ANAT1101 Module 1 Organization of the Human Body
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structures of the body.
Physiology
The study of how the body functions.
Organizations of the Body
Atoms
Molecules
Organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Human
Atoms
The smallest units of matter.
Molecule
Atoms bonded together.
Organelle
Units in a cell that perform a specific function.

Cells
The smallest living unit. They make up all living organisms and perform essential functions.
Tissues
Groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organs
Structures made up of different tissues that work together to perform specific functions in the body.
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to carry out complex functions necessary for the survival and health of an organism.
Human
All organ systems working together.

Integumentary System
Consists of:
Skin
Hair
Nails
Key Functions
Protection
Temperature Regulation
Water Retention
Sensation
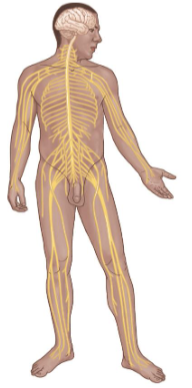
Nervous System
Consists of:
Brain
Spinal Cord
Key Functions
Control, regulation, and coordination of other systems.
Faster response than the Endocrine System.
Sensation
Thinking and processing.
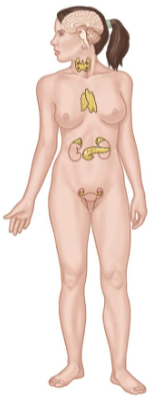
Endocrine System
Consists of:
Pituitary Gland
Adrenal Gland
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Gland
Pancreas
Key Functions
Control, regulation, and coordination of other systems.
Slower but longer lasting than the Nervous System.
Hormone production.
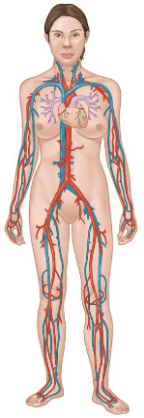
Circulatory System
Consists of:
Heart
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Key Functions
Distribution of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, immune cells.
Elimination of wastes.
Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance.
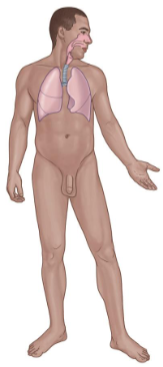
Respiratory System
Consists of:
Lungs
Nose
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Key Functions
Absorption of oxygen.
Discharge of carbon dioxide.
Acid-base balance
Speech
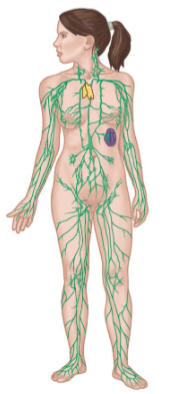
Lymphatic System
Consists of:
Lymph nodes
Lymphatic vessels
Lymph
Spleen
Thymus
Key Functions
Fluid balance
Maintains blood pressure
Defense against disease
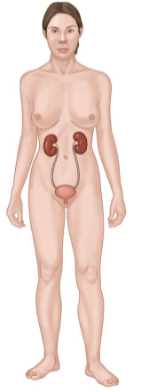
Urinary System
Consists of:
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Key Functions
Excretion of wastes.
Control of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance.
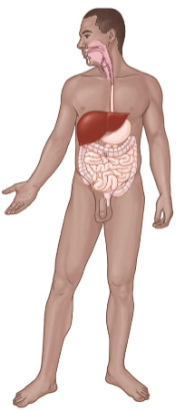
Digestive System
Consists of:
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Small and Large Intestines
Liver
Pancreas
Key Functions
Breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Elimination of wastes.
