Eyelids
1/236
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anterior Segment - Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
Eyelash condition where eyelashes turn toward the ocular surface
Trichiasis
In trichiasis the eyelid is in the _____ (normal/abnormal) position and lashes frow from the _____ (right/wrong) place.
normal; right
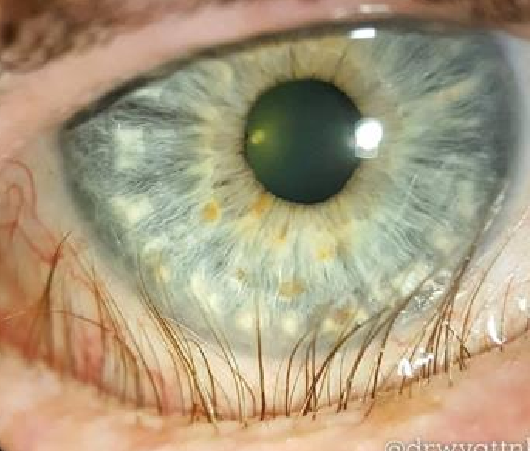
What eyelash condition is this?
Trichiasis
What is trichiasis caused by?
Scarring of the tarsal plate and/or conjunctiva (from trauma, surgery, or trachoma from chlamydia trachomatis)
Eyelid inflammation
Epiblepharon
Conjunctival cicatrizing disorders (OMMP, SJS, TEN)
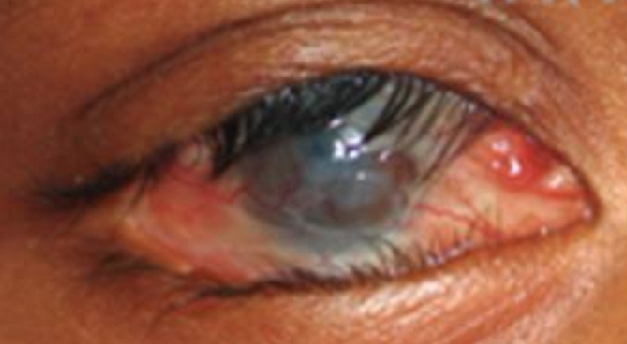
What condition is this?
Trachoma
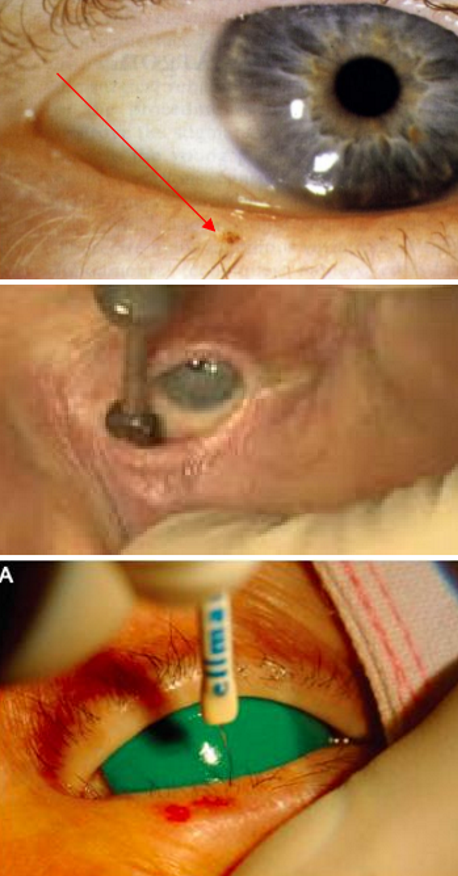
This is the management of what eyelid condition:
Protect the ocular surface
Lubrication
Contact lenses
Epilation - lash removal
Forceps (every 6-10 weeks)
Argon Laser Photocoagulation
Cryotherapy (cold gas freezes lash follicles)
Radiofrequency ablation (ablates root of lash follicle)
Trichiasis
Eyelash condition where the pre-septal portion of orbicularis oculi and extra fold of tissue override the lid margin (usually the lower lid)
Epiblepharon
Eyelash condition that is congenital, relatively common, bilateral, and has no definitive cause.
Common in Asian, Hispanic, and Native American populations
Epiblepharon
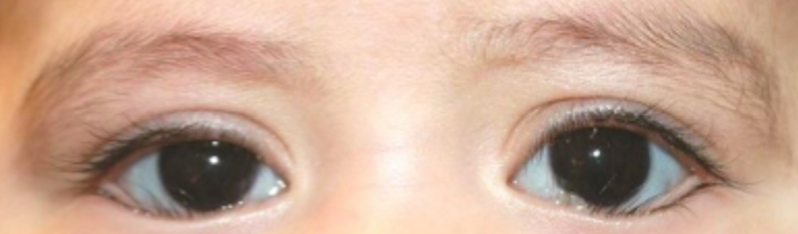
What eyelash condition is this?
Epiblepharon
What eyelash condition can resolve with facial bone growth by 2 years old?
