Wildlife Management Exam 3 - Population Dynamics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Why is it necessary for wildlife biologists to understand population dynamics for effective management?
identify when issues (population declines) occur so adaptive management can happen
Identify when success (population increase) occurs to justify management practices
Ensure long term viability of wildlife populations
Define population.
group of individuals of the same species in an area where they can interact (birth/death rates, abundances, and age structures are relevant)
Define population growth rate, open population, closed population
how number of individuals in population changes (increase/decrease/no change) through time
open population: ones where immigration/emegration occurs (what actually happens in life)
closed population: immigration/emigration does not occur (theoretical, only happens when species are in an area that they cannot navigate across/disperse)
used only to estimate populations within a certain time frame (breeding season)
Define carrying capacity.
maximum population size that can be sustained in an area
Define negative feedback.
increase/decrease in one factor causes corresponding decrease/increase in another (stabilizing)
fluctuations in carrying capacity (drop in one causes increase in another to keep carrying capacity stable)
Draw a logistic population growth curve
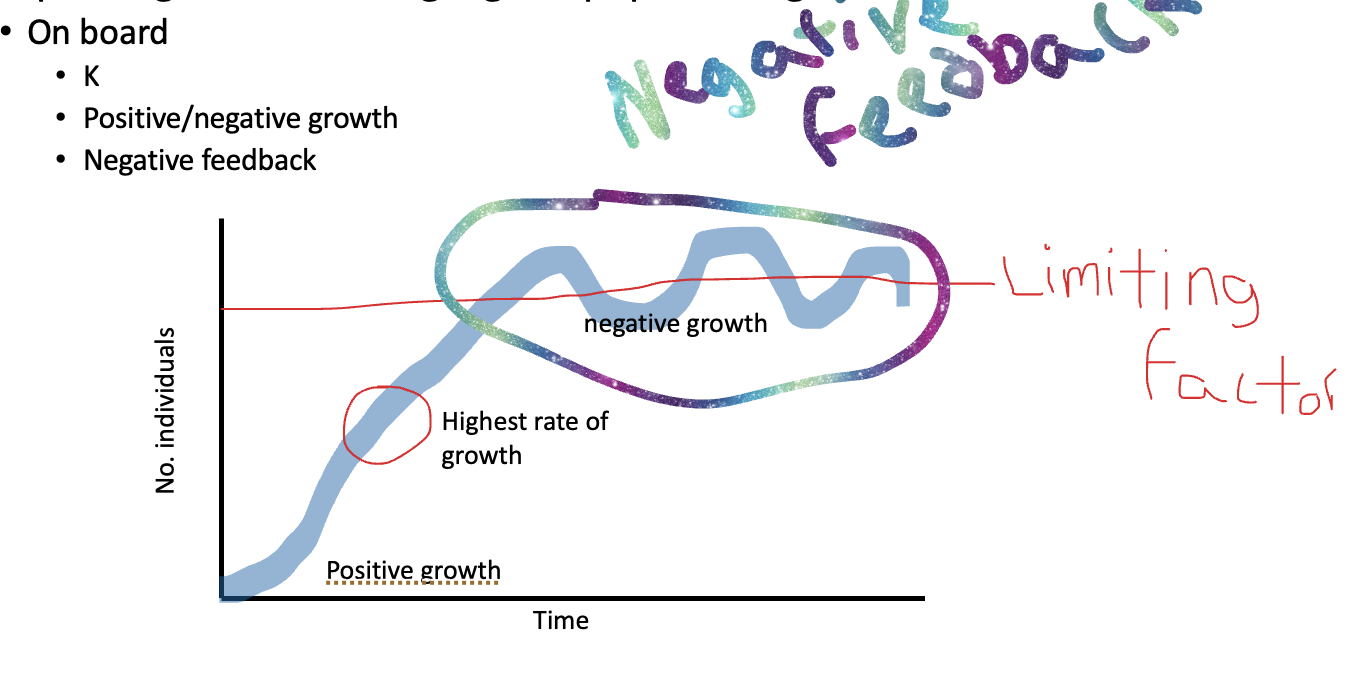
Define limiting factors. Why do you need to identify them?
environmental variables limiting population growth
Ex. food, cover, water, space
need to identify them as otherwise you are putting resources/$$ into a target species, but you will not get the tarted effect of growing the population due to the limiting factors.
