Academic Decathlon Economics
1/290
Earn XP
Description and Tags
nigga tron
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
291 Terms
What mechanism produces a high amount of coordination within our modern economy?
The interaction between supply and demand
Within markets what determines the price at which each product or service sells and the quantity?
The actions of buyers and sellers
Who responds to market prices?
Individual buyers and sellers
What is the central topic of microeconomics?
The interaction of supply and demand
What is a market?
A market is composed of all the buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.
What are the examples of markets that are highly organized?
New York stock exchange, Chicago Mercantile exchange.
What is different about highly organized markets and non-organized markets?
In Highly organized markets buyers and sellers come together at a single location, and an auctioneer helps to set a price at which exchanges take place.
What is an example of a highly competitive market?
Gasoline
What is a perfectly competitive market?
If the good or service is highly standardized, the number of buyers and sellers is large, and the participants are well informed about the price.
In a perfectly competitive market buyers and sellers can buy or sell as much as they want without influencing what?
The market price.
What is quantity demanded of any good?
It refers to the total amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price over a specific period of time.
what is the law of demand?
If the price of the good is higher, buyers will demand less of the good; if the price is lower, then they will demand more. This principle shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
What is the result of a cost benefit analysis that rational decision makers use when deciding how to allocate their resources?
Demand Curve
What increases when the price of a good increases?
Opportunity Cost
What is a demand schedule?
A table that shows the quantity of a good that consumers are willing to buy at different prices. It illustrates the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
What is a demand curve?
A graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by consumers at various price levels.
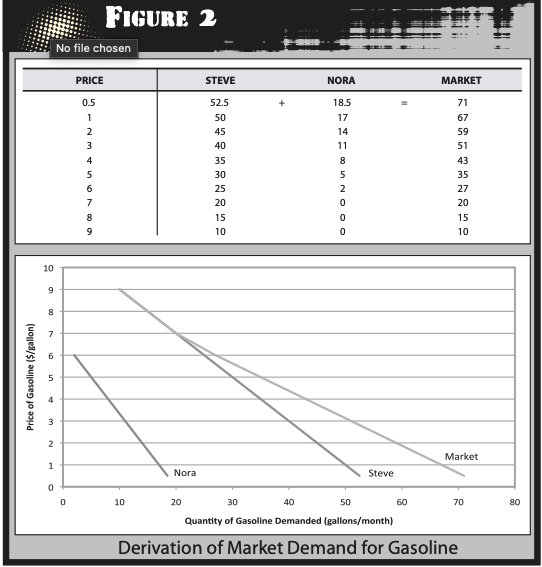
How to find the market demand schedule?
Add up the quantity that every consumer will purchase at each possible price?
How do we add two demand curves so we obtain the market demand?
We add horizontally. The prices aren’t added to the demand curve only the amount of the object. This means that at each price point, we sum the amount of products demanded by all consumers to get the total demand in the market.
What are some important factors affecting the quatity demanded other than price?
Income, The price of related goods, Tastes, Expectations, and the number of buyers.
Is Demand positively or negatively related to income?
Positively related, when income rises the quantity demanded rises, but when income falls the quantity demanded falls
What are goods called when Demand is positively related to income?
Normal goods
What are goods for which quantity demanded falls as income rises?
Inferior goods, LOW QUALITY GMO FOODS.
When a decline in the price of one good causes a reduction in the quantity demanded of another, what is the called?
Substitutes
When a decline in the price of one good causes a increase in the quantity demanded of another, what is the called?
Complements
What is supply?
it is the amount that sellers of that good are willing to and able to produce.
What is the most important factor in influencing quantity supplied
The price that the sellers recieve.
What is the positive relation between price and quantity supplied? The higher the price is, the greater the quantity that suppliers will want to produce.