If not, surgical repair, but can recur
Epiblepharon
Eyelash condition that is a rare, chronic, autoimmune disease:
Bilateral blistering and scarring of conjunctiva and cornea
Relapsing-remitting
Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (OOMP) or Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid (OCP)
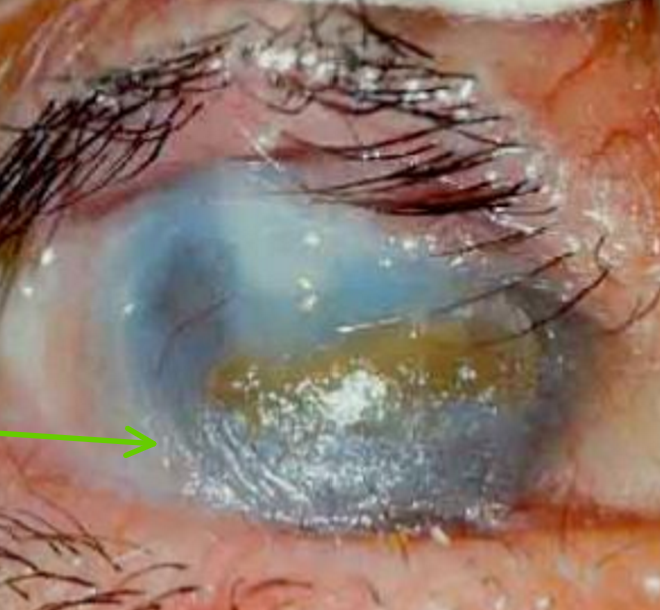
Eyelash condition that is vision-threatening
20% blindness from cornea scarring
Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (OOMP) or Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid (OCP)
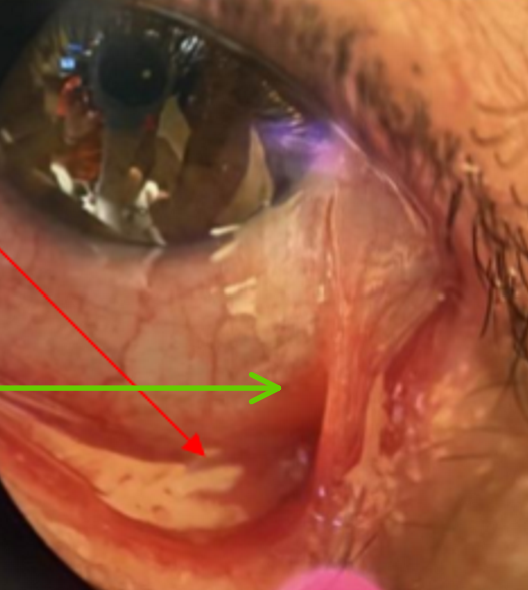
Eyelash condition that can be misdiagnosed in early stages, until symblepharon forms
F > M, age 60+
Treat systemically and ocular involvement
Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (OOMP) or Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid (OCP)
Eyelash condition that is a rare, severe skin reaction triggered by Type VI hypersensitivity reaction primary to medications (sulfonamide antibiotics, anticonvulsants) or infection
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) & Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
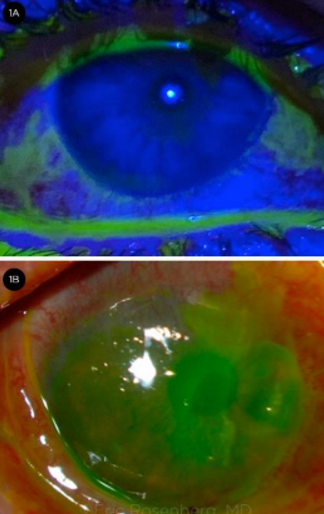
Eyelash condition that is potentially vision and life-threatening
Damages mucous membranes
Acute: conjunctival hyperemia, corneal epithelial defects
Chronic: severe cicatrization of lids and conjunctiva (→ trichiasis)
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) & Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
How do you diagnose SJS/TEN?
Biopsy
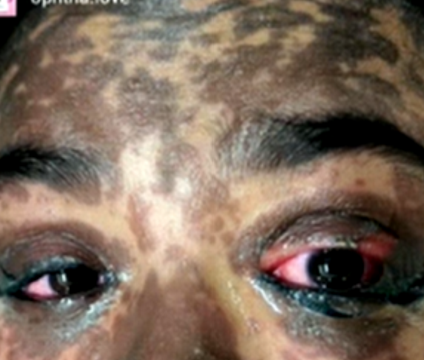
What eyelash condition is this?
<10% of body surface area
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)
What eyelash condition is this?
>30% of body surface area
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
Eyelash condition where there is a “double” row of lashes
Finer, thinner, and shorter than normal lashes
Can turn toward the ocular surface like trichiasis
Distichiasis
In distichiasis the eyelid is in the _____ (normal/abnormal) position and lashes frow from the _____ (right/wrong) place.
Normal; wrong
Where does the second row of lashes grow from in distichiasis?
Meibomian glands
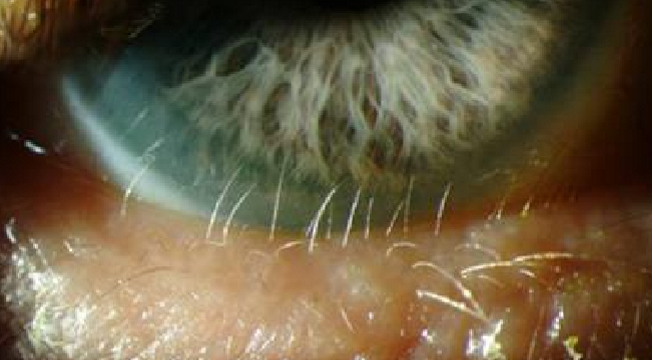
What eyelash condition is this?
Distichiasis
Is congenital or acquired distichiasis isolated and associated with lymphedema (L-D Syndrome)?
Congenital
Is congenital or acquired distichiasis caused by chronic blepharitis, OMMP/SJS/TEN, chemotherapy, or trauma?
Acquired
This is the management of what eyelash condition:
Protect the ocular surface
Lubrication
Contact lenses
Epilation - lash removal
Forceps (every 6-10 weeks)
Argon Laser Photocoagulation
Cryotherapy (cold gas freezes lash follicles)
Radiofrequency ablation (ablates root of lash follicle)
Surgery
Lid splitting of anterior and posterior lamella to access lash follicles and then non-surgical method to remove lashes
Distichiasis
Eyelash condition where there is a loss of lashes (and eyebrows)
Madarosis (aka Milphosis)
Is congenital or acquired madarosis caused by Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Ichthyosiform erythroderma?
Congenital
Is congenital or acquired madarosis divided into non-scarring and scarring types?
Acquired
Is non-scarring or scarring acquired madarosis caused by:
Blepharitis
Dermatological conditions
Systemic conditions
Autoimmune
Infection
Makeup reaction
Trauma
Trichotillomania
Eyelid tattooing
Cocaine vape, barbiturates
Medications
Miotics, cholesterol, anticoagulants, BOTOX
Non-scarring
Is non-scarring or scarring acquired madarosis caused by:
Malignant lid tumors
Cancer
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Scarring
Is non-scarring or scarring acquired madarosis reversible (non-destruction of the hair follicle)?
Non-scarring
Is non-scarring or scarring acquired madarosis irreversible (destruction of the hair follicle)?
