Biology in Focus Chapters 1-3
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
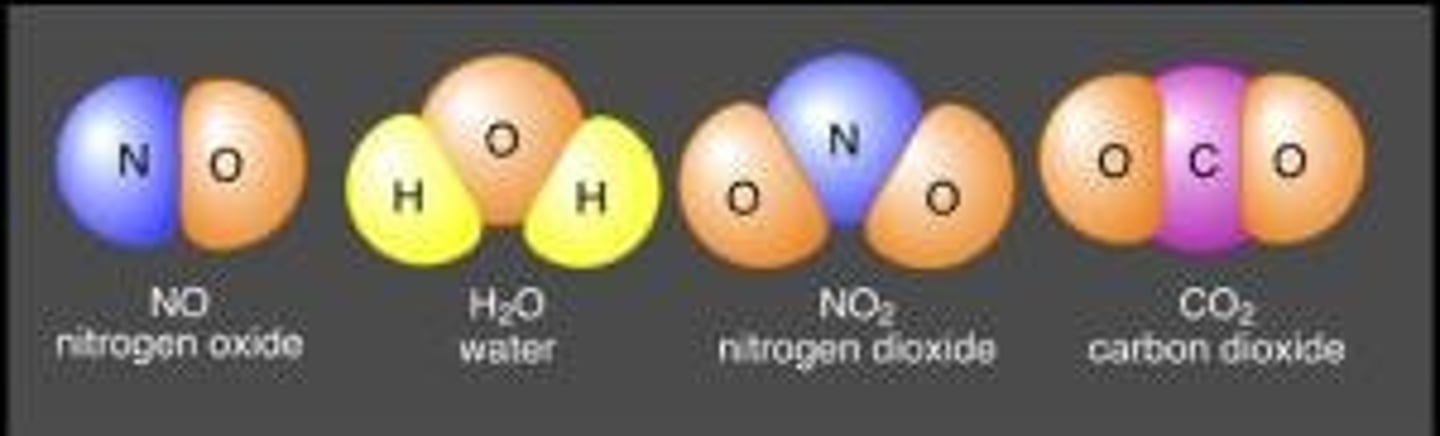
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio
Essential Elements
An element required for an organism to survive
Humans need 25; plants need 17
Trace Elements
required by an organism in only minute quantities
Atom
the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element
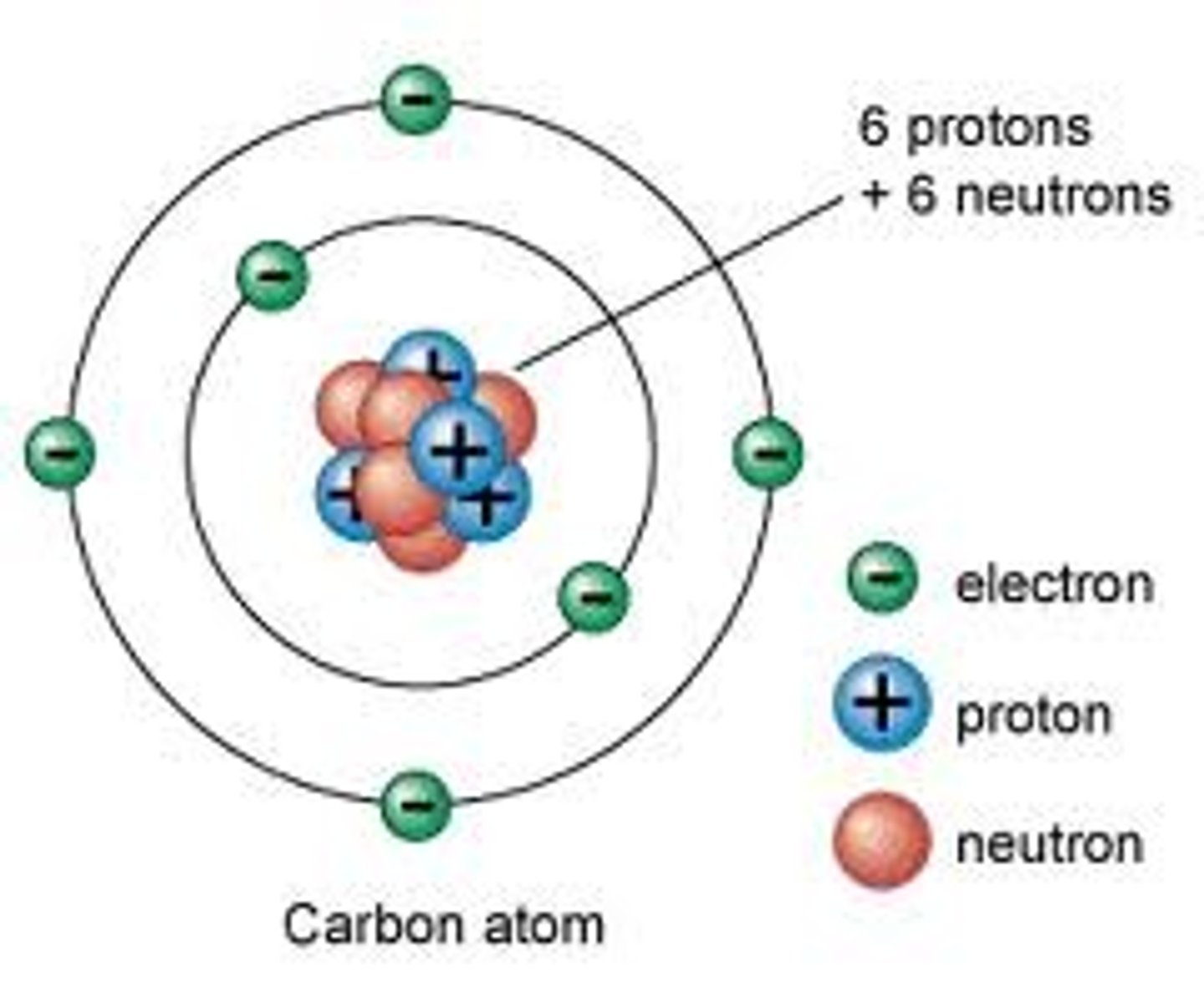
Neutrons, Protons, Electrons
3 Subatomic particles that atoms are made up of
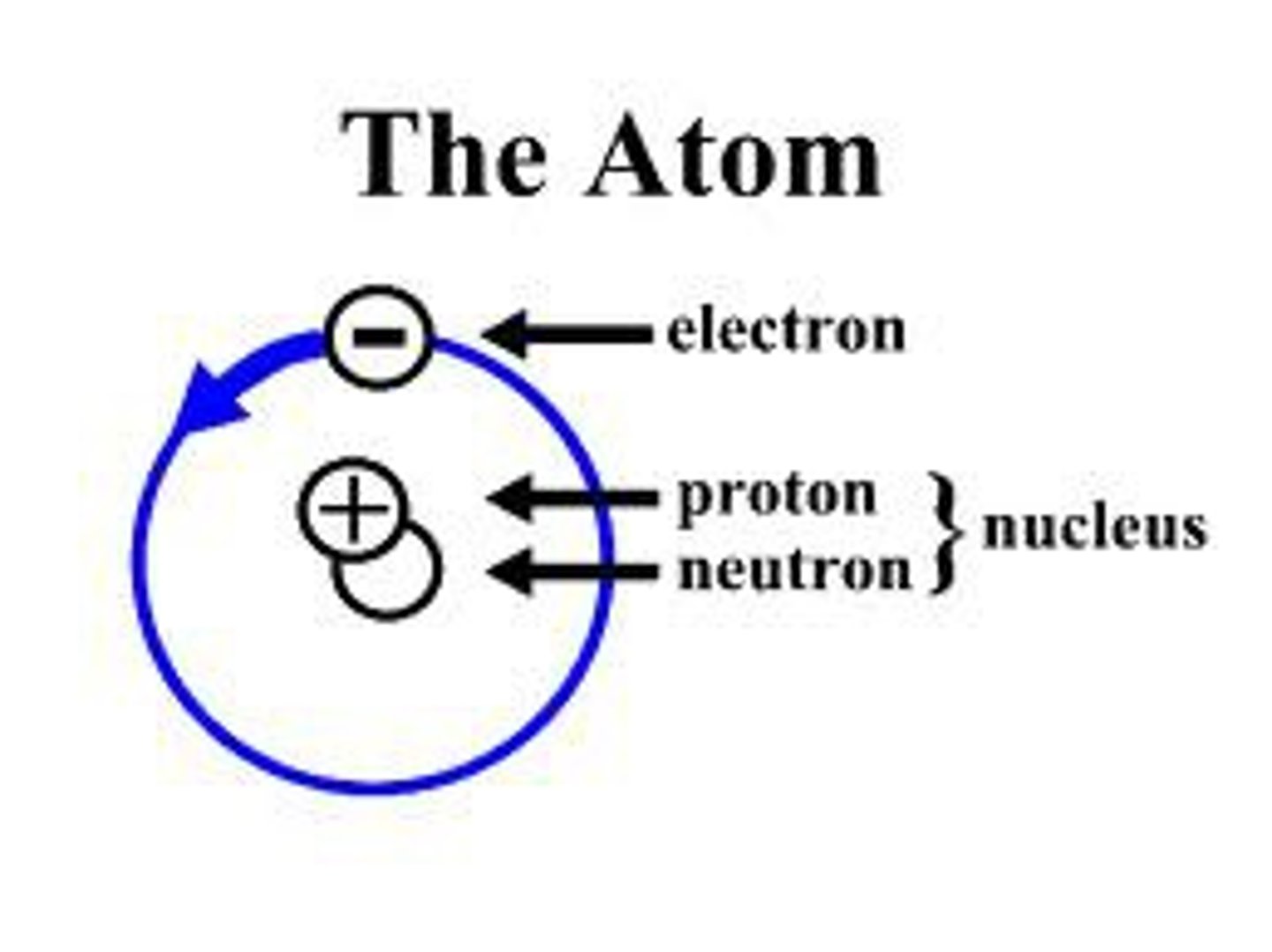
Atomic Nucleus
An atom's central core, containing protons and neutrons
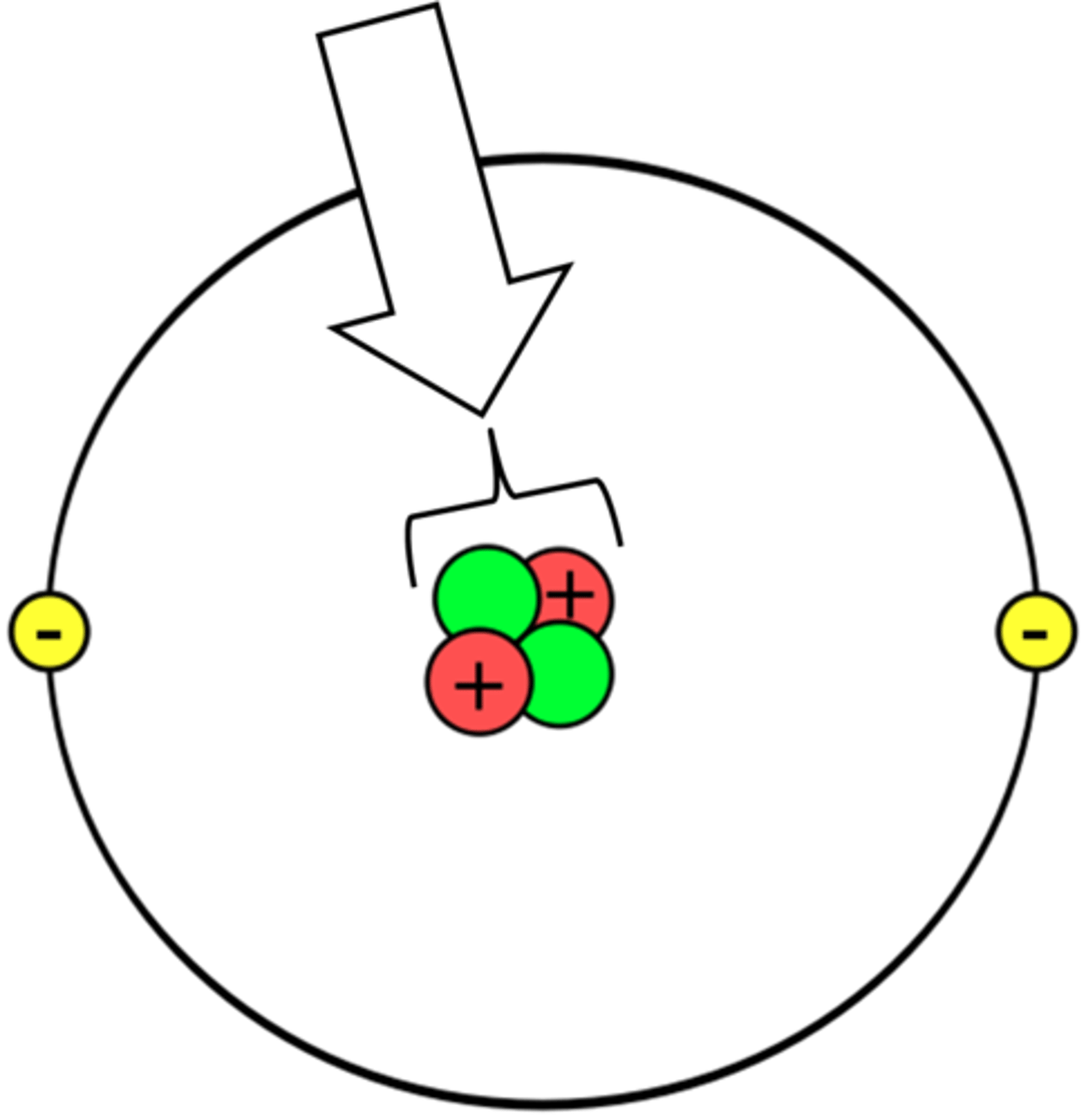
Dalton
A unit of measurement for atoms and subatomic particles
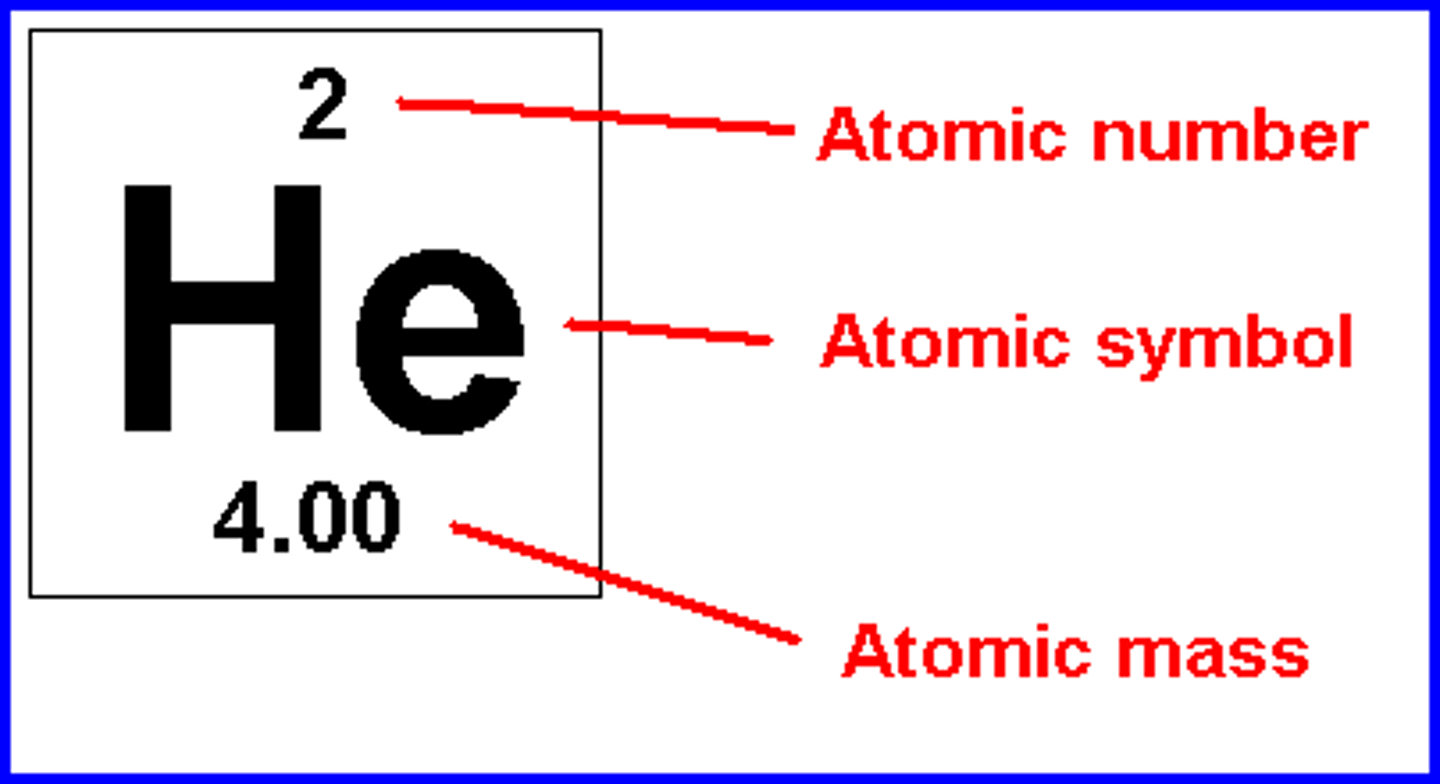
Atomic Number
Number of protons in the nucleus
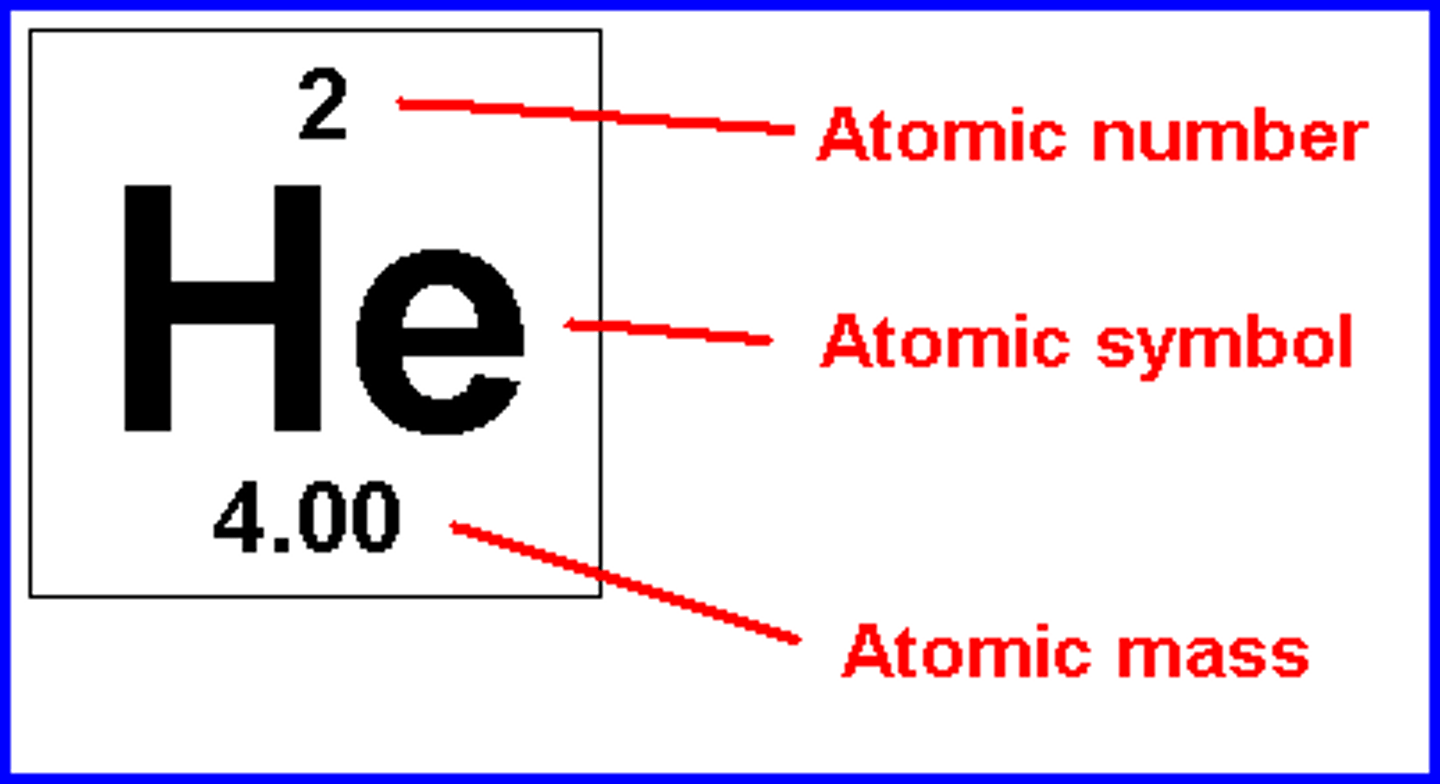
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
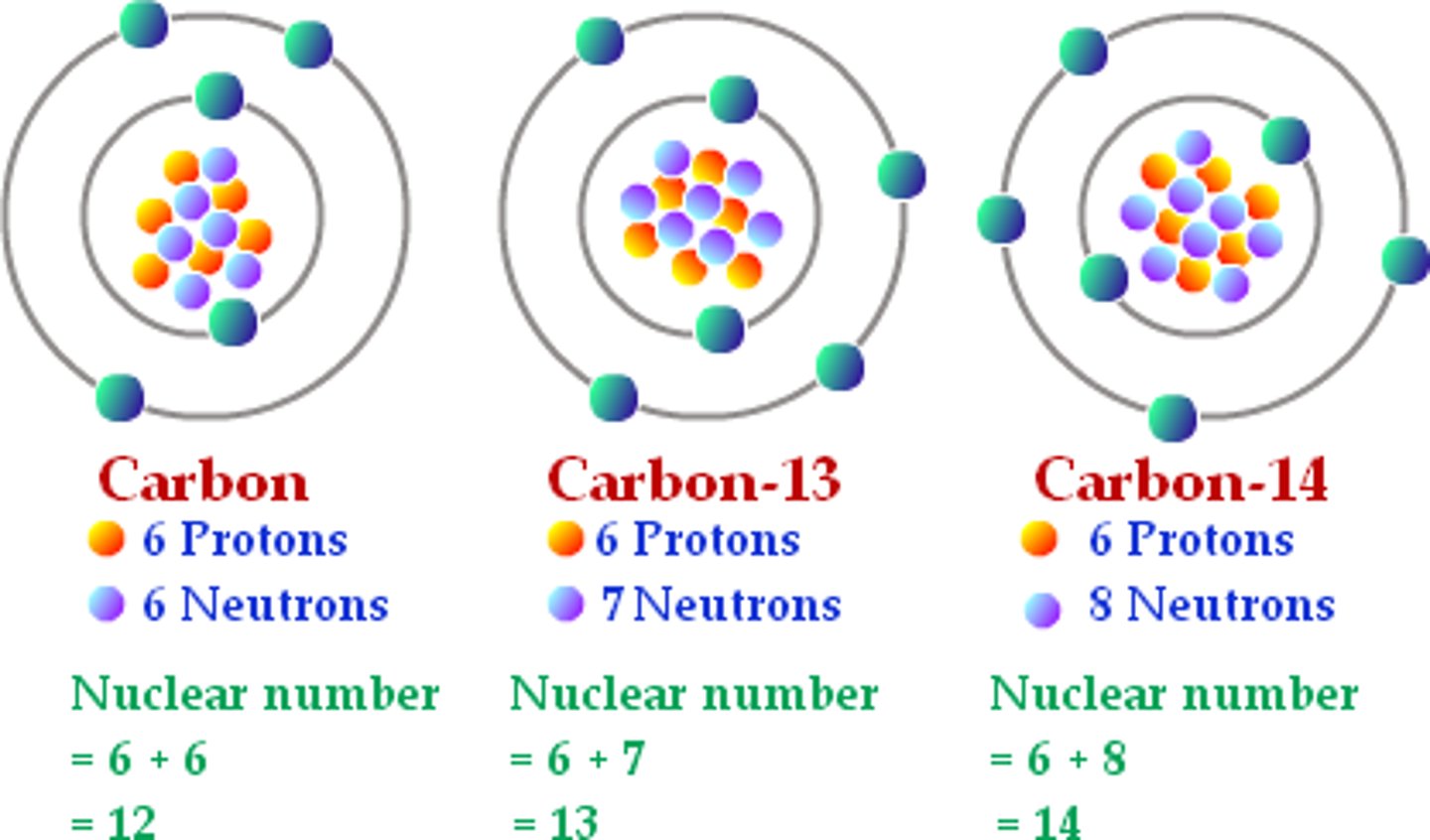
Isotopes
same element, different number of neutrons
Energy
Capacity to cause change

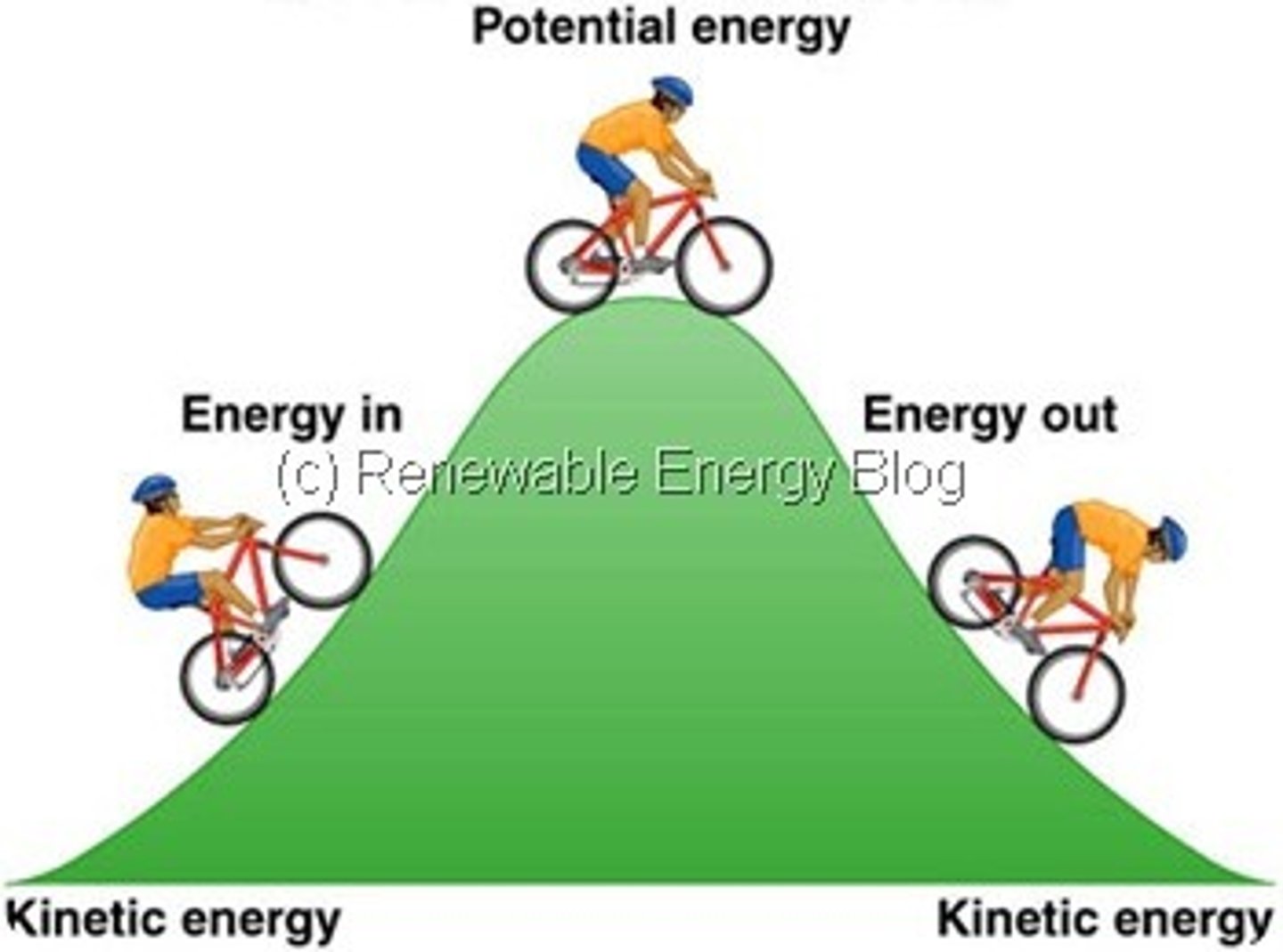
Potential Energy
Stored energy; the energy an object has due to its location or structure
