Week 3 Objectives 1103 (NM Instrumentation)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
QC performed on GM and ISM and how often
Battery functionality: daily
Source check: daily
Calibration: annually
QC performed on DC and how often
Constancy: daily - record radionuclide activity, assess reliability
Linearity: quarterly - ability to measure range of high and low doses
Accuracy: annually - measure validity of calibrator reading
Geometry: only after installation or repair
2 main categories of radiation detectors
Gas filled and scintillation
3 types of gas filled detectors
Dose calibrator, Geiger Mueller, ionization survey meter
Name 4 types of scintillation detectors
Well counter: 1 PMT; highly sensitive for blood or urine samples or wipe surveys
Uptake probe: 1 PMT and NaI crystal; measures radioactivity of capsule before administration
Gamma camera: multiple PMT, for imaging
Surgical probe: no PMT and e- measured directly; used to locate lymph nodes, parathyroid, or tumors made radioactive
What does scintillation mean
Producing or giving off light
Which type of detector systems operate off simple principles
Gas filled
Name the different imaging instruments in NM
Gamma camera
PET
Which detectors operate on complex principles
Scintillation
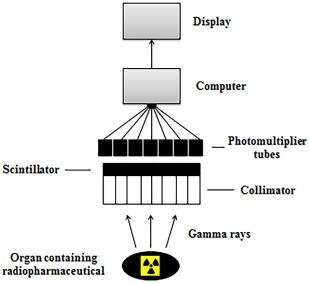
List and identify components of a gamma camera
Collimator: only allows “good information” gamma rays to pass through
Scintillator: NaI imaging crystal takes gamma rays and converts to visible light
Computer: takes light and turns it into electrical signals that form an image
Display: show the image