Scarring
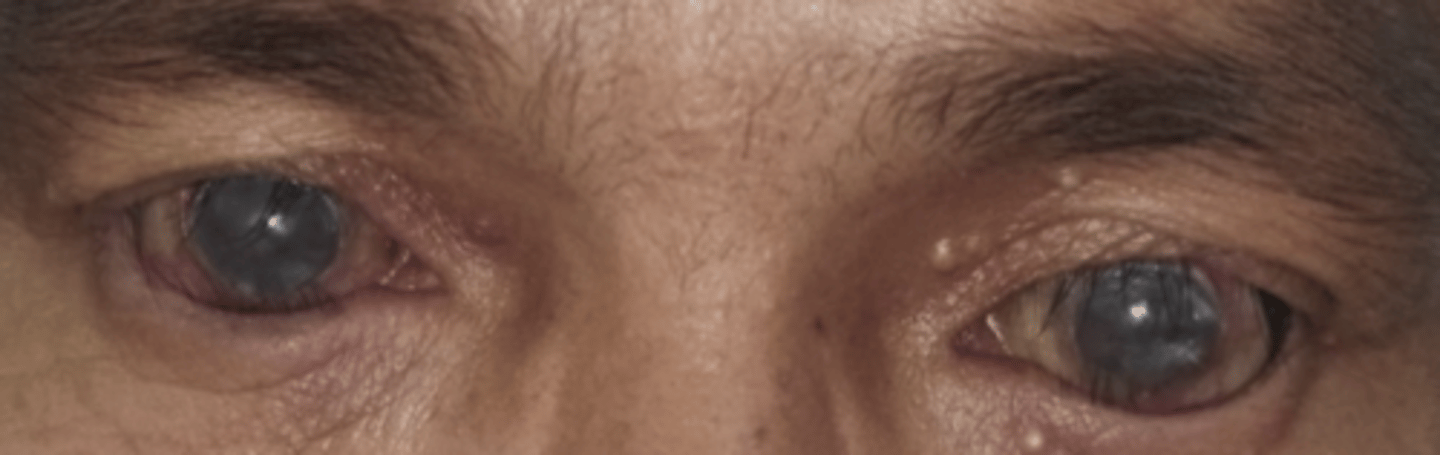
What eyelash condition is this?
Madarosis
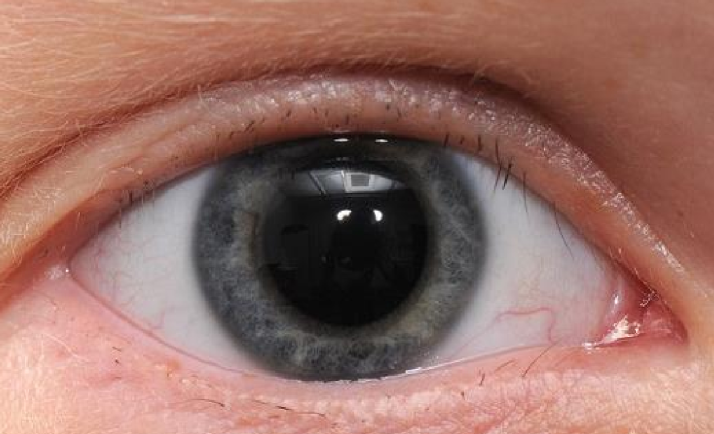
What eyelash condition is this?
Madarosis
This is the management of what eyelash condition (non-scarring type only):
Treat underlying cause
Discontinue offending agent/medication, if possible
Self-inflicted - patient education; reduce stress/therapy
Lash serum
OTC or Rx bimatoprost (Latisse)
Educate re: potential side effects of prostaglandins
It can darken the color of the iris and deepen the sulcus
Madarosis
Abnormality of melanin in hair follicles
Poliosis
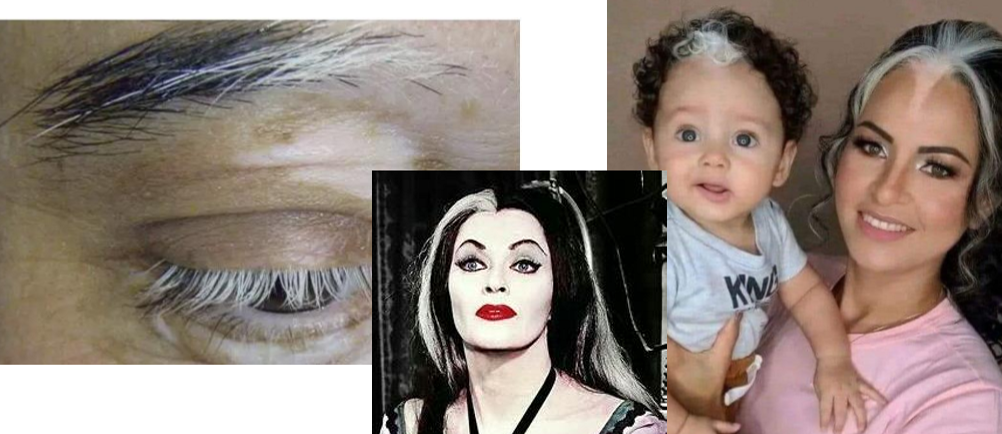
What eyelash condition is this?