Electron Shells
Depicted as simple circles around nucleus; each shell holds differing numbers of electrons
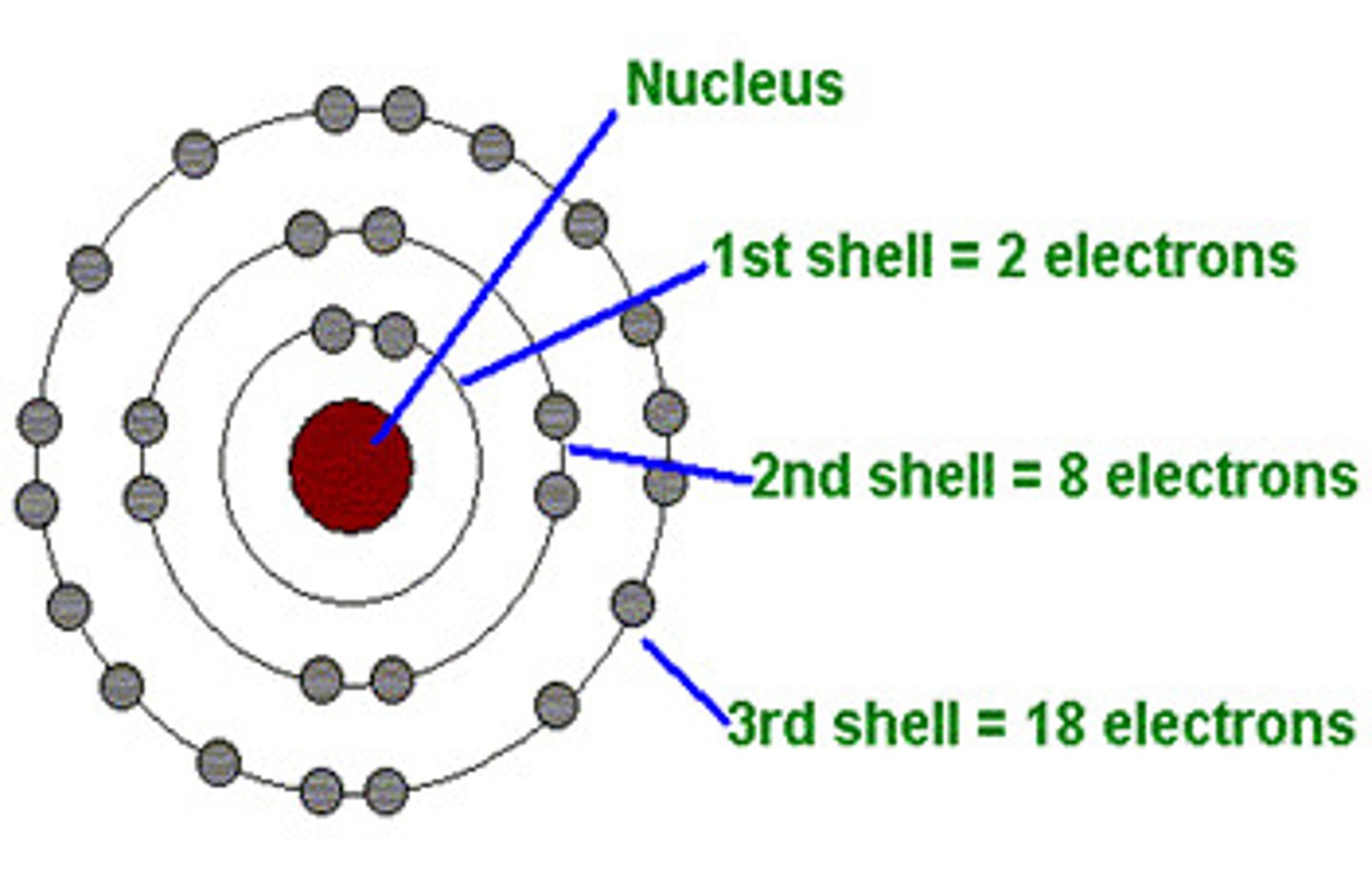
Table of Elements
All elements organized in a table
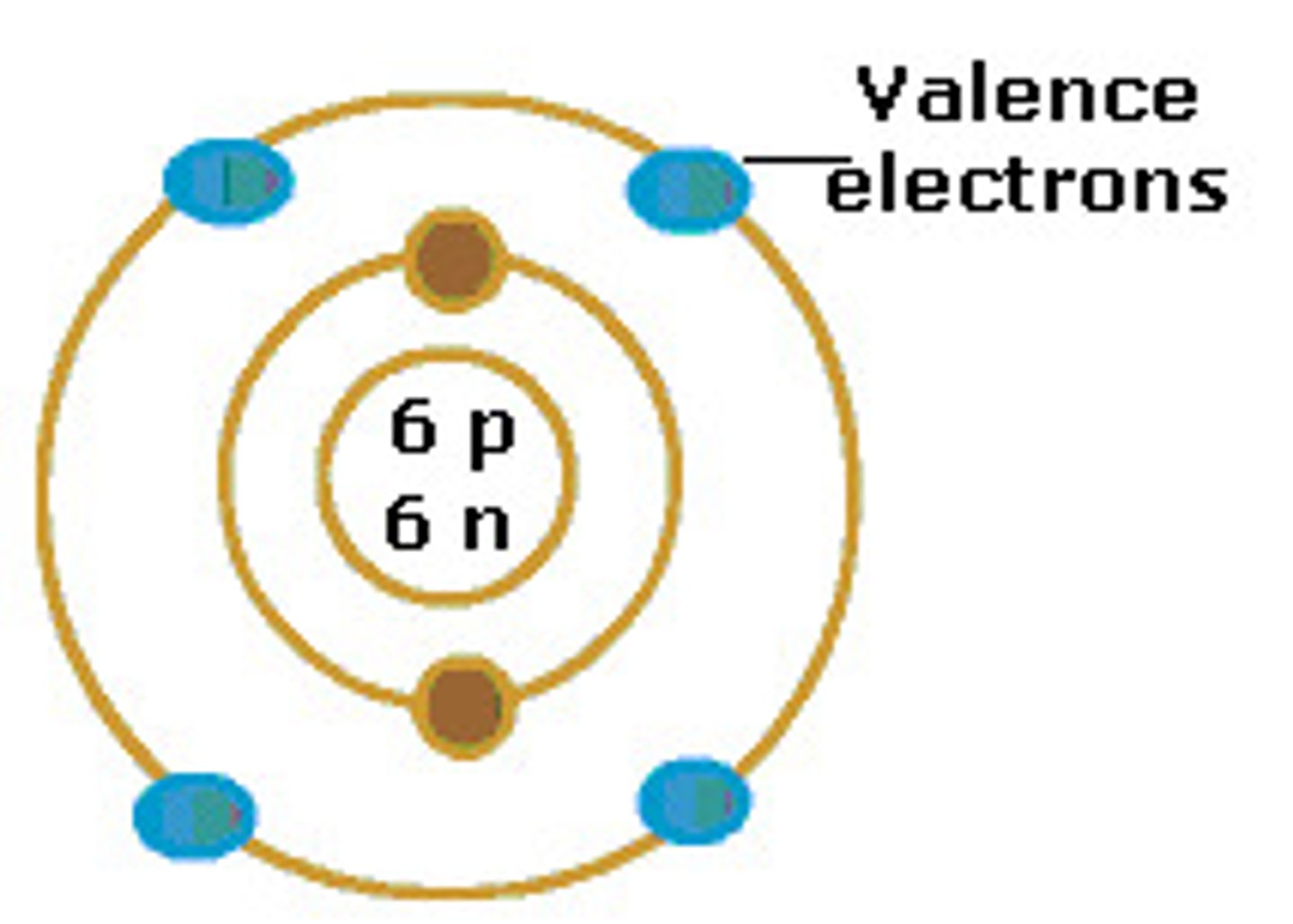
Valence Electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy orbital of an atom
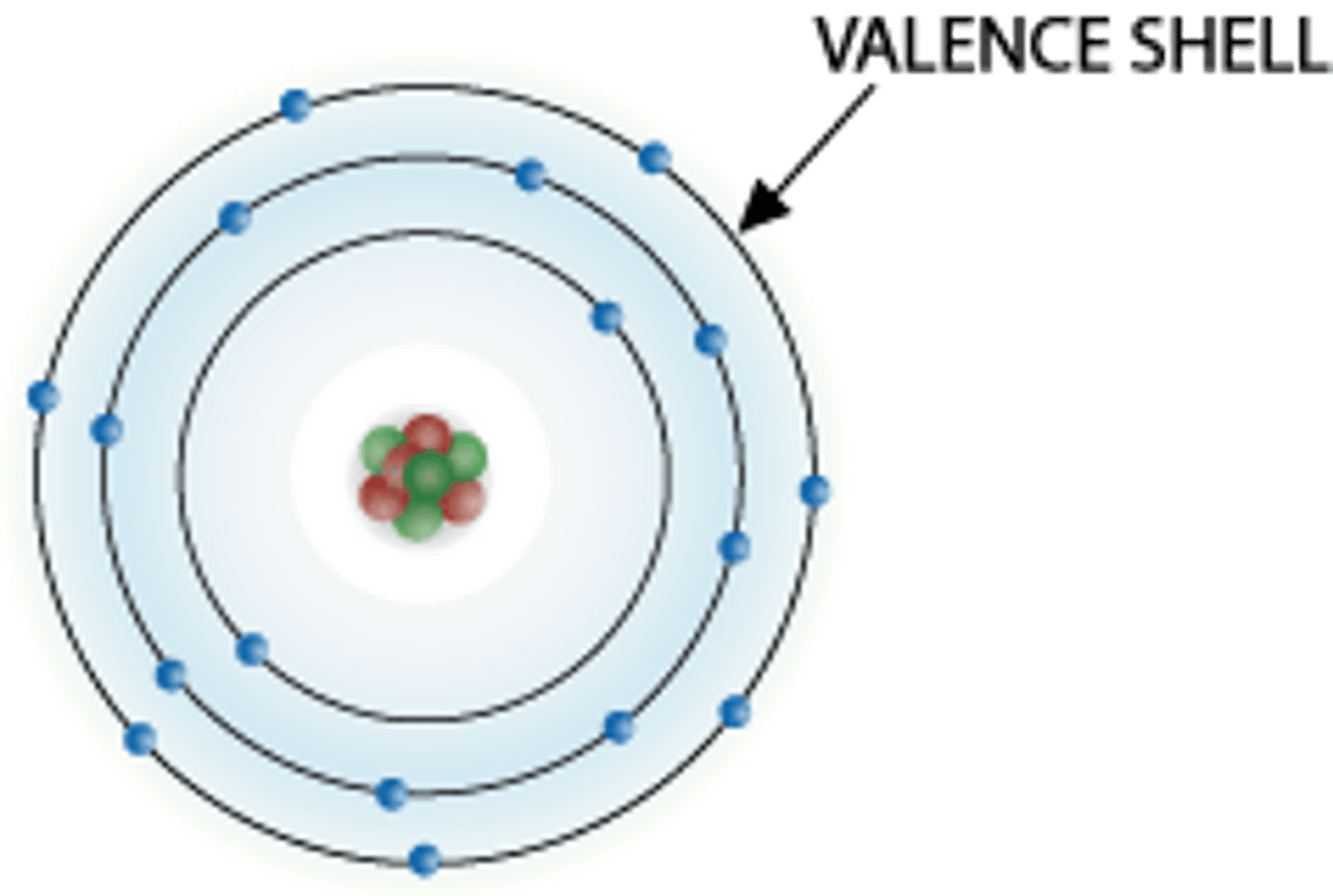
Valence Shell
Outermost electron shell
Inert
Chemically inactive
Chemical Bonds
Attractions that hold atoms together
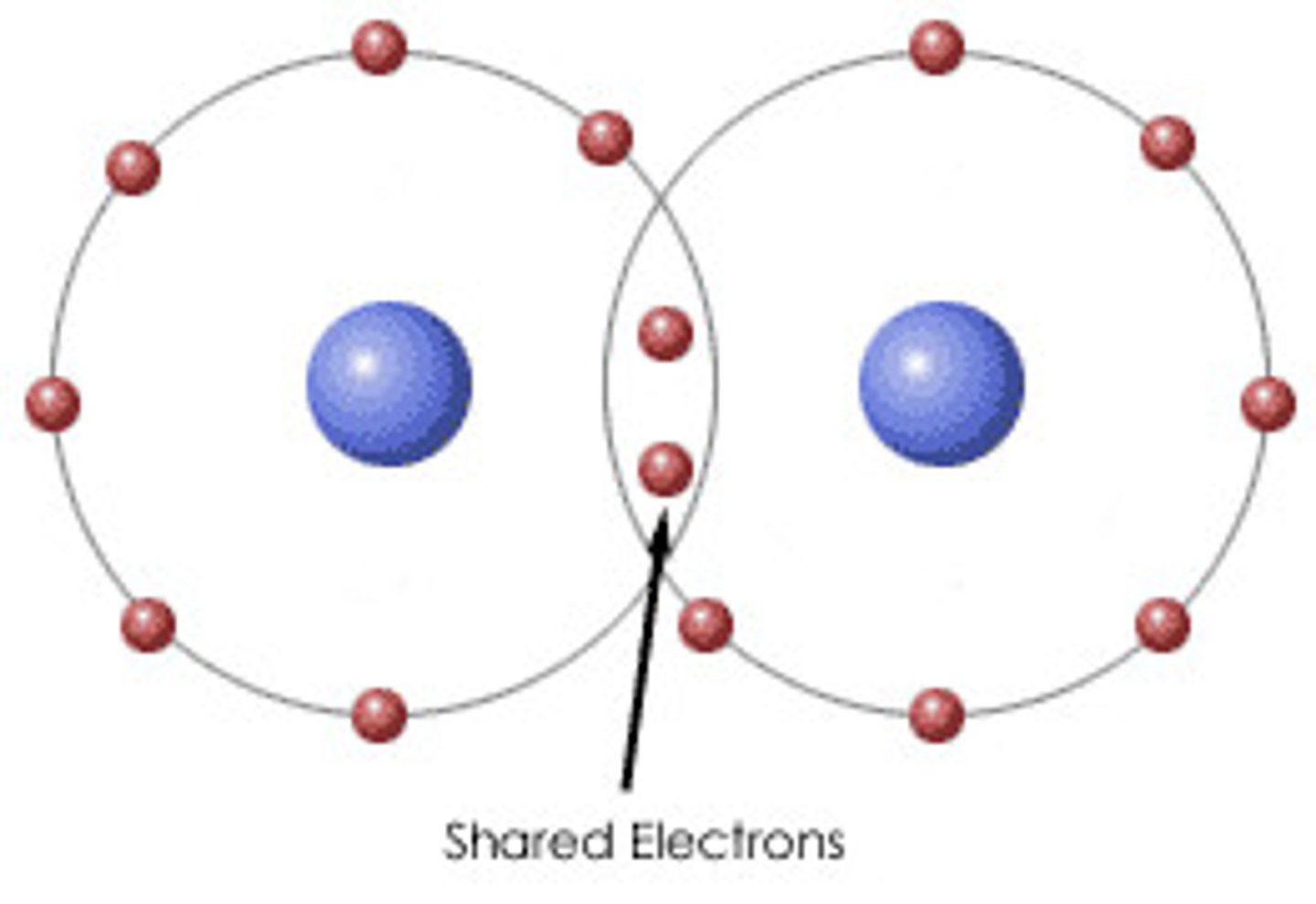
Covalent bond
The sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms
Does not dissolve into water well
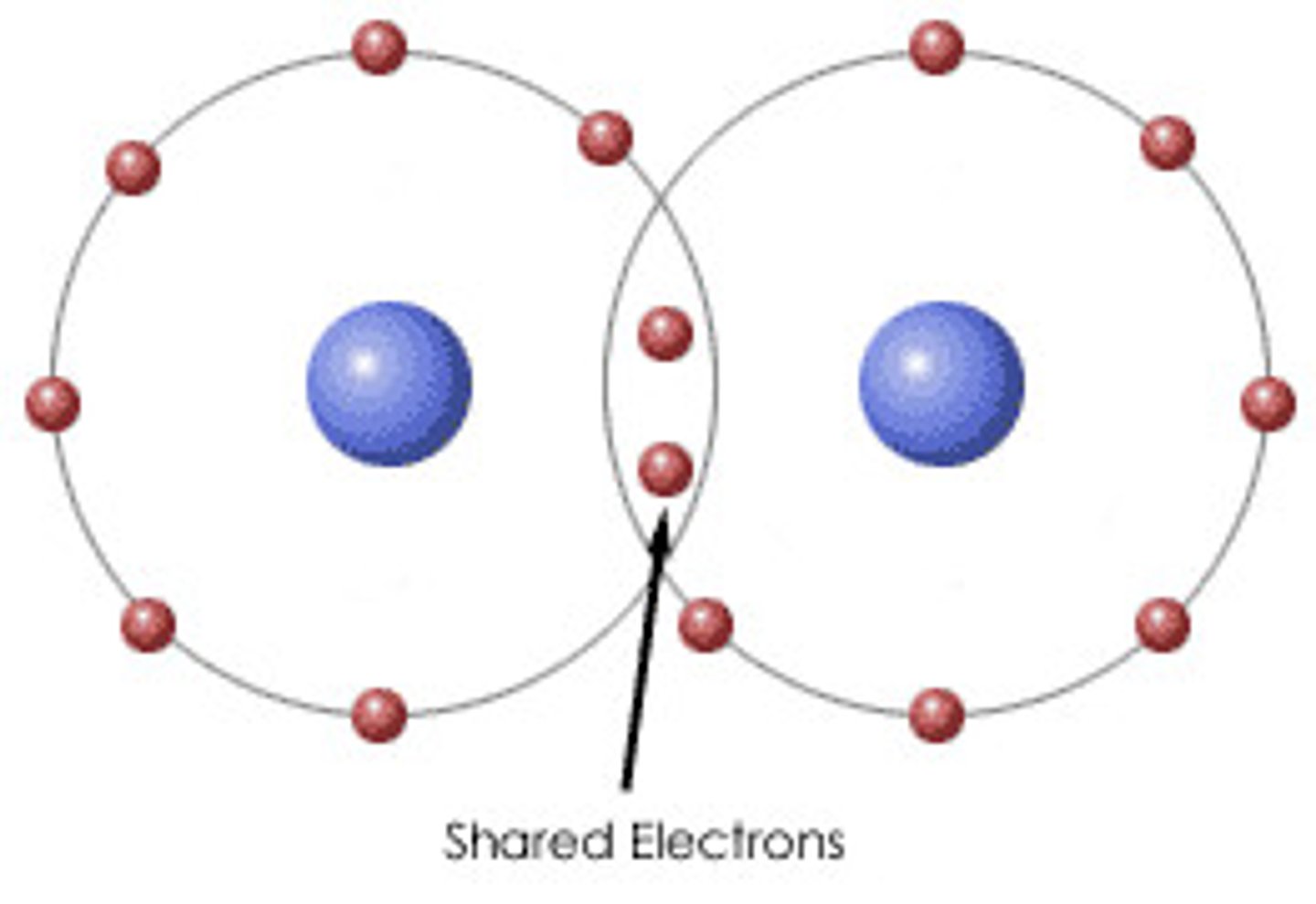
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
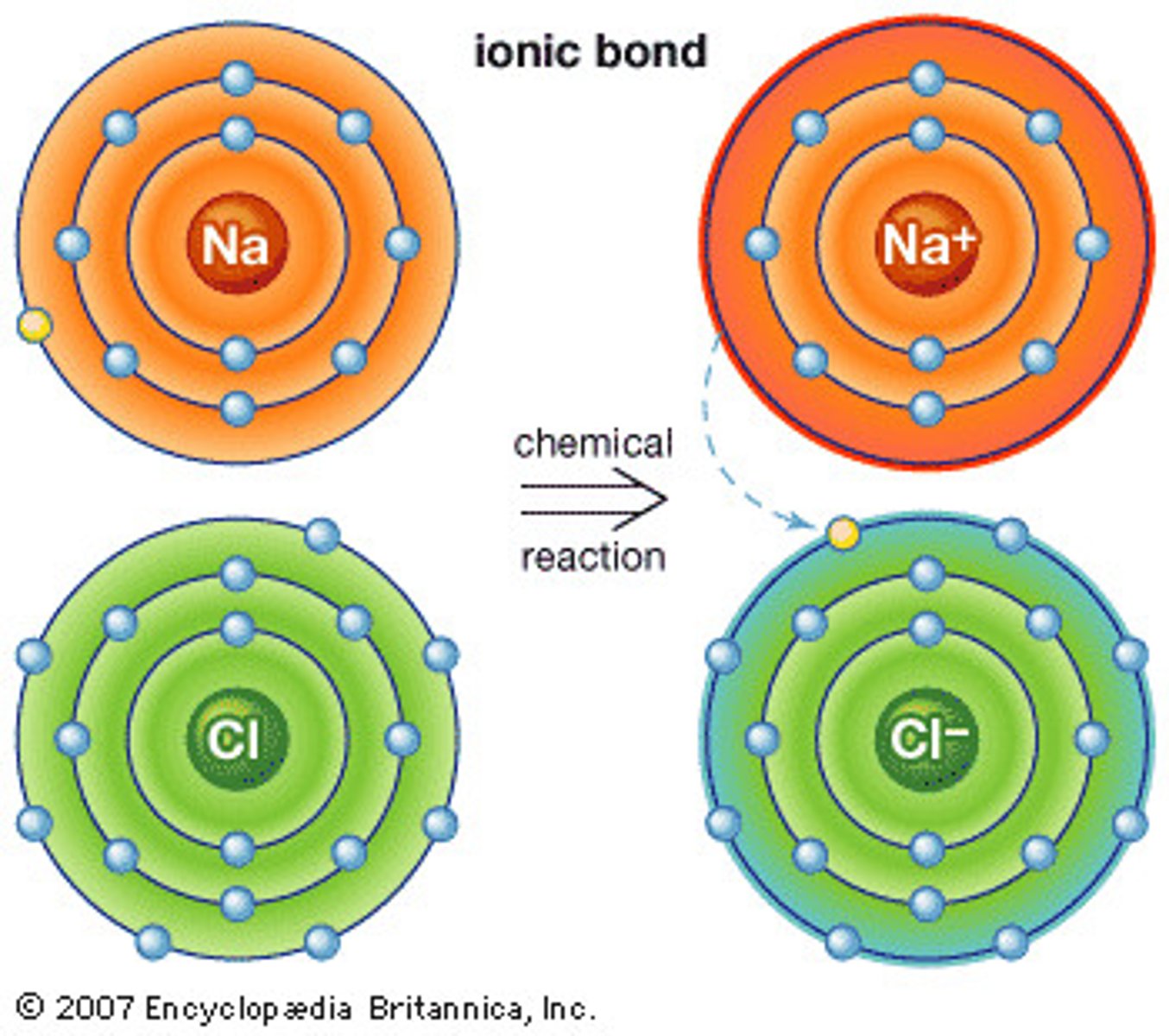
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Easily dissolves in water
Single Bond
2 atoms share a pair of electrons
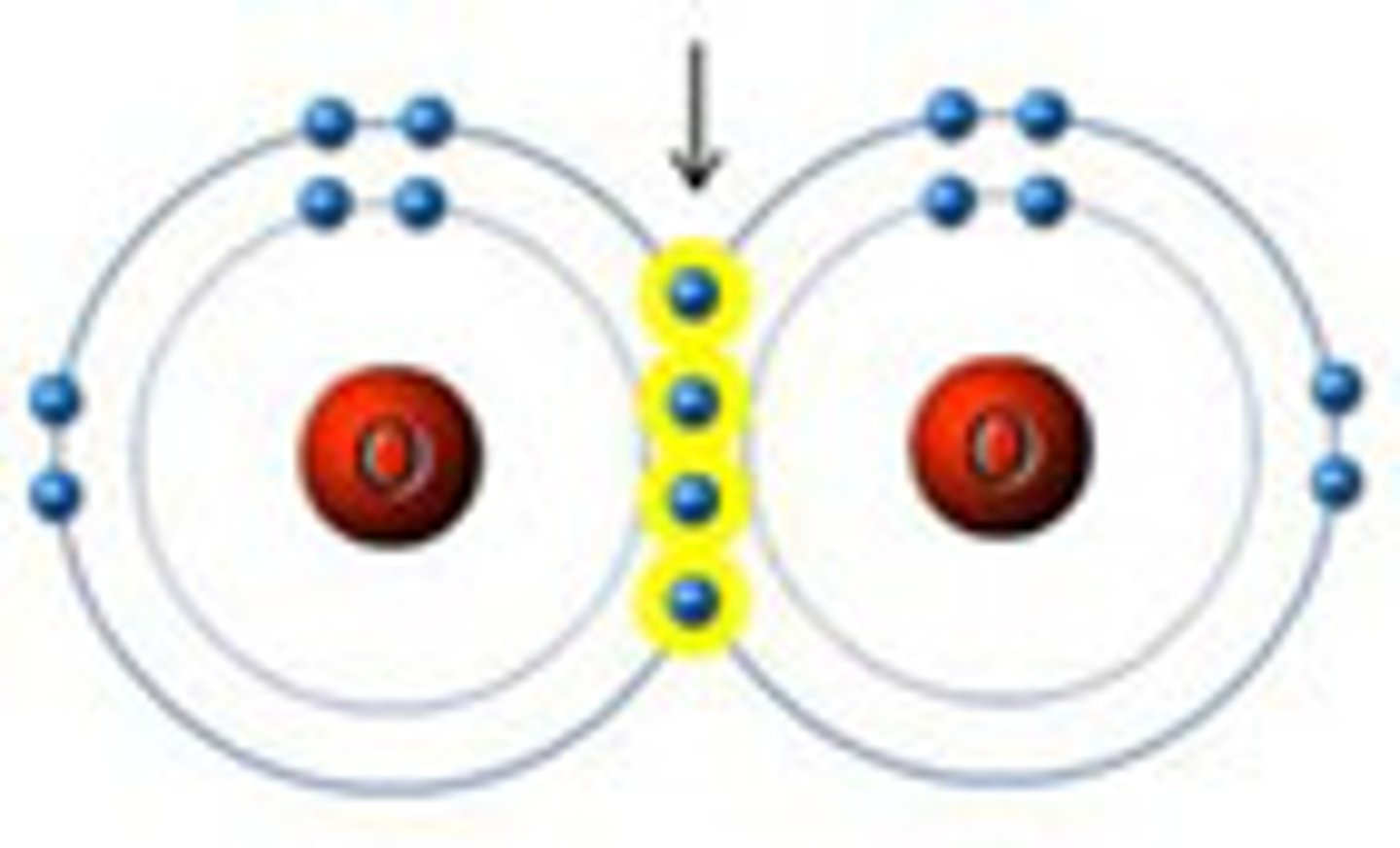
Double Bond
4 electrons are shared
Valence
Bonding capacity of an atom
How many more electrons it can hold in its outer most shell
Electronegativity
Attraction an atom has for electrons
Higher Number = Stronger Attraction