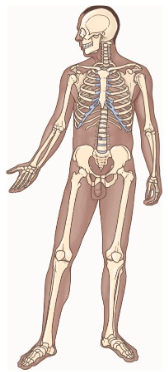
Skeletal System
Consists of:
Bones
Cartilages
Ligaments
Key Functions
Protection
Support
Movement
Blood cell formation
Stores minerals
Muscular System
Consists of:
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Key Functions
Movement
Posture
Heat production
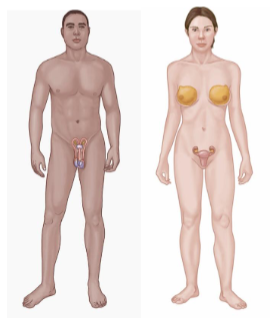
Reproductive System
Consists of:
Testes
Vas deferens
Ovary
Uterus
Key Functions
Produce offspring
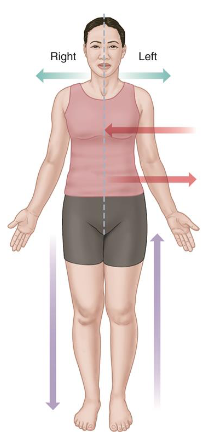
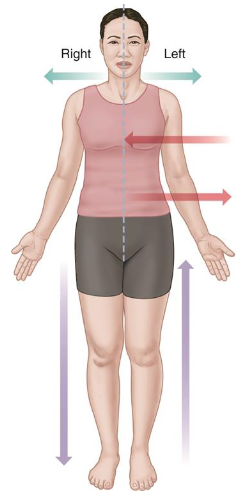
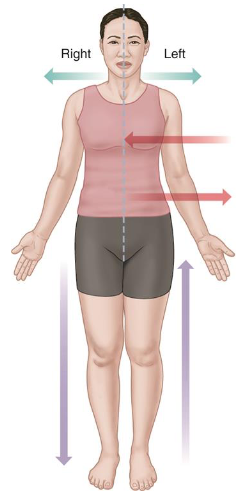
Anatomical Position
Standing upright with arms at sides.
Face, palms, and feet face forwards.
It is used when communicating between health professionals.
Right and left are the patient’s right and left.
Proximal
Usually applies to limbs (arms or legs).
Closest to the trunk/origin (shoulders, chest, lower abdomen, back, buttocks)
Distal
Usually applies to limbs (arms or legs).
Farthest to the trunk/origin (shoulders, chest, lower abdomen, back, buttocks)
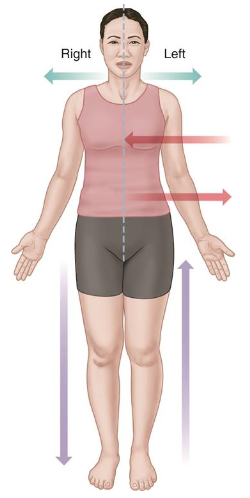
Medial
Toward the body’s midline/center.
Lateral
Away from the body’s midline/center.
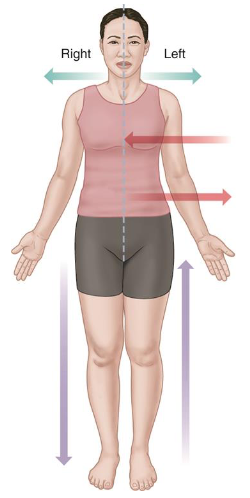
Anterior
Also called as Ventral.
Toward the front of the body.
Posterior
Also called as Dorsal.
Toward the back of the body.
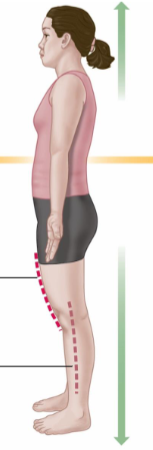
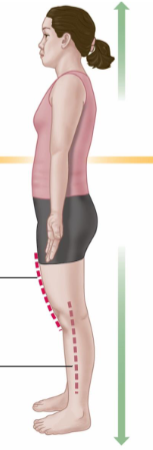
Superior
Above the body; toward the head.
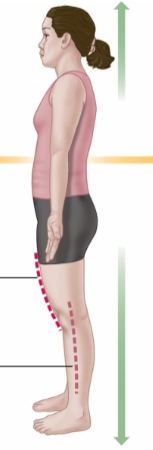
Inferior
Toward the lower part of the body.
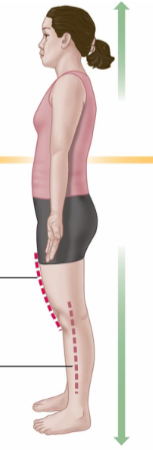
Superficial
Located near the surface of the body or a structure, often used to describe the position of organs or tissues.
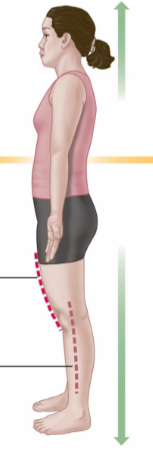
Deep
Away from the surface of the body or a structure, indicating a position that is further inward compared to superficial.