Poliosis
Is congenital or acquired poliosis caused by:
Piebaldism
White forelock and medial forehead depigmentation
Waardenburg Syndrome
With deafness and iris heterochromia
Congenital
Is congenital or acquired poliosis caused by:
Chronic blepharitis
Medications
Melanoma
Autoimmune disease
Thyroid, sarcoidosis
VKH Syndrome: with uveitis and vitiligo
Herpes Zoster
Stress
Age
Acquired
Eyelash condition where there is no effective treatment, but temporary measures include hair dye and eyelash tinting
Poliosis
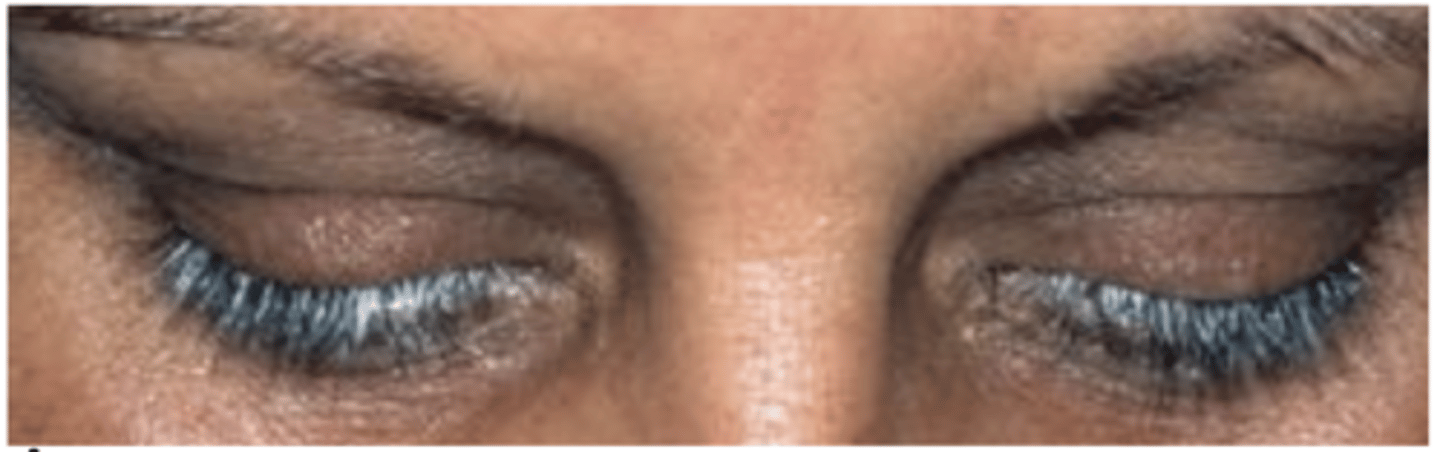
What eyelash condition is this?
Poliosis
Abnormally long eyelashes
>12mm centrally, >8mm peripherally
Also increased curling, thickening & pigmentation
Trichomegaly
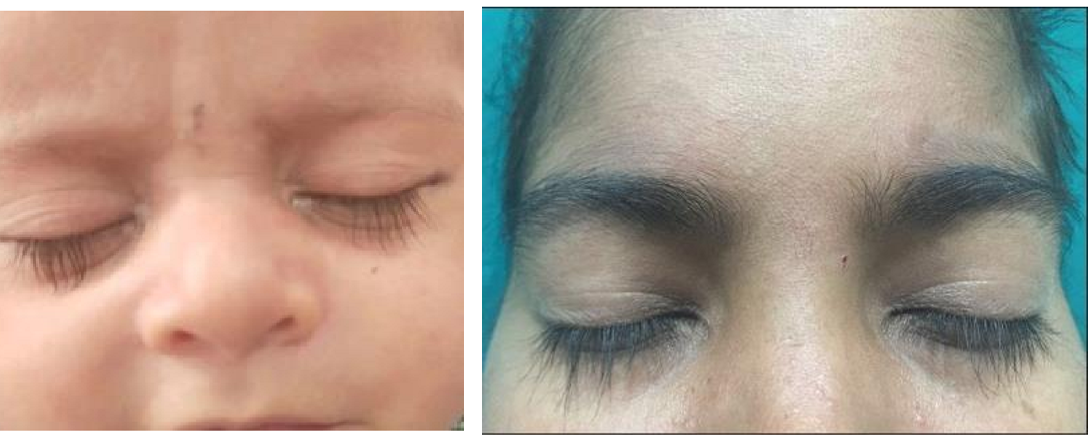
What eyelash condition is this?
Trichomegally
Is congenital or acquired trichomegaly: isolated or part of a syndrome
Oliver-McFarlane syndrome
Dwarfism, chorioretinal atrophy, intellectual disability
Congenital
Is congenital or acquired trichomegaly caused by:
Prostaglandins
Cancer drugs
VKC, HIV, connective tissue disorders
Acquired
Inward turning of eyelid
Entropion
Causes “Pseudotrichiasis” because the lid in in the wrong position.
Entropion
In entropion the eyelid is in a(n) _____ (normal/abnormal) position and lashes grow from the _____ (right/wrong) place.
Abnormal; right
What eyelid position condition has the following:
Symptoms
FBS
Tearing
Photophobia
Signs
Redness
Corneal involvement
Staining, infection, scarring
Entropion
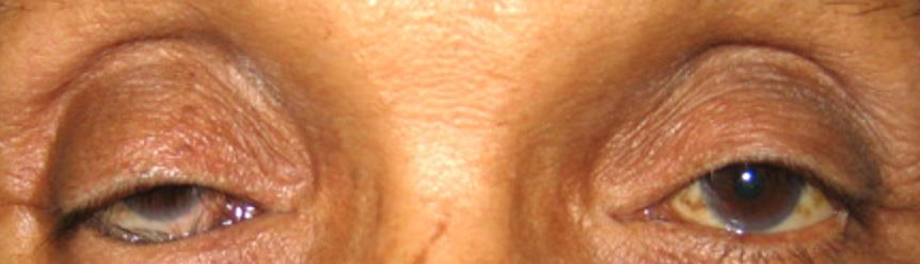
What eyelid position condition is this?
Entropion
What is the most common type of entropion?
Involutional (senile)
What type of entropion is caused by age?
Involutional (senile)
Does involutional entropion involve the upper, lower, or both lids?
Lower
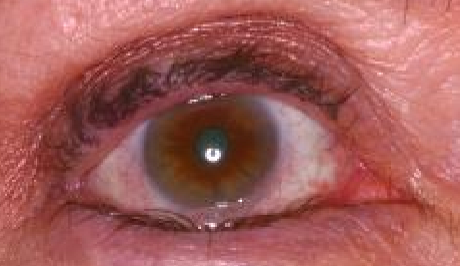
What type of eyelid position condition is this?
