Quiz/Test1 Greek Art/Arch
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms

Amphora by the Dipylon Master, Dipylon Cemetery, Athens, LG, ca. 750 BCE
-best painter of large funerary vases
-grave marker
-belly handle amphora, for a woman
-enitre vase is decorated
-Band in middle shoes prothesis scene;part of funeral where the body is layed out for people to pay respects
-body would normally be covered by shroud
-show people in composite view
-secondary decoration
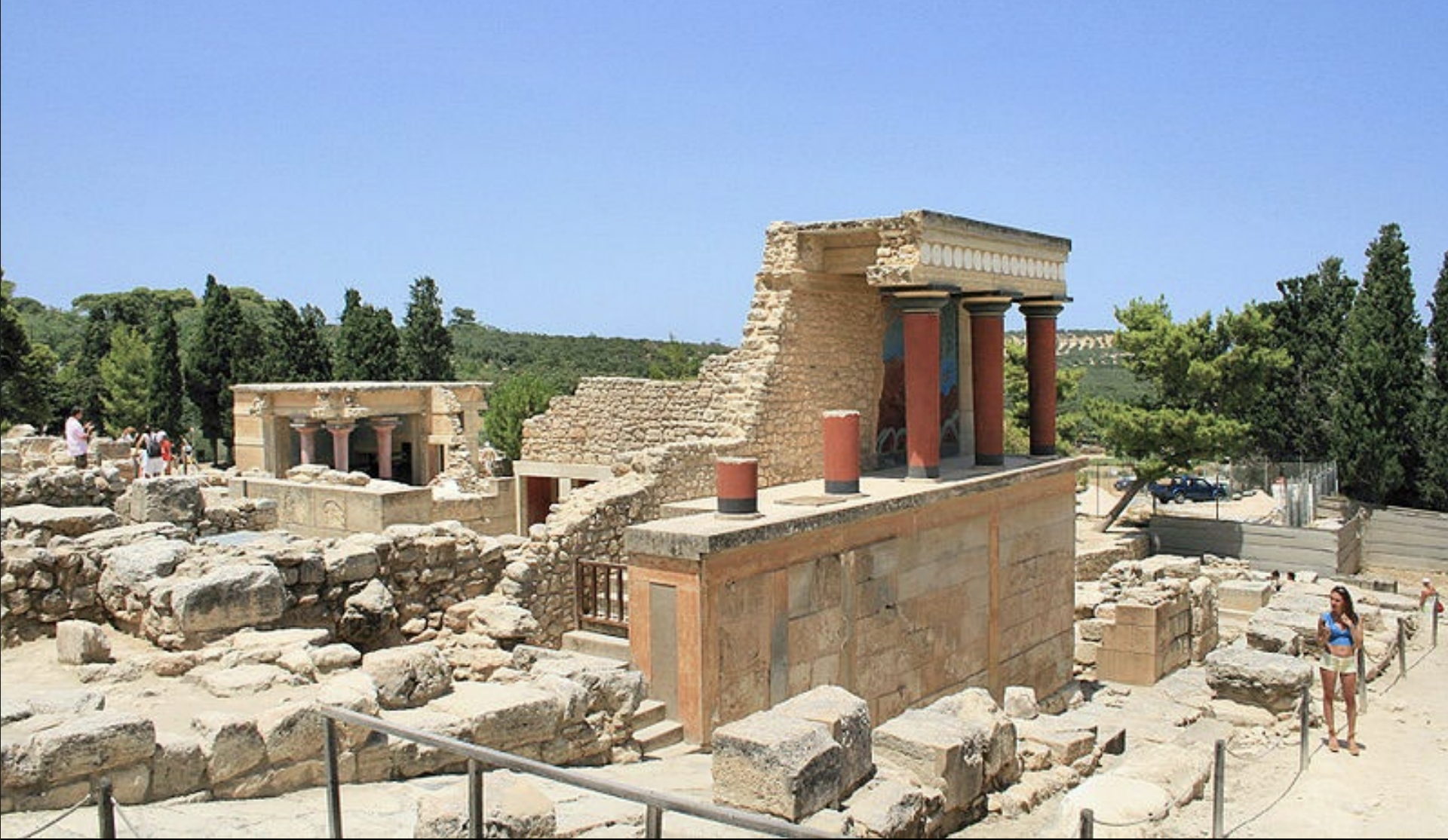

Palace at Knossos,LM, ca. 1550-1375 BCE
-largest palace in crete, most likely ruled by ruler of the area
-minoan
-residence, administrative center, manufacturing, storage center, agricultural goods, religious center
-ahslar masonry:rectangular blocks laid in horizontal pattern, no mortar
-unfortified
-Hall of Double Axes: double axis cut into stone walls, two large rooms connected by pier and door partitions
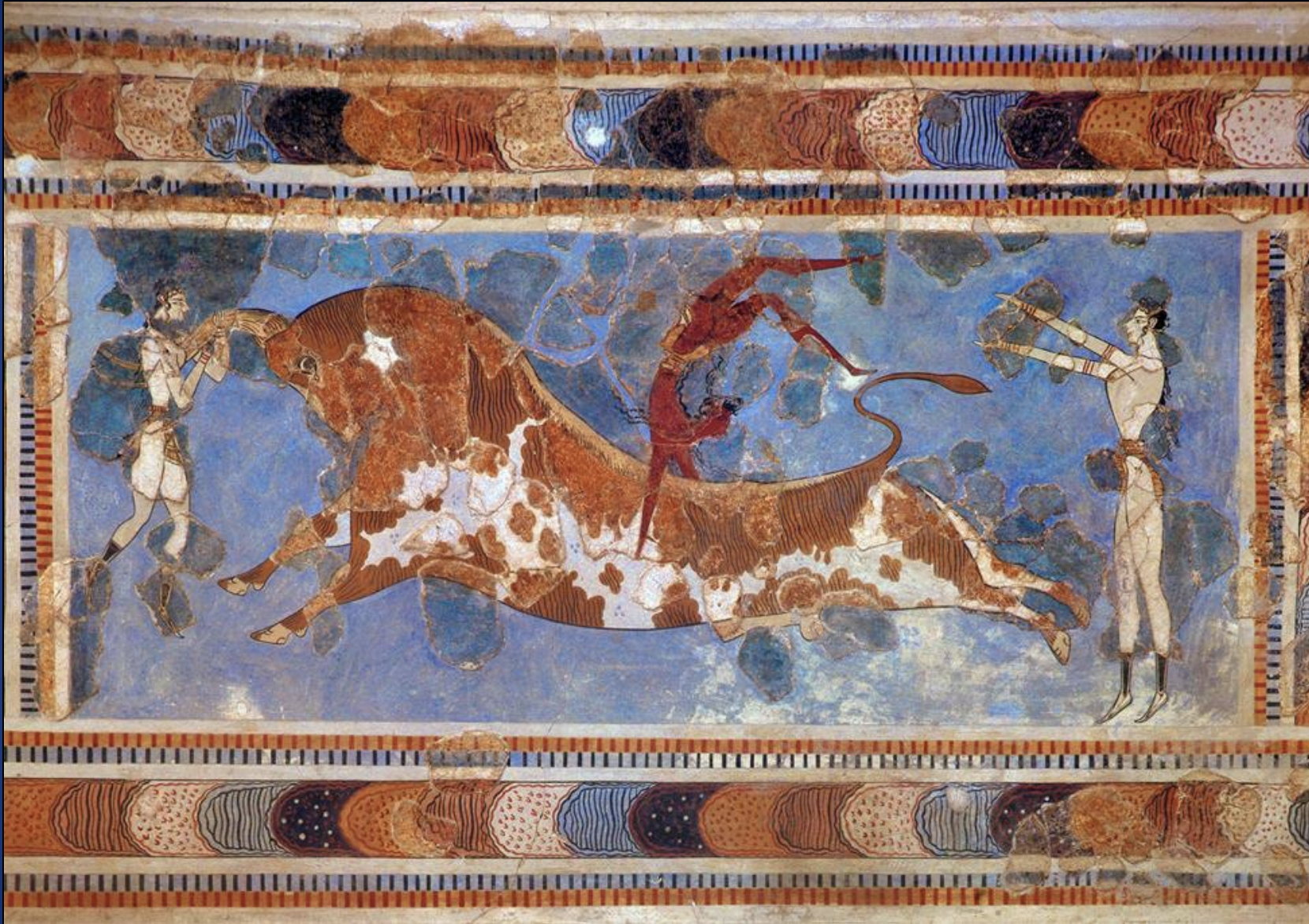

Bull Leaping Fresco from Knossos LM I, ca. 1550-1450 BCE
-show typical minoan man
-difference in gender based on color
-showing tradition of bull leaping
, Mycenae Citadel Wall Phase I: (LH IIIB): ca. 1300-1200 BCEca. 1380 BCE Phase II: ca. 1250 BCE Phase III ca. 1200 BCE,ashlar, cyclopean masonry, Cyclops
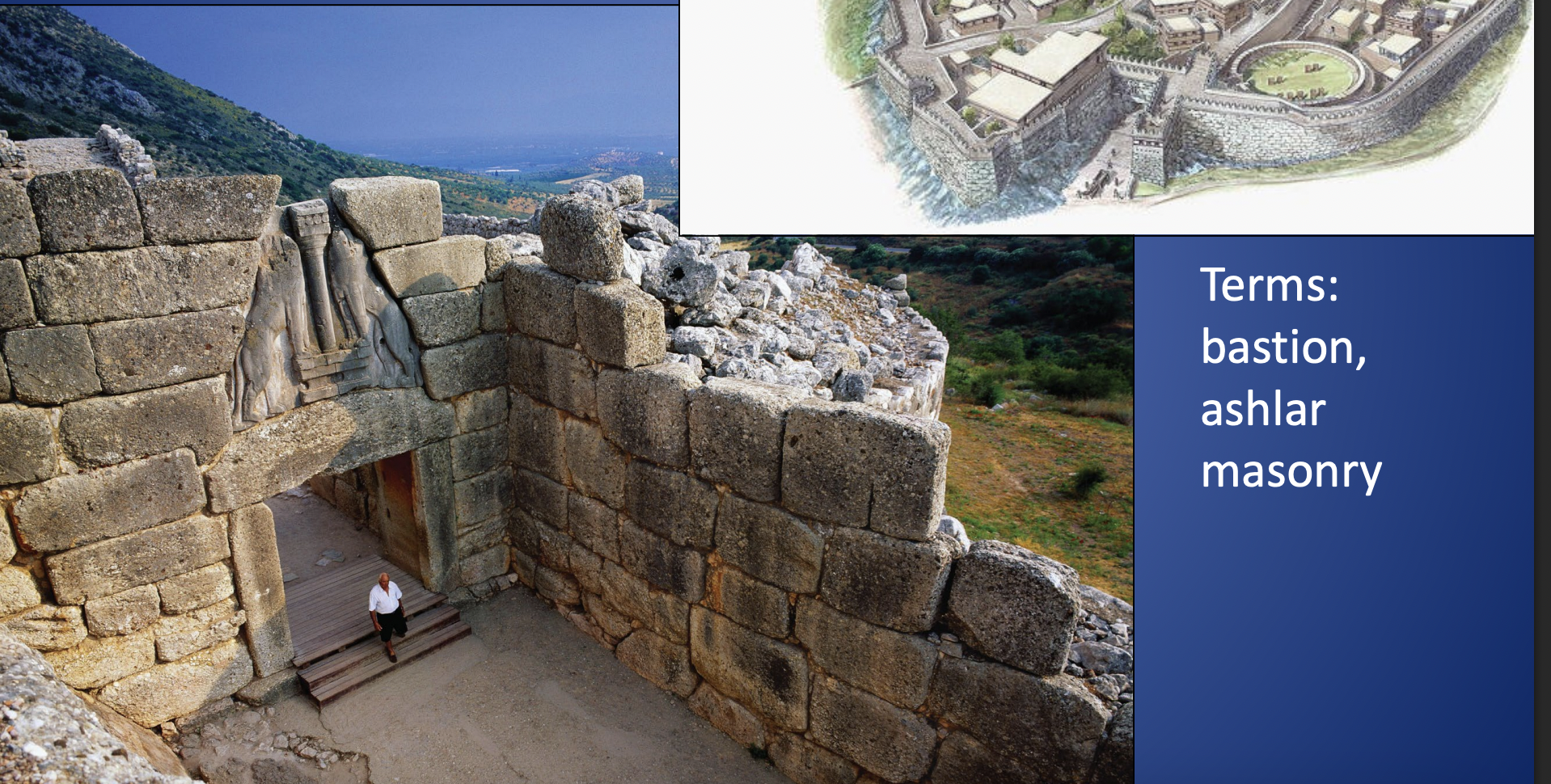

Lion Gate, Mycenae, LH IIIB, ca. 1250 BCE,projection bastion, makes soilders file into small space, relieving triangle and lintel block, decorated with a pair of lions, possible could have been griffins, minaoan style column.

Palace at Pylos, LH IIIB, ca. 1300-1200 BCE
-on a hiltop, unfortified, violently destroyed by fire, ashlar block masonry , rubble and framework for houses,2 flights of stairs,coutryard, megaron
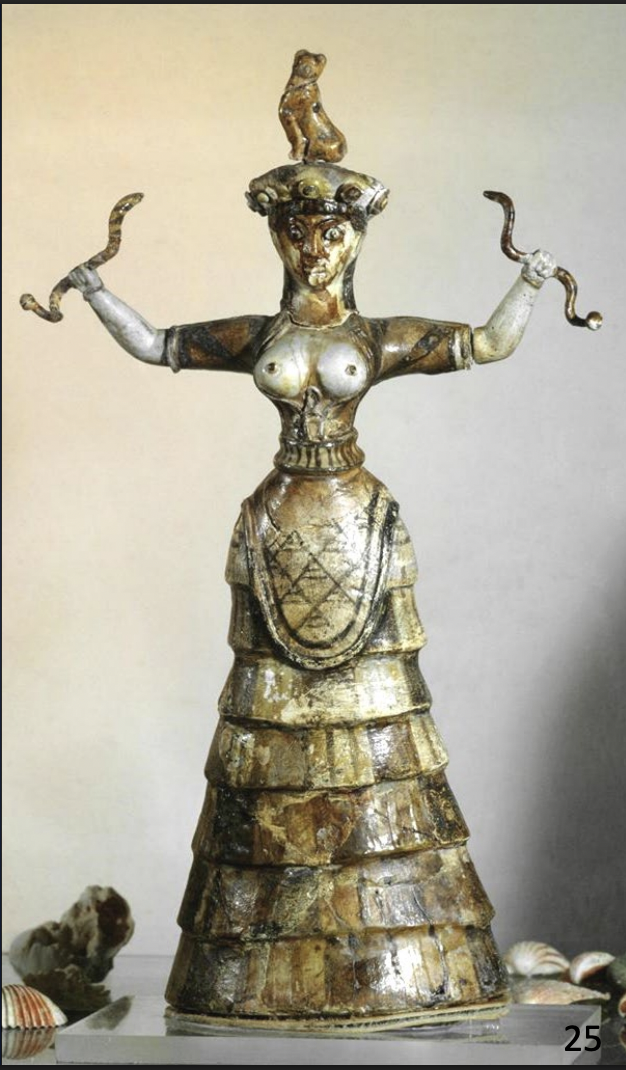

Snake Goddess/Priestess from the Palace of Knossos MM III, ca. 1700 BCE
-bare breast, bell shaped skirt, tight belt and apron
-snakes around arms, waist and shoulders
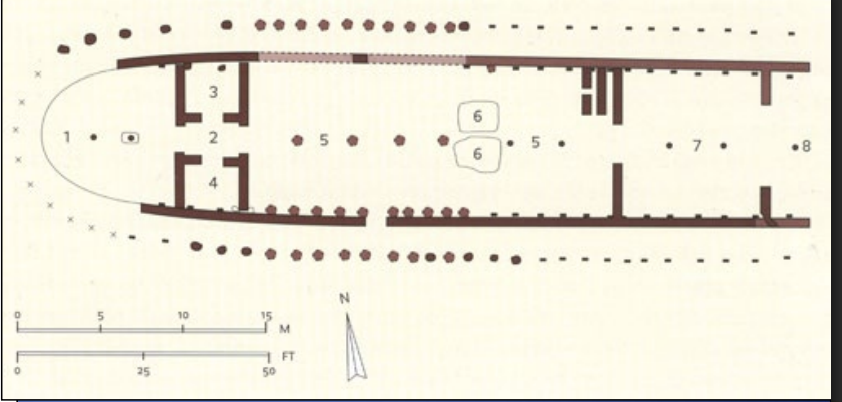
Plan and Reconstructions of the “Heroon” at Lefkandi, 10th c BCE EG
-apsidal
-largest known building from the dark age
-dtone sockle with mudbrick walls
-funeral complex
-center pit with north and south compartments
-for human remains and horse
-there is room for a pyre, where human remains are burned
-a heroon is a shrine where a hero was worshipped
-most likely was owned by a rich family
-cemertary beside heroon where phoenician seal was found, eqyptian necklace menaing there was trade
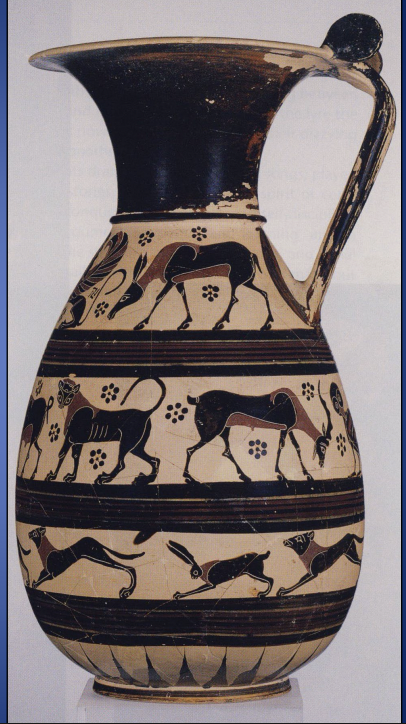