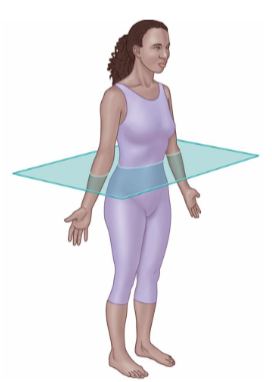
Body Planes
Divide the body or organs into sections.
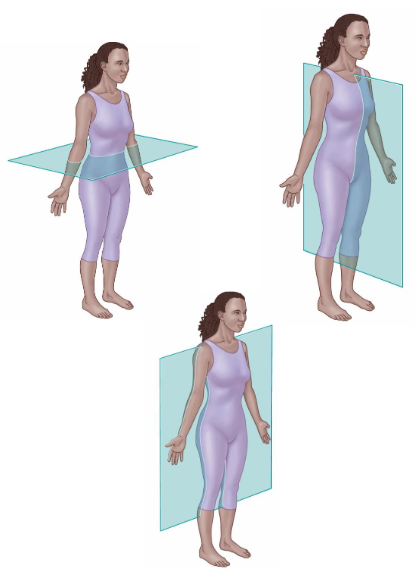
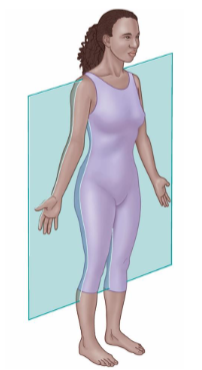
Sagittal Plane
Divides into right and left sides of the body.
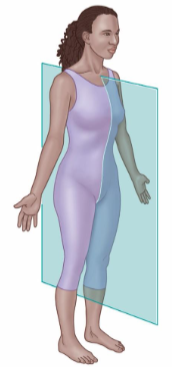
Frontal Plane
Also called as Coronal plane.
It divides into anterior and posterior sides.
Transverse Plane
It divides into superior and inferior sides.
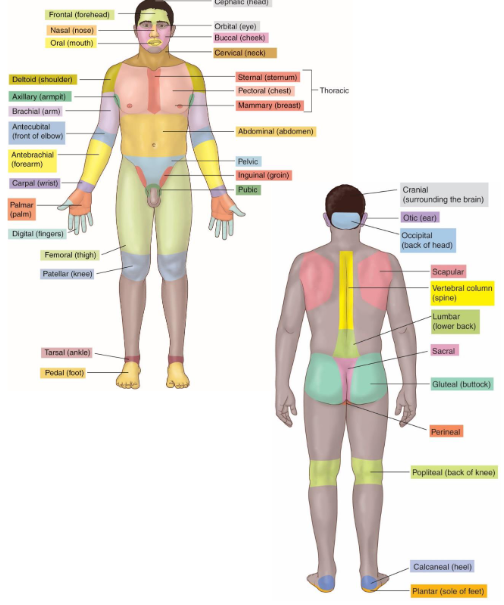
Body Regions
It describe the body areas for medical exams and procedures,
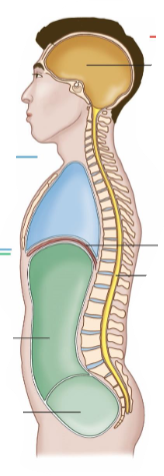
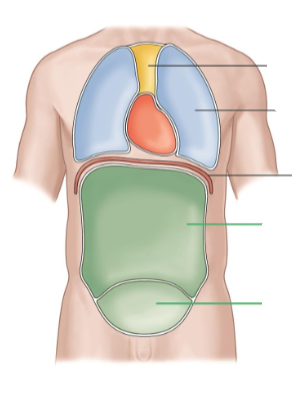
Body Cavities
These are the spaces in the body that house organs.
Ventral Cavity
It is the front of the body.
It is separated into thoracic and abdomen by diaphragm.
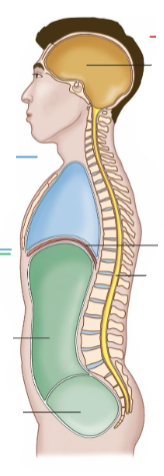
Abdominopelvic Cavity
It contains the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity.