Entropion
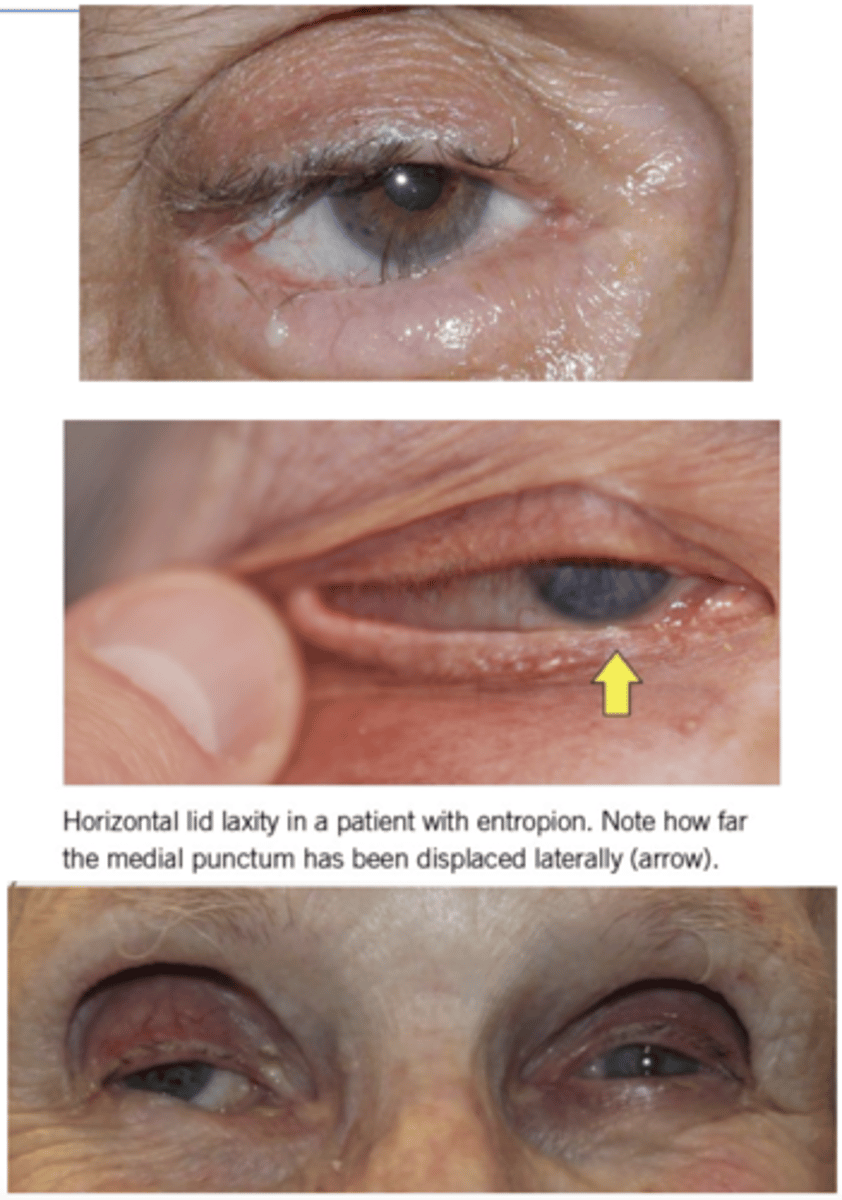
What type of entropion happens due to "O'HARE"?
Overaction of palpebral part of orbicularis oculi
Pulls inferior part of lower tarsal plate
Horizontal lid laxity caused by stretching of cantonal tendons
Atrophy of tarsal plate
Retractor dehiscence of the lower eyelid retractors
Enopthalmos of the globe
Involutional (senile)
What type of entropion happens when conjunctival fibrosis shrinks the posterior lamella?
Cicatricial
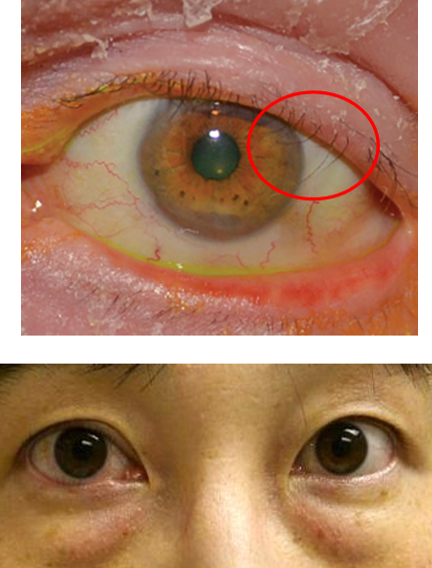
What type of entropion is this?
Cicatricial
Does cicatricial entropion involve the upper, lower, or both lids?
Both
What type of entropion is difficult to treat and has a high recurrence?
Cicatricial
What type of entropion is caused by the following:
Autoimmune: OMMP
Infectious: trachoma, herpes
Trauma
Chronic use of glaucoma drops
Cicatricial
What type of entropion is caused by the following and is often associated with involutional entropion:
Post ocular surgery
Inflammatory ocular conditions
Blepharospasm or hemifacial spasm
Spastic
What type of eyelid position condition is:
A type of dystonia
Involuntary, tonic, spastic bilateral lid closure
F > M, 50+
Blepharospasm
What can cause blepharospasm?
Idiopathic, Parkinson's, psychotropic meds
How do we treat blepharospasm?