Protocorinthian Olpe, ca. 650-625 BCE Late Procornithian
-pitcher, used to pour out liquis at symposium
-black figure technique
-animal style decoration
-incision and added red
-typical of procorinthian style
-rosettes
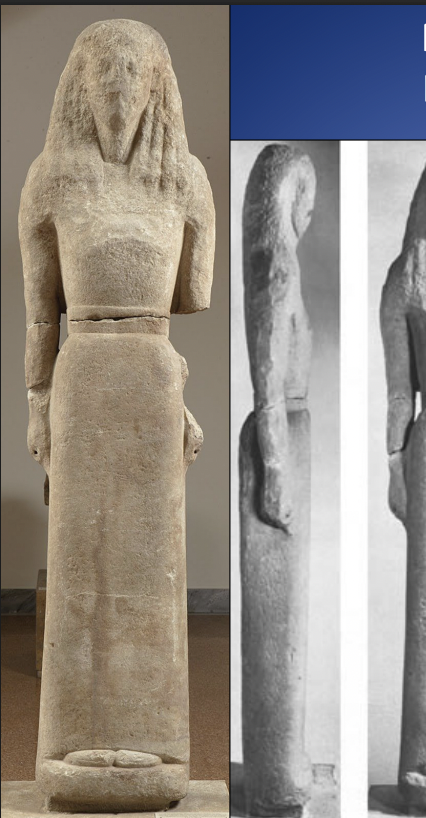

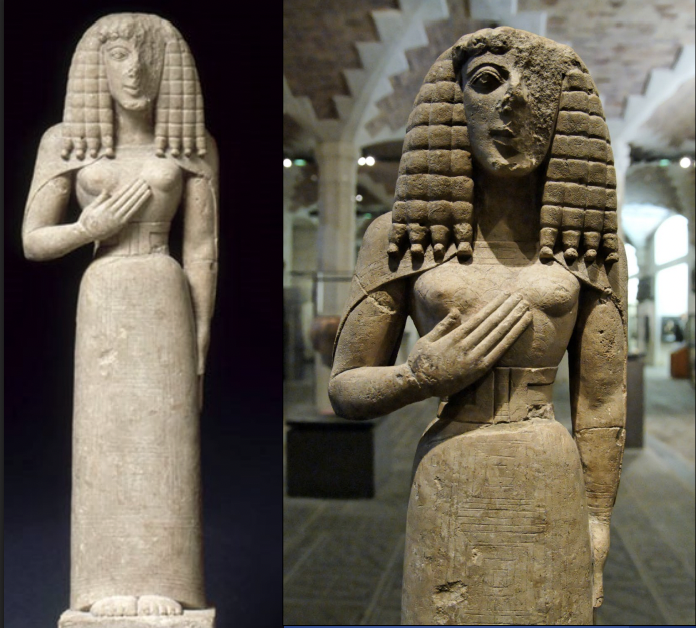
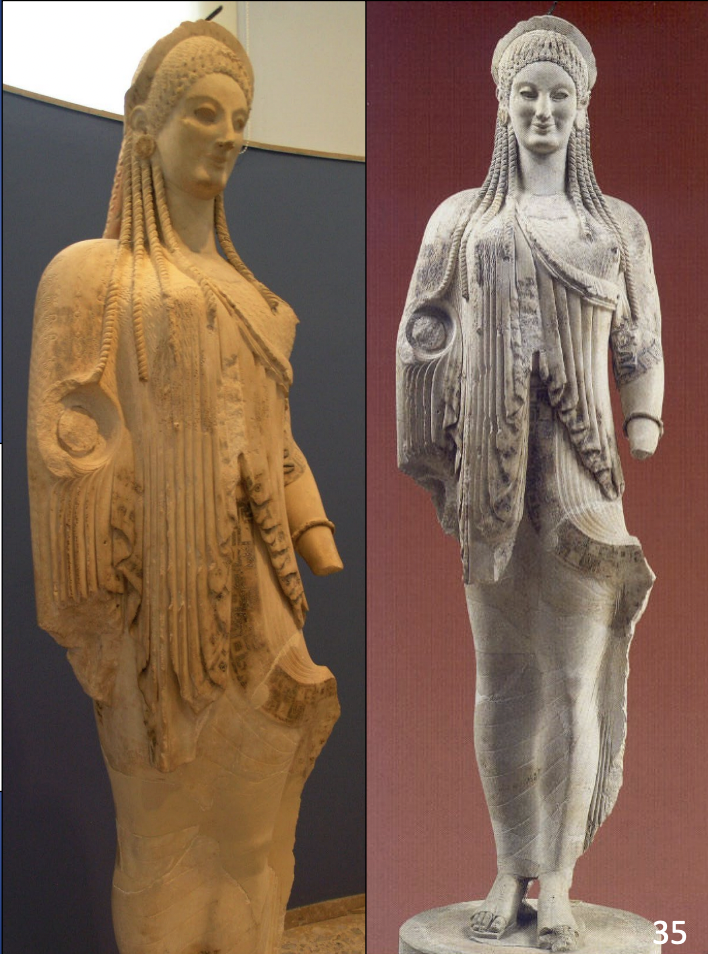
Marble Statue of Nikandre, Delos, ca. 640 BCE, H. 5’ 9”
-found at island that is sacred to apollo
-statue shows two innovations: statue is over life sized + use of marble, show influence of egyptian
-Statue is Kore: standing clothes fmale
-Daedalic stule: triangle head, hair, clothes
-possible to be godess, nikadre, or worshipepr
-has text inscribed onto statue: boustrephedon, egyption custom

Bronze Horse Votive, Olympia, ca. 750-700 BCE Geometric
-possible significance of horse votive
-stylized, depicted an artificial way of drawing horses
-similar to style that was painted on hoses
-geometric period
-Late Geometric Period

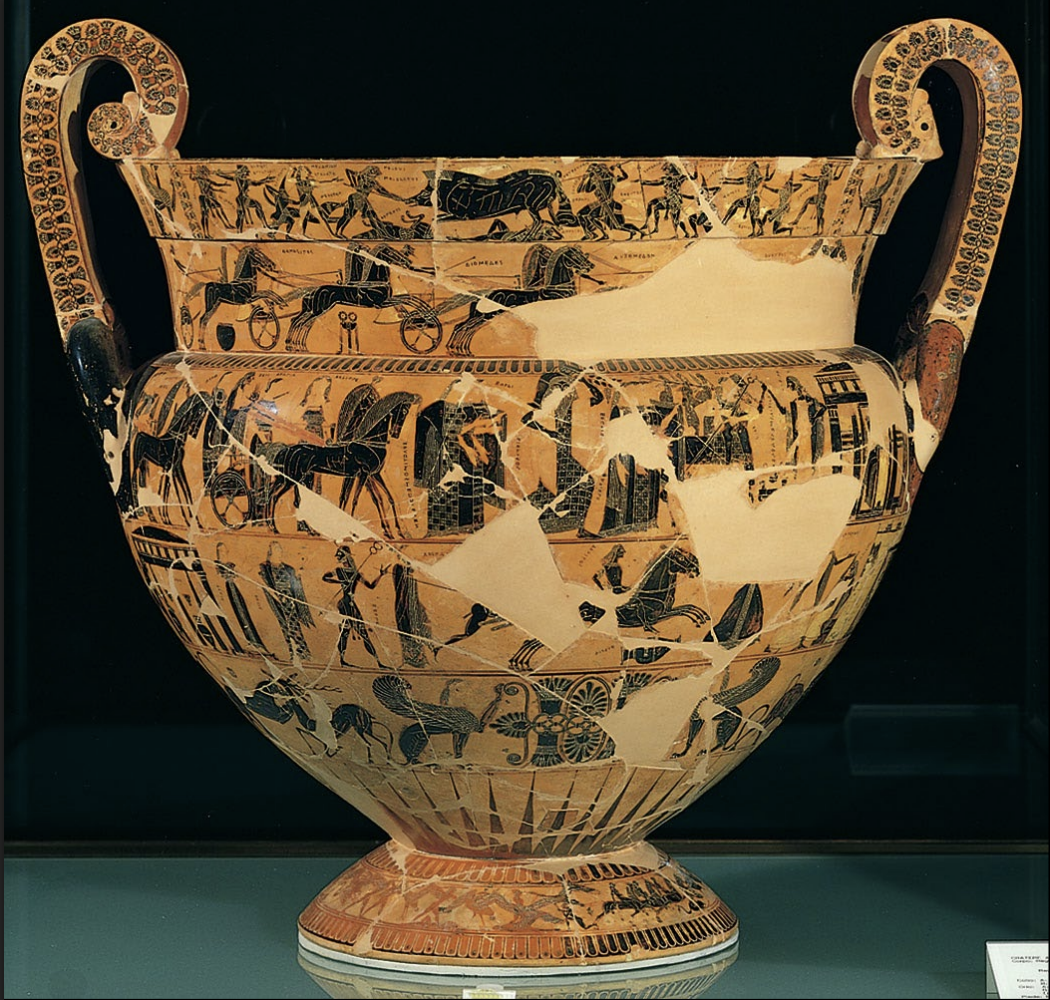
Chigi Vase (Olpe), by the Macmillan Painter, Corinth, ca. 650 BCE
-not typical for procorintian style
-division into small friezes seen in animal style but is with humans
-showing narrative scenes with oplites and earliest depiction of them through art
-a lot of amount of overlap
-use of different colors, yellow, brown, which is unusual in black figure painting
-includes procession of horemen hunting
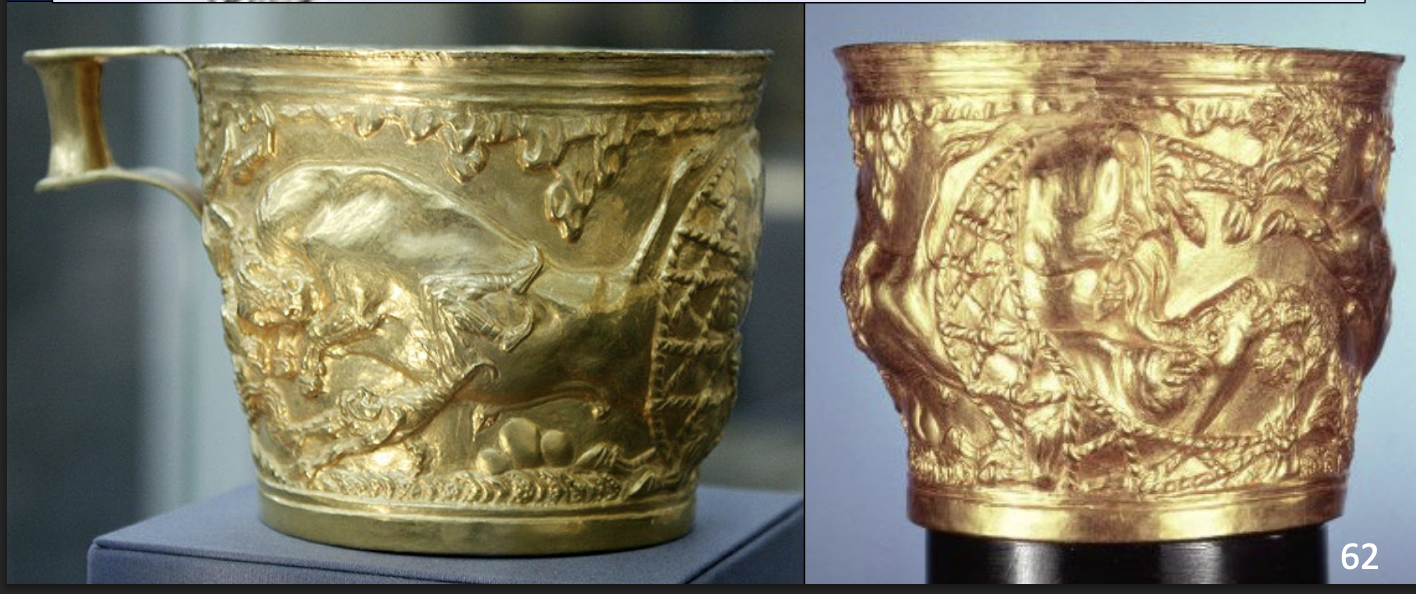

Vapheio Cups in a Mycenaean tomb, but probably of Minoan manufacture, gold, LM I, ca. 1550-1450 BCE
-evidence of trade and contact
-tecnique of reposse, hammering back to raise pattern
-showing peace vs violent capturing of bulls
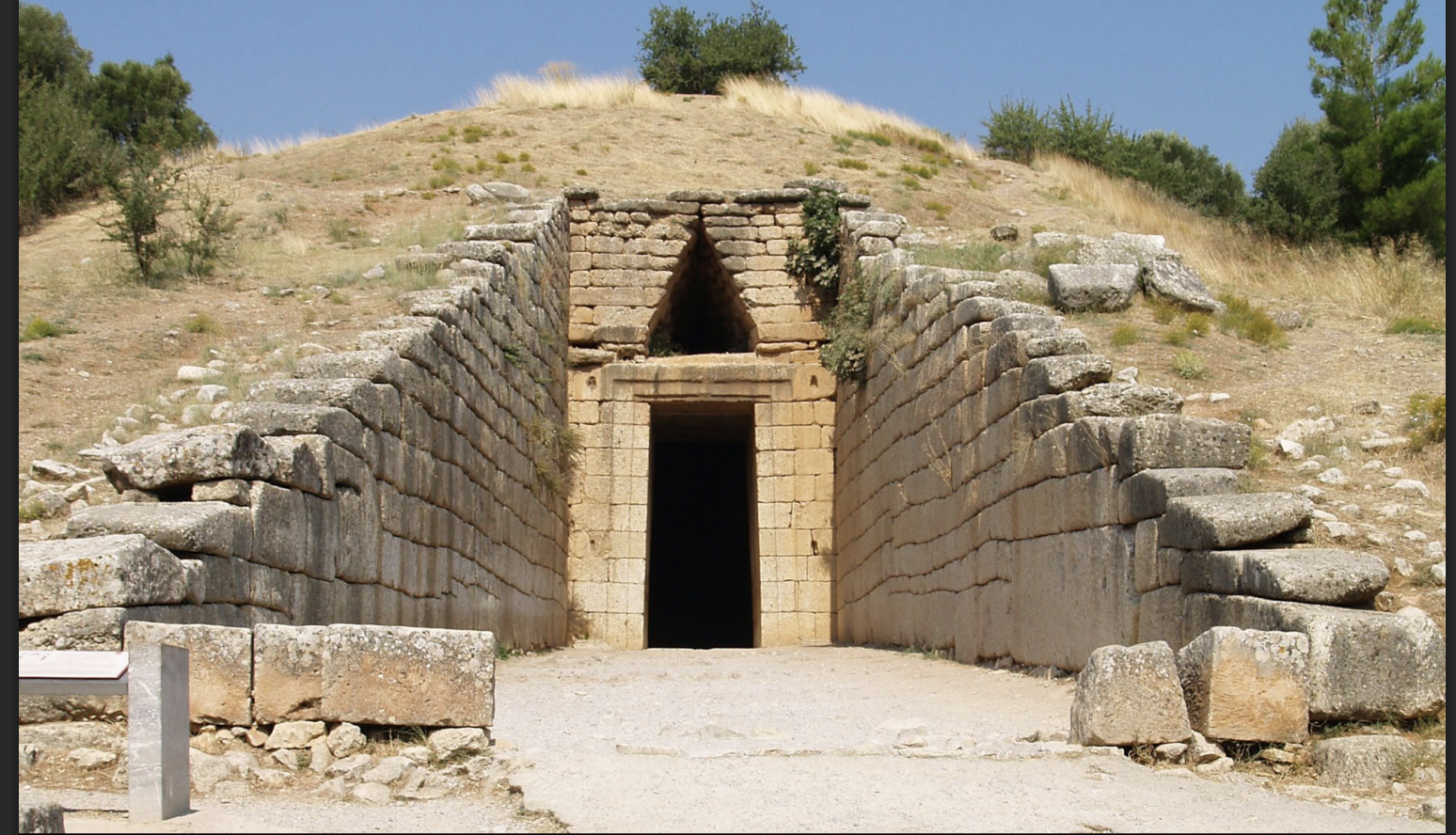