Law of supply
How is a supply curve obtained?
by adding the quantities supplied at each price by all the suppliers
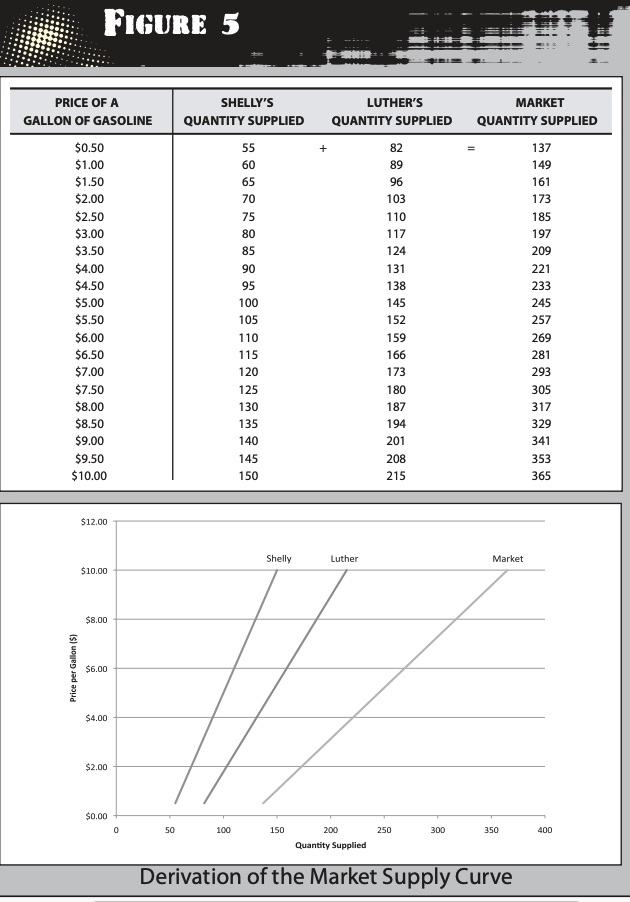
What factors may cause a shift in the supply curve?
Input prices, Technology, expectations, and number of sellers.
What are inputs?
Inputs are any of the things that suppliers have to purchase to supply a produce. Like the price that gasoline stations must pay their suppliers for gasoline is a major cost in doing buisness.
If the price of gasoline falls where does the supply curve shift?
To the right because the quantity of gasoline supplied will increase.
How does technology cause changes in the supply curve?
It can increase the effiency of things. Like in the gas station the pump for gas can go from full service to self service reducing the labor cost
How does expectations cause changes in the supply curve?
If suppliers expect prices to change in the future they may shift their supply accordingly. An increase in prices may cause a decrease in the quantity produced.
How does the number of sellers cause changes in the supply curve
As more sellers enter the market the quantity supplied will increase. More sellers more supply then a shift right in the supply curve and vice versa.
At what point will the market settle too? characterized by the meeting of the demand and the supply curve
The equilibrium
What is an equilibrium?
A point at which all the forces at work in a system are balanced by other forces, resulting in a stable and unchanged situation.
What is an economic definition of an equilibrium?
when no participant in the market has any reason to alter his or her behavior
Even in an equilibrium what is possible?
There will still be buyers who complain that the price of gasoline is too high and would like the price to be lower, and similarly supplier who complain that the price is too low and would like it to be higher.
What place do competitive markets tend to gravitate towards?
The equilibrium quantity and price
what are the desirable consequences of a competitive market?
Extremely effective method of allocating resources, It maximizes the benefit that buyers and sellers receive from this exchange,
What important information is conveyed when the market for a good is at an equilibrium?
It allows potential suppliers to know the value that consumers place on the good, and it allows potential demanders about the opportunity cost of supplying the good.
What does this communication between buyers and sellers in the equilibrium allow?
It insures that scarce goods and services are produced at the lowest cost and allocated the buyers who value them the most highly.
What is a consumer surplus?