Anti-cholinergic meds, Botox injections (lasts ~12 weeks)
Entropion test where you:
Have the patient forcibly blink
Look for internal rotation of lid and lagophthalmos
Orbicularis override test
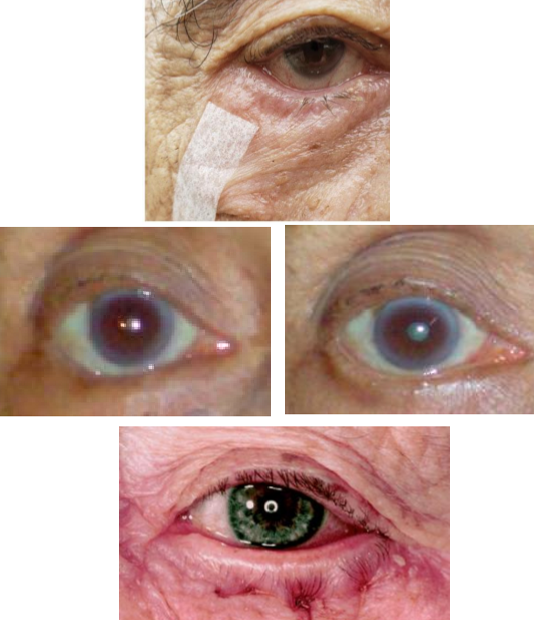
What type of eyelid position is managed temporarily by:
Protect the ocular surface:
Lubrication
Bandage CL
Lash epilation
Lid taping
Botox for blepharospasm
Quickert sutures
Tighten lower lid retractors and every lid
Entropion
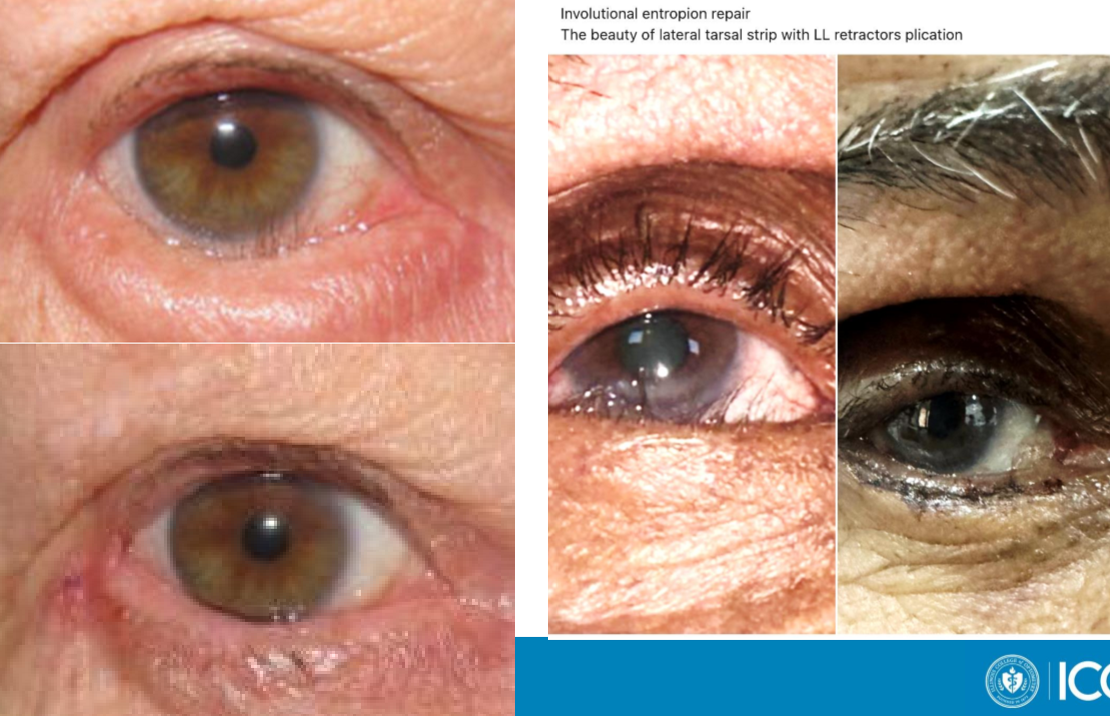
What type of eyelid position is managed permanently by:
Involutional: lid surgery
Cicatricial: mucous membrane or amniotic membrane graft
Spastic: antibiotics or immunosuppressives
Entropion
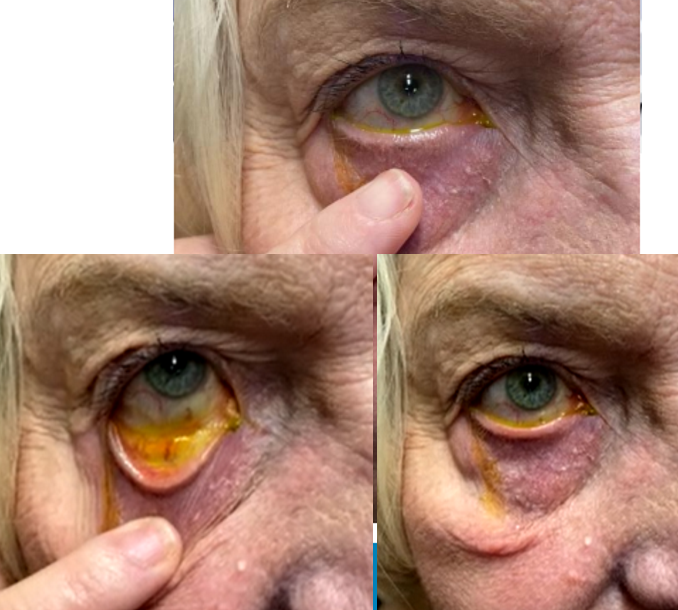
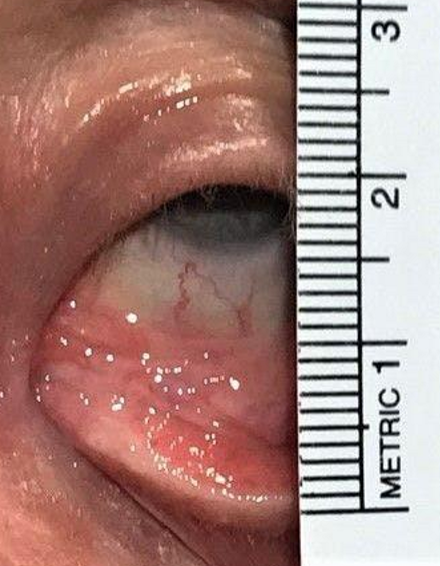
Outward turning of the eyelid
Ectropion
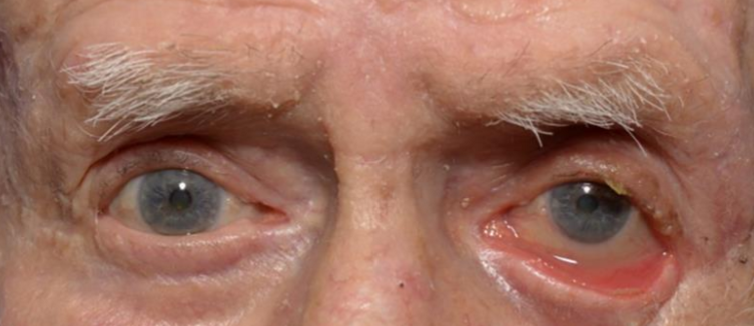
What eyelid position condition is this?