Why would high/low oscillations in negative feedback be problematic?
Species could easily go extinct if something were to happen
weather can strongly impact: especially ground nesting birds like turkeys
What are population dynamics driven by?
BIDE parameters:
Births (+)
recruitment: number of new juveniles added to the population (as not all born will survive, this is more accurate)
Immigration (+)
enter population
Deaths (-)
survival rate: 1- mortality rate
Emigration (-)
leave population
*Immigration and emigration are dictated by dispersal (permanent movement from one population to another)
What is the equation to calculate future population size?
Nt+1 = Nt + B + I – D – E
Nt+1 future population size
Nt population size at that time
**Note that if your population census was done every 10 years than your future calculations will be based on 10 year intervals.
What is age structure?
proportion of individuals of certain ages in a population
Ex. 30% 1 yr olds, 40% 2 yr olds, 10% 4 yr olds
Higher survival for adults than fawns
What facilitates estimation of abundance and density?
vital rates
Define abundance and density.
Abundance: number of individuals in a population
Density: abundance per unit area
gives us a standard comparison to make (ex. between years, different sites) (allows you to scale observation to a common amount of space)
What is the equation for population growth rate?
population growth rate = changes in abundance or density through time
What is the geometric growth rate or discrete growth rate? What about the exponential growth rate or instantaneous per capita growth rate?
Geometric growth rate/discrete growth rate
λ = Nt+1 / Nt where t = time (e.g., a given year)
Exponential growth rate/instantaneous per capital growth rate
λ = er where e = 2.718 or r = ln(λ) where ln = natural logarithm
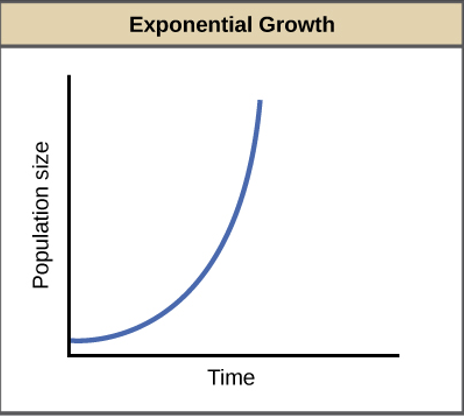
this is key to understanding population dynamics (J shaped curve)
Lamda vs r
Lambda:
easier to understand
good when communicating with mangers/general public
discrete time steps not realistic (populations change in a continuous basis, not these descrete steps)
<1 decrease, >1 population increase
r
less intuitive by easier to work with mathematically
easy to compare among species
can be averaged across time intervals
negative = decline, positie = increase
good when communicating with researchers/biologists. preferred for population ecologist
Is population growth ever exponential?
No! Except for human population (technology, modern medicine) and some types of bacteria
What is the importance of variation/uncertainty in population dynamics?
process variation: variability in population processes (birth rate, etc.) resulting from nature/management
Two types: natural variation (uncontrollable random events -weather), deterministic factors (associate with management activities to increase/decrease population - ex. trapping predators to increase waterfowl chick survival)
Sample variation/observation error
secretive wildlife, imperfect detection
Equation for projecting population change for single or multiple steps
Single steps:
Nt+1 = Nt λ or Nt+1 = Nt (er)
Multiple steps:
NT = N0 (λT) or NT = N0 (er*T) where N0 = starting abundance and T = number of time steps
What are factors that affect population dynamics which slow/reduce growth
stochastic/random factors: genetics, envirometnal
deterministic factors: habitat, predation, disease
Density dependance: positive or negative (too many inviduals, browse line, etc.)
**these 3 factors create environmental resistance