Nonpolar
Electrons are shared equally
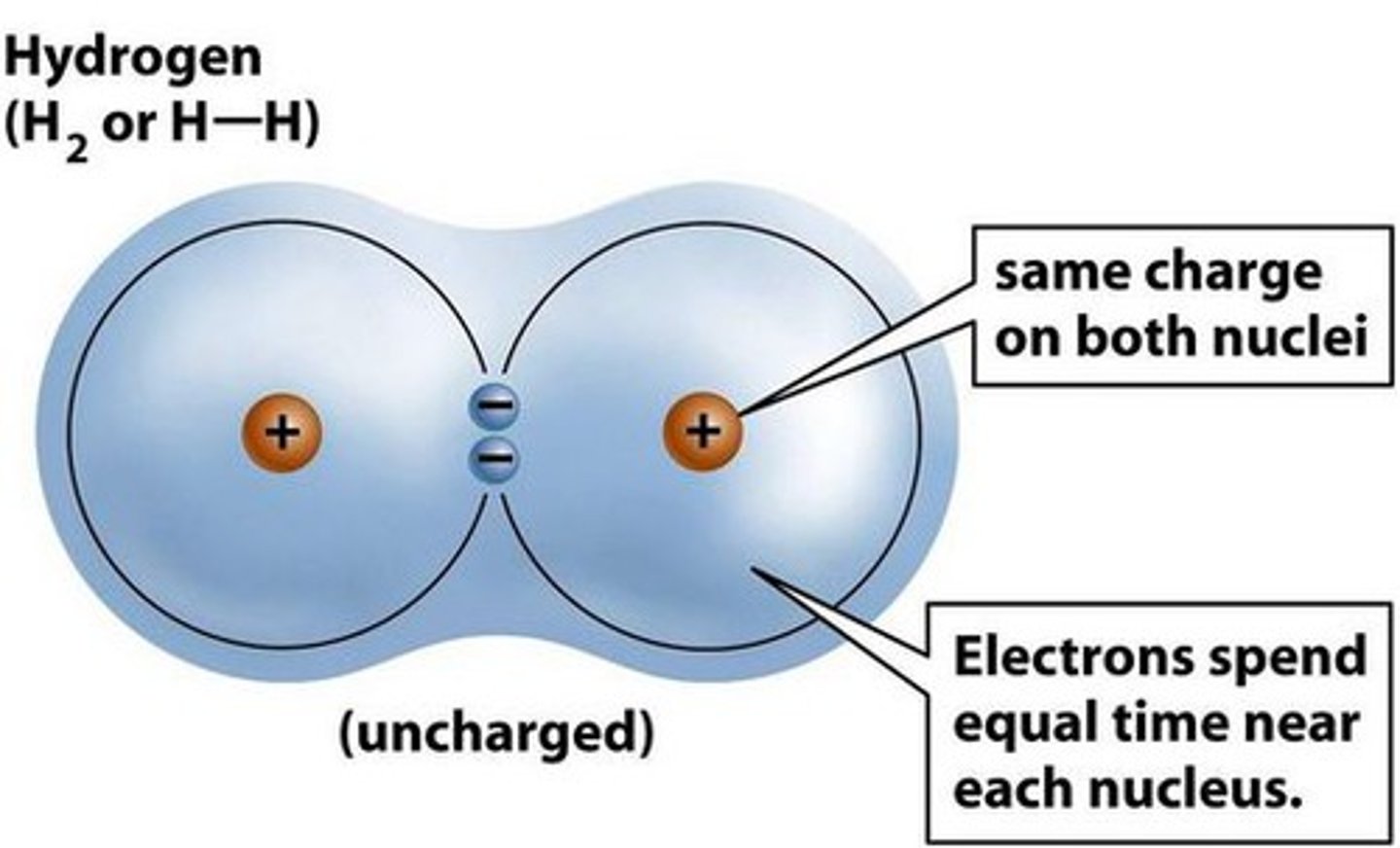
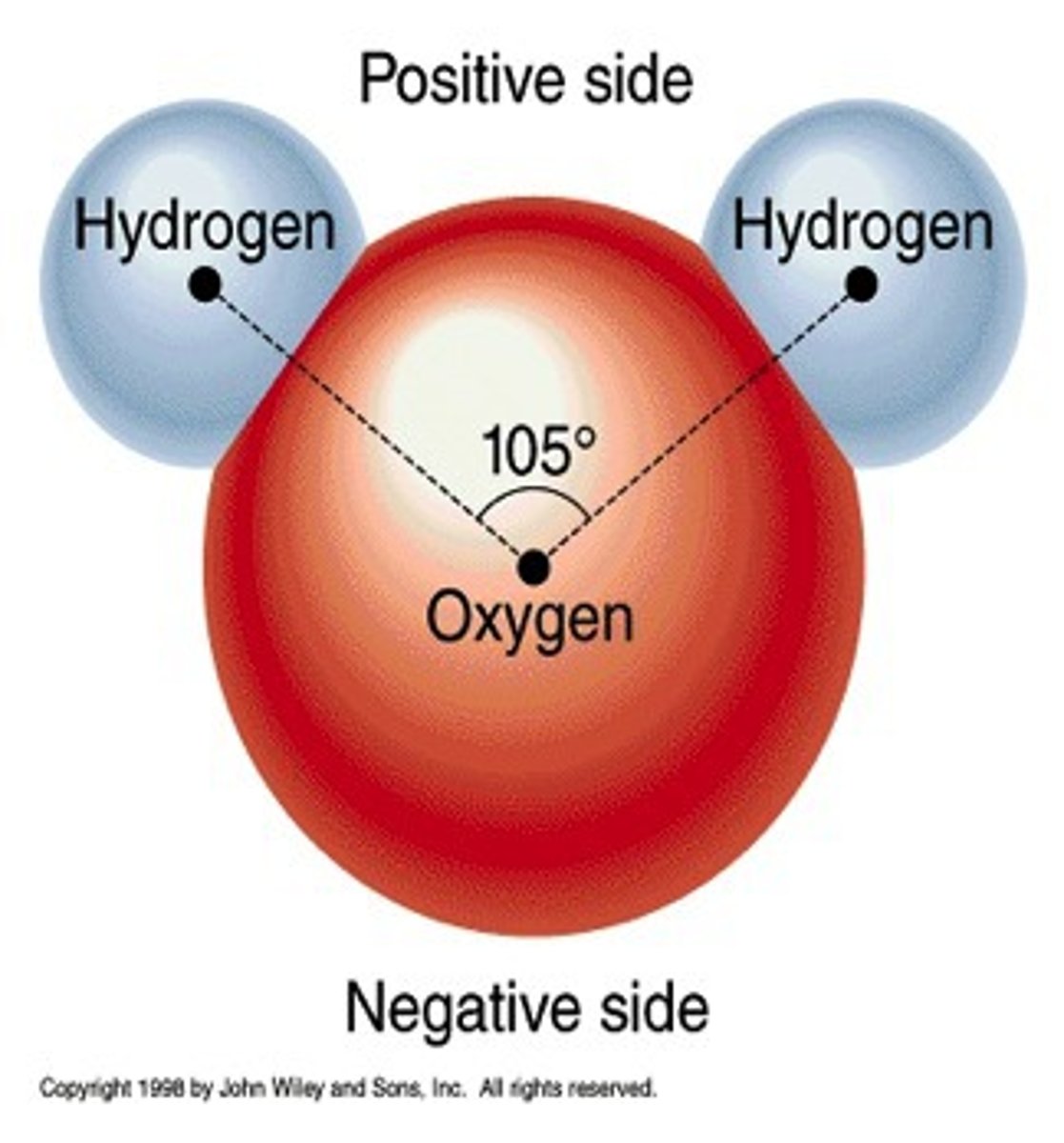
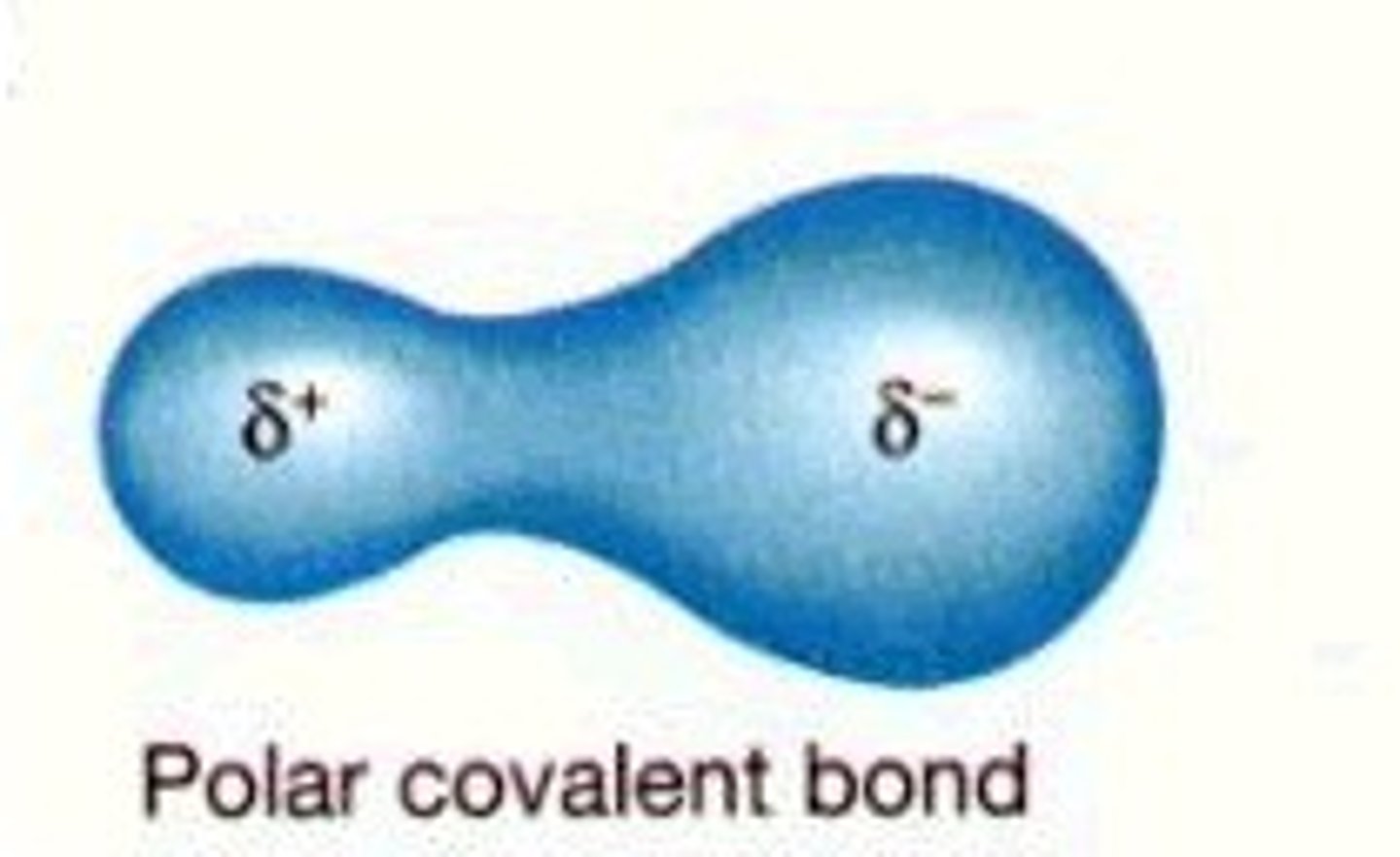
Polar
Electrons are not shared equally
Molecules have a partial negative and partial positive side
Ions
Charged atoms (+ & -)
Cation
Positively charged ion

Anion
Negatively charged ion
Ionic Bond Example
NaCl (Table Salt)
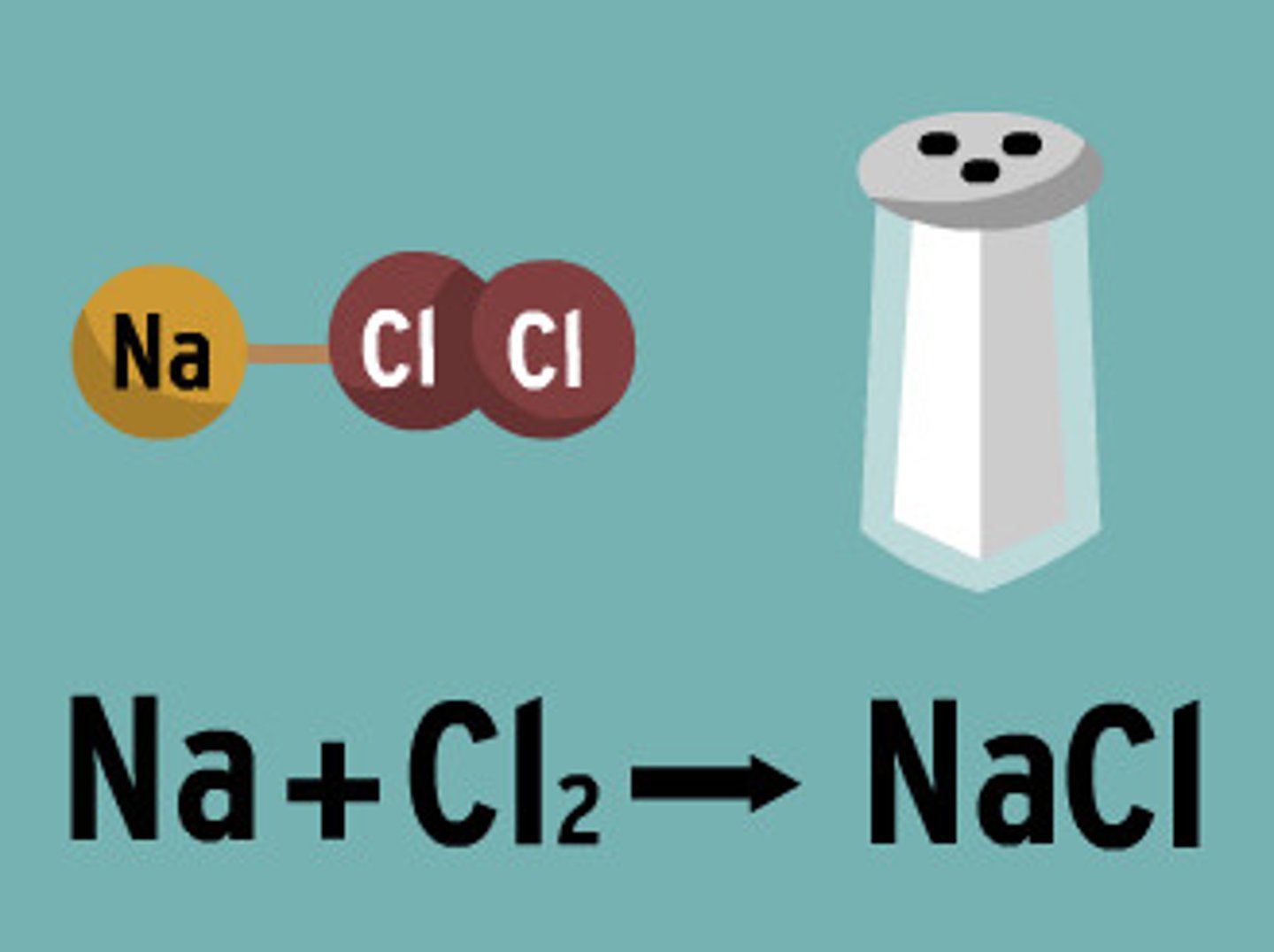
Ionic Compounds (Salts)
Compounds formed by ionic bonds
Hydrogen Bond
The attraction between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge and another atom with a partial negative charge
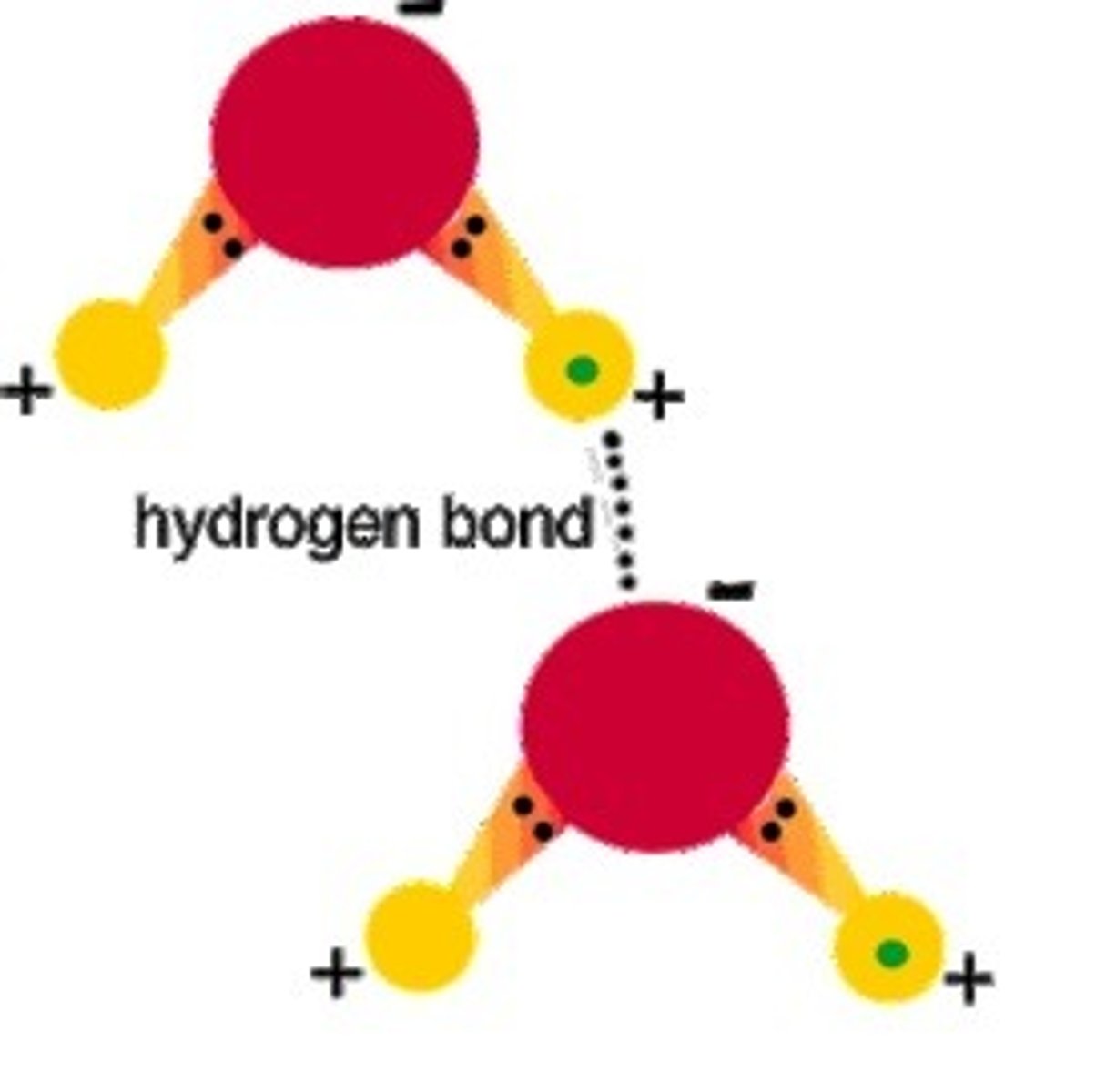
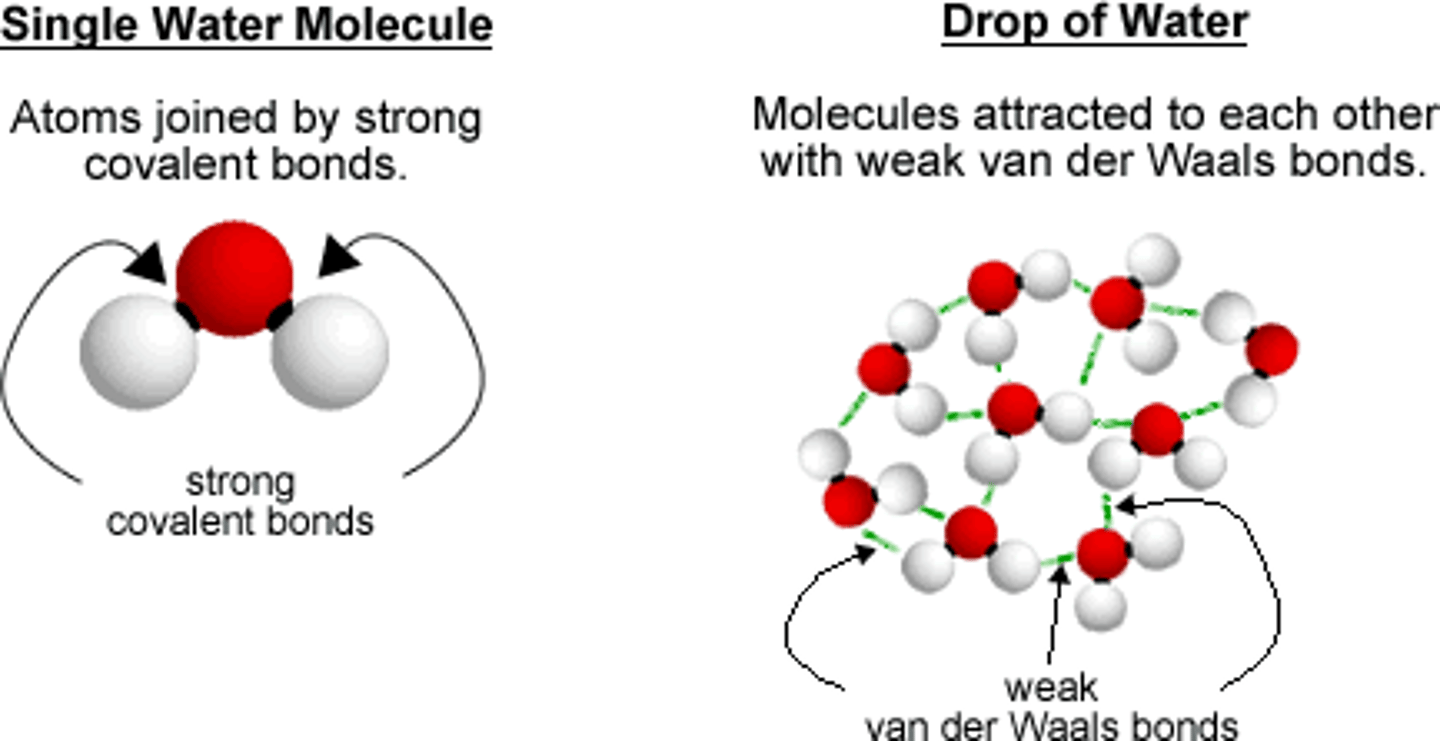
Van Der Waal Forces
Attraction between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules
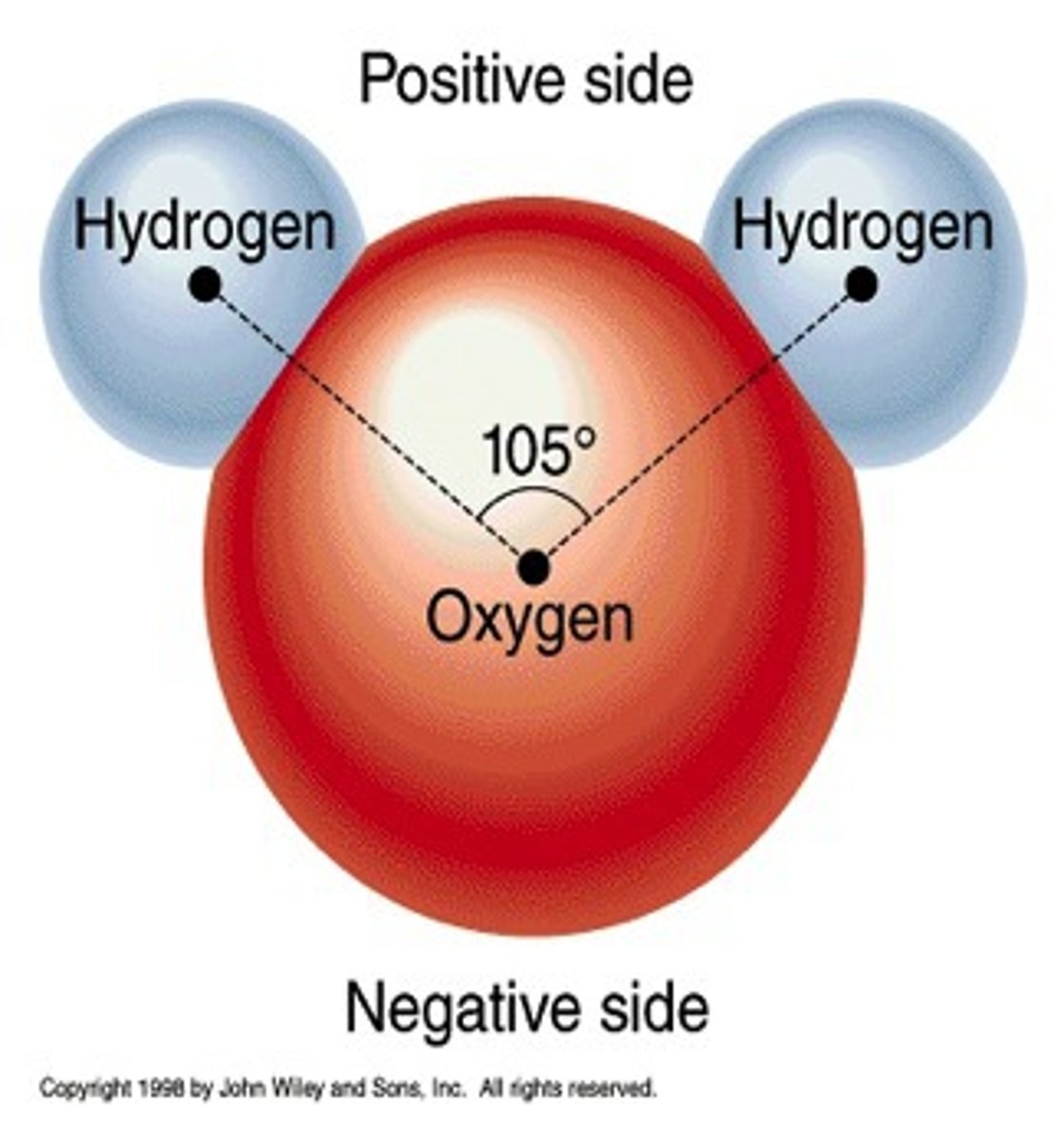
The shape H20 is in
"V"
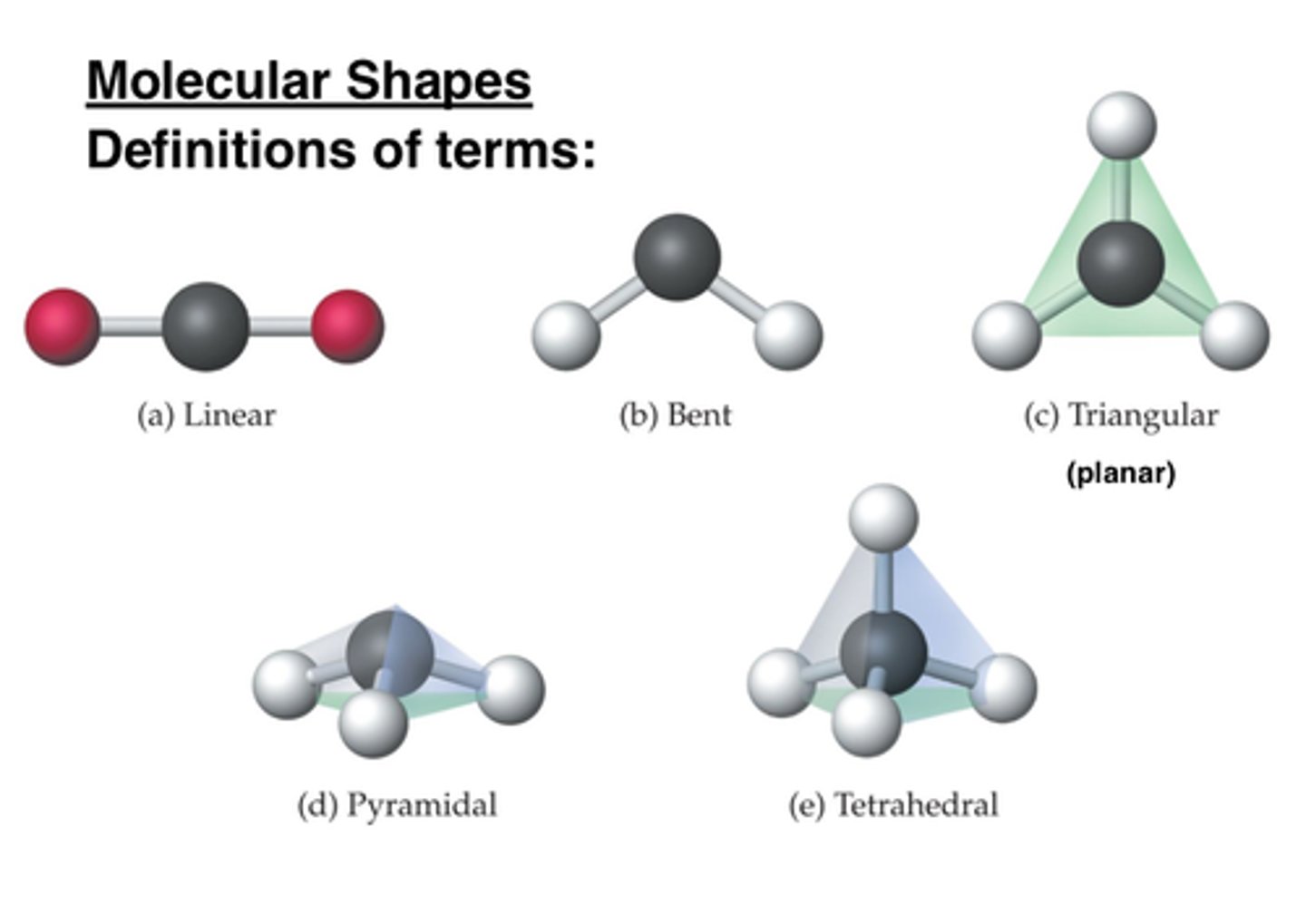
Molecular shape
Determines how biological molecules recognize and respond to one another
Reactants
Starting material in a chemical reaction
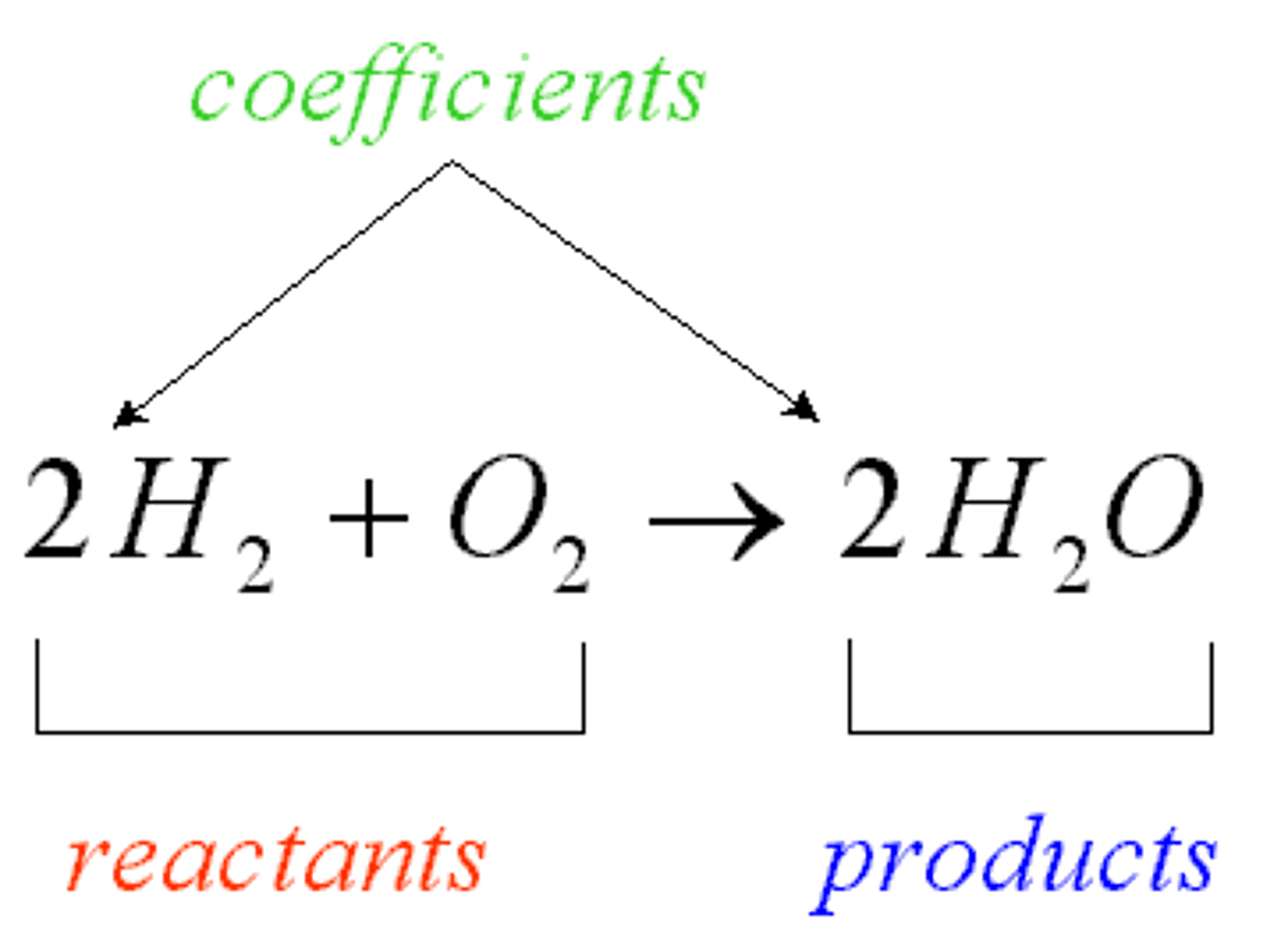
Products
Ending materials in a chemical reaction
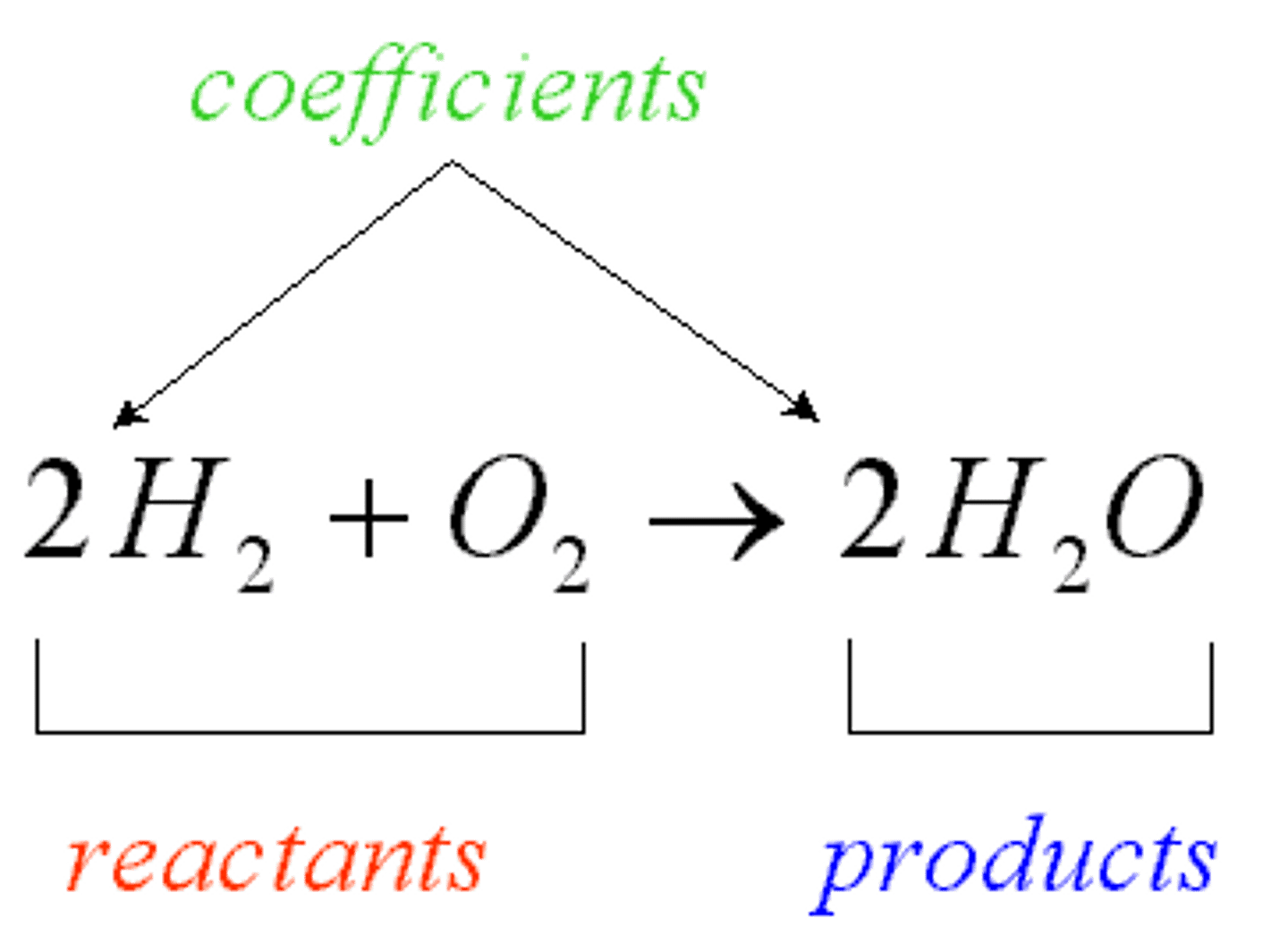
