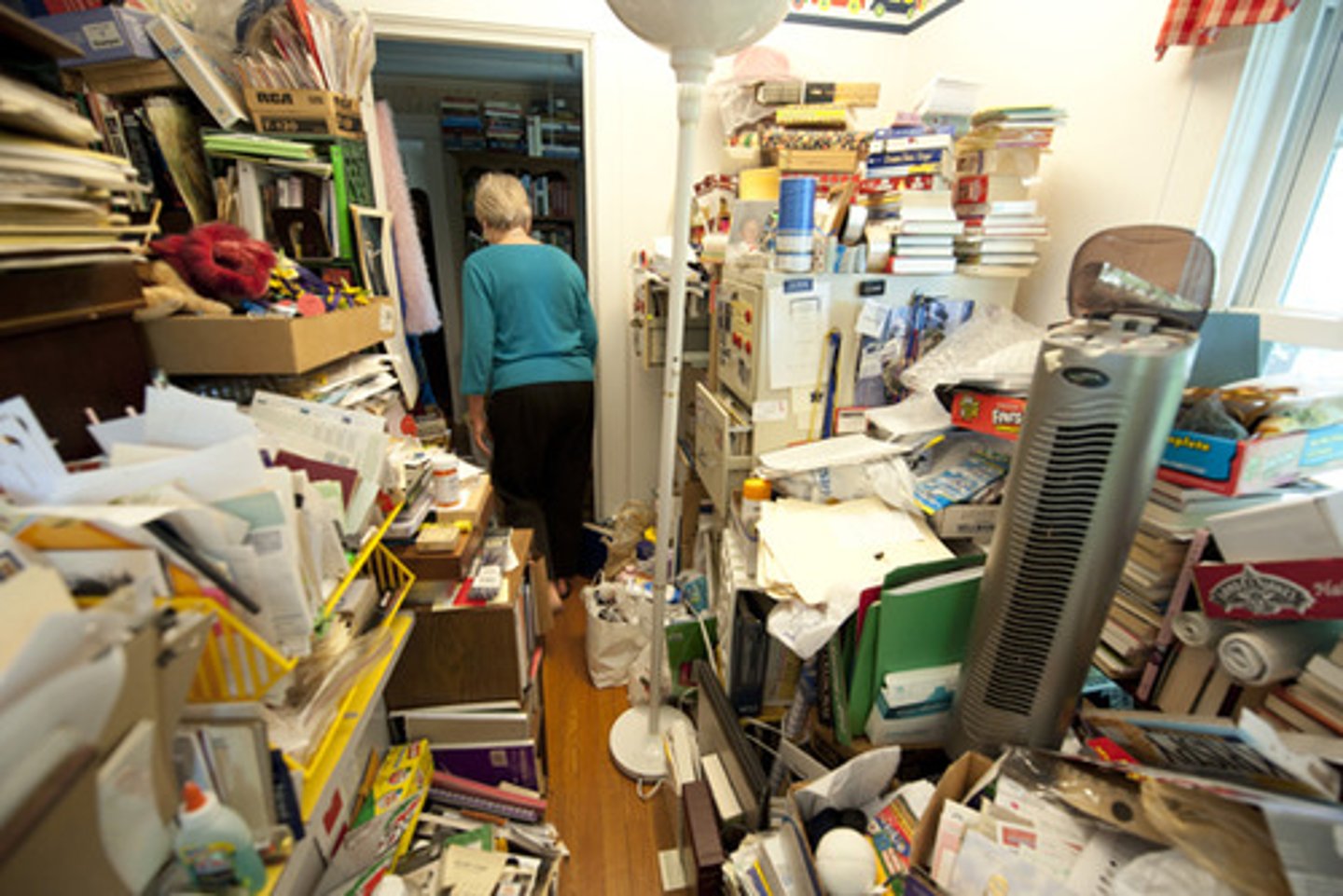
Hoarding Disorder
Persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value

PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder)
an anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience

Dissociative Disorders
a category of psychological disorders in which extreme and frequent disruptions of awareness, memory, and personal identity impair the ability to function