Treasury of Atreus,LH IIIB, ca. 1250 BCE,
-built into existing hillside
-tholos tomb
-dromos view:entrance leading to the tomb
-lined with ashlar masonry
-entry has a lintel block and relieving triangle'
-corebelled masonry
-has original relief decoration:m green marble,engaged columns
NOT ON EXAM
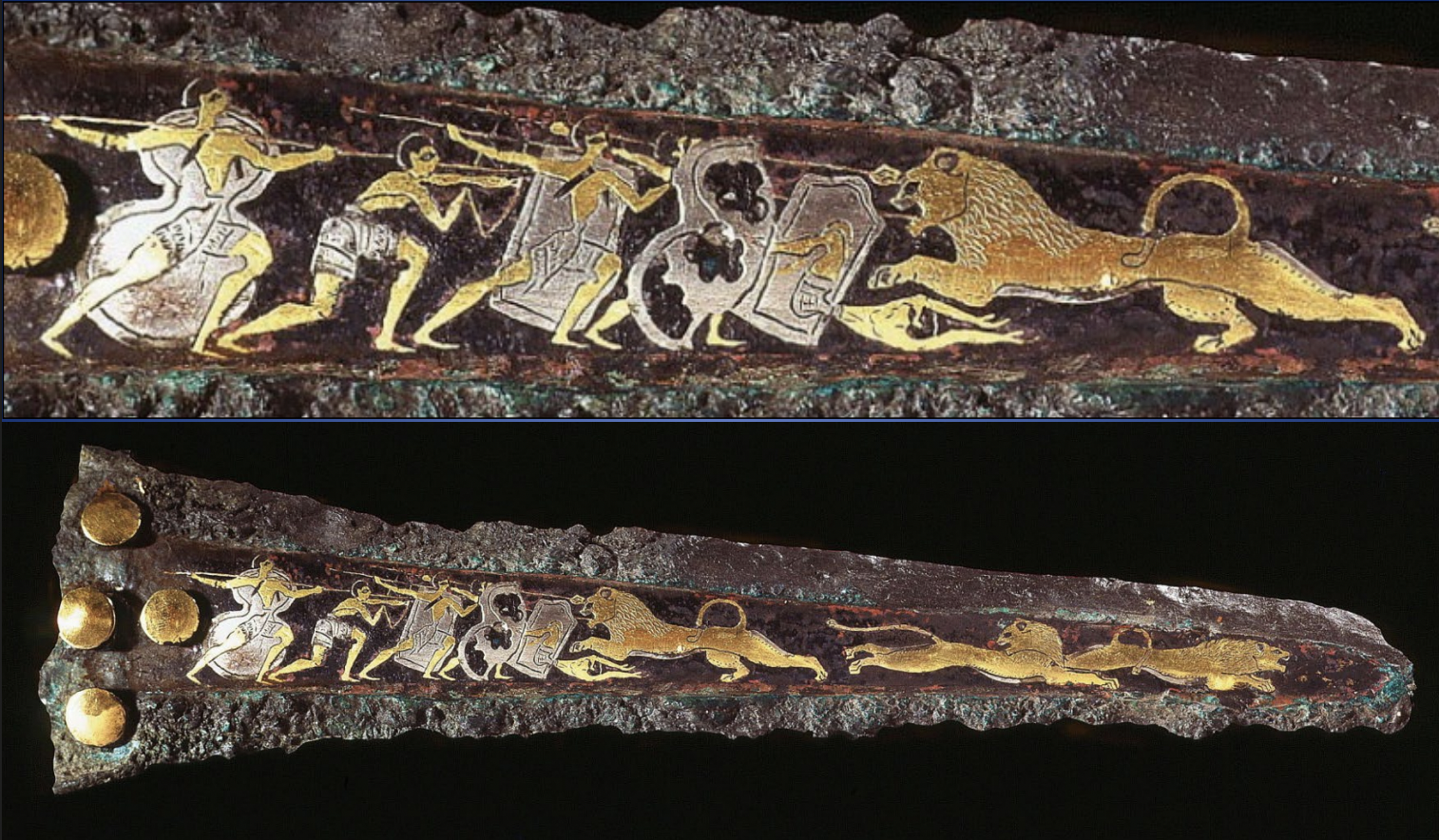

Bronze Dagger Blade with a Lion Hunt,Grave Circle A, Mycenae, LH I, ca. 1550-1500 BCE
--style of dagger is minoan seen in waist and flying gallop pose
-owner is mycenean
-show influx of wealth in mainland greece
NOT ON EXAM

“Very Rich Athenian Lady,” Athenian Agora, MG, ca. 850 BCE, lady was very rich, 50 vessels, gold jewelry, belly handle amphora, decoration accents imporant of vase.
NOT ON EXAM
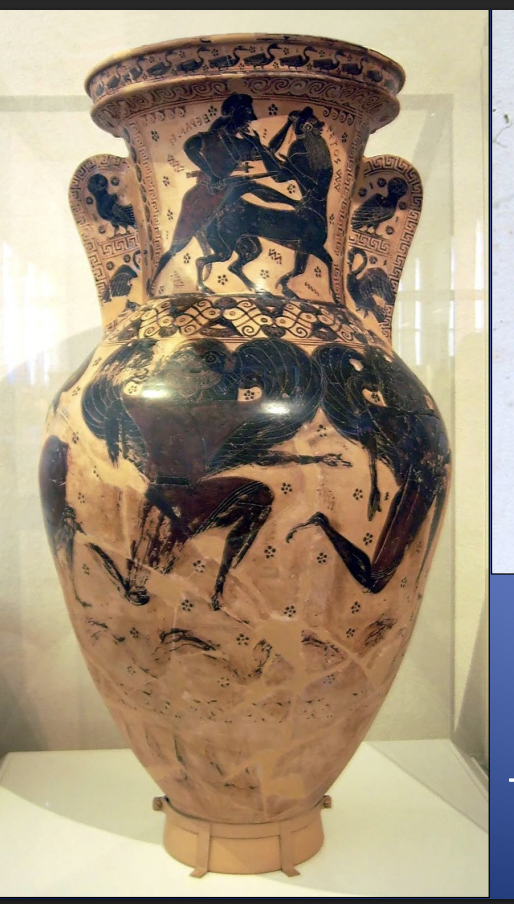

Late Protoattic/early Black Figure amphora by the Nessos Painter, Orientalizing Period, ca. 625-600 BCE
-balck figure technique
-shows mercules fighting centaur nessos and shows gorgons
-insciptions on vases start to become popular
-centaur is grabbing beard in pleading motion
-pose of gorgons are in knee running position
-belly amphora
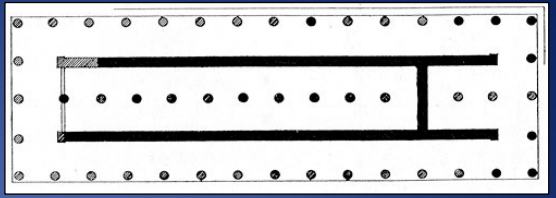
Cf. Temple of Apollo at Thermon, ca. 625 BCE (Orientalizing Pd.)
-stone bottom and mudbrick walls
-structure of wood and terracotta tiles for roof
-temple is long and narrow, typical
-houses cult statue
-back porch
-Early Doric style
-colmuns would be in doric style as metope has a wooden triglyph and narratives of greek yths
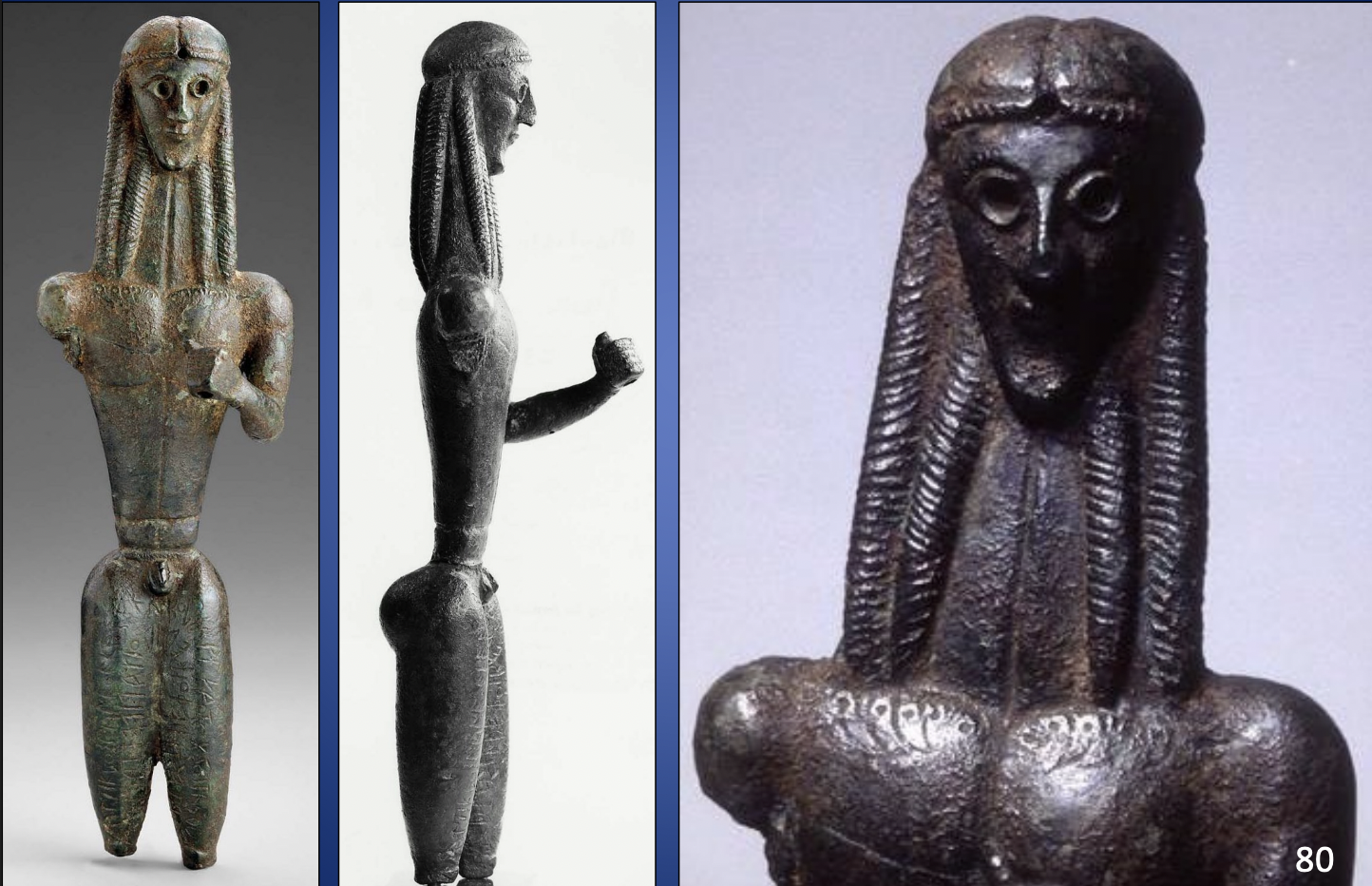

Bronze Statuette dedicated to Apollo by Mantiklos, from Thebes, ca. 700-680 BCE, H. 7 4/5”
-has lingering traits of geometric style shown in triangle chest
-eyes were inlayed with contrasting material
-unknown who it represents base on hole in hand
-lines at wasit and shoulder show may have been wearign chestplate
-inscription on legs is one of the first greek sculpture inscribed with dedication
-writing on body gives orientalizing style
-writing on base is greek while this inscription shows “quid pro quo” which is gift for gift,
-bourstrophedon, epyptian inspiration

Limestone Statuette from Auxerre (France), ca. 640 BCE, H. 25 ½”
-limestone
-most likely made in crete
-in gesture of worship
-deadalic style triangles
-suggests artist who had woodwrokign skills could do this
-
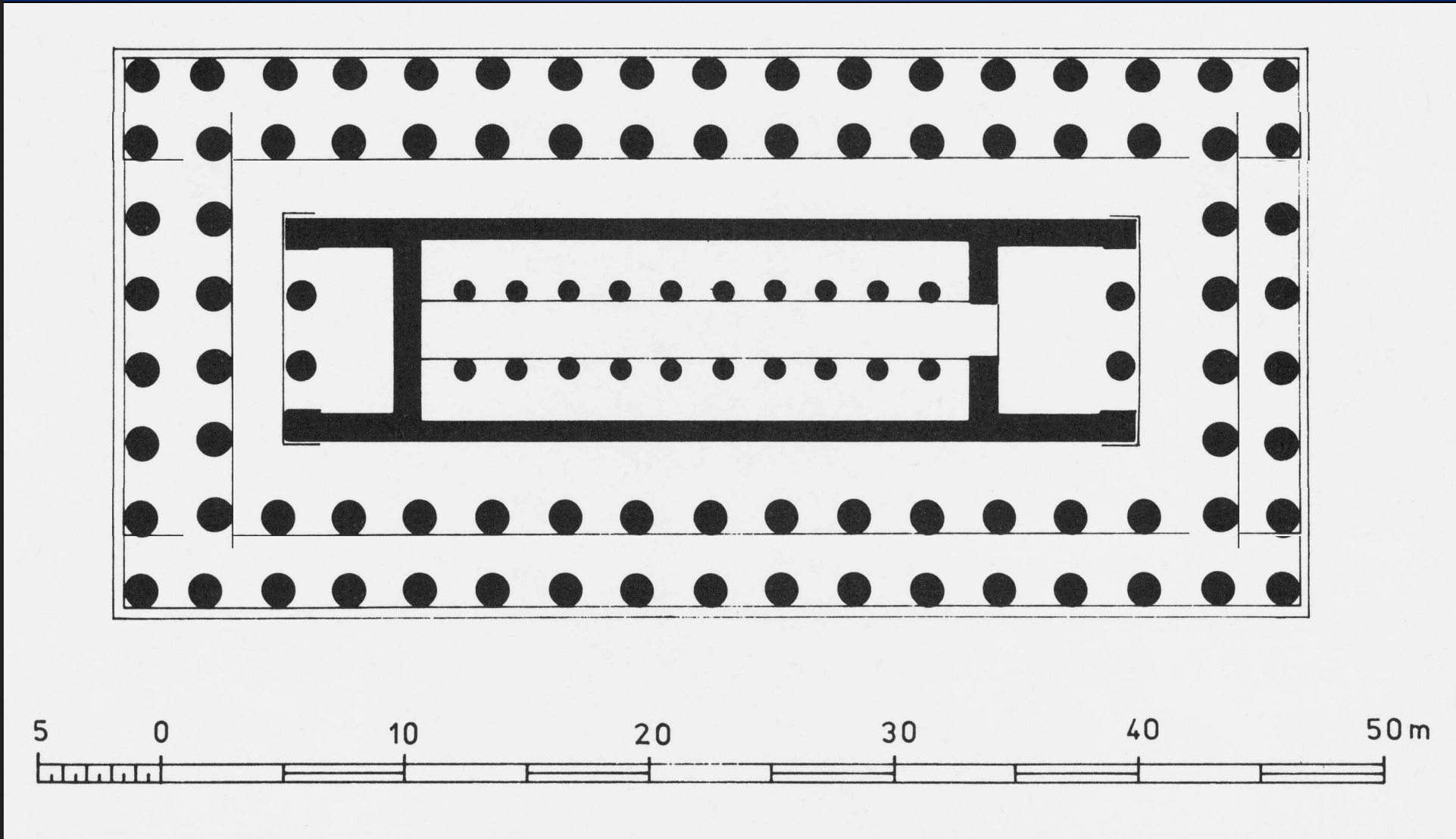
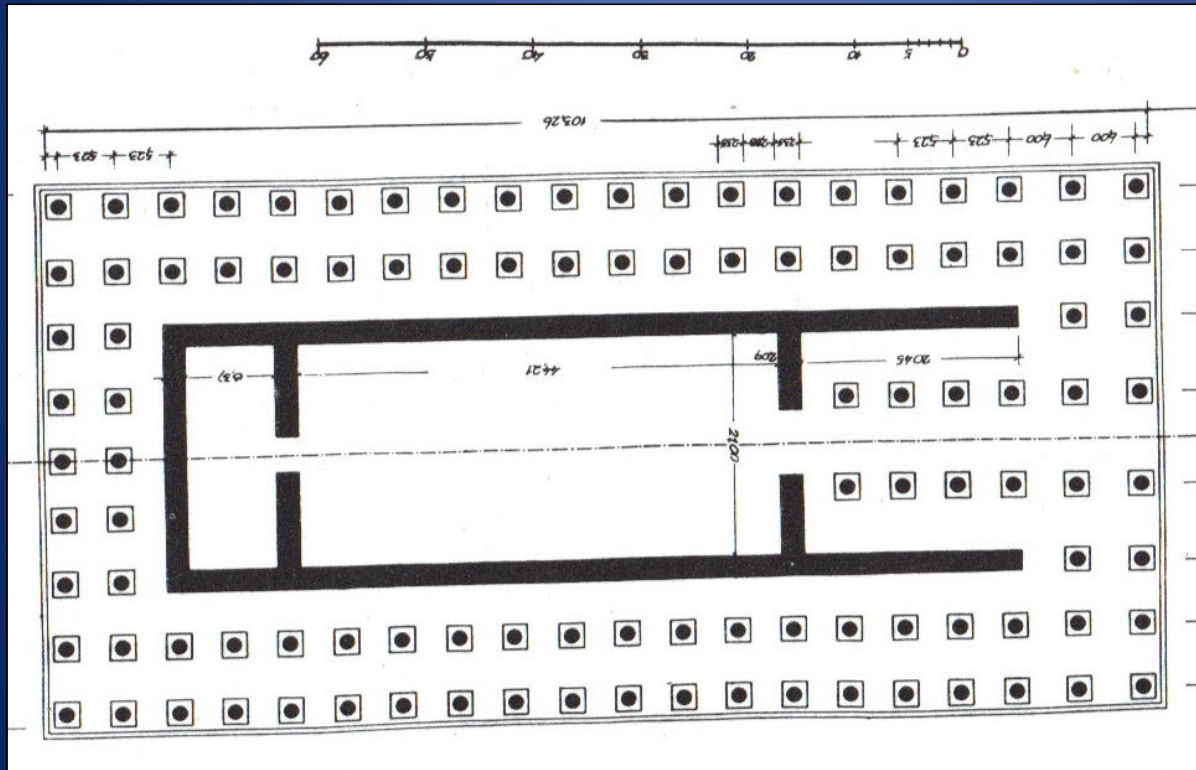
: Temple of Artemis at Kerkyra,580BCE
ARCHAIC
limestone
-first doric temple built completely in stone
-8×17 columns, enough room for another set of columns on inside (pseudodipteral)
-two porches with 2 columns in antis
-earliest psedudipteral-has doric angle contraction
Temple of Artemis at Ephesus,560BCE
ARCHAIC
-contemporary with Hera III
-one of the earliest Ionic temples
-size of a football field
-deep porch with access to cella and small room that had unknown function
-King Croesus paid for some of the columns
-some columns have a relief at the bottom for decoration