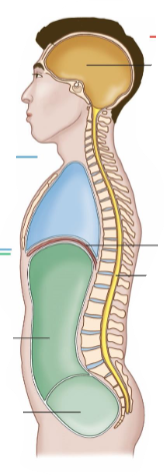
Dorsal Cavity
It is at the back of the body.
It is a continuous cavity.
It contains the cranial cavity and the spinal cavity.
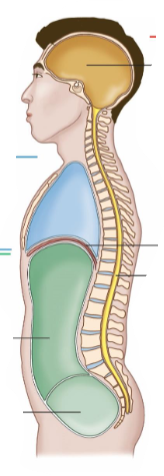
Cranial Cavity
It contains the brain.
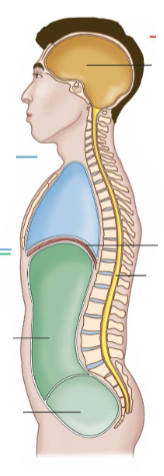
Spinal Cavity
It contains the spine.
Mediastinum
It contains the heart.
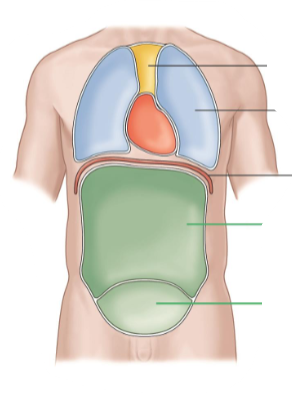
Pleural Cavity
It contains the lungs.
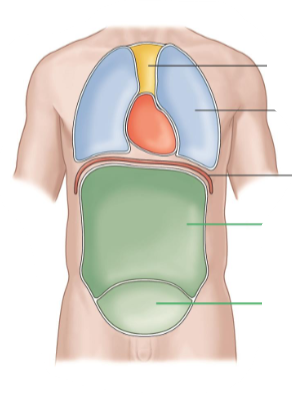
Abdominal Cavity
It contains many digestive organs.
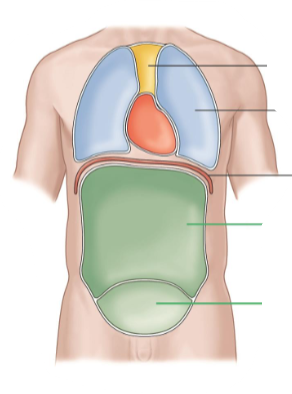
Pelvic Cavity
It contains the bladder and reproductive organs.
Homeostasis
It is the state of internal balance, despite changes to the internal or external environment.
It is kept stable and within the narrow range through participation of all organ systems.
It is mainly achieved by negative feedback.
Negative Feedback
It is when the end result shuts off the system.
It prevents a change from becoming too large so homeostasis can be maintained.
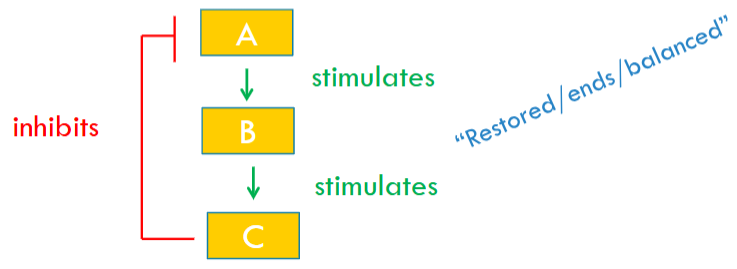
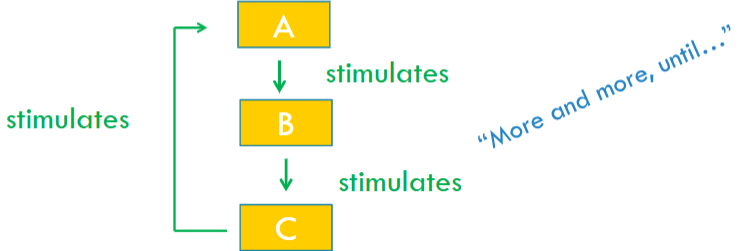
Positive Feedback
It is when the end-product reinforces the stimulus and amplifies the system (until it shuts off due to another stimulus).