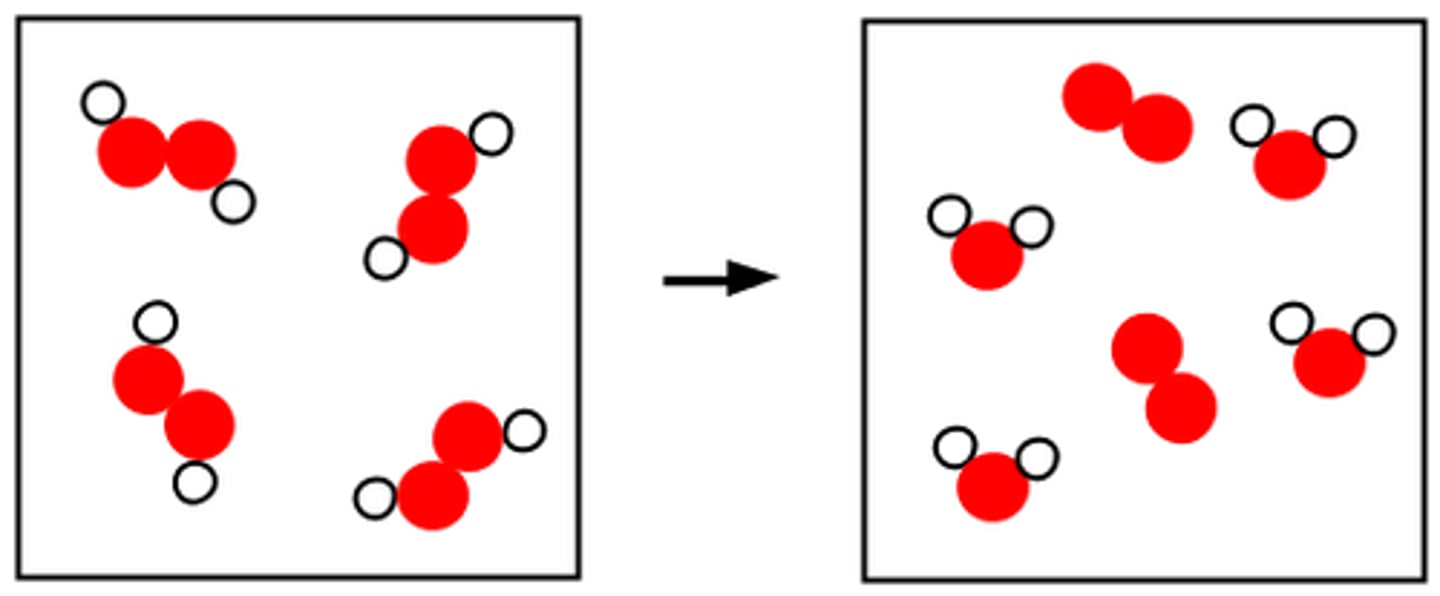
Conservation of Matter
The principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
Reactions can only rearrange atoms
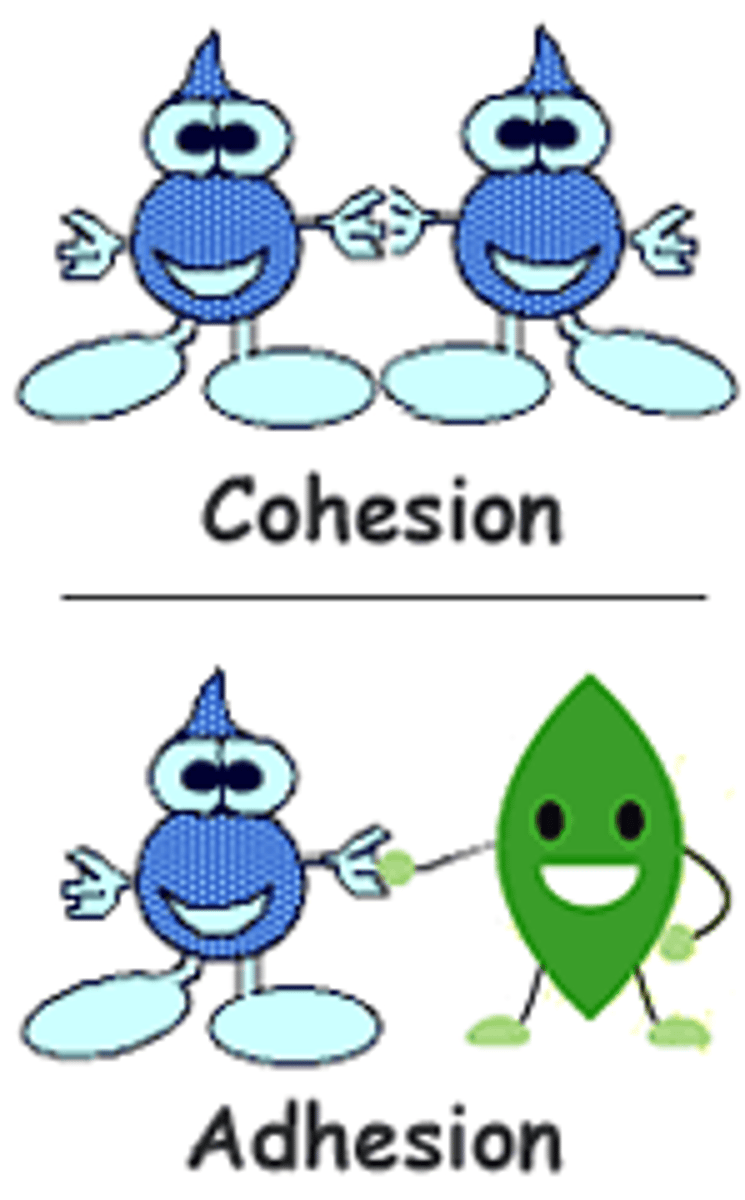
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Aids in the transport of water & nutrients
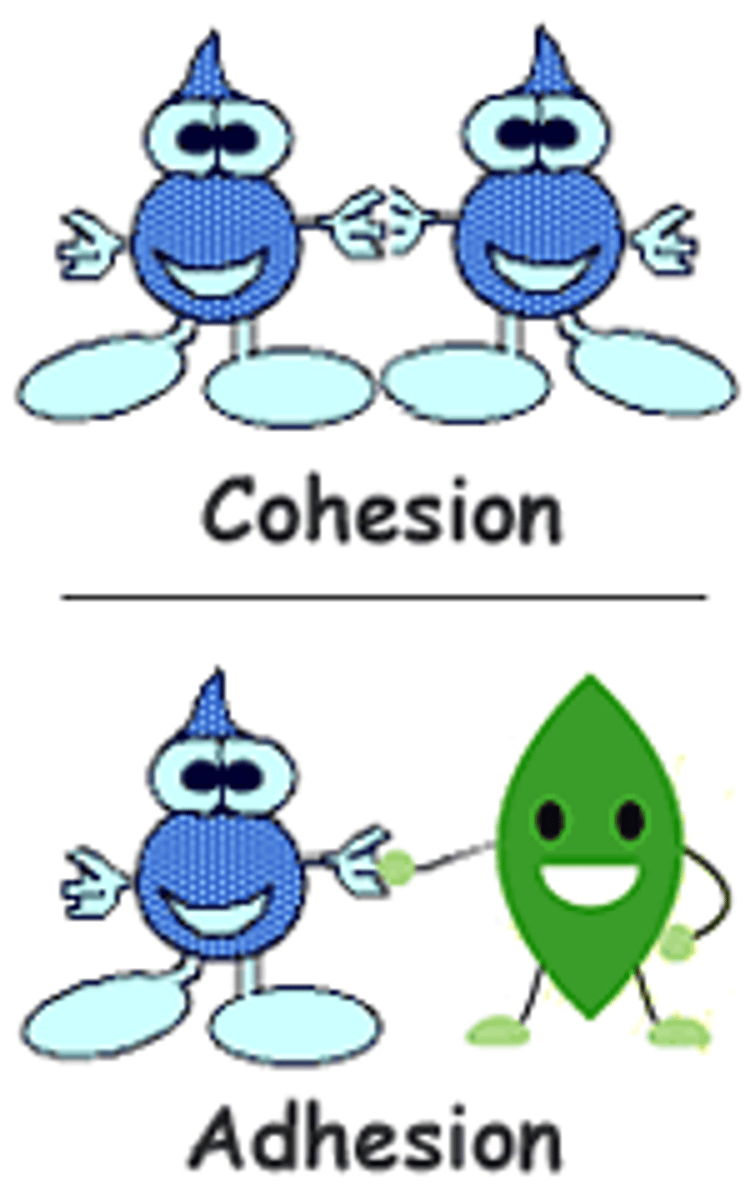
Adhesion
Attraction between molecules of different substances
The clinging of one substance to another
Helps to counteract the pull of gravity
Surface Tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion

Thermal Energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules
Temperature
Average kinetic energy
Calorie
Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C
Specific Heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius
Water has a high specific heat, meaning that it can help regulate temperature
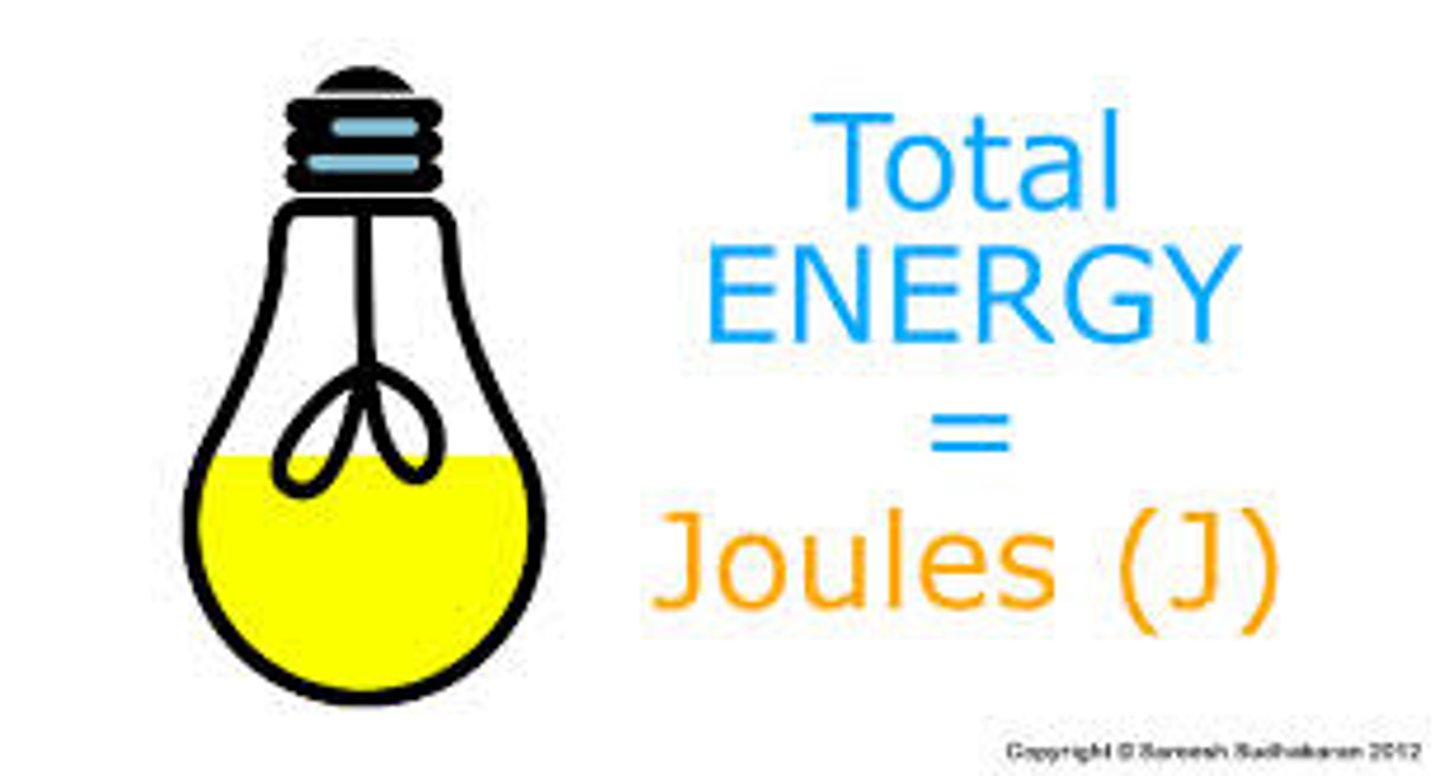
Joule
Unit of energy
Heat of Vaporization
The quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from a liquid to gas
[Water] Helps to moderate Earth's temp by having a high heat of vaporization