Siphnian Treasury, Delphi, marble, ca. 530 BCE
ARCHAIC
-richly decorated in scultpure
-very closely datable
-Has a Kore that replaces one of the columns
-has a continuous frieze and Ionic Treastury
-East frieze has the council of the gods and trojan war, the other frieze shows a gigantomachy, battle between gods and giants

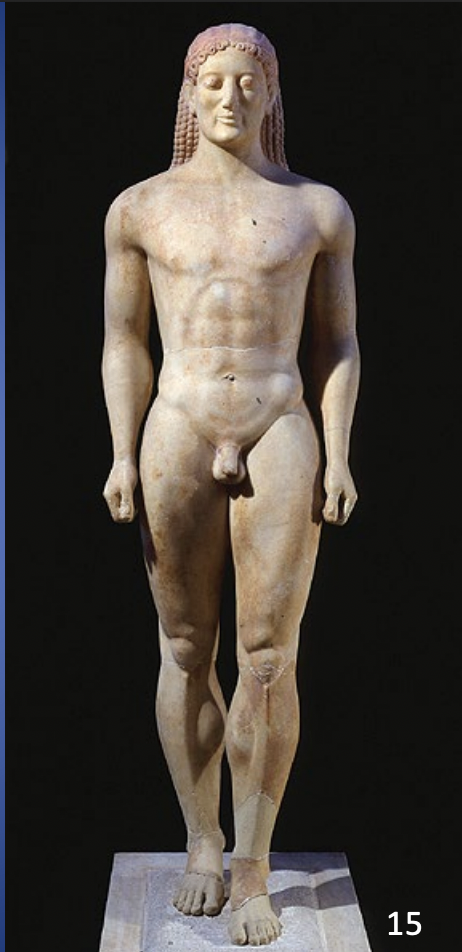
New York Kouros, said to be from Attica, ca. 600 BCE, marble, H. 6’ 4 ½”
ARCHAIC
-called new york because held in new york
-well above normal height
-left leg step forward, inspiration from egyptian sculpture
-arms down in fists
-stiff frontal perspective
-space between arms and legs
-archaic in patterns seen on muscles,bones,tendons, shown as grooves or ridges
-head is too big for body

Anavysos Kouros, ca. 530 BCE, from Attica, marble, H. 6’ 4 ½”
ARCHAIC
-inscription on base speaks how Croesus died in battle
-function of piece is as a gravemarker
-has more naturalistic proportions
-head smaller more realistic to 3d details
-head has archaic smile
-patterning in hair
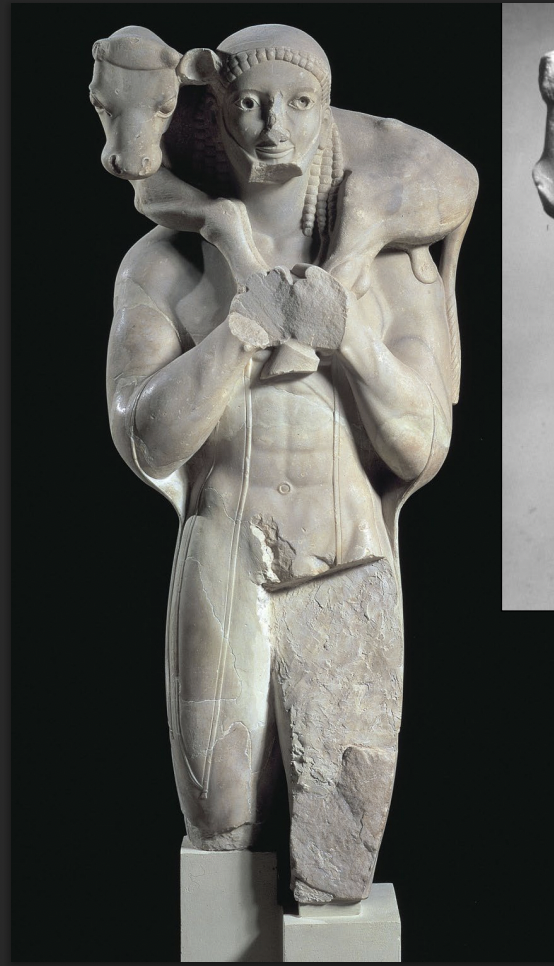

Calf Bearer (Moscophoros), dedicated by Rhonbos, Athens Acropolis, 560 BCE, marble, H. 5’ 5”
ARCHAIC
-not a Kouros as seen in position and subject
-bearded man, full grown adult
-is a votive showing a person carrying a votive offering
-clothed
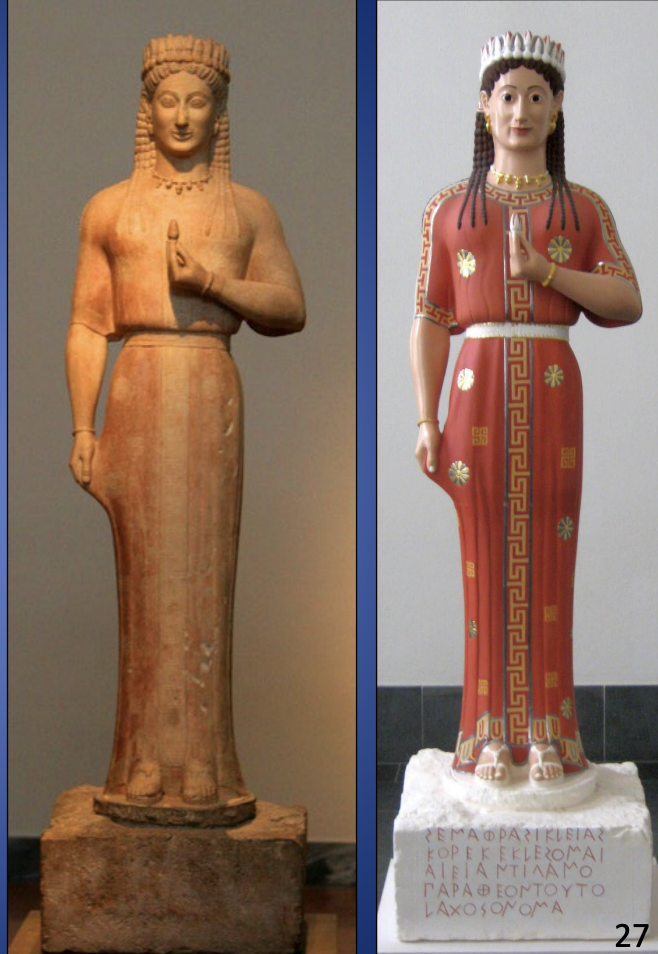

Phrasikleia, from Merenda (Attica), ca. 540 BCE, marble, H. 6’ 1”
ARCHAIC
-grave marker of Phrasikleia
-Kore-unmarried woman
-common name of persephone
-even though phrasikleia is not married in life, hopefully she is brideof Hades in afterlife in inscription
-rich jewlery
-

NOT ON EXAM
Kore 682, Athens Acropolis, ca. 520 BCE, marble, H. 5’ 11”
-chiton w himation
-votive
-separate right arm
-has complex patterns and folds
-folds respond to hands
had a meniskos, bronze disk to protect head

NOT ON EXAM
Franҫois Vase, Attic Black-figure Volute Krater, by Kleitias (painter) and Ergotimos (potter), from Chiusi, Italy, 570 BCE,
-showing a scene of Athens talking over Corinth
-Athens is influenced by Corinthian techiques in painting
-only one frieze has animals others are narrative greek mythology
-over 200 figures, archictecture and inscriptions
-top frieze is most important as it is the tallest
-dhowing a procession of guests and gods to the werdding of peleus and thetis, parents of herakles
-singifigane found in italy means that athenian vases are being exported.
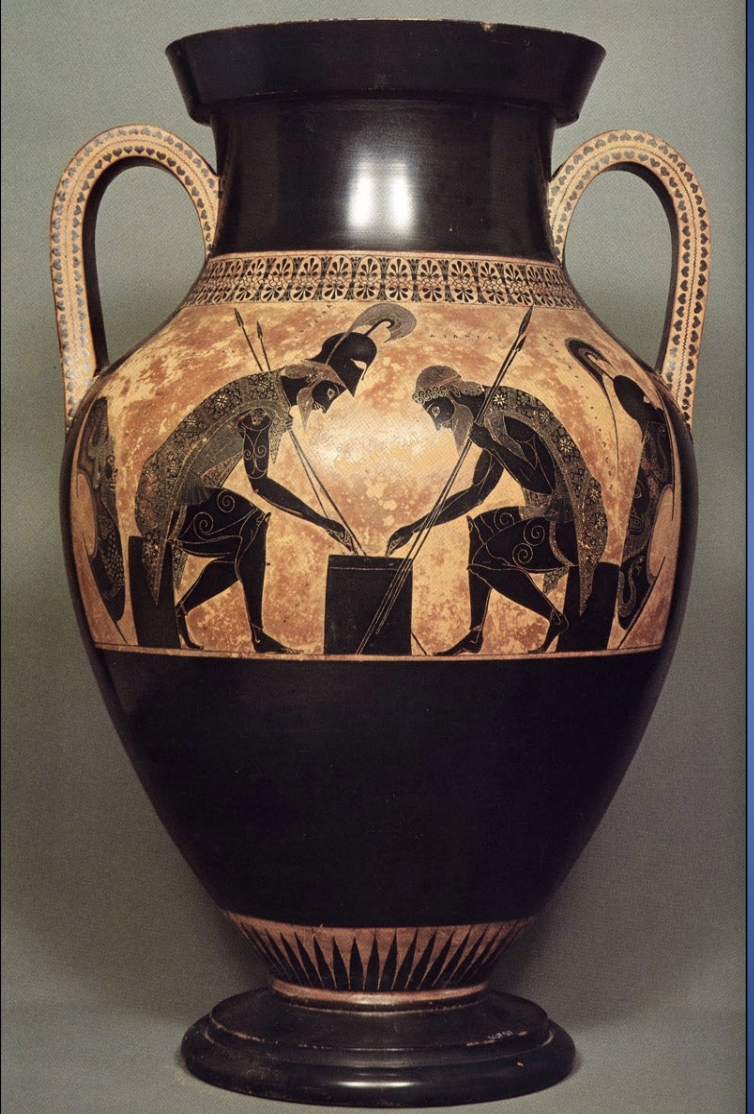

Attic Black-figure Amphora by Exekias: Achilles and Ajax Playing a Game, ca. 540-530 BCE
ARCHAIC
-heroes Achilles and Ajax, identified by inscriptions, are shown seated and intensely focused on a game
-The inscriptions coming from their mouths clearly state their scores: Achilles calls out "four" (tesara) and Ajax says "three" (tri)
-black-figure technique
-represent the competitive rivalry between the two warriors or a metaphor for their shared fate, as both would meet untimely deaths
-
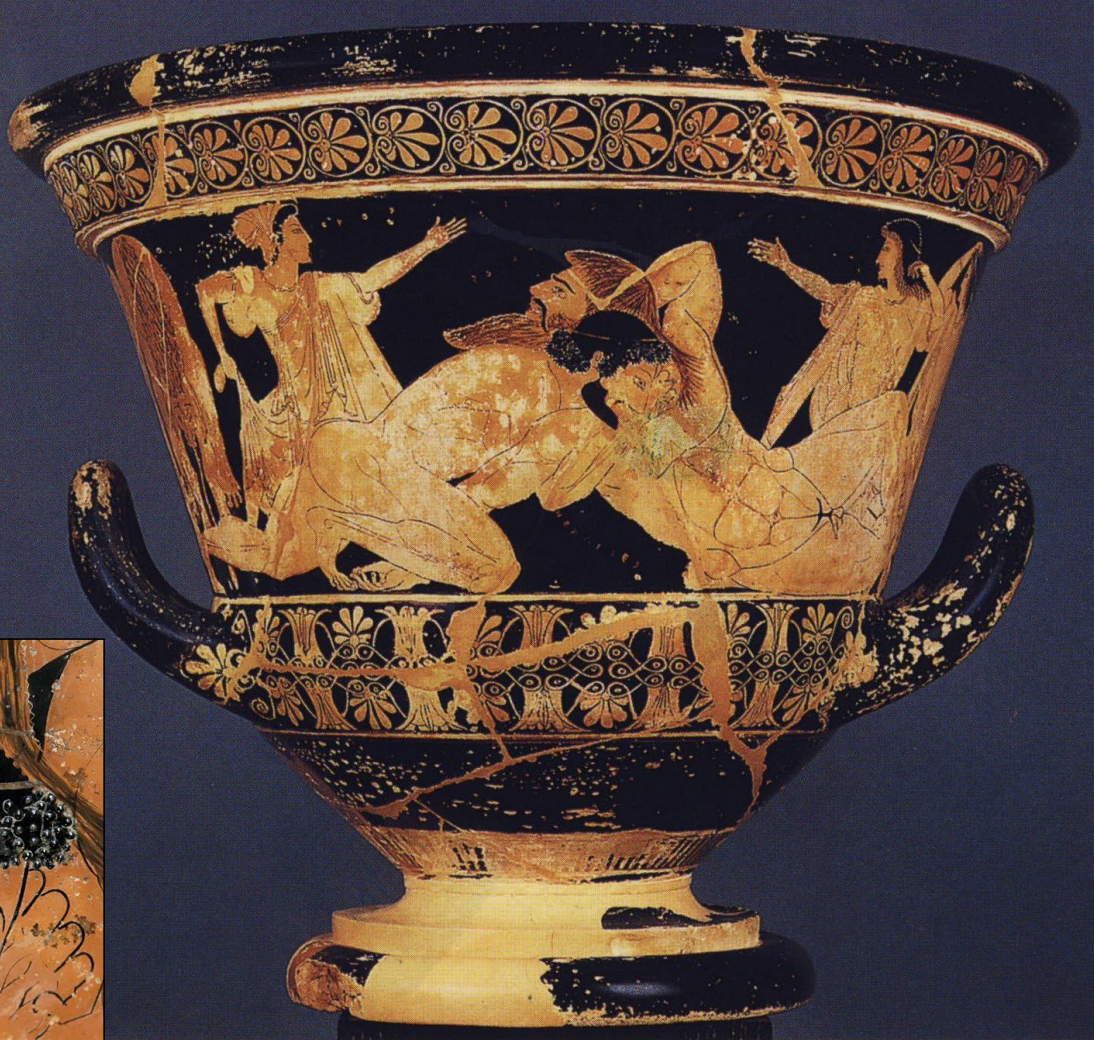

Attic Red-figure Calyx Krater by Euphronios: Herakles and Antaios, ca. 510-500 BCE, H: 19”
ARCHAIC
One of the Pioneers: using new boldness and experimenting with new poses and views
-Antaios is a giant, seen with unkempt hair, representing the barbarians. Herakles is the hero of greek civilization
-herakles lifting him in the air and strangling him, showing strength of greeks
-new pose of frontal torso with frontal leg.
-Rare depiction of showing emotion in archaic art
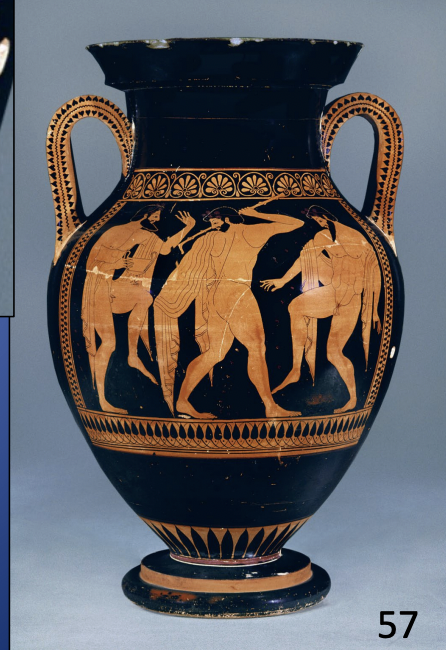

Attic Red-figure Amphora by Euthymides: Three Revelers, from Vulci, Italy, ca. 510 BCE, H: 23 3/5”
ARCHAIC
-showing man coming back from symposium, drunk
-done in red figure, where the subject is now most popular to be everyday life
-man dressed in himation with styalized folds
-eye is frontal but iris is more forward for natural look
-painters are competing with eachother
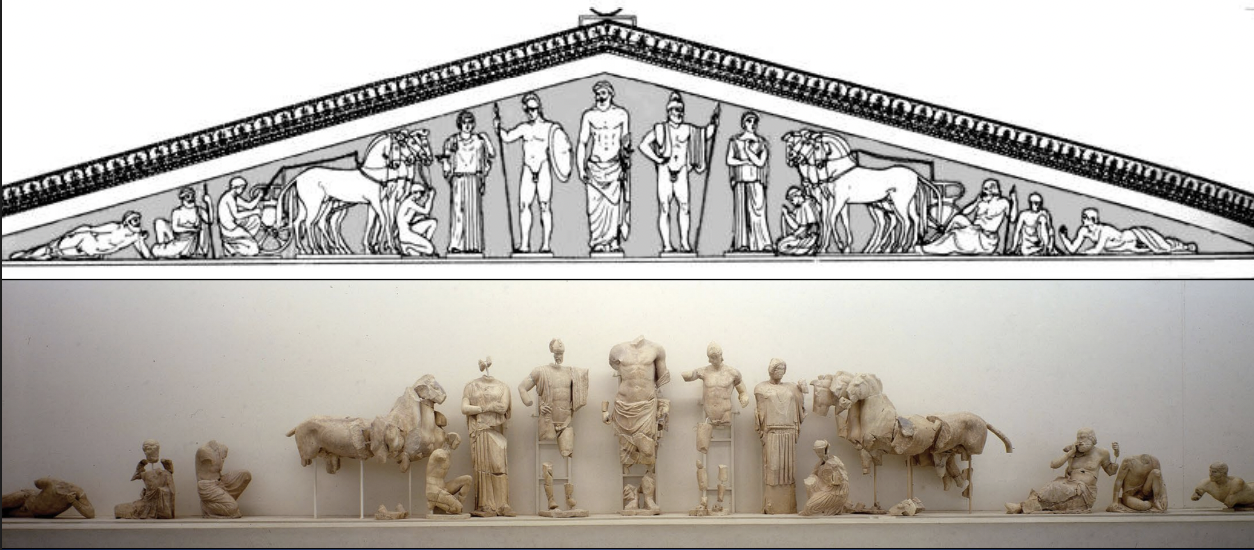