A consumer suprlus is when the consumers pay less than they are willing to pay for it. Like if Sai could have paid 3 dollars for bread and the bread was only 2 he would have a consumer surplus.
What does the height of the demand curve represent?
It represents the buyers willingness to pay.
What does the height of the supply curve represent?
willingness to supply of the marguinal seller
What is a marginal seller?
The seller who would leave the market if the price were any lower
What is a producer surplus?
A producer surplus is when producer gets extra benifit when they sell something at a price higher than the minimum the would have accepted. Sai sells apples and is willing to sell an apply for 1 dollar, yet the market is willing to buy an apple for 3$ so that is the producer surplus.
What happens when we combine the consumer and producer surplus?
It provides a measure of the total benefits the market participants receive from their interactions.
What is the pareto efficieny and what satisfiers it?
it is when the there is no way to make anyone better off without reducing the welfare of someone else. And we achieve that when there is an outcome that maximizes the total surplus.
What things are being developed that allow suppliers to produce things at a lower cost?
New inventions and technology
Whether the producers benifit from a shift right in the supply curve depends on what two factors?
The increase in sales causes an increase in producer surplus,but the lower price reduces the producer surplus on the wuantity that was previosly being sold.
When we cause a decrease in buyers and a decrease in demand what is the effect on the market?
The demand curve for the product shifts to the left, and as a result the intersection of the supply and demand curve shifts down and to the left along the market supply curve for the product. After this shift, the equilibrium price and quantity both decrease.
What is the price elasticity of demand?
It measures how much the quantity demanded responds to a change in price. The formula is calculated by percentage change in quantity demanded/ percentage change in price.
why will the price elasticity of demand ratio always be negative?
Because the law of the demand, the quantity demanded of a good is negatively related to its price, so the ratio will always be negative. However, it is conventional to ignore this sign when discussing the elasticity of demand, because we take the absolute value.
What does the price elasticity of demand reflect?
How responsive consumers are to changes in the price of a good. The greater elasticity, the greater the proportionate change in the quantity consumers demand due to any given change in the price.
When is demand said to be elastic?
When a one percent change in price results in a greater than one percent change in the quantity demanded. So a change in price of one percent causes a greater change in the amount of product that is being demanded.
When is demand said to be inelastic?
When a one percent change in the price results in less than one percent change in the quantity demanded. So a change in the price of one percent causes less the one percent change in the number of people that are willing to buy the product despite the price change.
Why do economists use elasticity?
It provides a measure of the responsiveness of demand to price changes that is independent of the units of measurement. For example a demand in liters curve would be different than a demand in gallons curve, yet the elasticity will be the same in both cases.
Will Goods with high substitutes have a high price elasticity of demand or low?
High because consumers can easily switch from one product to another.
Will Goods with no or low substitutes have a high price elasticity of demand or low?
It will tend to be lower because the consumers are not as easily able to switch between different products.
Will items regarded as necessities have a lower or higher price elasticities of demand?
They will have a low elasticity.
Will a broad market have a low or high elasticity of demand
I will have a lower elasticity of demand because there are fewer substitues of a wider market. For example cola has a high elasticity because there are many different cola drinks and many different substitues, yet soda has less substitues because it has a broader market.
Will a flatter demand curve have a high or low elasticity?
I will have a low elasticity. In a demand curve the quantity demanded is the x and the price is the Y. So a small change in the Y results in a big change in the X.
What happens to elasticity as you move down along a linear demand curve?
Elasticity falls continuously as you move down the curve. As you move down (to lower prices and higher quantities), the demand becomes less sensitive to price changes, so elasticity decreases.
What does the slope ∆P/∆Q = e represent on a linear demand curve?
It represents the constant slope of the linear demand curve, where ∆ means “change in.” For a straight (linear) demand curve, the rate at which price changes compared to quantity (the slope) stays the same all along the curve.
What is the formula for elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve?