Ectropion
What eyelid position condition occurs when the lid is not in apposition to the ocular surface?
Unilateral or bilateral
Ectropion
What eyelid position condition has the following symptoms?
Epiphora d/t poor tear flow into puncta with increased tear lake
Tears run down cheek
Redness, irritation, dryness, FBS
Ectropion
What eyelid position condition has the following signs?
Thickened, hyperemic, and possible keratinized conjunctiva
Eversion of punctum
Mucus discharge
Corneal involvement
Exposure, staining, neurotrophic infection
Ectropion
What type of ectropion is the most common?
Involutional (senile)
What type of ectropion is caused by weakness of the pretarsal part of the orbicularis oculi or laxity of canthal ligaments?
Involutional (senile)
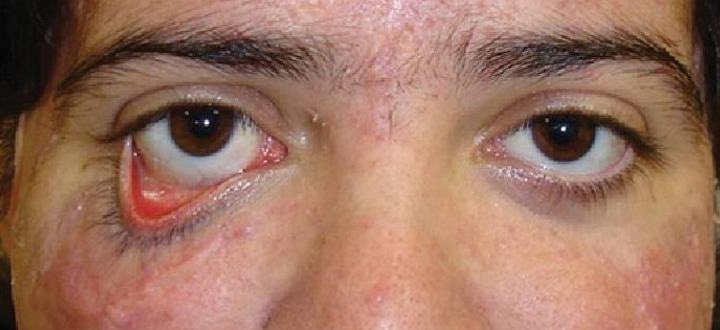
What type of ectropion is caused by the shortening of the anterior lamella, trauma, scarring, chronic sun exposure, or inflammation?
Cicatricial
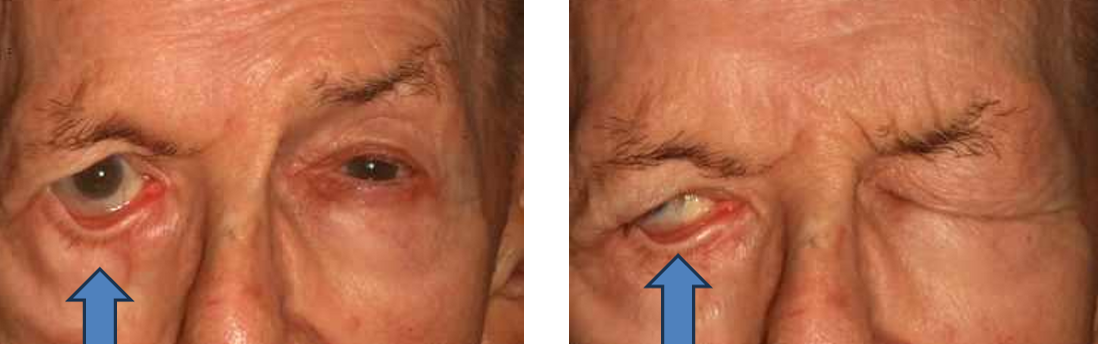
What type of ectropion is caused by CN VII (Facial) palsy?
Stroke, tumor, surgical complication
Look for Bell’s phenomenon
Paralytic
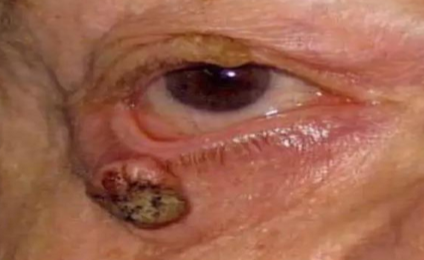
What type of ectropion is caused by mass or edema that physically pulls the lower lid down?
Chalazion, orbital fat, tumor
Mechanical
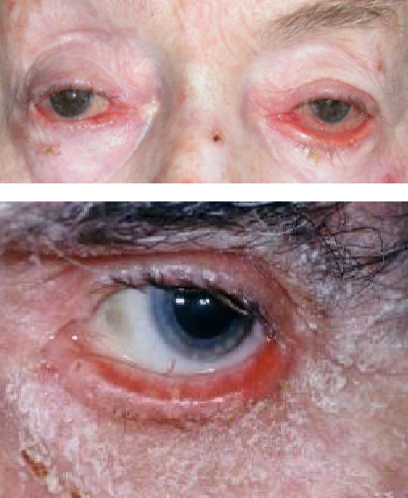
What type of ectropion is caused by tightening of the lid skin?
Eczema, rosacea, atopic dermatitis, medications
Inflammatory
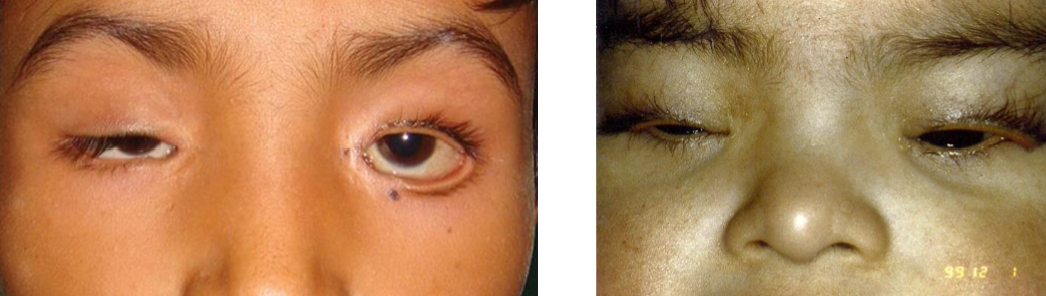
What type of ectropion is caused by chromosomal abnormalities?