Temple of Zeus at Olympia, East (Front) Pediment: Preparation for the Chariot Race between Pelops (suitor) and Oinomaos (king of Pisa and father of Hippodamia) for the hand of Hippodamia, marble, H. of Zeus (as preserved) 10’ 2 ½, 560BCE
Early classical
-shows prepration of chariot race between Pelops and Oinamos for hand of Hippodamia
-Pelops bribed and put pin in Oinomos chariot that made him fall and die
-represents moral lesson for olympic competitios about cheating
-Severe style shown in strong chin and thick eye lids
-drapery reflected in weight shift on person with straight vertical folds
-interest in anatomy shown in different gestures and poses
-showing Iamos, the seer prochet, showing emotion and peeople at different ages.
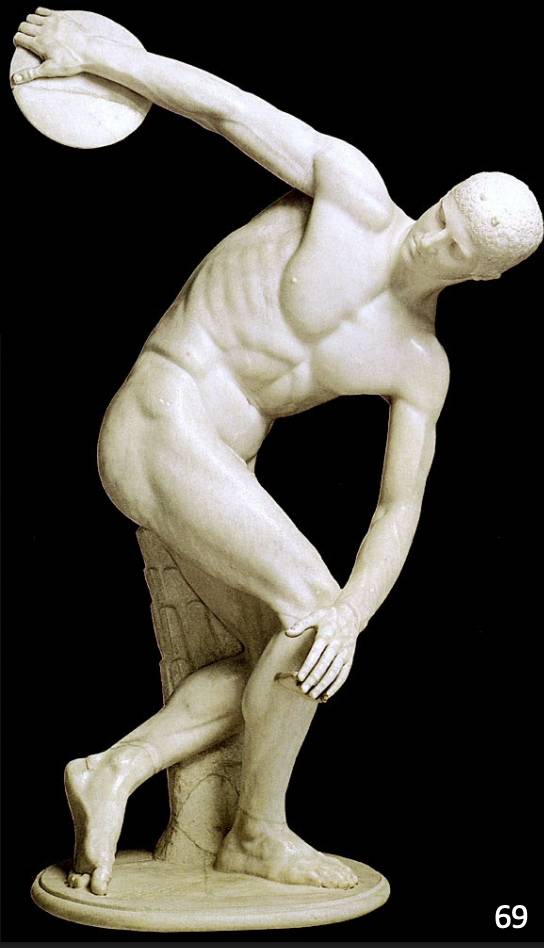

Diskobolos (Discus Thrower) by Myron, Roman marble copy of a Greek bronze original of ca. 450 BCE
early classical
-copy of Greek Bronze
-made with aid of pointing machine tool, measuring device to copy scale
-2 points show guarantee of authenticity
-pause in action
-muscles attempted to be shown but not correct based on tension
-interest in anatomy
-support in tree trunk and hands on knee to keep structure
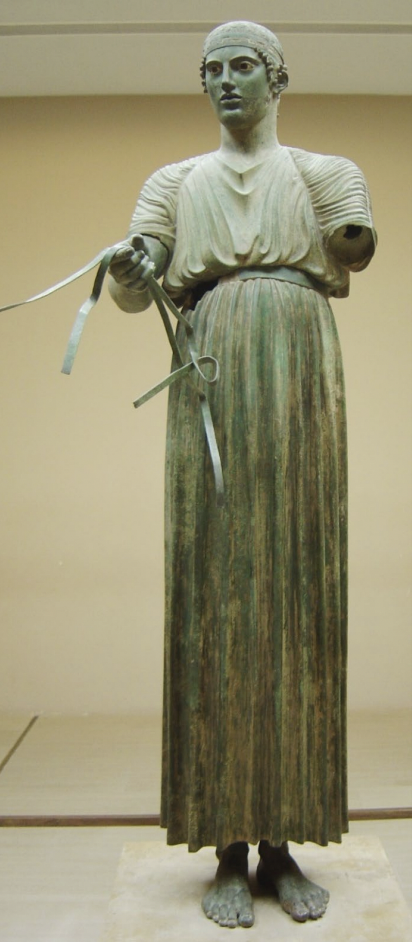

Delphi Charioteer, 460s BCE, bronze (with copper, silver, onyx),
-burried, property of gods
-over lifesize
-holding parts of horses
-long linen chiton crossed in back to avoid getting stuck while riding
-proportionally starnge because of long legs
-optical correction for riding a chariot
-slightly turned right but there is equal weight
-inlaid eyes
head, body, arms all made at different times

-
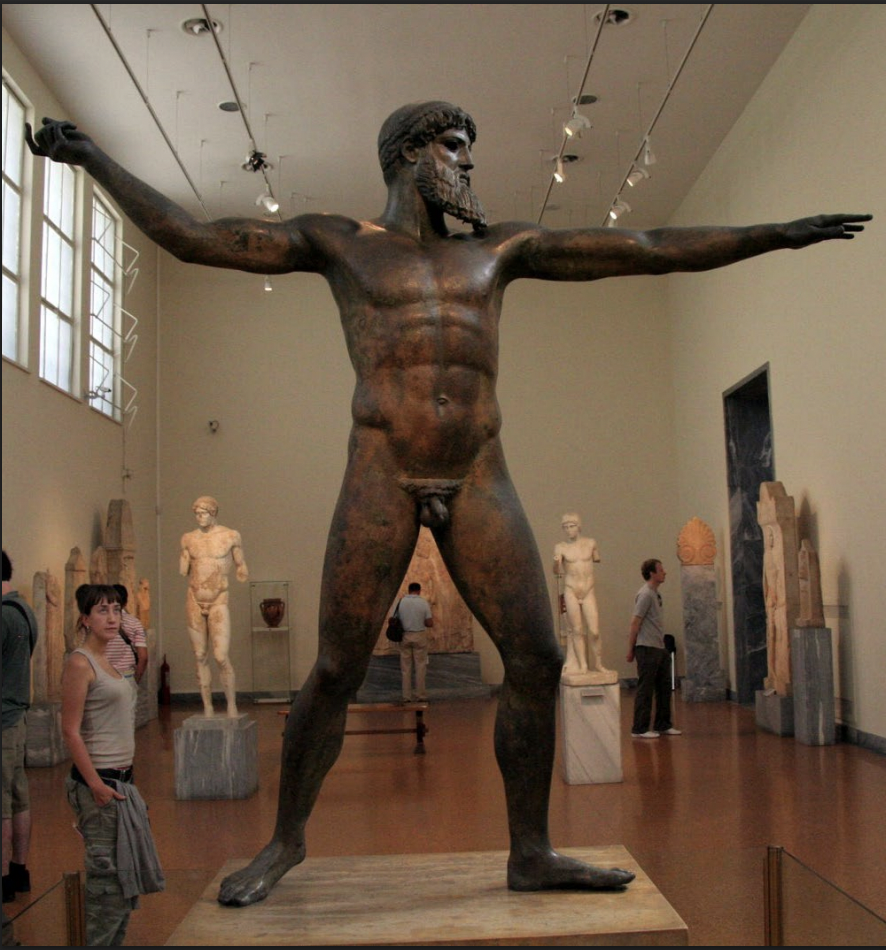
Cape Artemision Zeus or Poseidon, ca. 460-450 BCE, bronze,
early classical
-found in shipwreck
-was throwing a thunder=zeus, was throwing triton=poseidon
-flat when viewed from another angle
-early classical= momentary pause in action
-inlaid eyes, fine detail in hair and beard, patches of imperfections from errors

Riace Bronzes, ca. 460-450 BCE
early classical
-found in a shipwreck
-statues most likely from Greece to Rome
-statues exhibit weight shift
-inlaid eyes
-one cap unknown, possibly a helmet of a hoplite, other hat possible “Alepekis” which is a hat of fox fur
-statues perhaps displayed at Athenian Acropolis
-Possible to have represnted difefrent skin colors based on layeing on bronze

Attic Red-figure Krater by the Niobid Painter: Death of Niobe’s Children, 460 BCE,
early classical
-Myth of how Niobid boasted about children and being a better mother than Leto, in return her children killed her children
-New approach to showing 3D space by makng mountains / rocky landscape but still all are same scale
-higher figures were meant to be farther away
-some inspiration for this were monumental paintings
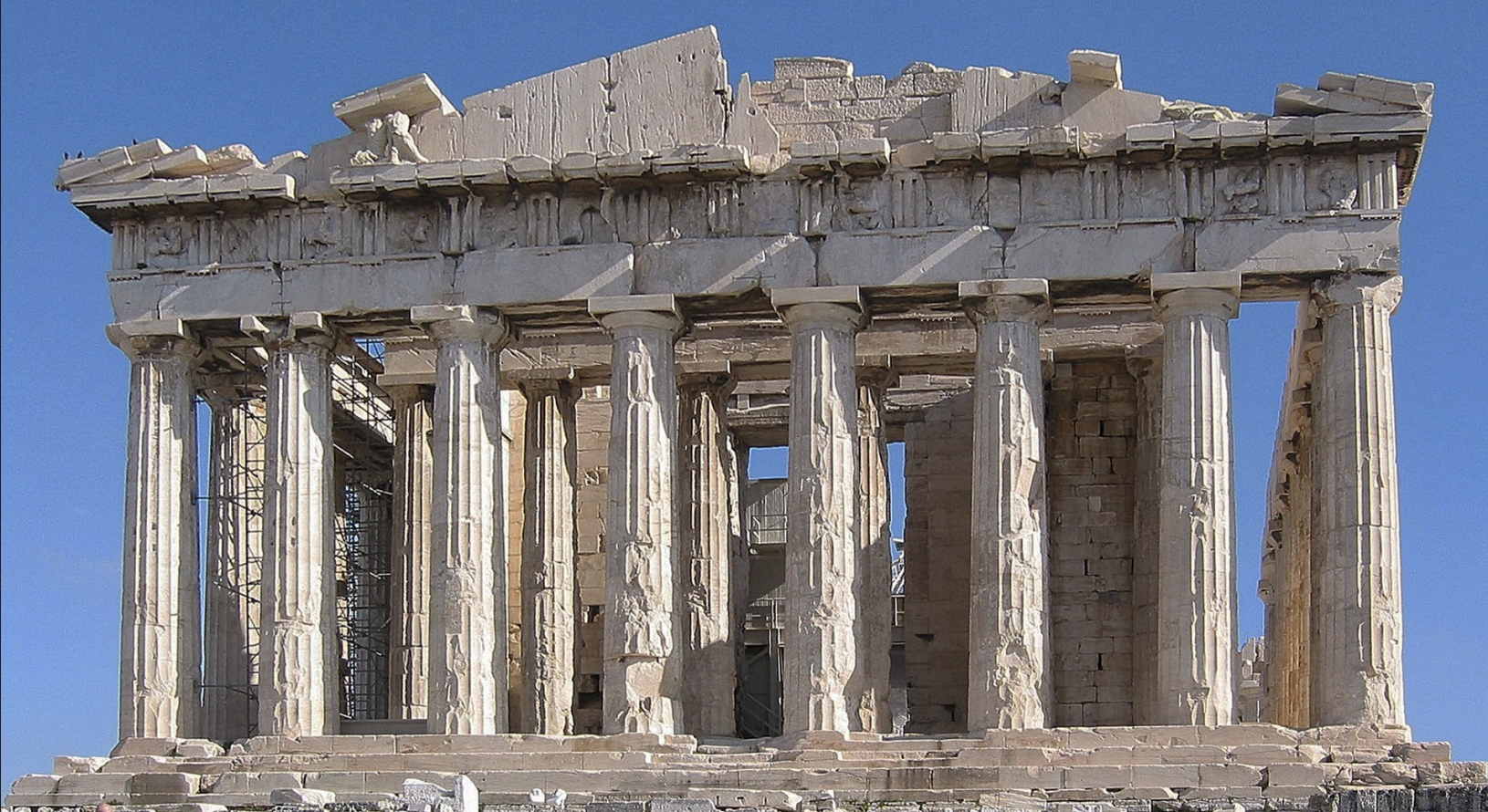

Parthenon (Temple of Athena Parthenos), 447-432 BCE
HIGH CLASSICAL
-Doric Temple
-Architects: Kallikrates and Iktinos
-built of pentalike marble
-cella with cult statue
-optical refinement: stylobate curves down at the ends, corner columns thicker, closer together, doric angle contraction, long walls of cella lean inward , entablature and pediments lean outward
-Scultupture in metopes, both pediments, and ionic frieze
Metope Subjects: centauronomy, amazonomachy, trojan war, gigantomachy, power of greek civilization over barbarians
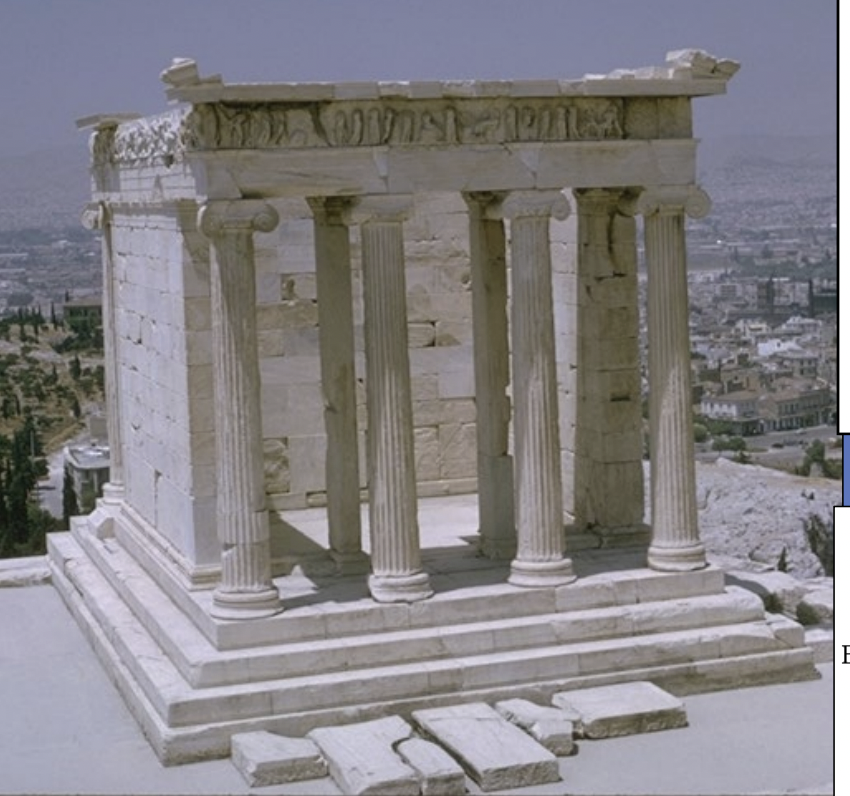

Temple of Athena Nike, mid -to -late 420s BCE, marble
HIGH CLASSICAL
Not peripteral
It's an Ionic temple because it has a continuous sculpted frieze
Has only four columns in the front and in the back
It originally had bronze struts, and it creates just an opening at the center
This temple was made with short and “stubby” Ionic columns because it was standing on this plain, heavy bastion
On the east front of the temple were the gods
On the south front, we can see the Greeks fighting against the Persians, and the Greeks are seen heroically nude
Both pediments were decorated with sculptures
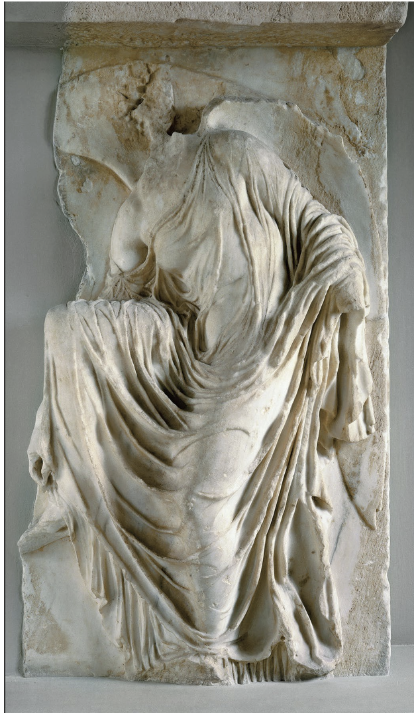