![<p>The quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from a liquid to gas<br><br>[Water] Helps to moderate Earth's temp by having a high heat of vaporization</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a4ffea02-80e0-46cd-97ef-18a8aff785fe.jpg)
Water's Properties
High heat capacity, high heat of vaporization, polar, universal solvent
All impact life on Earth
Evaporative cooling
when a substance evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down

Unique Features of Ice
Less dense than water because of the crystalline lattice structure
Freezes from the top-down
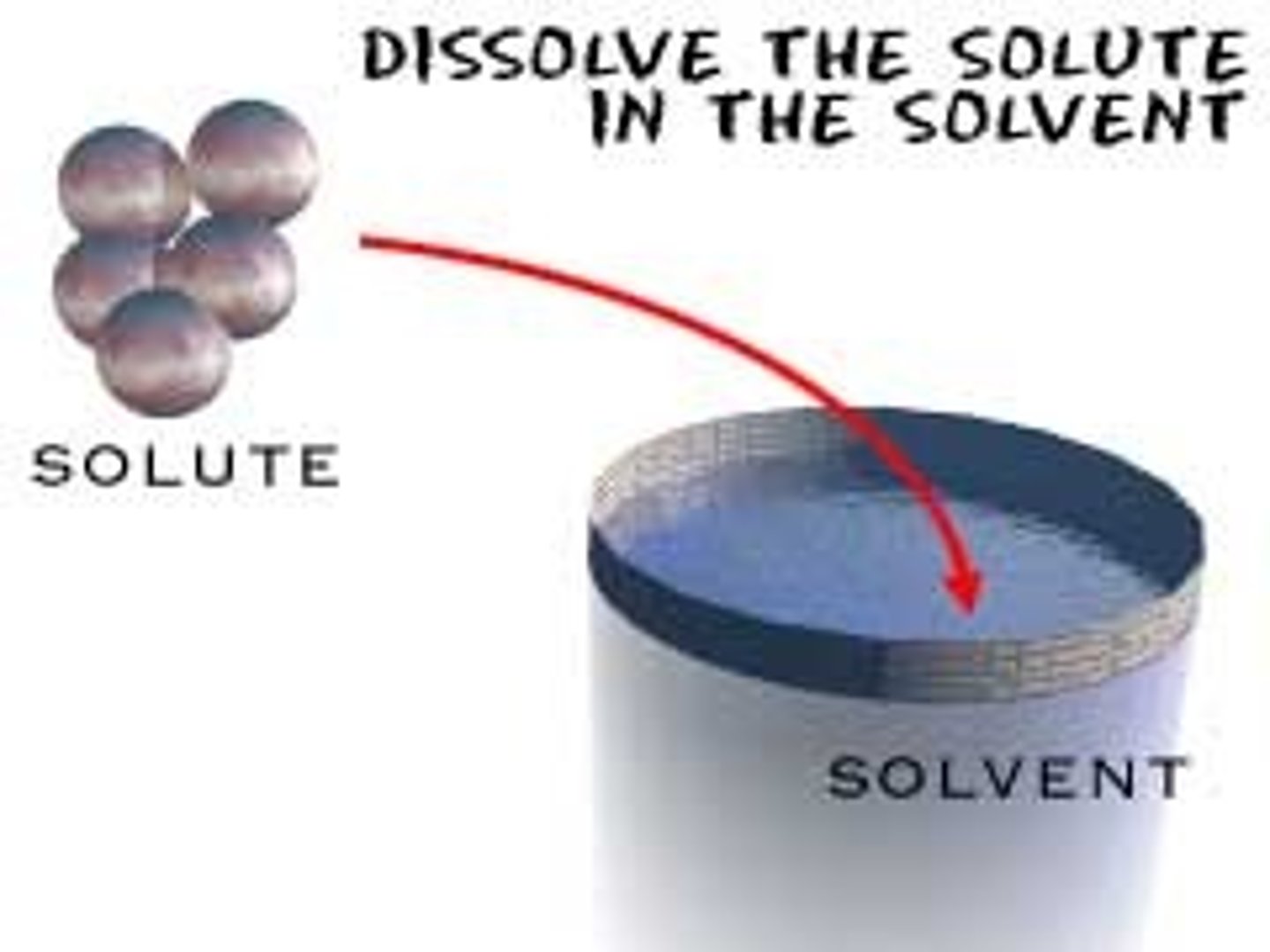
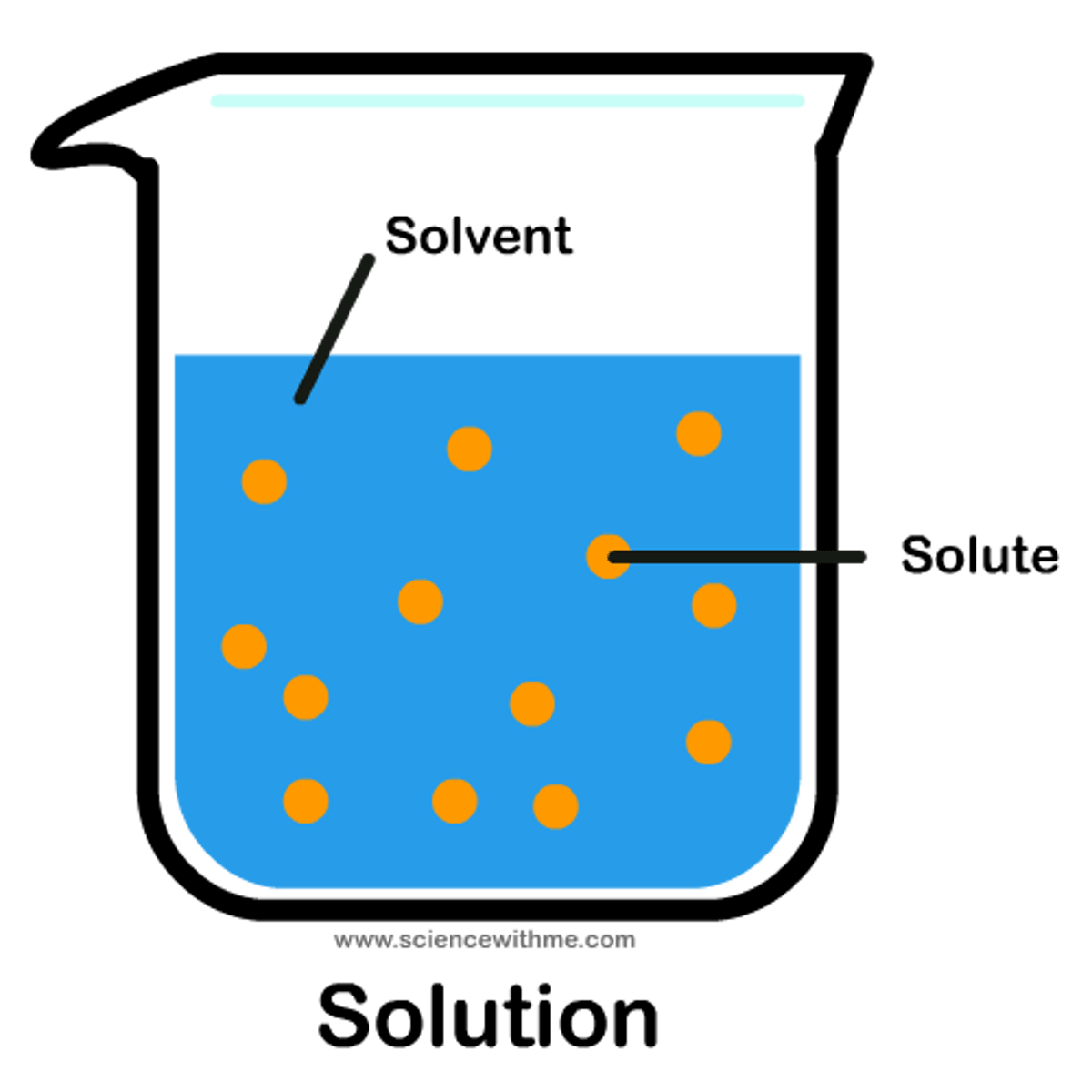
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
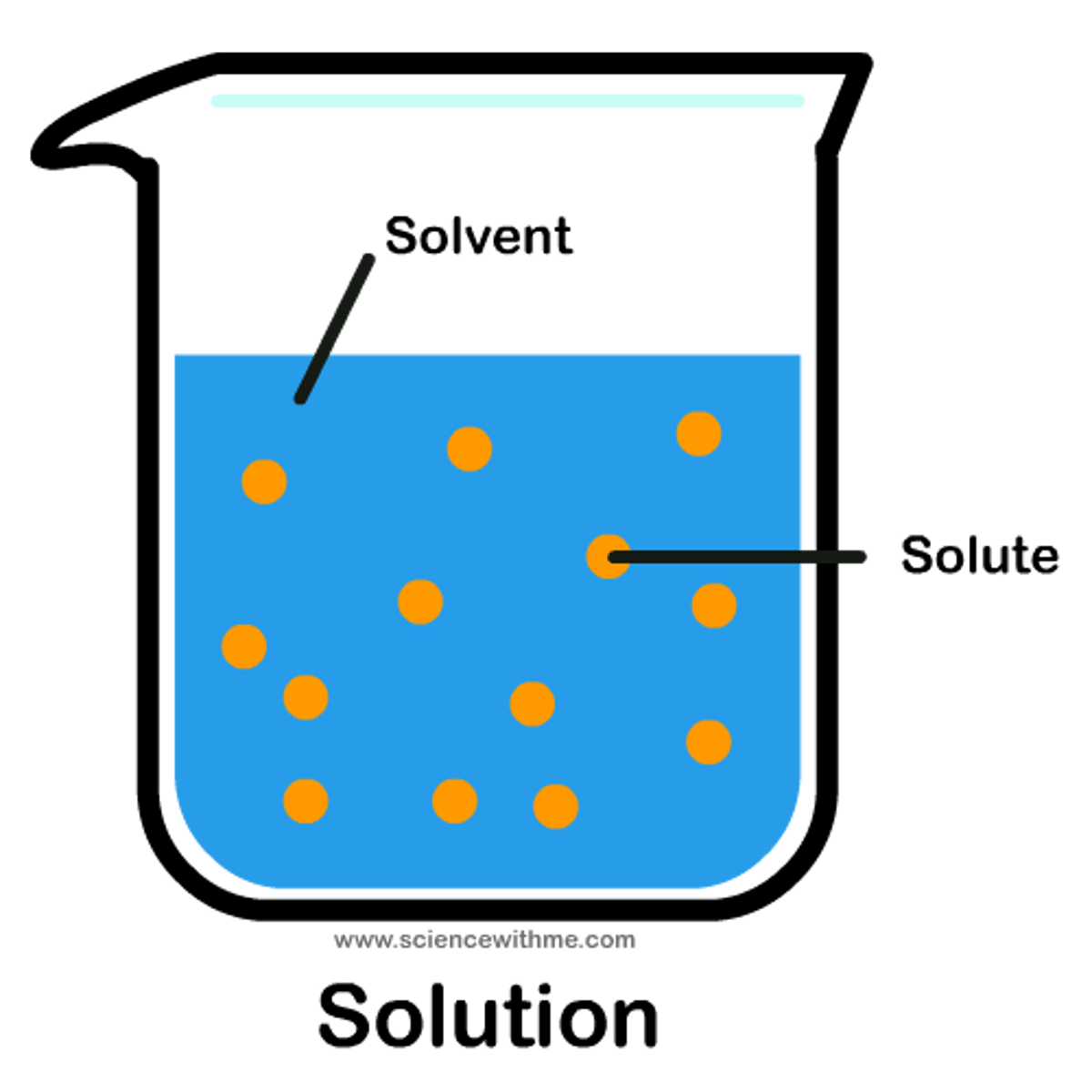
Solvent
The dissolving agent
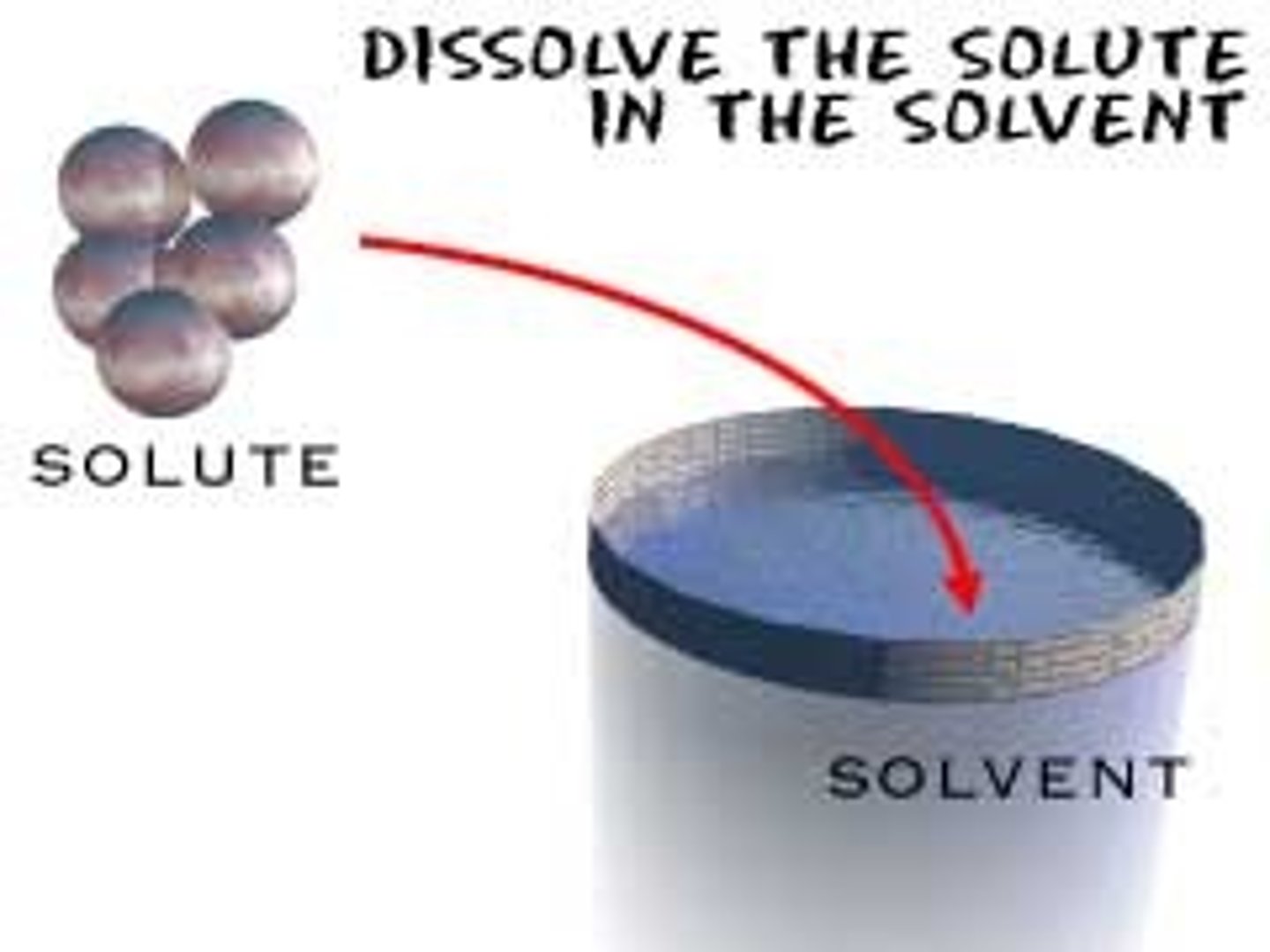
Solute
The substance that is dissolved
Aqueous Solution
A solution in which water is the solvent
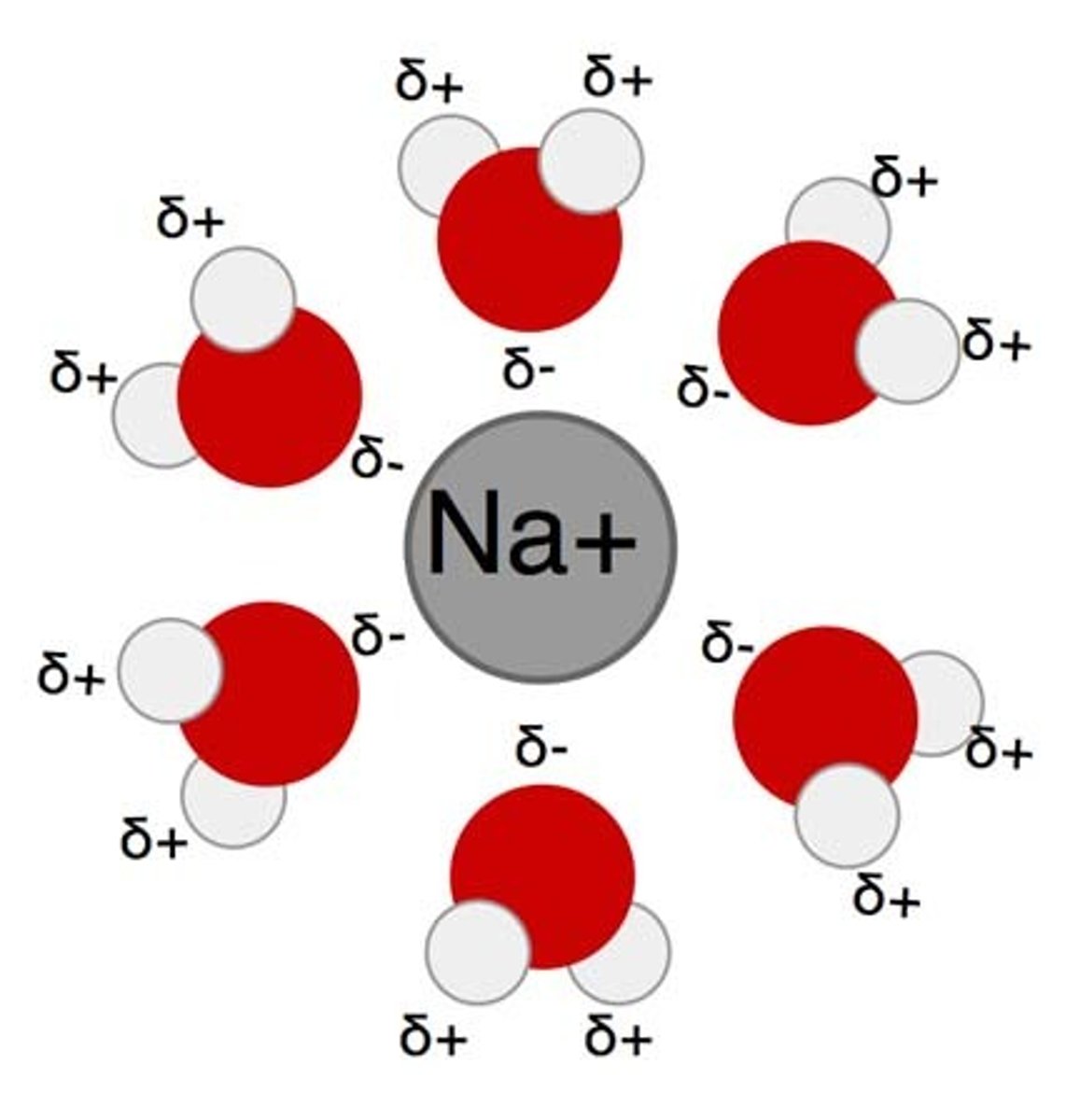
Hydration Shell
The sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Easily mixes with water
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Does not easily mix with water
Molecular Mass
The sum of the masses of all the atoms in a molecule