Blepharophimosis
Craniofacial disorder
Ptosis, wide-set eyes, poorly developed superior orbital rim
Down’s Syndrome
Congenital
Ectropion testing:
The distance from the corneal reflex to the lid margin in primary gaze
MRD
Ectropion testing:
The distance from the corneal reflex to the upper lid margin (~4-5mm)
MRD 1
Ectropion testing:
The distance from the corneal reflex to the lower lid margin (~5mm)
MRD 2
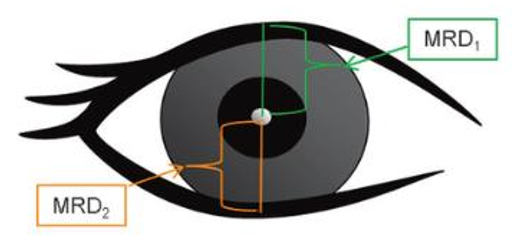
Ectropion testing:
MRD 1 + MRD 2 = ____
M: 7-10mm
F: 8-12mm
Palpebral fissure height (PFH)
Ectropion testing:
Pull down lower lid, hold for several seconds; let go and count the seconds until it returns to position
Snap Back Test
Ectropion testing:
Move the lid away from the globe
Measure the displacement of the lid margin from the globe
>10 mm is abnormal
Lid Distraction Test
What is an abnormal result in the lid distension test?
>10mm
What lid position condition could be treated by the following?
Temporary
Protect the ocular surface
Lubrication
Contact lenses
Lid taping
Tarsorrhaphy - glue
Permanent
Tarsorrhaphy - suture
Surgical repair
Ectropion
Eyelid position condition where the upper eyelid(s) are lower then the normal position
Ptosis
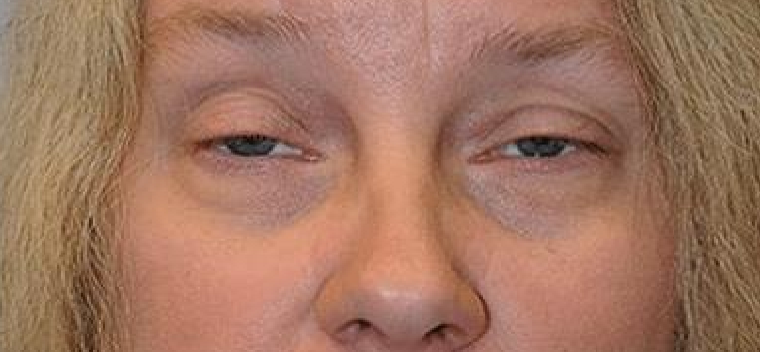
What eyelid position condition is this?
Ptosis
The lid appears to be in an abnormal position but it isn’t
Pseudoptosis
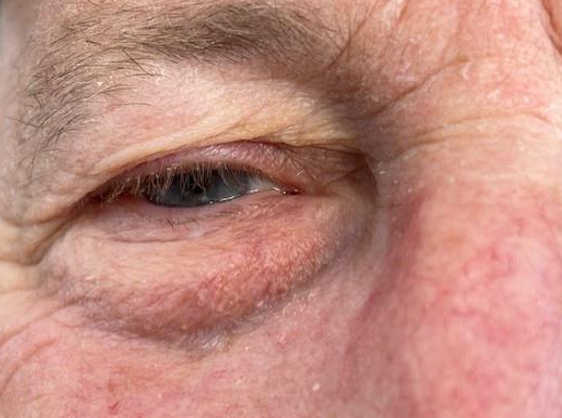
Type of pseudoptosis that is an age-related “sagging” of upper and lower lids
M>F
Eyelash ptosis
Dry eye
Epiphora
Lateral canthi are touching
Superior VF defect
Dermatochalasis
Type of pseudoptosis that is characterized by rare, intermittent, repeated episodes of painless upper lid edema
Spontaneous resolution
Unknown trigger, pathogenesis
Starts in childhood and improves with age
Leads to aponeurotic disinsertion
Thin, wrinkled “tissue paper” lids with discolored periorbital skin
Blepharochalasis
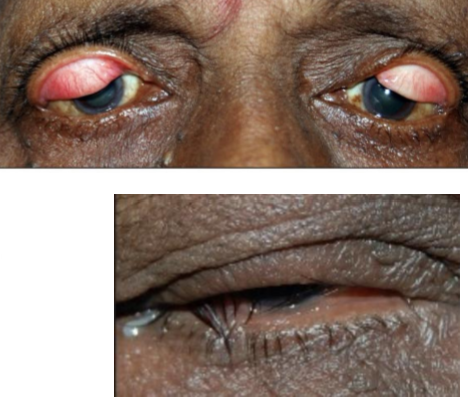
Type of pseudoptosis characterized by a decrease in elastin of eyelid skin and/or tarsal plate
Easy superior lid eversion
Papillary conjunctivitis
Ropy discharge
Poor apposition to ocular surface
Association with sleep position if unilateral
Lid and lash ptosis
Lagophthalmos
Abnormal lid position
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome (FES)
FES is associated with what other condition?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
What are the risk factors of Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)?
Obesity
Middle ages man
Snoring
Large neck girth
Alcohol use
What are the ocular associations of FES
Keratoconus
Glaucoma
Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NA-AION)
What eyelid position condition can be treated with the following?
Treat OSA - refer for a sleep study
Treat ocular surface disease
Use overnight shield or lid tape to prevent eversion
Weight loss
Lid surgery
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome (FES)
Type of pseudoptosis typically acquired:
Caused by age or trauma
Laxity of the CT, skin, or frontalis muscle
Descent of the brow fat pad
Temporal > medial
Mimics dermatochalasis
Brow ptosis
How do you differentiate dermatochalasis from brow ptosis?
Lift the brow
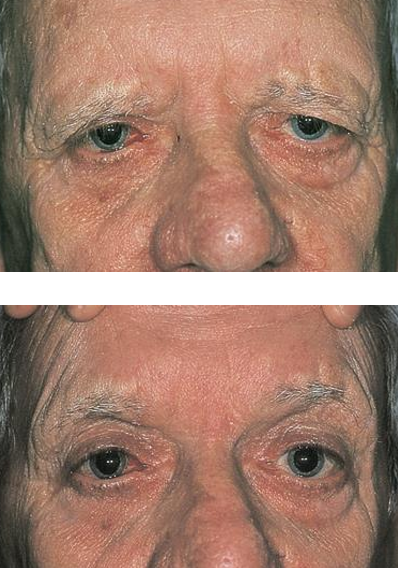
How could you treat a brow ptosis?
Temporary
Fillers, BOTOX
Best for younger patients (improperly placed can also cause
Permanent
Brow lift