Sandal Binder relief from the Nike Balustrade, marble 410-405
HIGH CLASSICAL
The woman is seen bending over, fiddling with her shoe, and removing her shoe before stepping on sacred ground
Wears a chiton because she's got buttons on the top part of her chiton, but over the chiton, she wears a himation, which is dropped over her left arm
The drapery looks like it's sticking to her body, almost as if her drapery were wet
Ribbon drapery because it looks like they applied ribbons on the himation
This sculpture isn't really realistic because
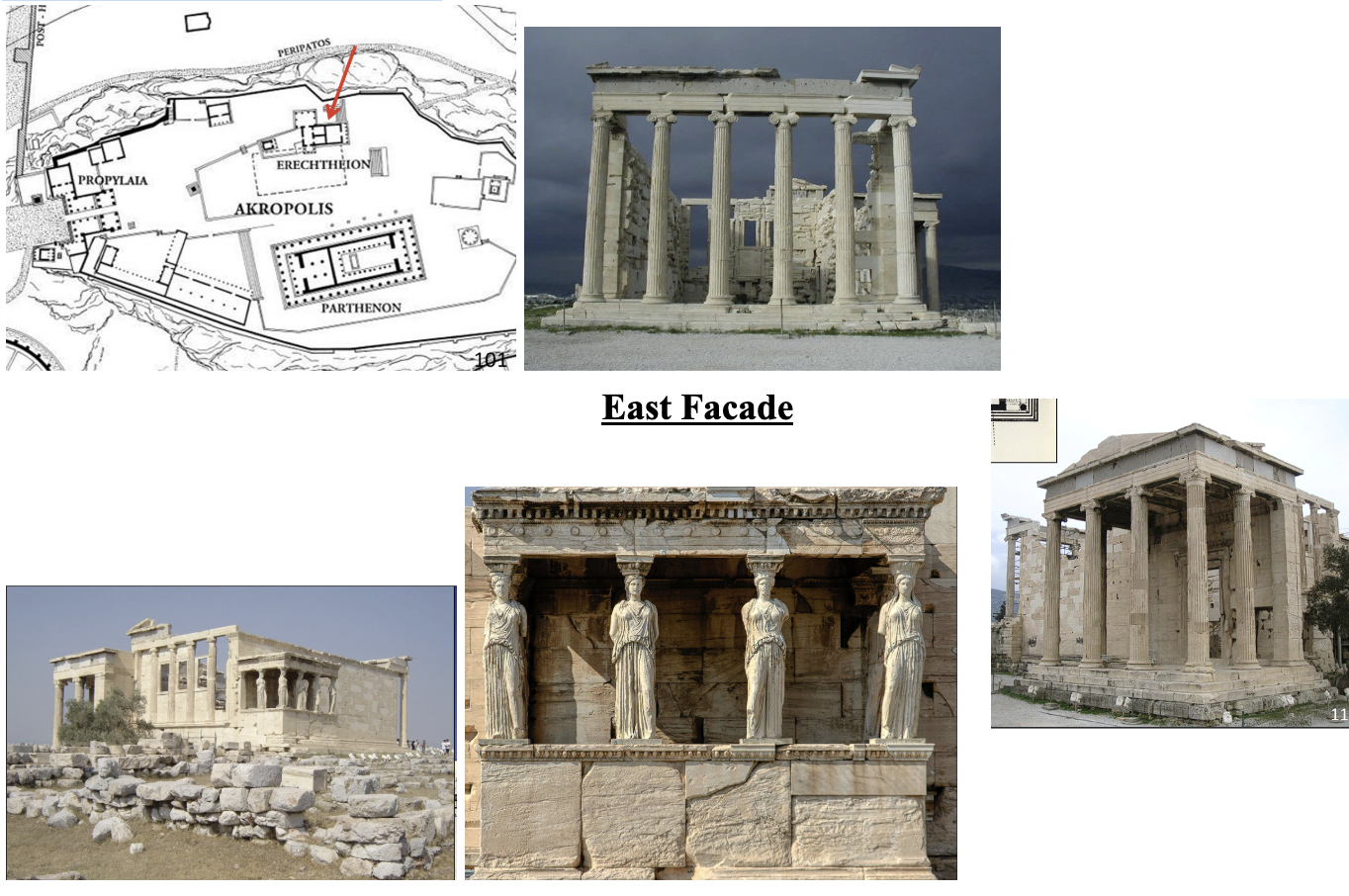
Erechtheion began in the 430s, main construction 409- 406 BCE, marble (with blue-gray limestone frieze)
HIGH CLASSICAL
Begun in the 430s
It is an Ionic temple
Has a blue-ish gray limestone frieze
This temple housed the venerable old olive wood cult statue of Athena Polias that received a new peplos every year during the Panathenaic Festival, but before the Persian sack (480 BCE), the olive wood statue of Athena Polias had stood in the Late Archaic temple
Seen taller from the sky
Has two weird projecting porches on the North and South sides of the temple because it had an uneven ground, and needs to accommodate many traditional relics and cult areas
Was not preserved
Possible that the western half was divided, but not very clear
In the East Facade, there was a pediment with no sculpture
The frieze was made of blue-gray limestone; everything else was made of marble
The figures are fragmentary, so we don't know the subject
The north porch of the temple has the Ionic order
On the floor of the porch, there was an opening, which was mirrored in the opening at the ceiling and roof. Why? Because the Greeks thought about what the Remnant of the contest between Athena and Poseidon was.
The South (Caryatid) Porch was built over the tomb/shrine of Kekrops
4 Caryatids at the front
The women take the place of columns and support the establishment on their heads
The women are seen wearing a peplos
The free leg pushed the drapery
The two on the left are mirror images

Doryphoros, Roman marble copy (from Pompeii) of a bronze original by Polykleitos of ca. 440 BCE, H. 6 11”
HIGH CLASSICAL
This was created by an artist named Polykleitos, but unfortunately, there are no preserved originals by him.
He also wrote a book called “The Kanon,” which outlined his theory on the ideal. The book was also not preserved
This statue was created by him to illustrate his theory
The bronze original did not survive
There were 50 Roman marble copies of these statues
This statue represents Akilles because of the sphere, and we know this because he is frequently shown in vases with his sphere.
He has a similar position to the Riace Bronzes because the right leg serves as the weight-bearing leg, and the left leg is the free leg.
In the high classical period, the heel is behind and raised from the ground
We can see a balance between tense and relaxed forms (both the right and left legs seem tensed, but both the left and right arms seem relaxed).
The muscles are emphasized, especially in the hip part
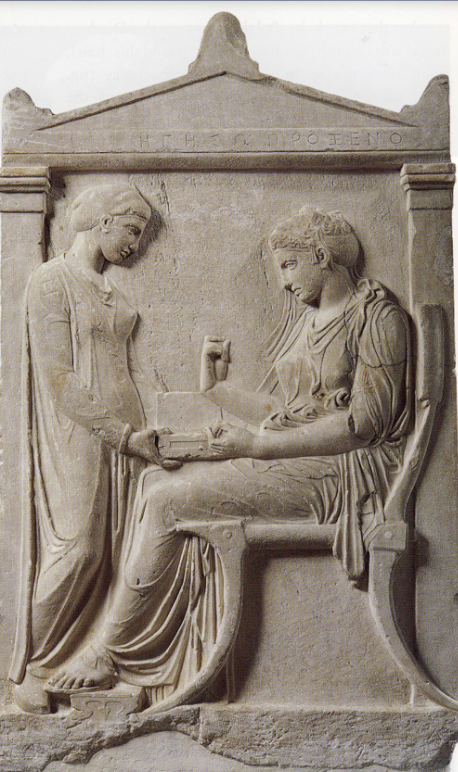

Grave Stele of Hegeso, daughter of Proxenos, from the Kerameikos Cemetery, Athens, ca. 410 BCE, marble, H. 5 2
Period: High Classical
Location: Athens
Figure overlap
It would have been painted
Has two figures
This Grave Stele has a much wider format
The architectural framework features two posts supporting a pediment and includes an inscription as well.
This Grave Stele shows the deceased in life
Has a three-quarter view
The drapery of Hegeso is pretty transparent
The facial expressions of the two figures are pretty neutral
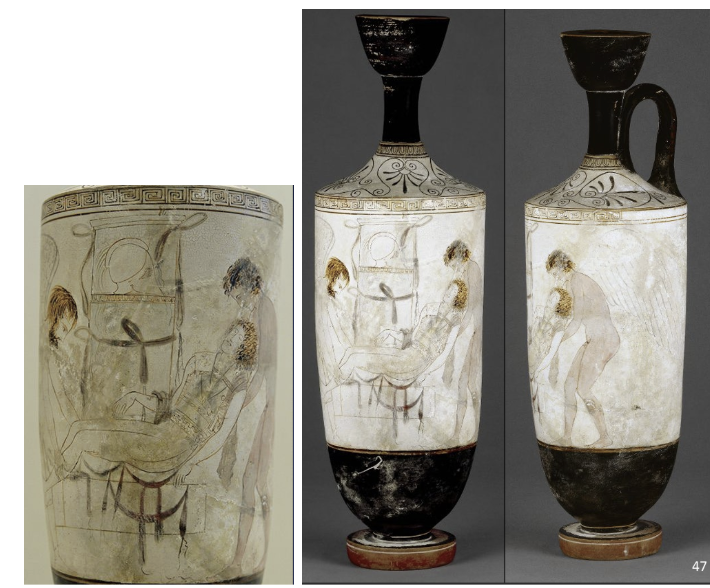

White ground Lekythos: Hypnos and Thanatos Carrying a Dead Warrior, ca. 410 BCE
Period: High classical
Shows Hypnos and Thanatos carrying a dead body to his tomb
Hypnos is shown beardless, while Thanatos is shown with a beard
It reflects on the Greek belief in the afterlife and symbolizes the transition from life to death
White-ground lekythos are not used in daily life, so they would usually be a grave gift because they weren’t very durable.
The function of the white-ground lekythos was that it contained olive oil, so that the mourners could pour it over the deceased.
Typical subject? Funerary scenes

Athenian “Owl” coin, 5th c BCE
HIGH CLASSICAL
Tetradrach: 4 drachma coin
Drachma: basic unit of coinage. A day’s wage for a skilled workman
Typically, coins had a head and a deity, and a local symbol in reverse
Obol: 1/6 drachma. 3 obols = daily pay for jury service
This coin had the head of Athena, where she is seen wearing a helmet, has earrings and a necklace, and the reverse was an owl, which was sacred to Athena
We can see an olive tree, which was the gift from Athena to the Greeks, and there's also a crescent moon
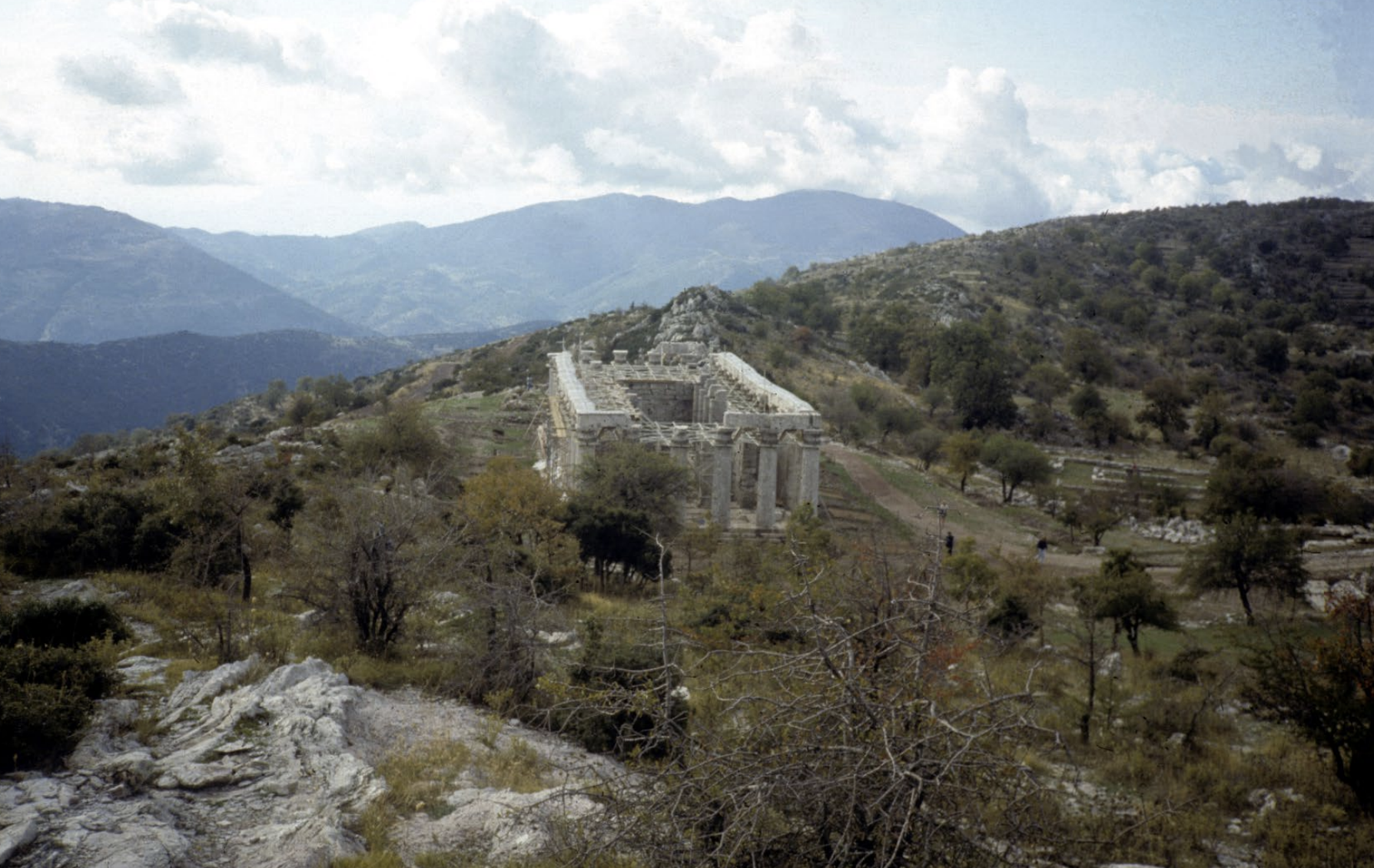

Temple of Apollo at Bassae, c. 430-390 BCE. Architect: Iktinos
-earliest known appreence of corinthian column capital
-doric temple
-mainly out of grey colored linmestone with white stucco and real marble on interior frieze
-6×15 columns, late classical, suprisingly long and narrow
-echoes from of temple nearby, orientated north south
-front porch, back porch, naos is unusual since there is a back room (adyton) and adyton can be accesed from peristyle
-inside the cella, the row of columns are ionic een though peristyle columns are doric and are engaged
-only one columns is freestanding: and is conrinthian!
-continuous frieze: centauromachy, and amazonomachy, one of last features to be finished
-details: relief is quite high and stocky and are stricking dramatic poses (centauronomachy), drappery: some parts cling as if wet, others flutter out
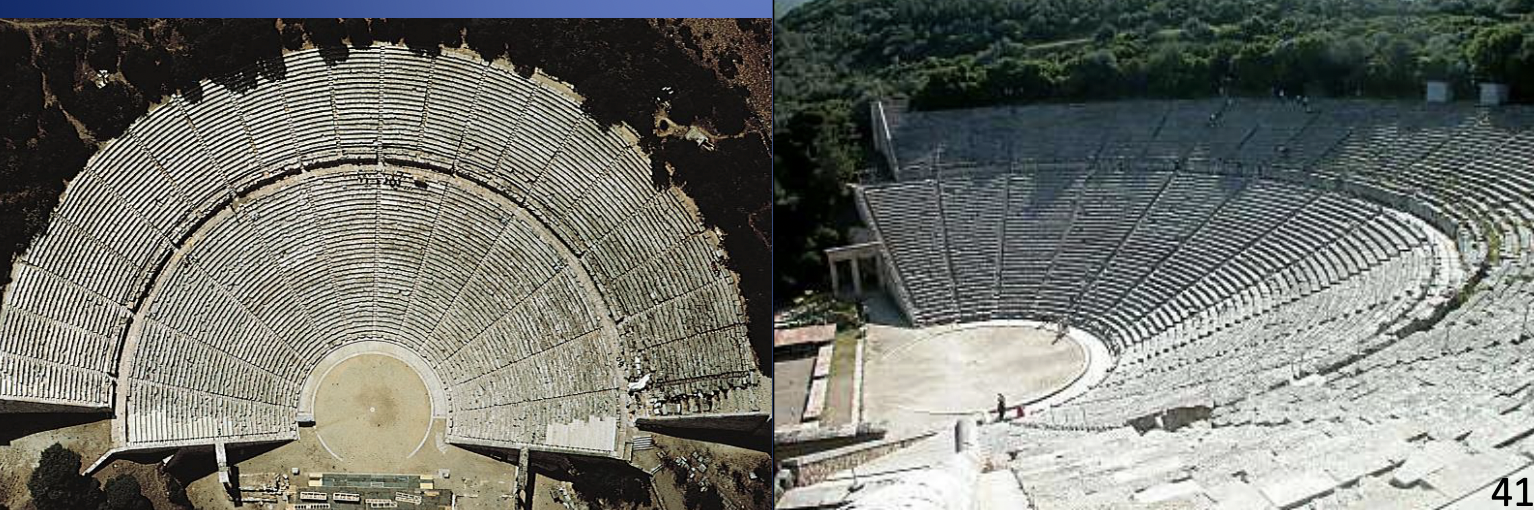
Epidauros Theater, ca. 300 BCE
-best presevred example of typical greek theatre
-bench style stone ceiling, supported by side of the hill
-seats occupy more than semi circle and is divided into sections, wedge shaped
-horizontal walkways divide the seats as well. 35 rows of seats, holds 12,000 spectators
-parts: orchestra (between seats and stage circular
-proskenion- risen wooden stage
skene: stage building, where actors change costumes
-everyone was male
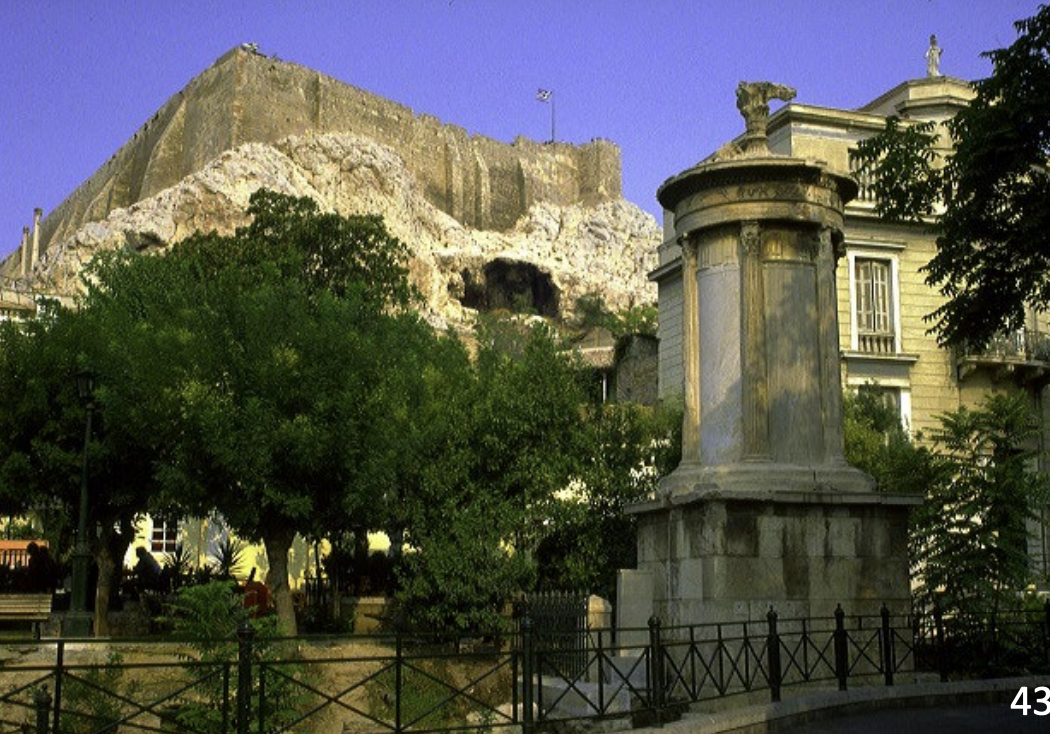