Mole
Avogadro's Number
6.02 x 10^23
Molarity
The number of moles of solute per liter of solution
pH
Hydrogen ion concentration
<7 Acid
>7 Base
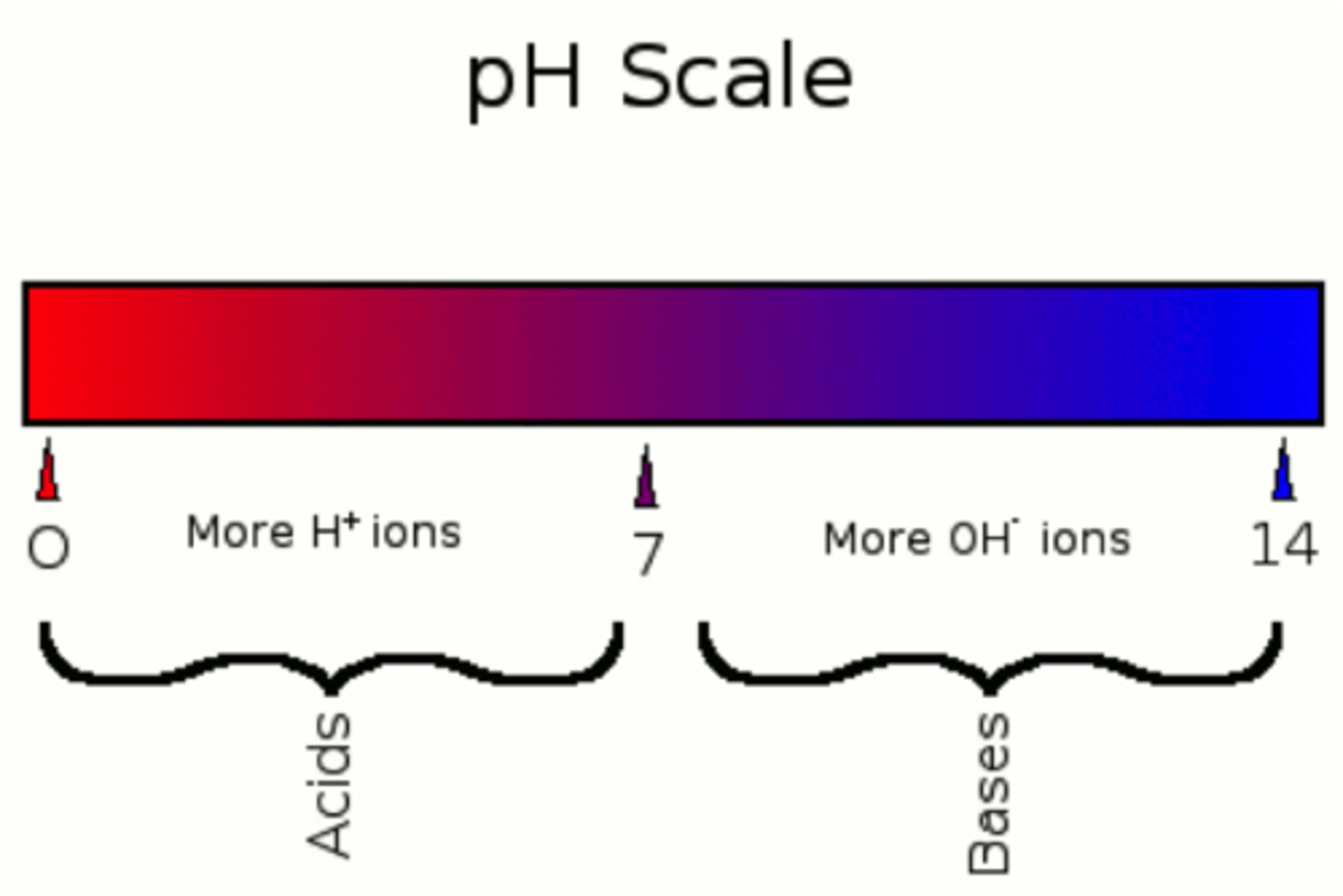
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution
Substance that resists changes in pH
Buffer
Organic Compound
Compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen
Ex. C6H12O6 (glucose)
Inorganic Compounds
Compounds that do not contain both carbon & hydrogen
Ex. CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules

Carbon's Valence
4 (meaning it can bond with a max of 4 elements)
Hydrocarbon
Organic compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
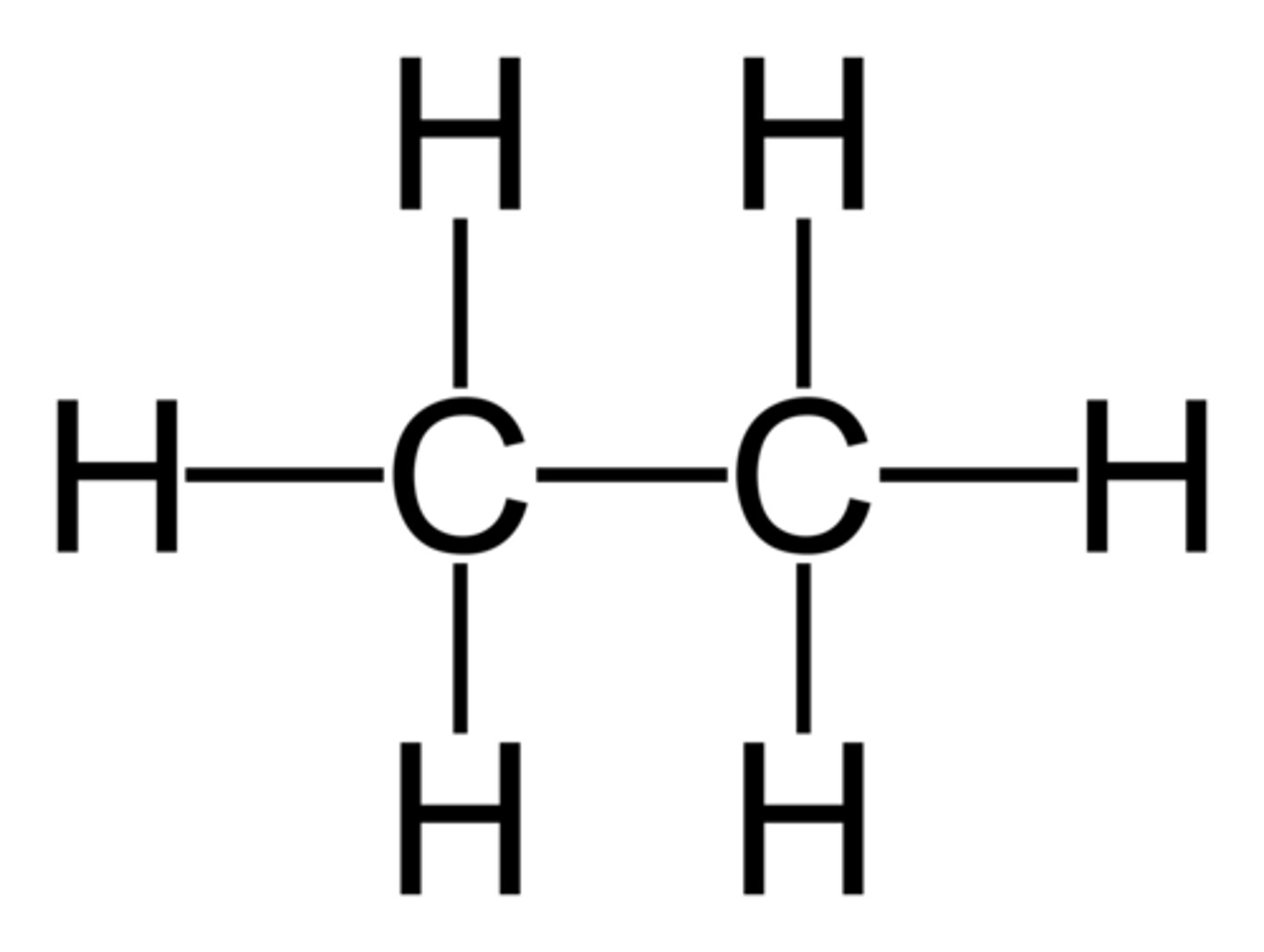
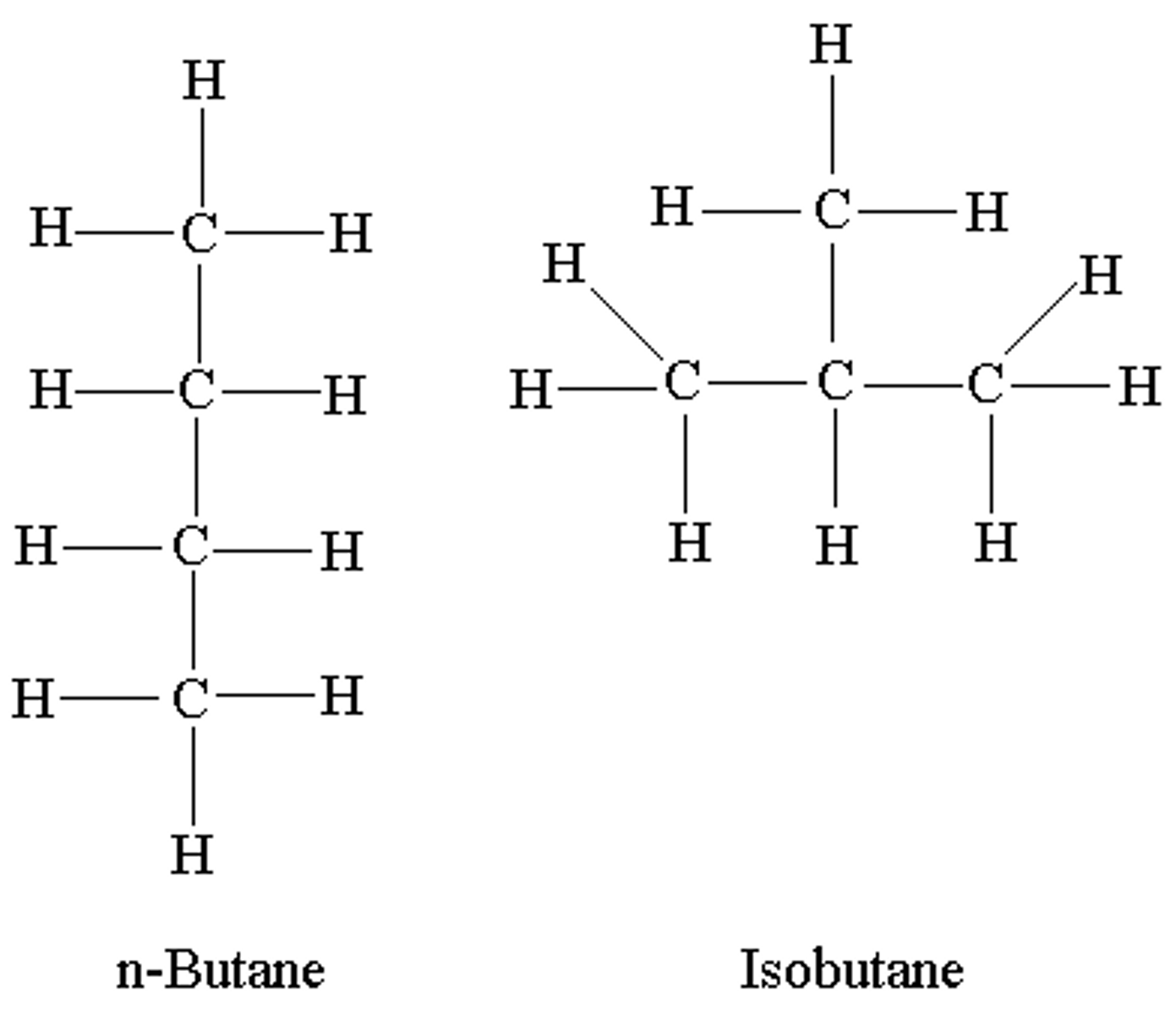
Structural Isomers
Substances that have the same amount and type of atoms, but differ in structure
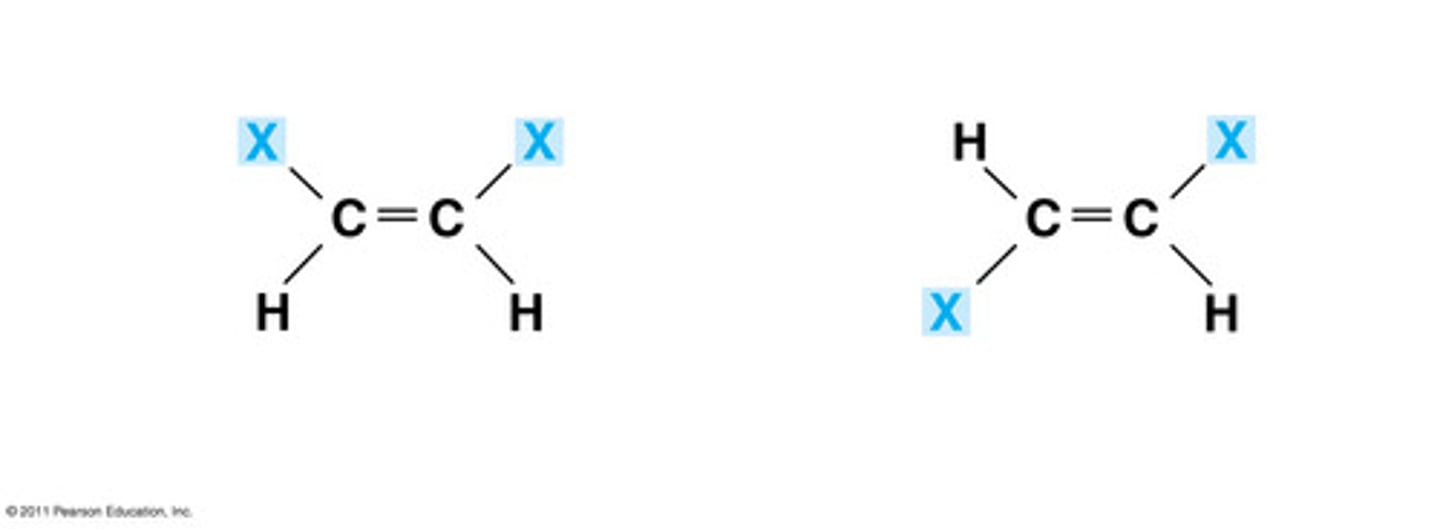
Cis-Trans Isomers
carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of double bonds
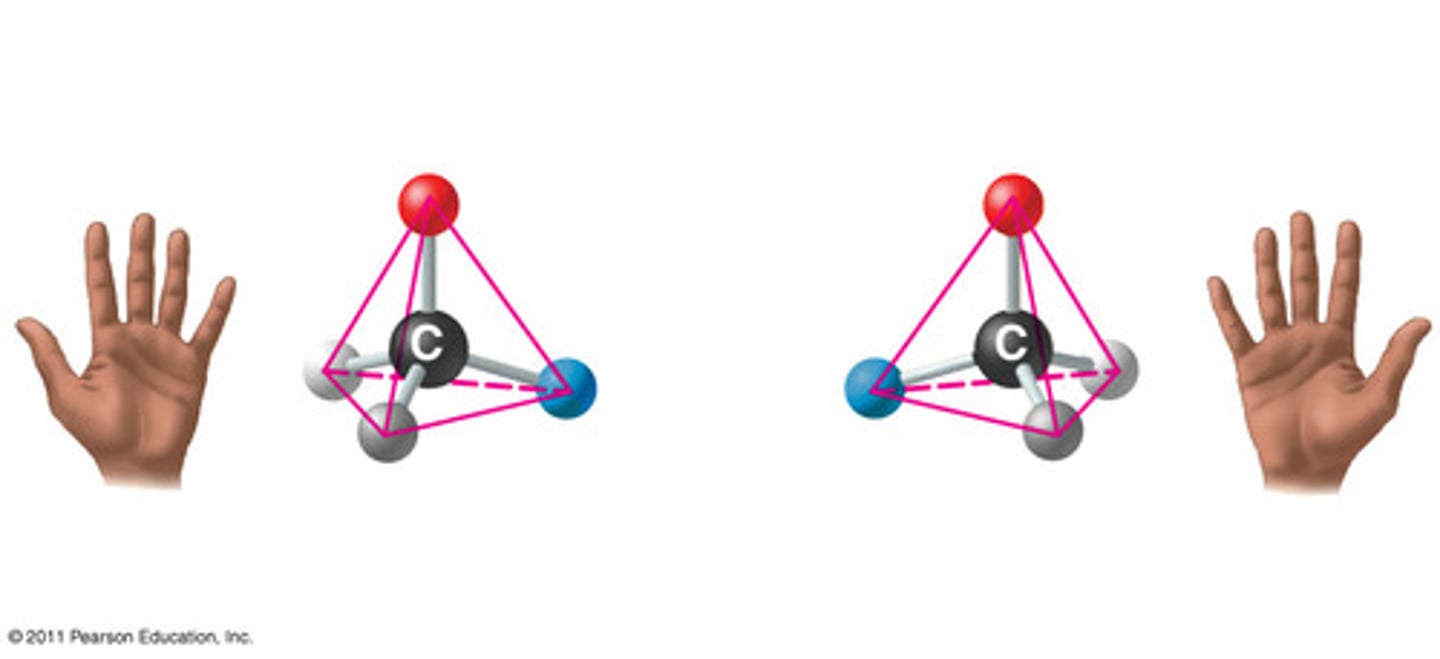
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other
Types of Isomers
structural, cis-trans, enantiomers
Functional Groups
