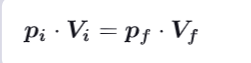3.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the number of Avogadro ? Where does it come from ?
Avogadro showed that if you take an amount of any substance (in grams) equal to its atomic or molecular mass, it always contains the same number of particles.
This fixed number is called Avogadro’s number, written as Nₐ : 6.02 × 10²³ particles per mole.
If a substance contains a total of N particles, we can group them into "packages" that each contain Avogadro’s number of particles.
Each package is called a mole, and the number of these moles is called the mole number, written as n.
What is the relationship between n, N and Na ?
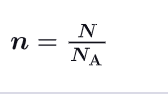
How can you calculate n (mole number) using m and M ?
m = mass of the substance
M = mass of 1 mole
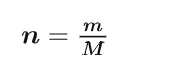
When can we say a gas is “ideal” ?
When it’s density tends to zero
What is the ideal gas law ?
R = ideal gas constant
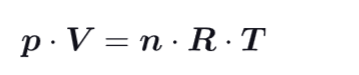
What is the other formulation for the ideal gas law using the Boltzmann constant (what is it) ?
k = R/ Na
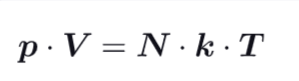
What is the modelcule’s velocity / root man square speed v_rms ? (write the demonstration)
v_avg : average of the squa
re of each particle’s speed
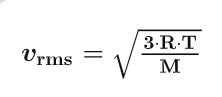
What is the formula for the average translational kinetic energy of one molecule of gas ?
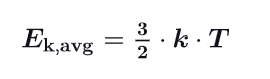
What is the mean free path ?
A kinetic parameter defining the average distance traversed by a molecule between collisions.
(Length of path / Number of collisions where v_rel = v_avg x racine de 2)!
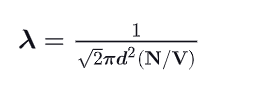
What is N/V ?
The molecular density (number of molecules per unit of containing volume)
What is the unit for the specific heat of gases ?
Unit of mole (instead of unit of mass)
Which assumption can we draw on the internal energy of monoatomic ideal gases (He or Ar) ?
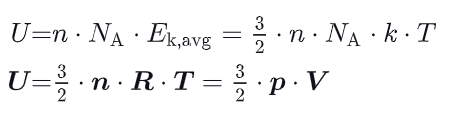
What is the molar specific heat at constant volume ?
Cv : constant volume
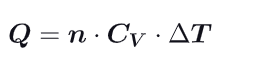
What becomes the first law (Delta U) at constant volume ?
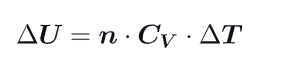
What becomes the formula for change of entropy for ideal gases ?
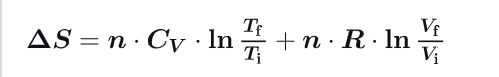
What is the formula for molar specific heat at constant pressure ?
(At constant pressure, the change in volume leads to a change in temperature , meaning that an amount of heat is either absorbed or desorbed by the gas)
What does the first law becomes for a gas with constant pressure ?
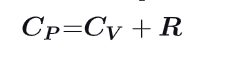
What formula can you establish about pressure, Volume and specific heat ration during an adiabatic reversible process ?
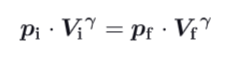
What formula can you establish about pressure, Volume and specific heat ration during an isothermal reversible process ?