Choragic Monument of Lysikrates (Lysikrates Monument), Athens, 334 BCE, marble and limestone
-winning monument for base to display bronze tripod of winning the choric
-circular on rectangualr base
-earliest known use of cornithian columns on exterior building
-engaged columns on gray limestone drum
-frieze shows scenes from life of dionysis
-pirate turning into dolphin
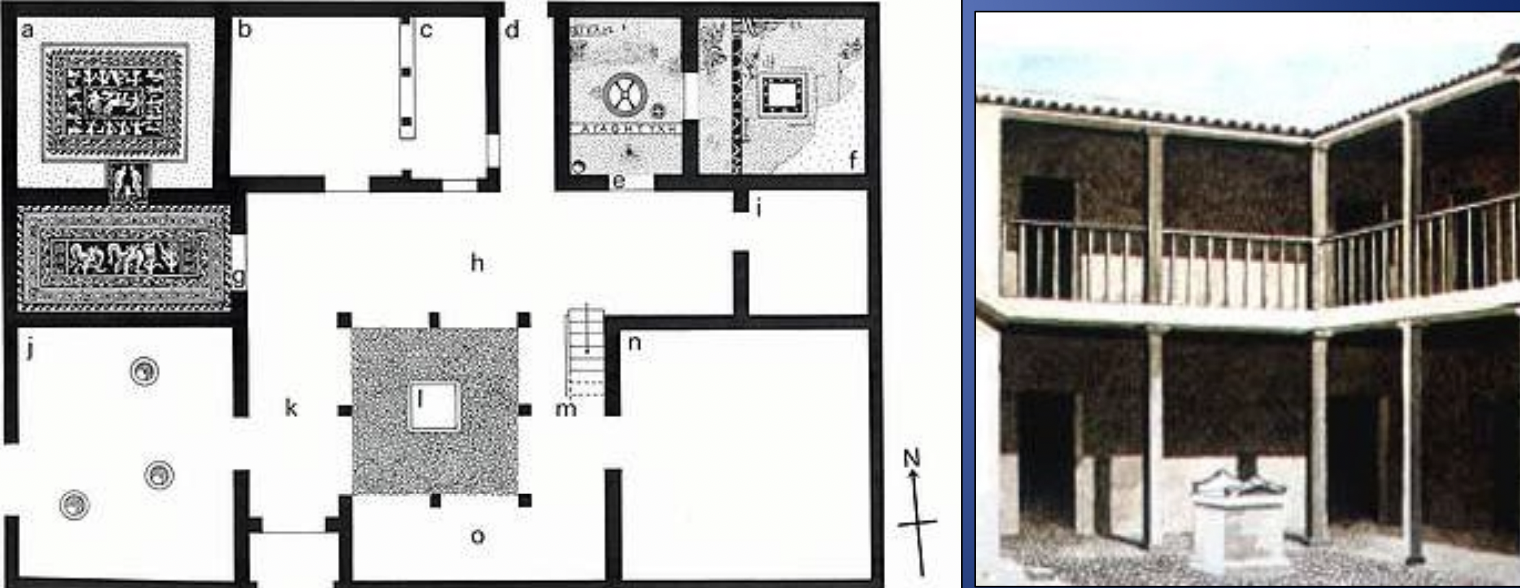
Villa of Good Fortune, Olynthos, 4th c BCE
-more elaborate arcitecture
-two stories tall, plain on the outside
-built around central courtyard with cobblestone altar
-”pastas house”: open courtyard surrounded by 1 or more side by roof collonade-decorated mosaics in bedroom suite where men would have dining beds 1a-had andron with vestibule: used specifically by men for dining and symposiums
-mosaic: dionysis ina. chariot surrounded by his followers
-doorway pan flanking a krater
-vestibule: thetis and nereids bringing achilles his new armor
appropriate because show scenes would give topics of conversation for symposiums
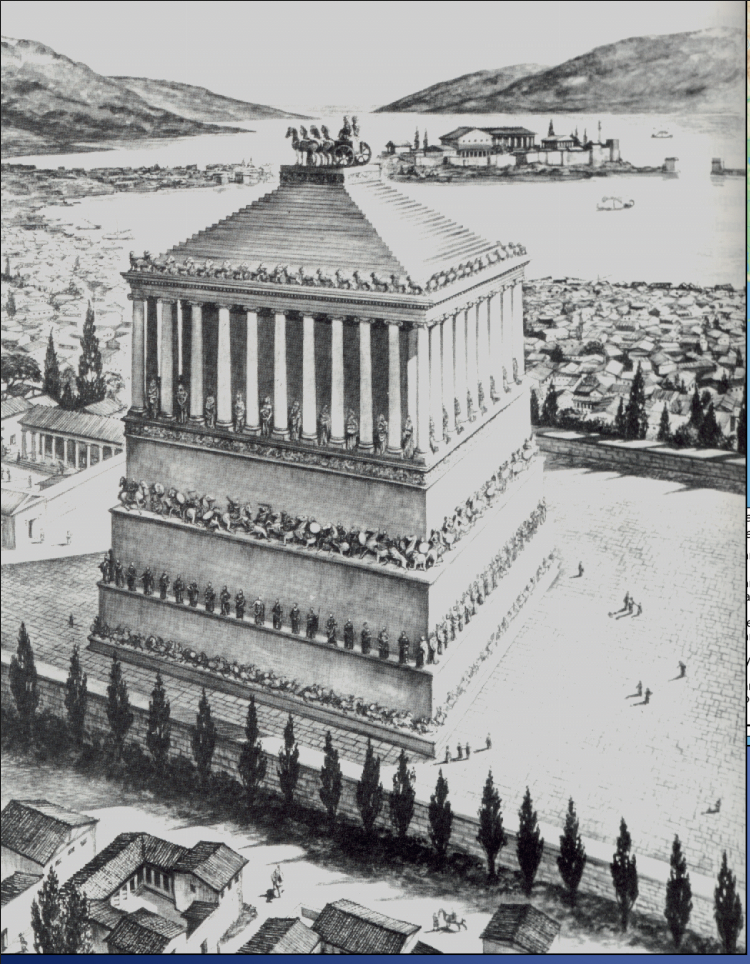

Mausoleum at Halikarnassos, ca. 350 BCE
-by king mausolos ruled 377-353
-one of the 7 wonders of the world
-part of the persian empire at the time
-statues on mausoleum possibly king mausolos and queen artemisia
-4th c hellenstics period sculpture:
-face intended ot be a portrait
-deep set eyes
-long wavy unkempt hair
-new interest in realistic portrait, tied to a larger trend of induvidualism
Frieze:
-greeks and amazons
-diagonoa twisted figures
-drappery clings
but also billows as if in a high wind
NOT ON EXAM
Tholos at Epidauros 360-340
-foundation walls laod in 6 concentric circles with pasage ways
-function is unknown, maybe a cenotauph (tomb like monument for someone burried elseware)
-26 doric columns, 14 corinthian columsn inside building
-richly decorated
-alterneated triglyths and decorated metopes with flowerrs
-lion heads and water sprouts
-with cornithian columns
-has a coffer (stepped recess that lightens the weight of the stone ceiling)
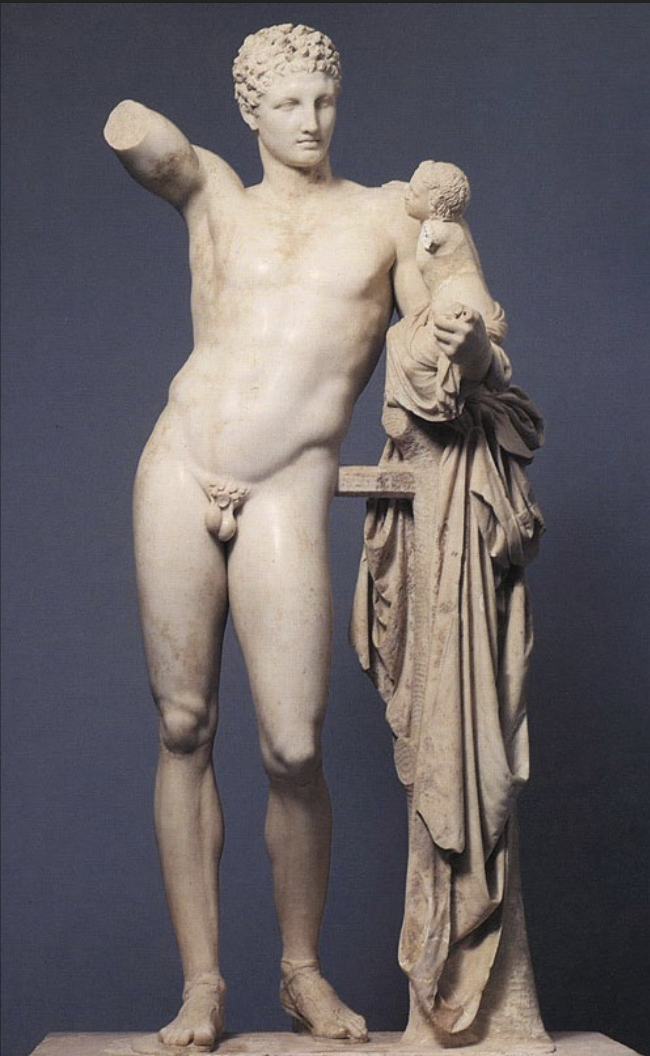

Hermes and the Baby Dionysus by Praxiteles, from Olympia, marble
High Classical
340 BCE original, roman copy 100bce
-Hermes hiding baby dionysis for zeus
-4thc of humanizing the gods
-domestic activity shown
-s curvature; typical for praxiteles
-legs have high classical weight and free leg
-resting arm on tree trunk draped with cloth
-engages space in front of hermes
-body proportions are slender, smaller head and soft blured features

Aphrodite of Knidos, by Praxiteles. Roman marble copy of a Greek marble original of 350 BCE
--roman copy of greek marble original 350bce
-specialized in marble
-very famous as it is first full nude female figure in greek art
-s curve
-long legs and small head
-right hand in front of genitals to cover?
-cloth draped over something, as tree from hydria
she is bathing
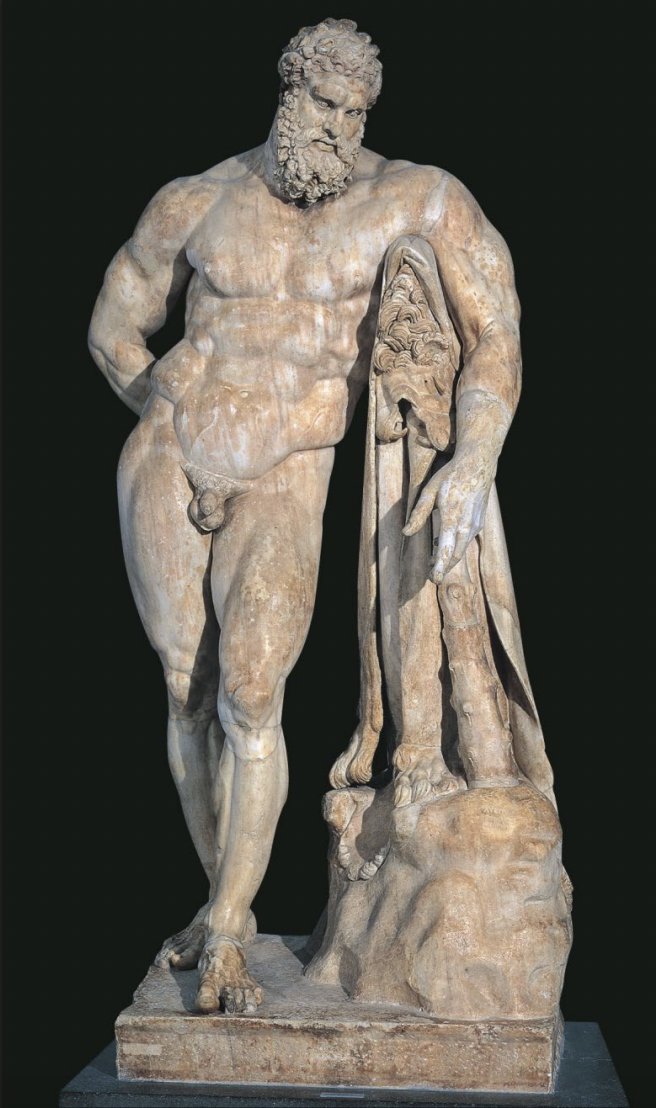

Weary Herakles. Roman marble copy of a bronze original by Lysippos of ca. 325 BCE
-tired, propping onto club
-support necessary bc figures are off balance and often leaning
-something in hand, possibly golden apple
-action and object show humanization of the gods
-extremly mascular, exagerrated

Portrait of Alexander the Great (the Azara Herm) Roman marble copy of an original by Lysippos, ca. 330 BCE
-lion hair, like a mane
-had a cowlick
-only allowed lysippos to make portraits of him
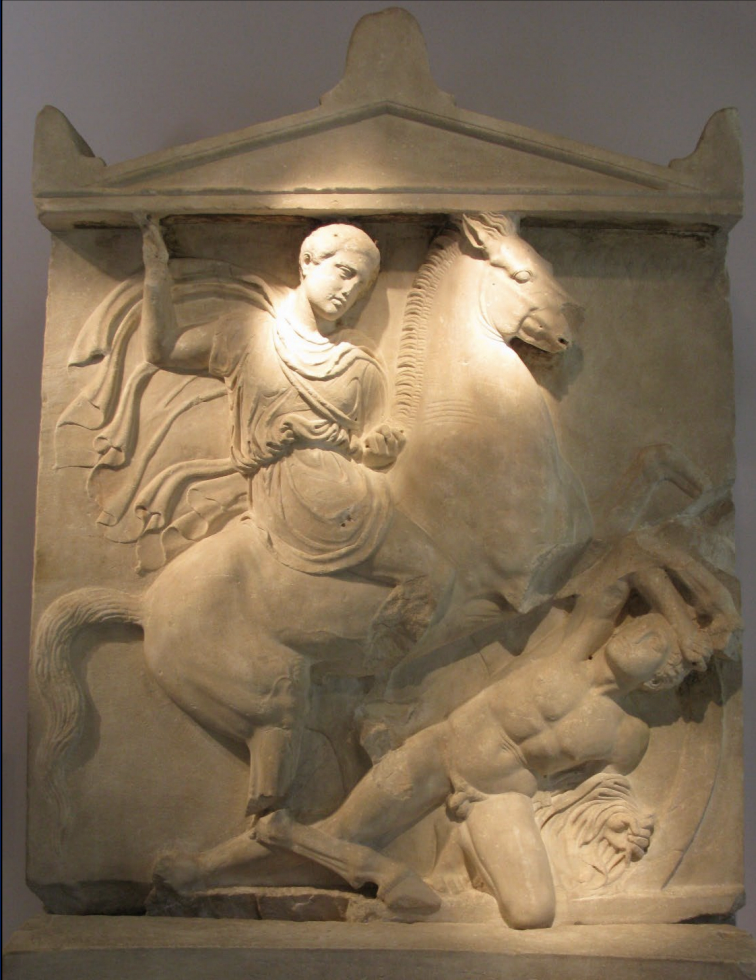