The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
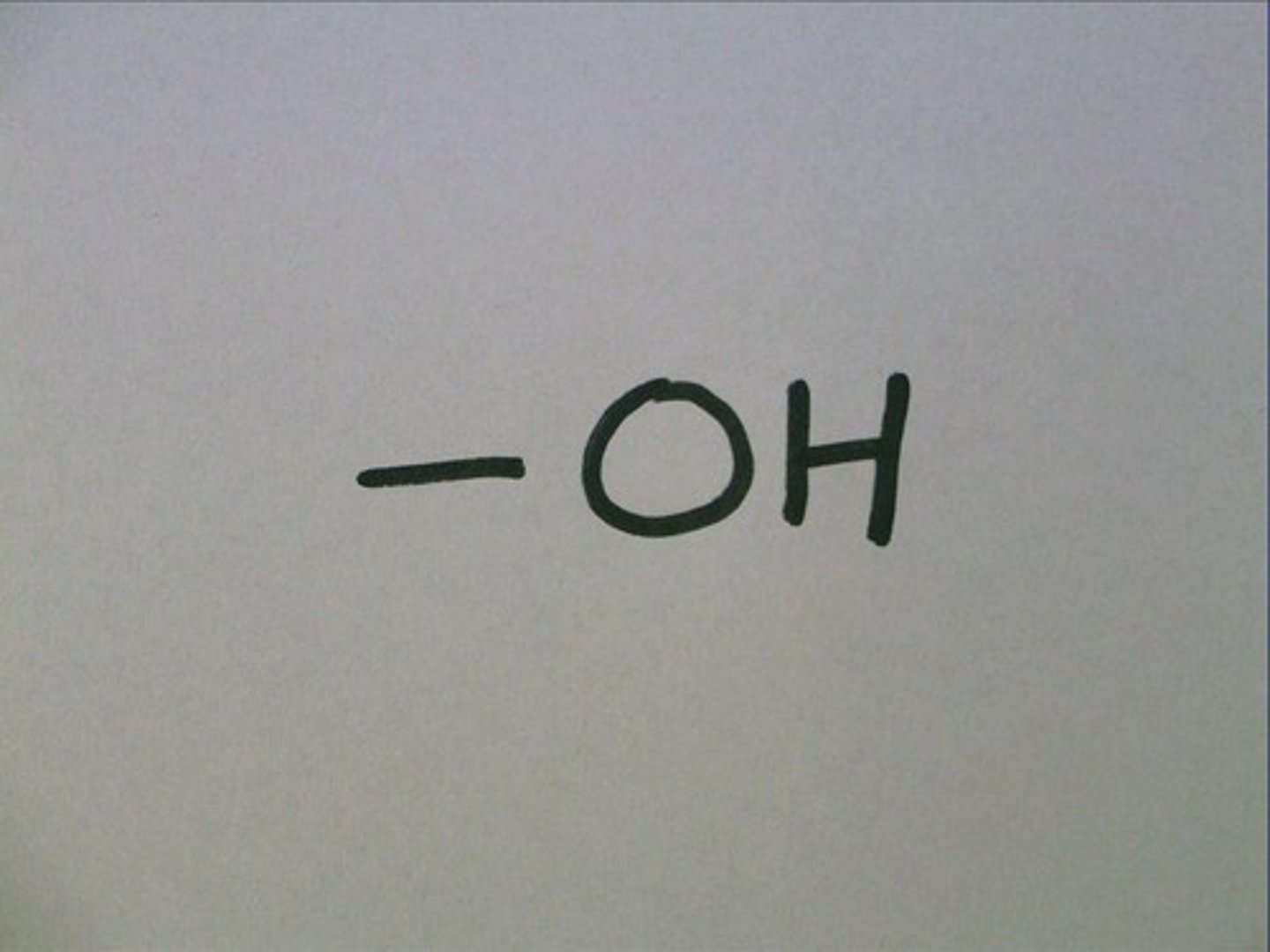
Hydroxyl Group
-OH
Name usually ends in -ol
Ex. alcohol
Hydrophilic
Carbonyl Group
>C=O
Compound names:
Ketone: Carbonyl group is within the carbon skeleton
Ex. Acetone
Aldehyde: Carbonyl group is on the end of the skeleton
Ex. formaldehyde
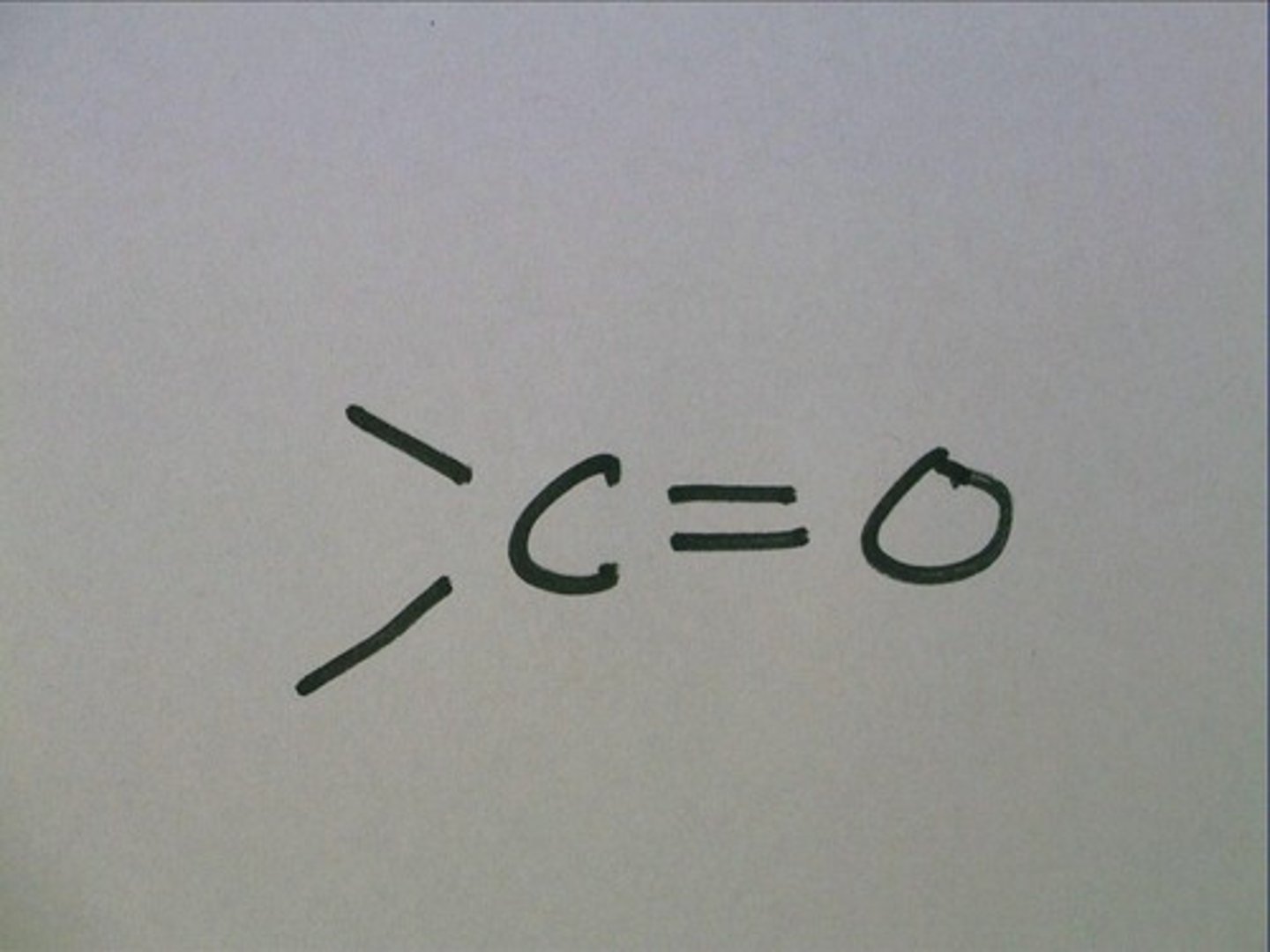
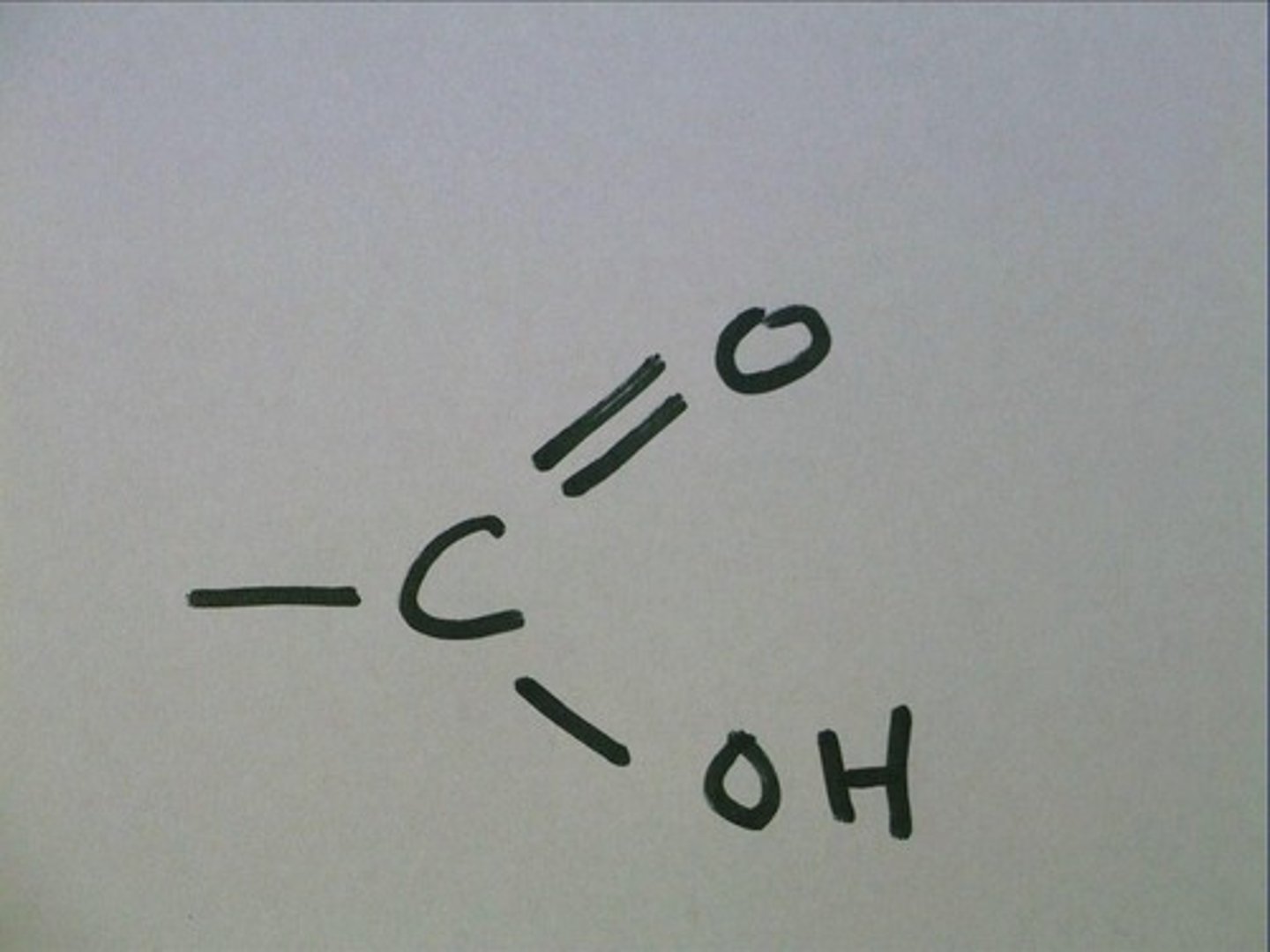
Carboxyl Group
-COOH
Compound name: Carboxylic acid, or organic acid
Forms acidic compounds
Ex. Vinegar
Hydrophilic
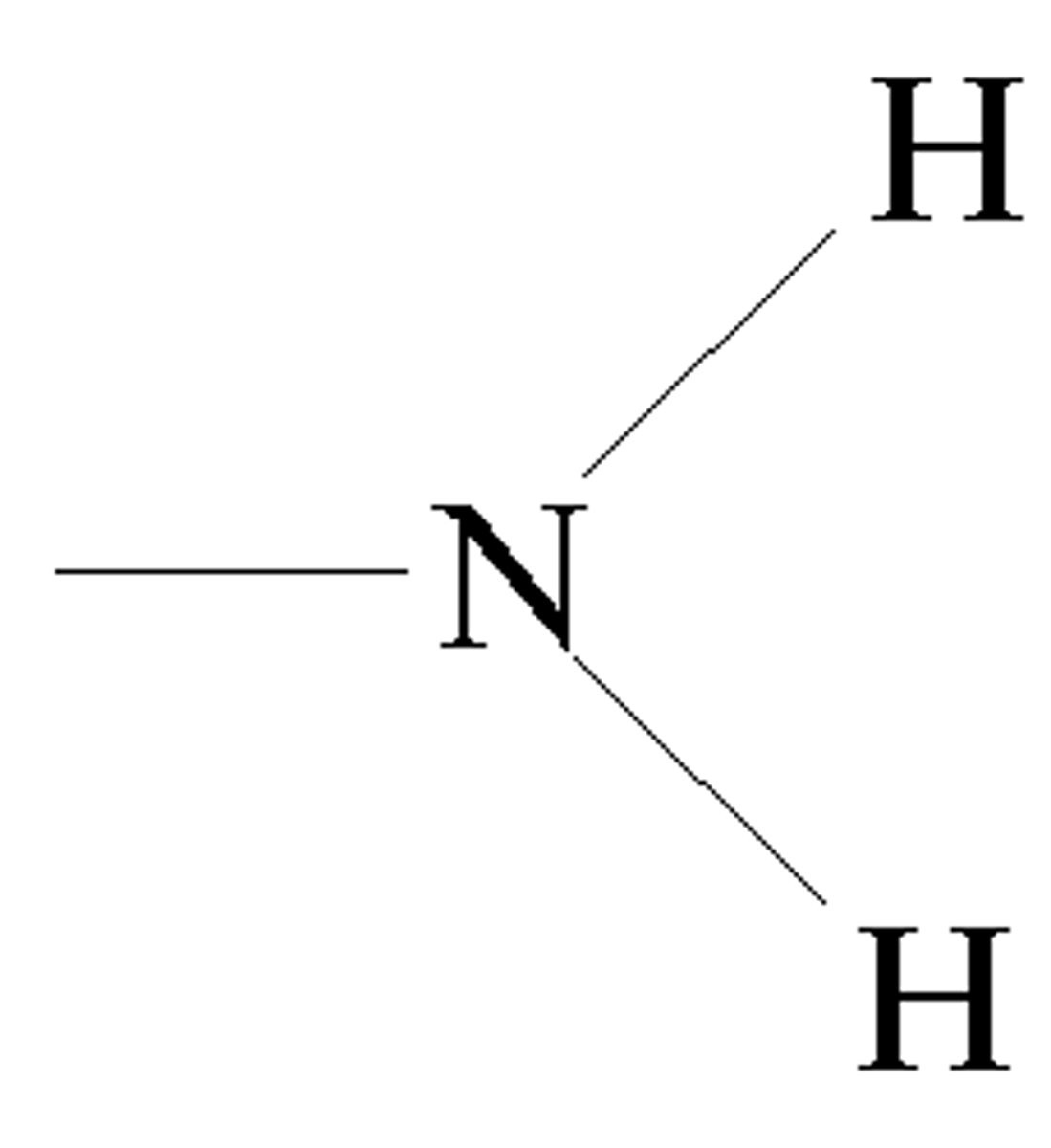
Amino Group
-NH2
^key feature
Compound name: Amine
Ex. Glycine
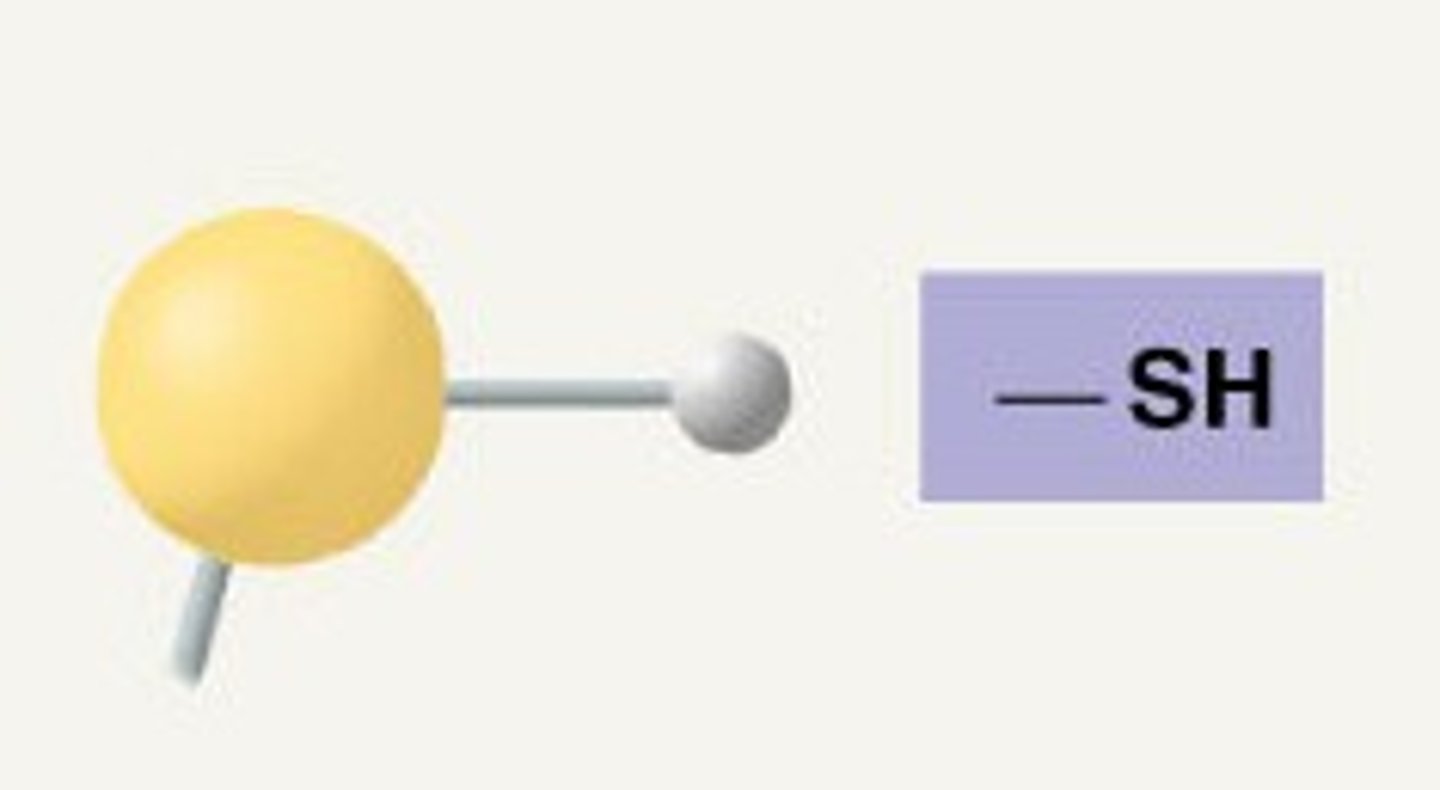
Sulfhydryl Group
-SH
Compound name: Thiol
Ex. Cysteine
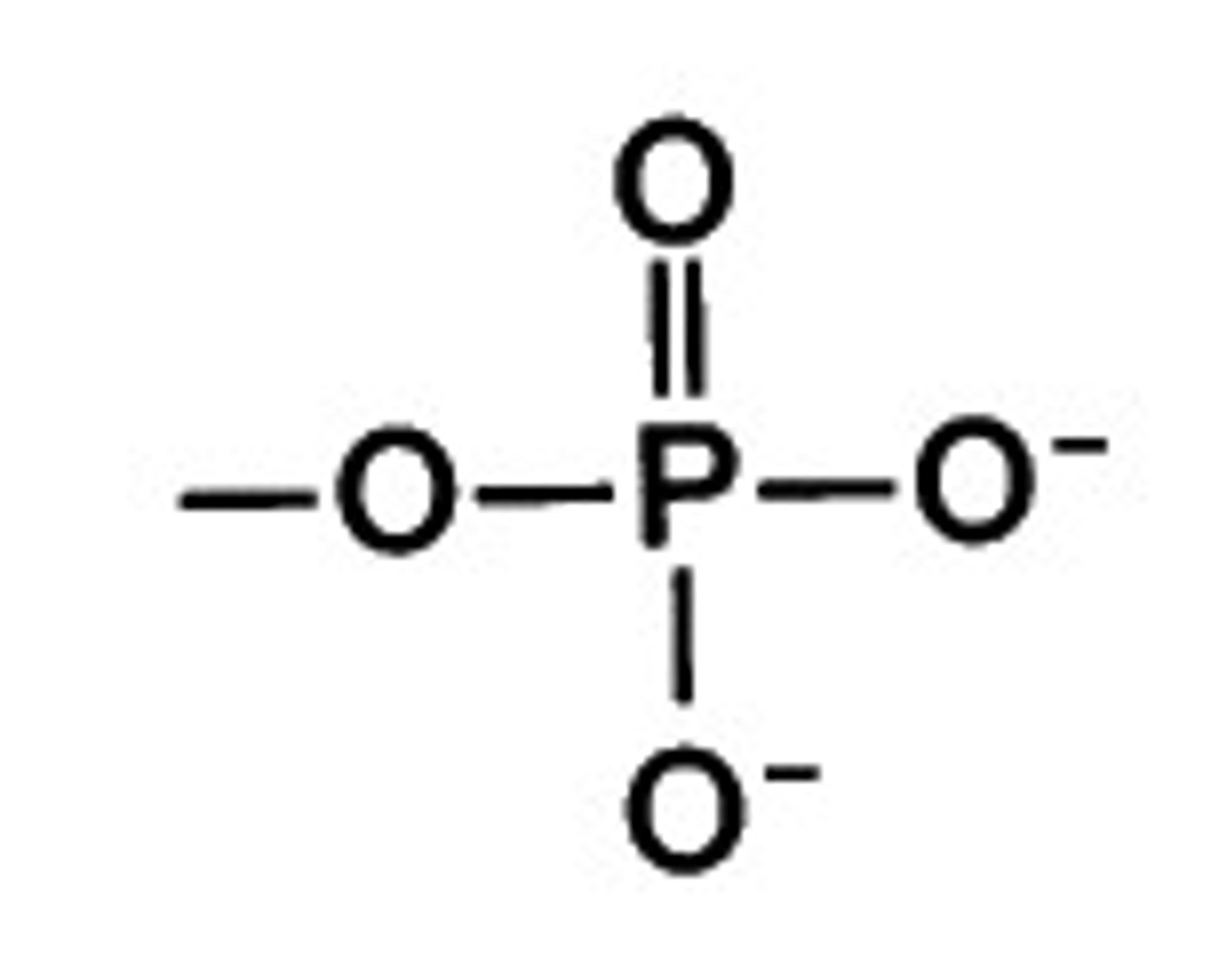
Phosphate Group
Phosphorous atom bonded to 4 oxygen atoms
Compound name: Organic Phosphate
Ex. Glycerol Phosphate
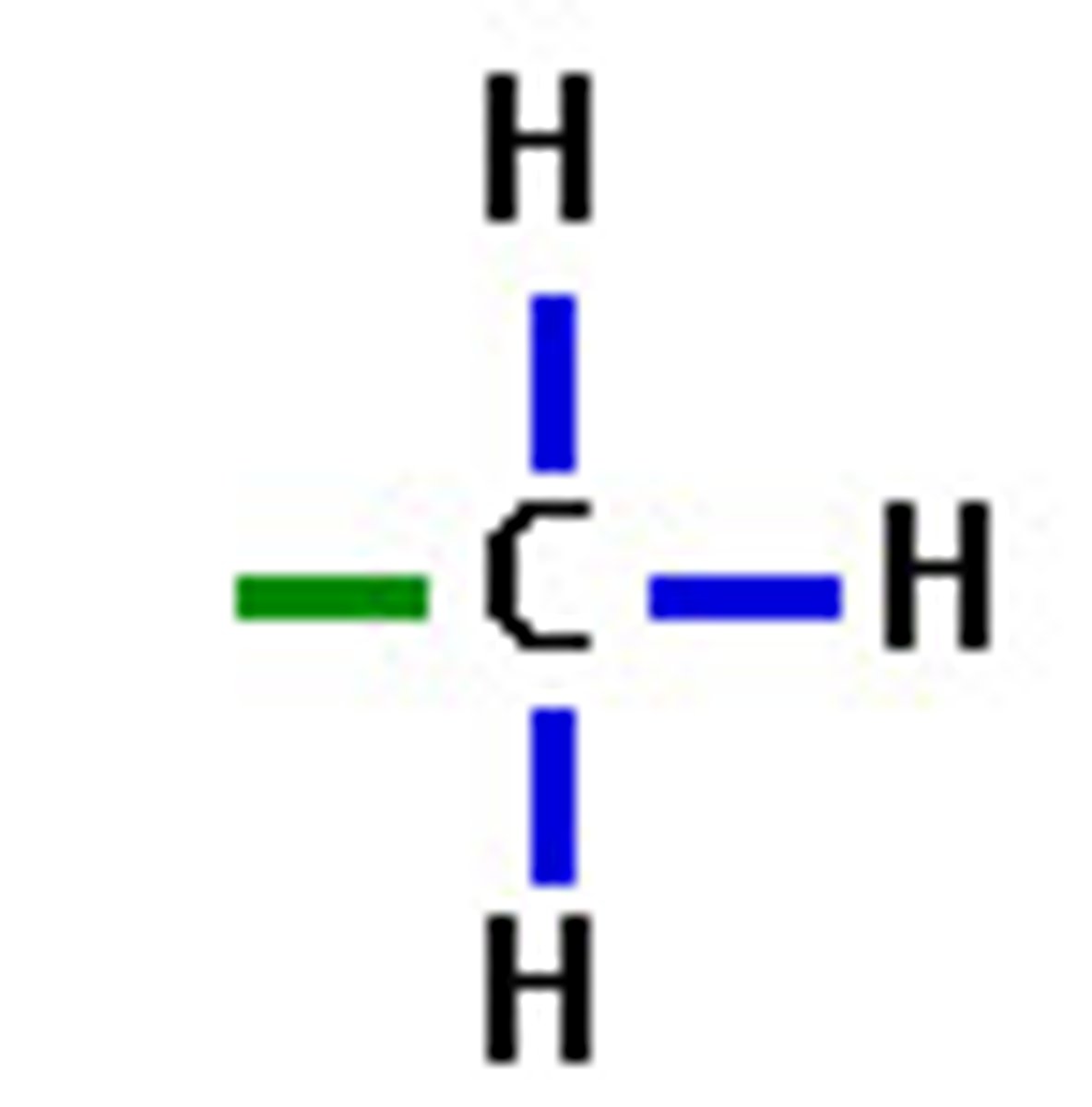
Methyl Group
-CH3
Carbon bonded with 3 other hydrogen atoms
Ex. Methanol
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
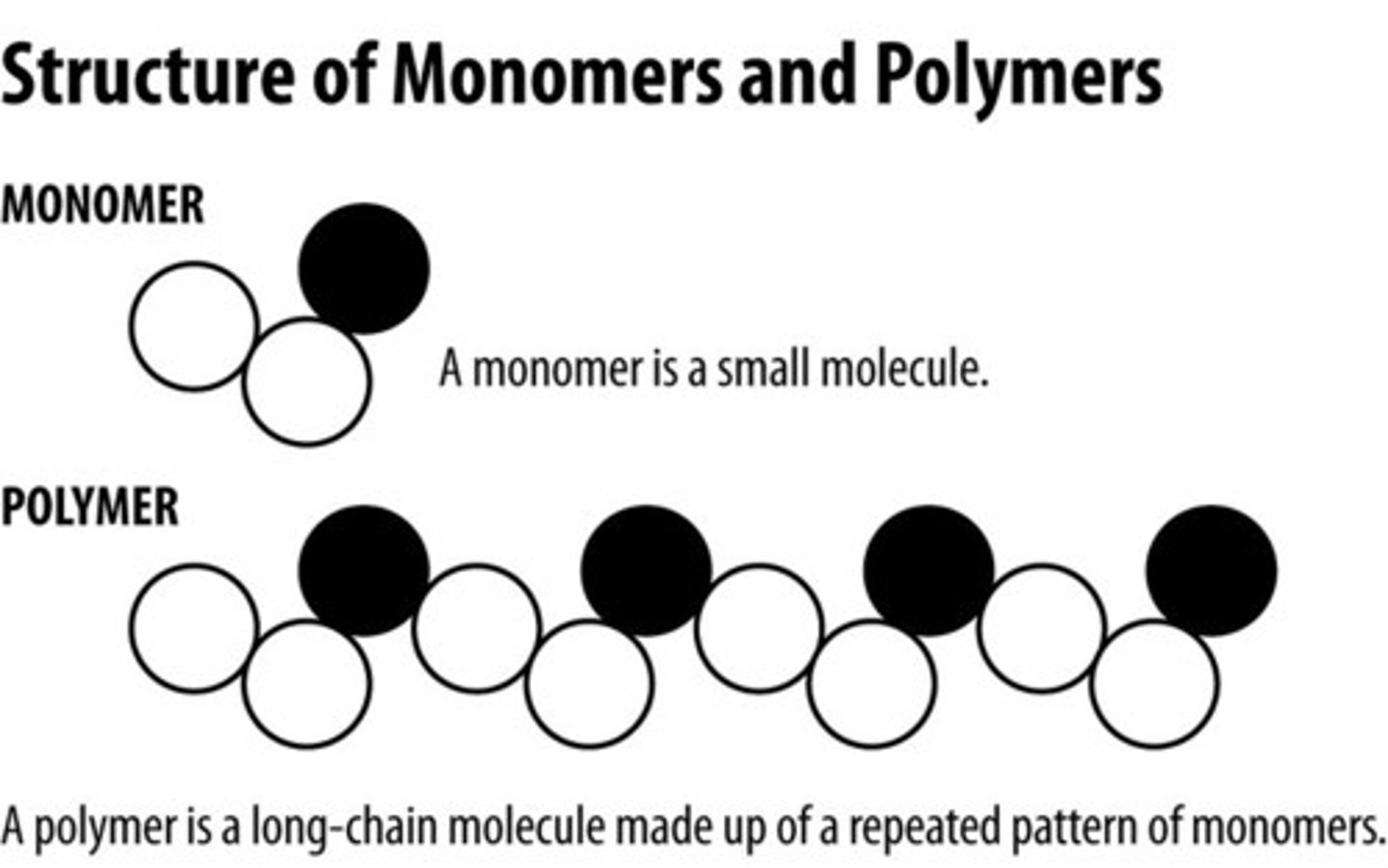
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds
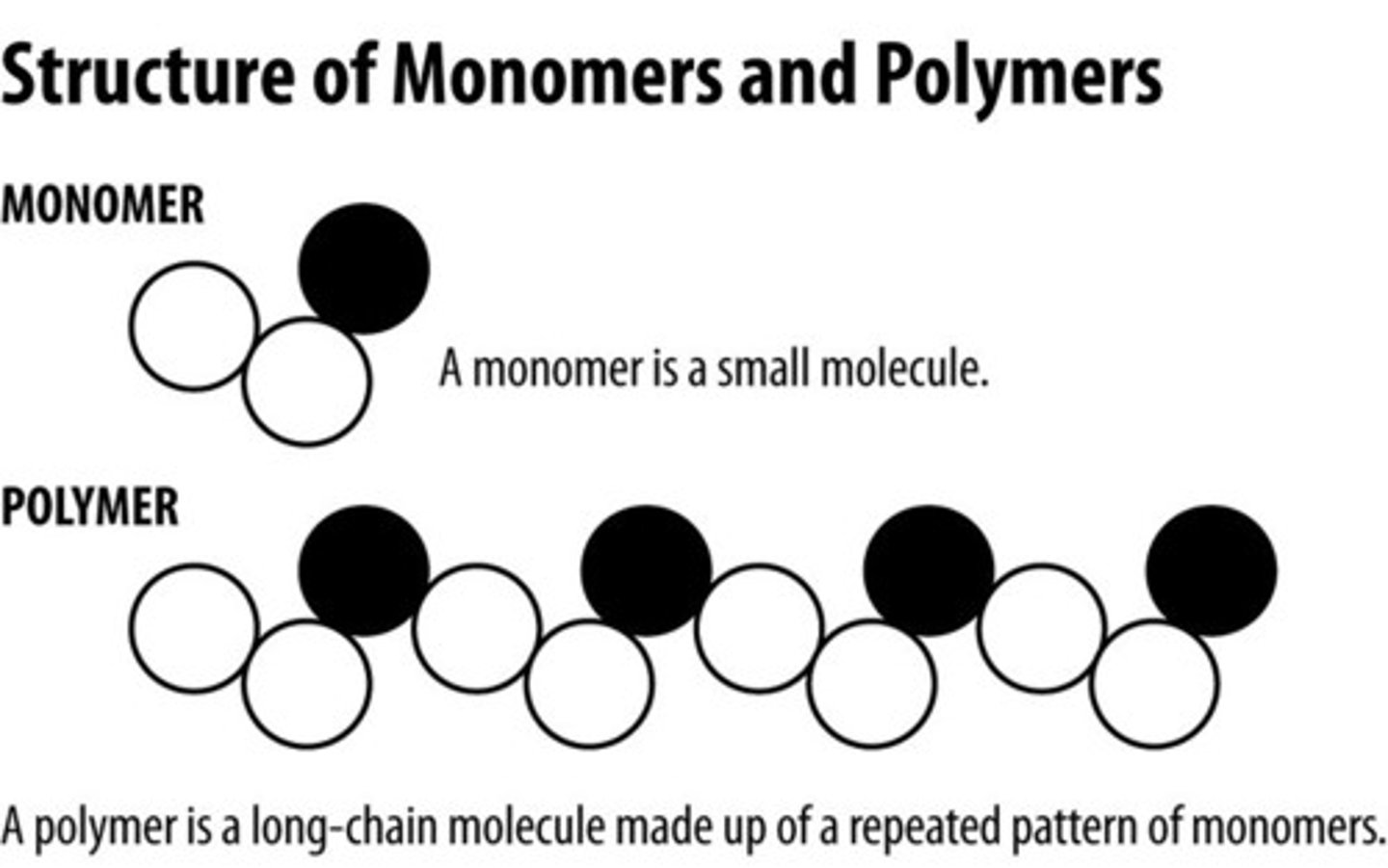