Grave Stele of Dexileos, Athens, 394-393 BCE
-square, topped by. pediment
-inscription: dexileos died in battle against spartans in 394
-shown fighting, on horse, delivering the final blow
-cloak pillows out as if wind
-heroic fighter done many times in greek and roman art
-this time showing nudity in a bad and weak sense
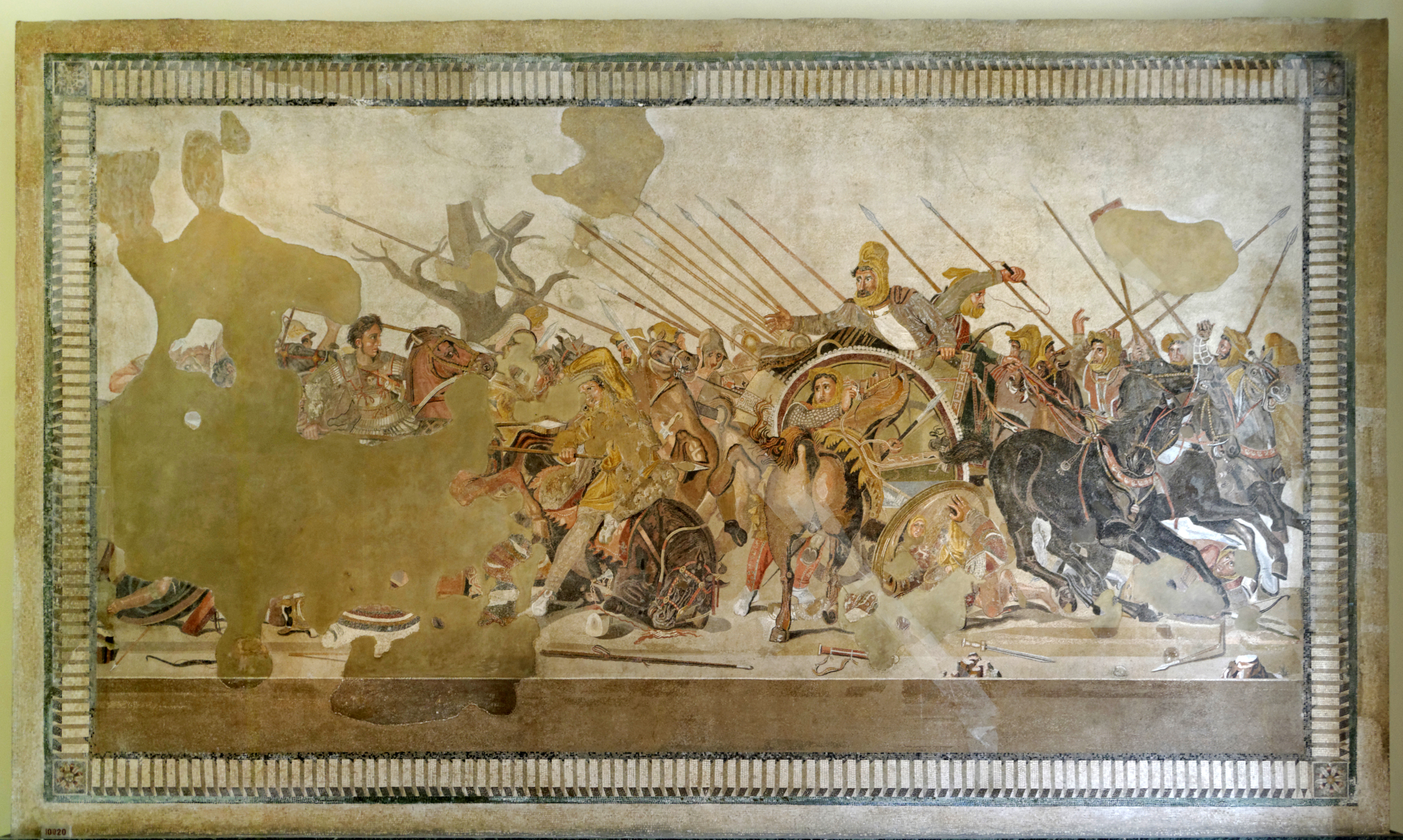

Alexander Mosaic, from Pompeii. 1st c BCE copy of a Greek painting by Philoxenos of Eretria, ca. 310 BCE, of the Battle of Issos (?)
HELLENISTIC
-made out of tessare (cubes of stone)
-showing the turning point of pattle
-Darius has agonozing look and hand reaching out, panicked
-artist highlighted alexander ad darius, bith raised up on horse or chariot, chest toward the viewer, looking at eachother
-alexander: not wearing helmet, to show mane hair
-may suggest bravery, includes image of warrior galloping on horse
-sense of depth of overlapping figures, objects in the foreground
-unrealistic
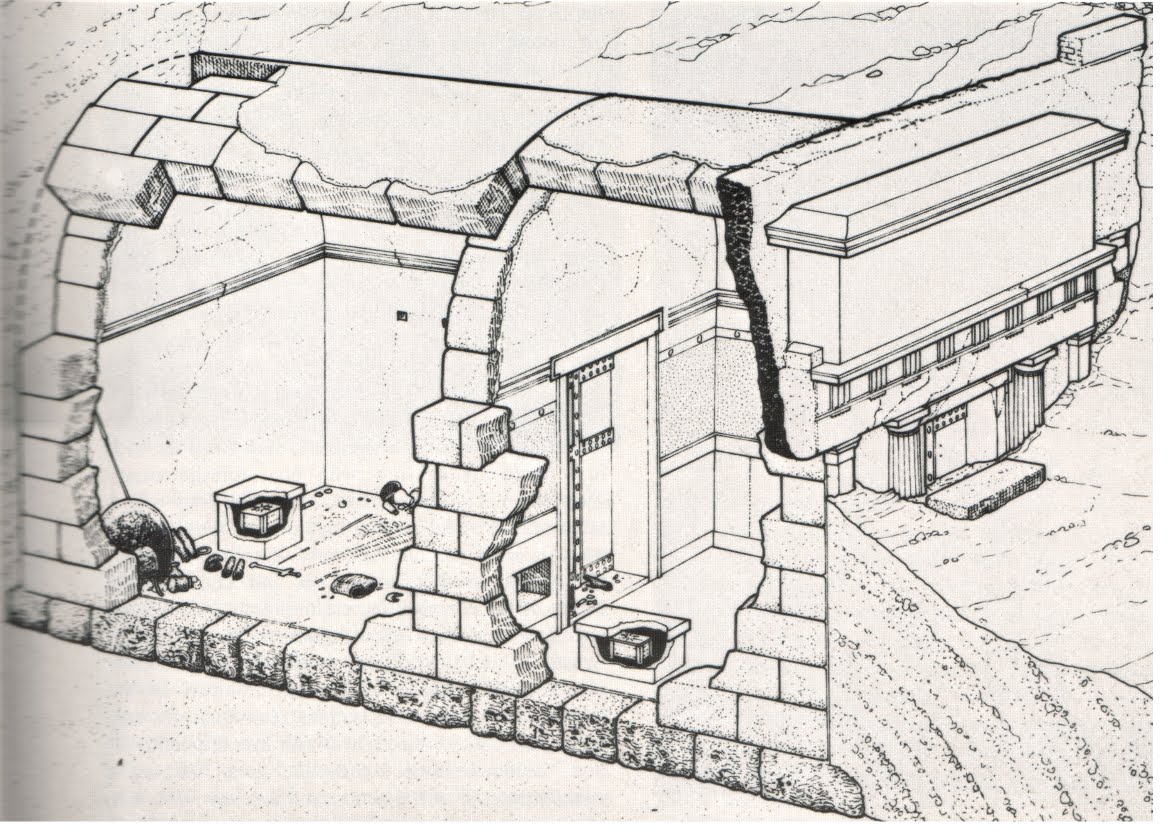
Tomb II, ca. 340-310 BCE,Vergina
-rear chamber, and ante chamber
-stone roof, ashlar masonry, trygliph metopes frieze and ionic frieze
-frieze shows a hunt, landscape of outside hulls, rock, and trees
-main chamber: armour, weapons, two tripods with inscriptions of prize from games at argos
-gilded silver diadem
-funeral couch decorated with ivory inlay
-silver symposium vessels
-marble sarcophogus: gold chest with lid with macedonian star
-gold wreath, and burries bones, bones around 35 years
latest pottery in the tomb is 325-310, philip died in 336
-lion hunt motif post dates phillip
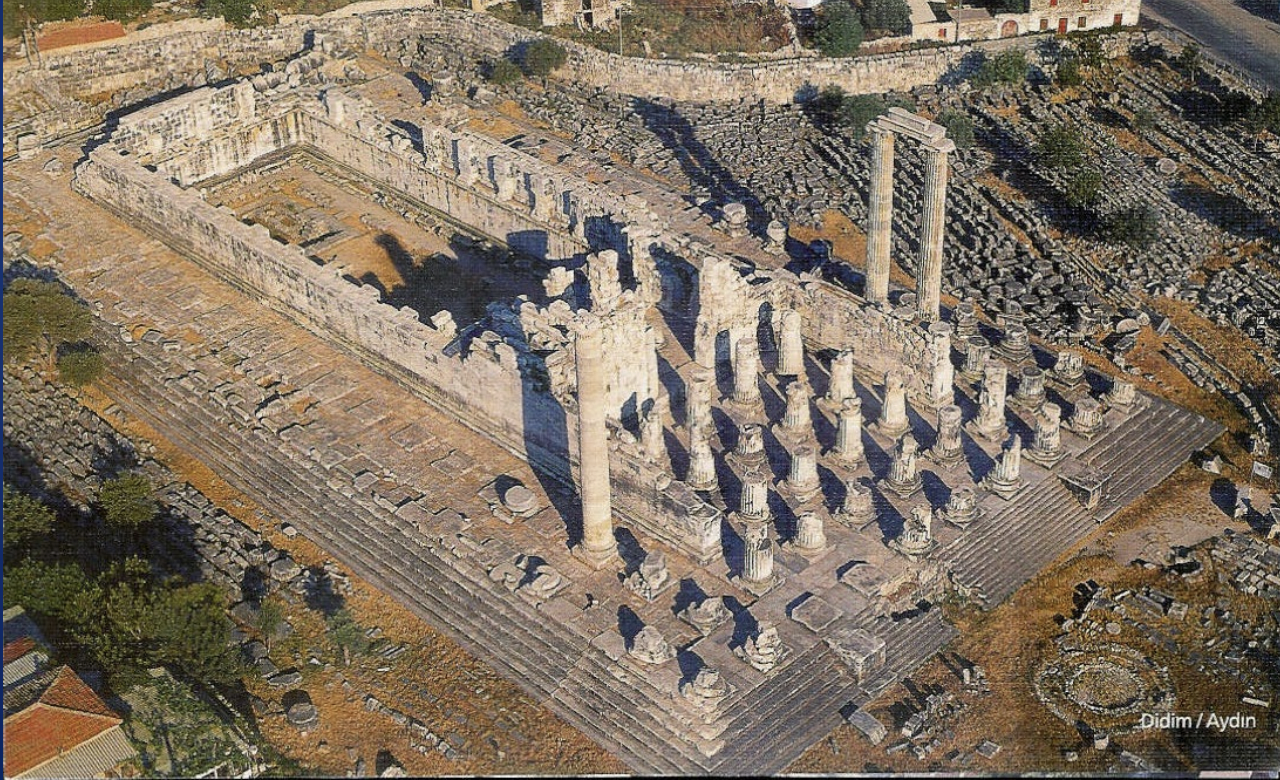

Temple of Apollo at Didyma, 330 BCE-130 CE
-displays hellenistic taste for dramatic manipulation of interior in unexpected ways
-plays on assumption on what temple should look like
-playing especially w cella
-from outside looks like an Ionic temple GIANT 360×160ft
-forest of columns on the outside, dipteral, 10×21 columns
-platform has 7 steps on all sides, front has 14 smaller steps
-under construciton constantly, COLUMNS DIFFERENT FROM EACHOTHER OR UNFINISHED
-back of pronaos- has a back door and the entrance to the cella is not there
pronaos has a raised treshhold 5 ft, would be the seciton where oracle responses are read
-said to be a oracular temple between apollo and zues
-OPEN AIR COURTYARD
-woshipper would write questions on lead and give to male priest which would ask oracle and then read oracle response
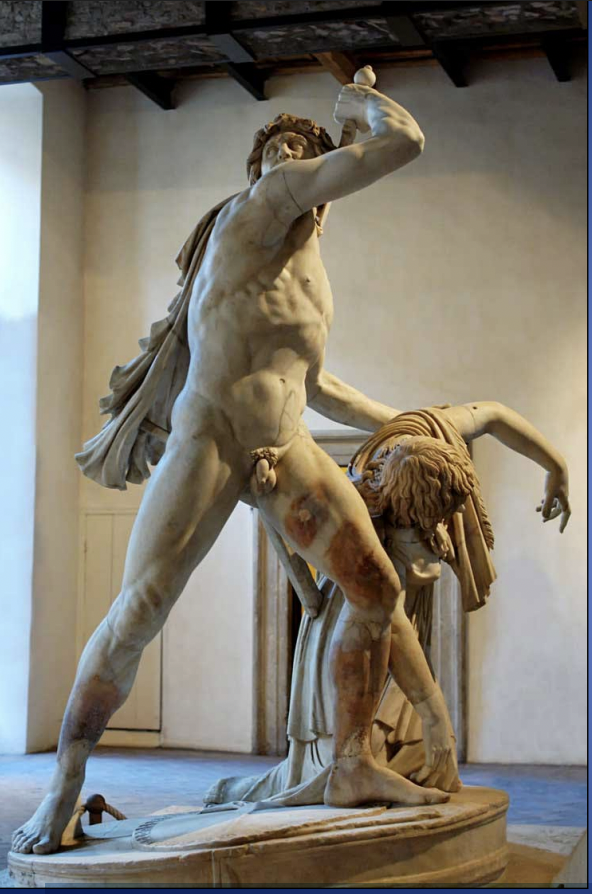

Gaul Killing Himself (Roman marble copy of the Hellenistic bronze original from the Pergamene Victory Monument, 220s BCE
-conveys pathos (pity)
-rather than being captured he kills himself and his wife
-extremly dramatic (hellenistic)
-complex grouping with points of view, twisted poses
-emphasis on muscles
-tension between alive and dead body

Great Altar at Pergamon 175-150BCE
-steps are only left on original as in Berlin Museum now
-dates to the reign of Eumenes II, defeat of the gauls
-Altar at the center
-U shaped enclosure with two wings, staircase, ionic collonade, stands on high base, decorated with sculpture
1.Great Atar- Giganomachy friezes; metaphor for defeat by Greeks of barbanism
of Giant Athena, Earth and Nike
-Athena wears a peplos and is holding up the Giant to kill it
-composition is crowded, diagolons, poses give movement, dramatic
-facees show agonized expressions, achieved with open mouth, deep set eyes, wrinkled skin
-Poses form a sort of X as they try to move
“Baroque” (dramatic) Style with elemets of High Classical Athens
-2. Zeus githing the Great Prophyion
-zeus frontal, giant frontal, zeus eagle also fighting giants, adaptation of poseidon on parthenon
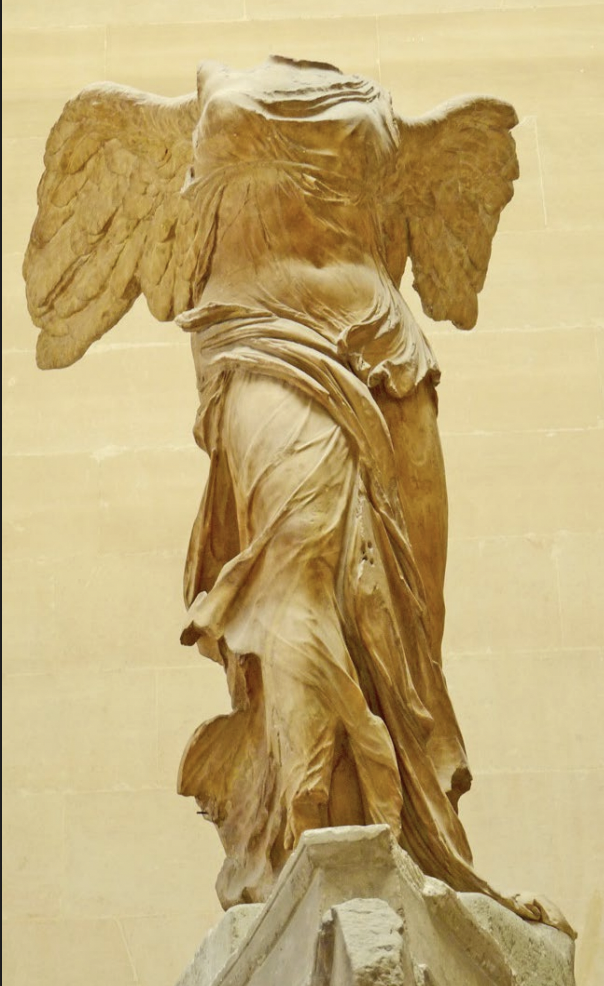

Nike of Samothrace, Sanctuary of the Great Gods, ca. 180 BCE, marble, H 8’ 1
-original greek statue
-commemorative of naval victory
-landing on the prow of a ship
-looks back to classical predecessors, much more dramatic and more theatrical
-shown just as landing, still in air, ship made of dark gray marble she is light marble
-shift set in reflecting pool of water with basic of boulders
-as nike is landing on shore, unknown fully if this is the interpretation