Monomer
"Building blocks" of polymers
Simple compounds
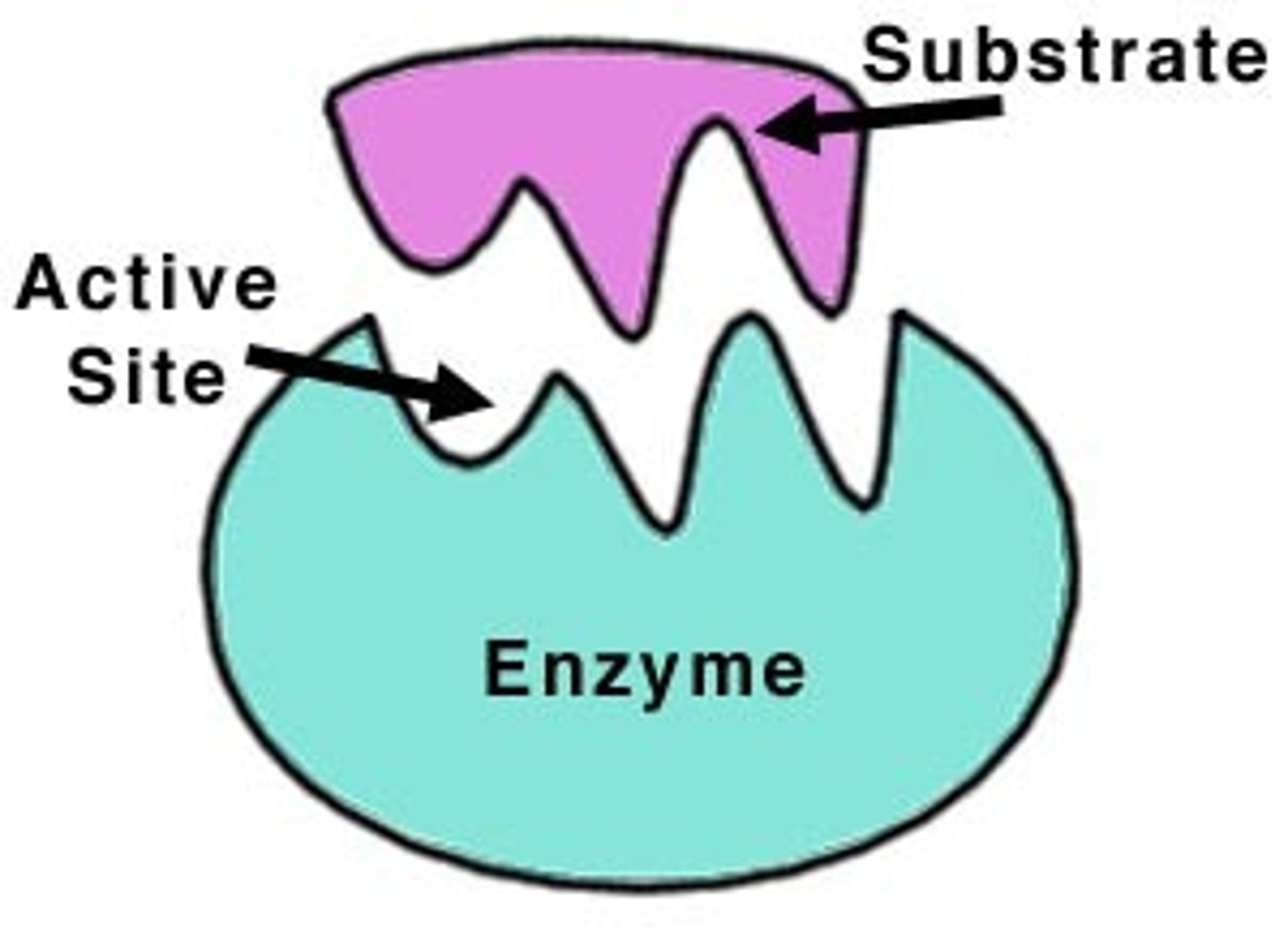
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
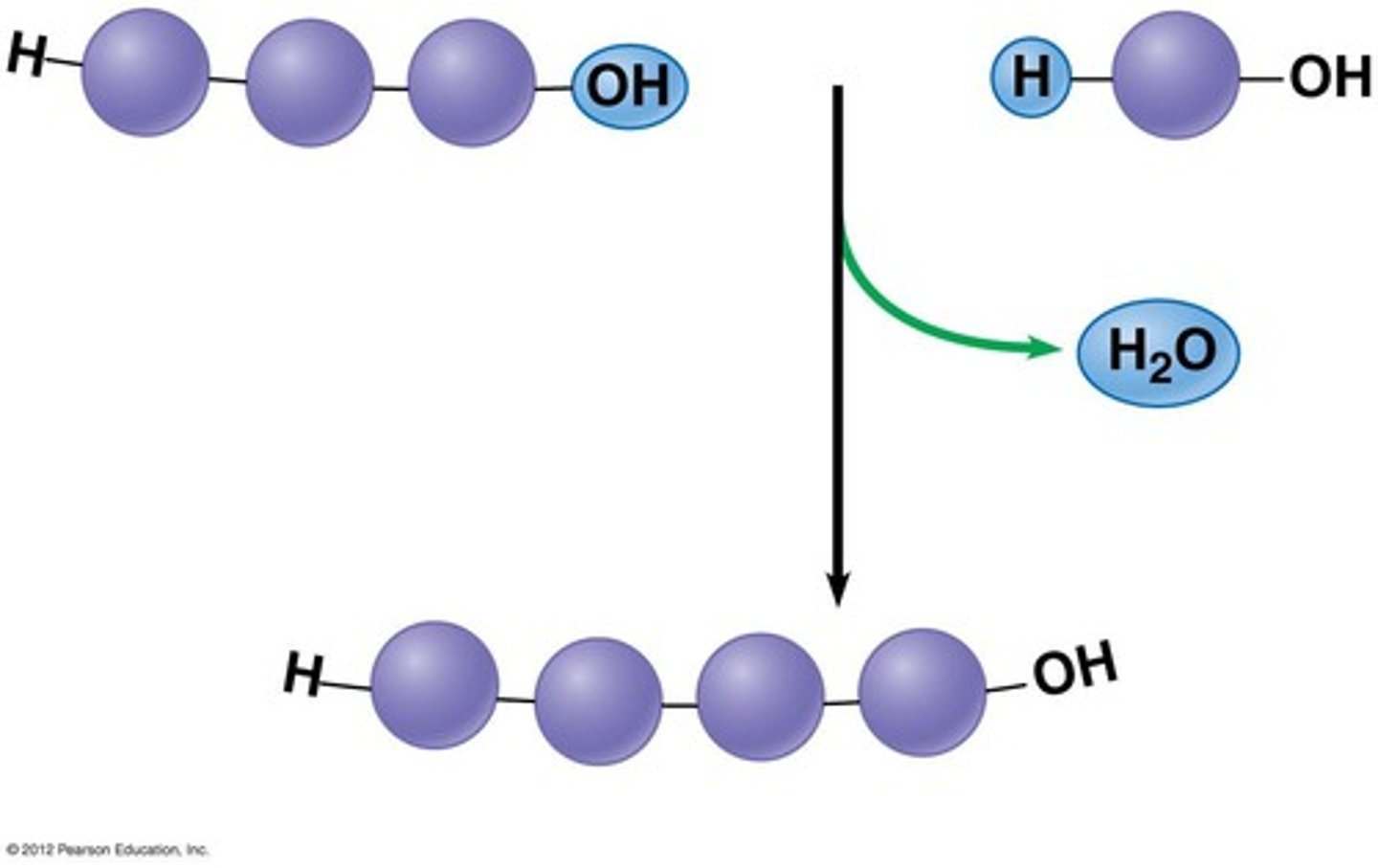
Dehydration Synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule
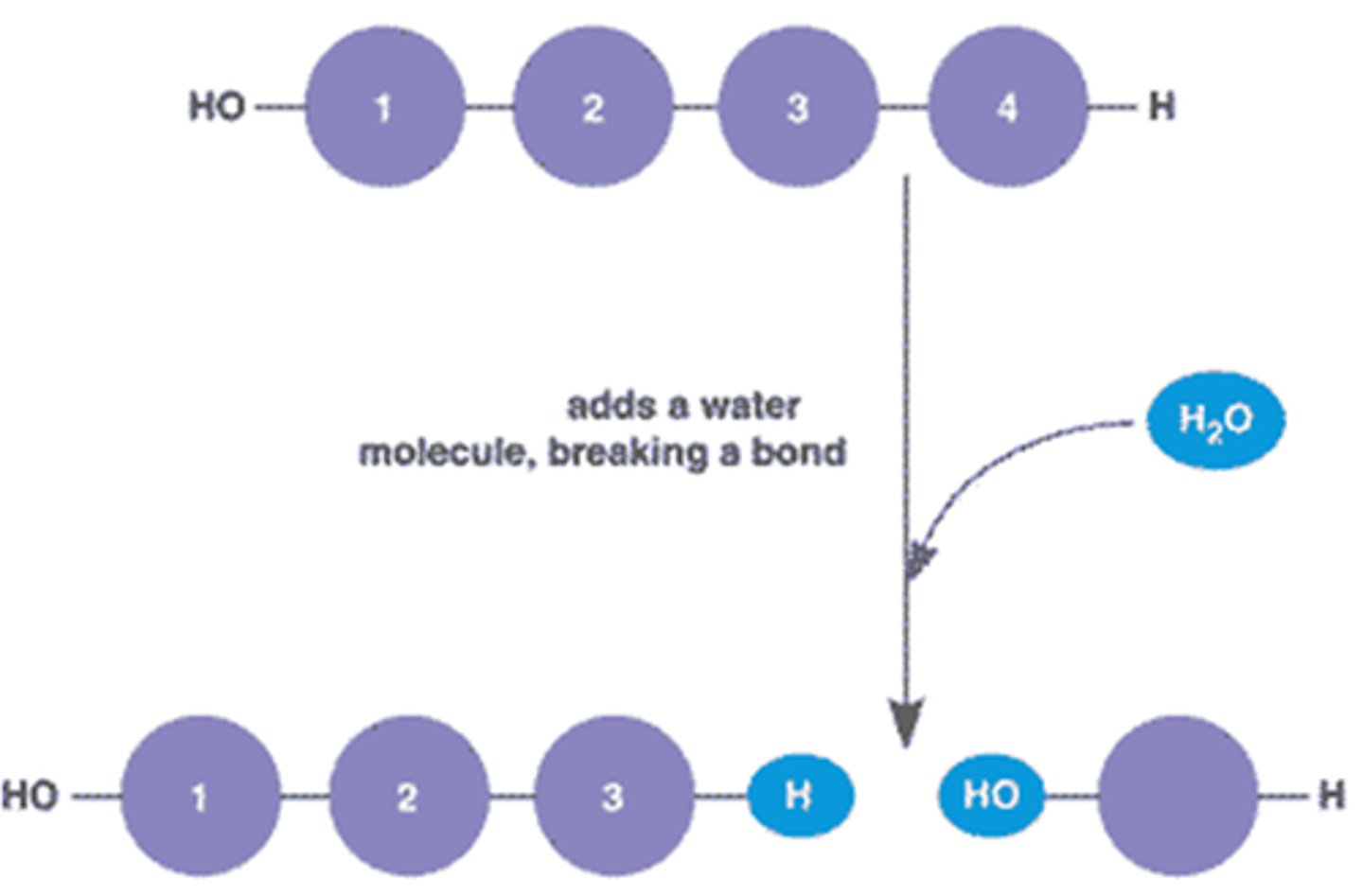
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Glycosidic Linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction
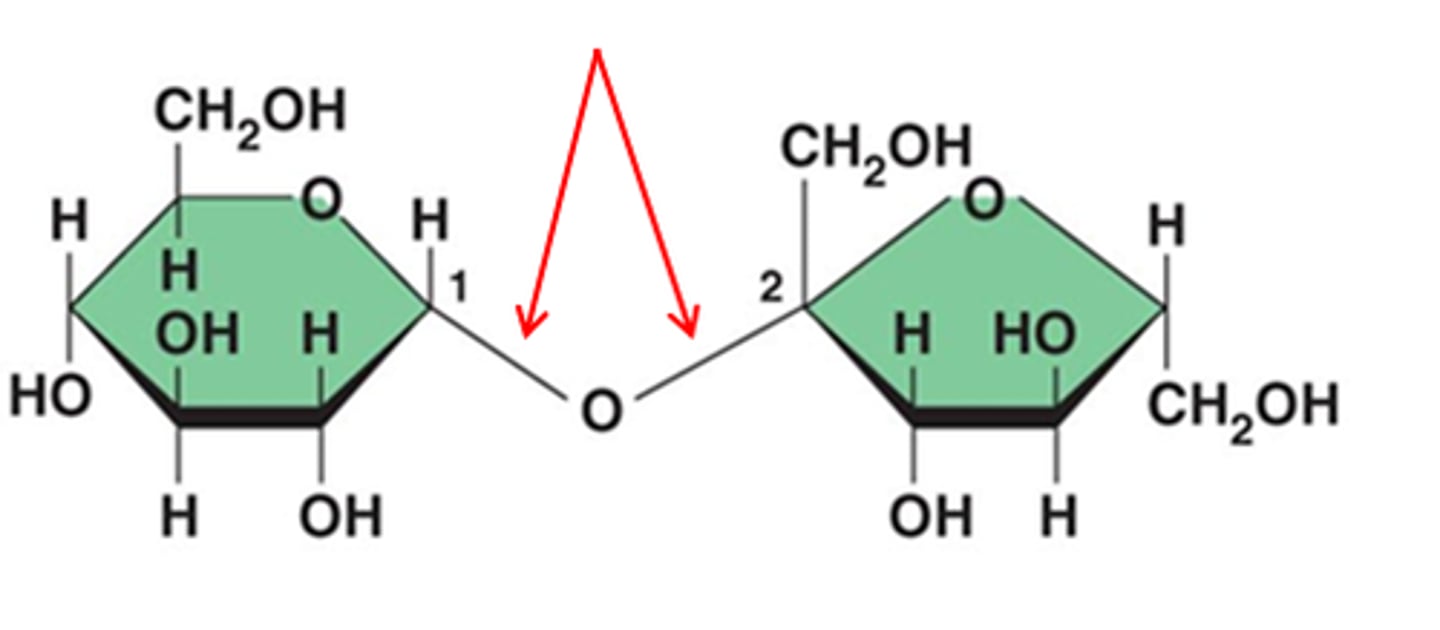
Polysaccharides
Large macromolecules formed from 100+ monosaccharides
Serve as energy storage or cell building material
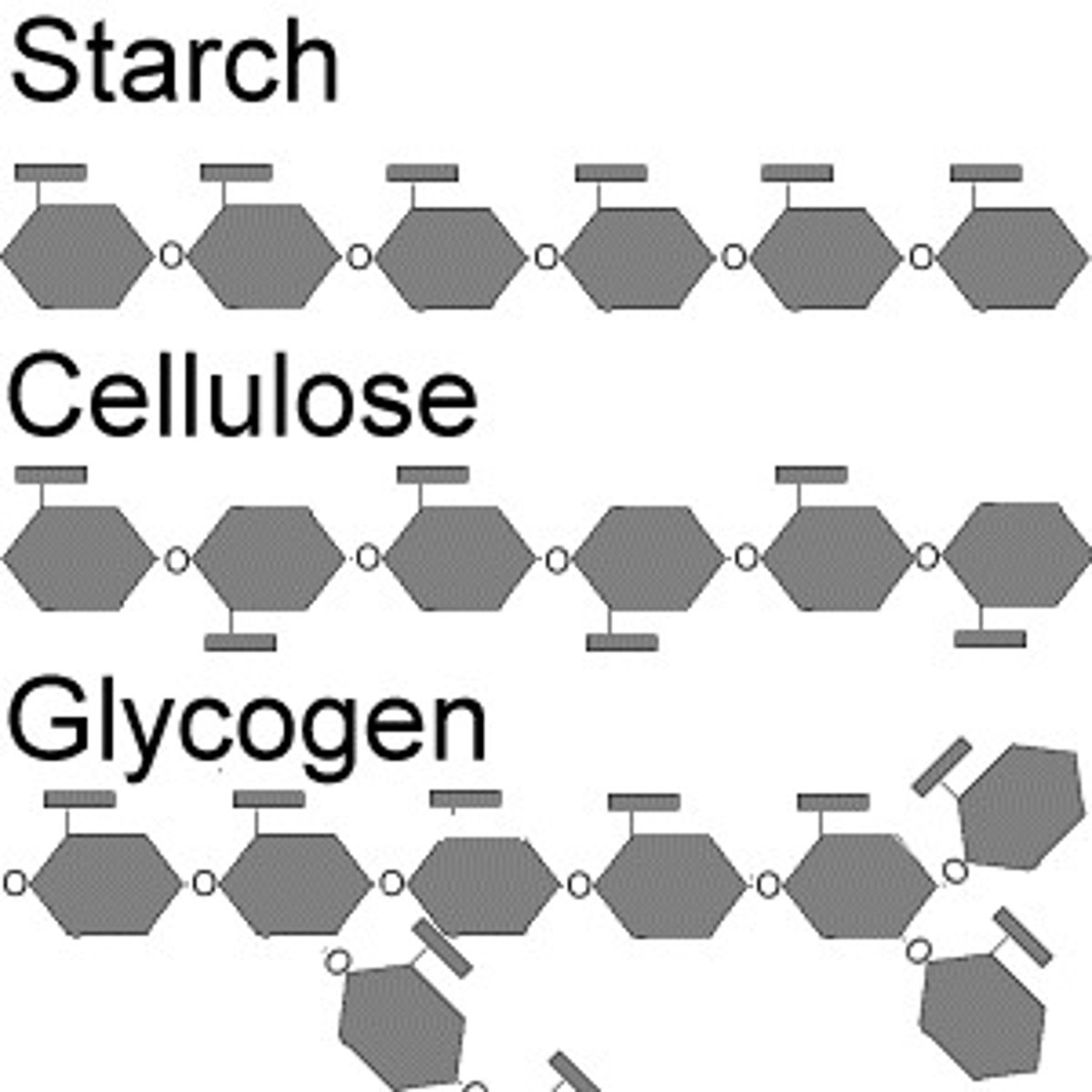
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Carbohydrates
Used for short term energy, structure, raw material, and cell communication
Made of simple sugars
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
*not a polymer
Proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues
Made of amino acids
Nucleus acids
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
DNA
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
Ex. Glucose
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
Ex. Lactose, maltose, sucrose