Elasticity = (1/e) × (P/Q), where e is the slope, P is price, and Q is quantity. This formula shows that elasticity depends on both the slope of the curve and the specific price and quantity at a point. As you move along the curve, P and Q change, so elasticity changes too.
As you move down and to the right along a linear demand curve, what happens to the ratio P/Q?
The ratio P/Q decreases because P falls and Q rises. Moving down the curve means price gets lower and quantity gets higher, so when you divide price by quantity, the result gets smaller.
Why does elasticity fall as you move down a linear demand curve?
Because (1/e) is constant and P/Q decreases, so elasticity decreases. Since the slope (1/e) doesn’t change, the only thing affecting elasticity is the P/Q ratio. As P/Q gets smaller, so does elasticity.
What does a perfectly elastic demand curve look like?
It is completely flat (horizontal), meaning any price change causes quantity demanded to change infinitely. f the price goes up even a tiny bit, people stop buying completely; if it goes down, they buy as much as possible.
What does a perfectly inelastic demand curve look like?
It is vertical, meaning quantity demanded does not depend on price. No matter how much the price changes, people buy the same amount—like with life-saving medicine.
What is the price elasticity of supply defined by?
(Percentage change in quantity supplied) / (percentage change in price)
What is the elasticity of supply reflect?
The ease at which suppliers can alter the quantity of production.
What are some factors that affect the elasticity of supply?
Ease and entry of exit, Scarce resources, and Time horizon
In relation to the elasticity of supply what does Ease of entry and exit mean?
If it is easy for new businesses to begin supplying a product or for those in the market to leave, then supply will tend to be more elastic. The supply of airline flights on a particular route is quite elastic because airlines can easily shift planes from one route to another to respond to changes in prices.
In relation to the elasticity of supply what does Scarce resources mean?
If an input required to make the good is scarce then the supply of that good will be scarce. For example property in a highl urbanized area. It will be highly inelastic because of how scarce the supply of in this case the land in a highly urbanized place is.
In relation to the elasticity of supply what does Time Horizon mean?
The longer the Time Horizon is the greater the elasticity of the product is. For example, an immediate shock in gasoline prices may result in an inelastic supply, because people wil still use gasoline, yet over a longer time it will be more elastic because alternatives to the new hikes in gasoline will be more available. IE electric cars.
What is total revenue defined by?
equilibrium price X equilibrium quantity
IF the price of a good is decreasing and the quantity is increasing, what will happen if to the revenue if the good is elastic?
The revenue will increase, because a decrease in the price will have a bigger effect in the increase of the demand of that product.
IF the price of a good is decreasing and the quantity is increasing, what will happen if to the revenue if the good is inelastic?
The revenue will decrease because a decrease in the price will have a much smaller effect in the increase of the demand of the product.
Is demand for milk elastic or inelastic?
The demand for milk is inelastic, because there are reletively few substitutes, and is a household staple.
Also since we have a broad market range, and broader market ranges have relatively inelastic demand. If the question was is animal milk elastic or inelastic, the answer would be more elastic than just milk
Is the supply for milk relatively elastic or inelastic?
The supply of milk is relatively elastic because there are many dairy farms, and it is easy for these farmers to expand or contract production given a time horizon of about a year.
In 1979 when middle eastern oil prices shot up, what did the federal government do?
They imposed a ceiling on prices in an effort to protect low income families.
What did cities like new york and chicago implement to to help lower income families?
The set up rent controls to make a maximum price that rents could be in that place.
What does implementing a rent or price ceiling do to the consumers and producers?
It reduces the producer surplus and the quantity of the product. However it increases the consumer surplus. Since the price is being capped, and decreased, so is the quantity of the good. This leads to less people being able to purchase the good leading to an unexpected downside.
What is a other consequence of implementing a price ceiling?
The total surplus is reduced
Now that price is no longer a driving factor for the selection of a good, the overall quality of the good decreases since there is no longer a price that can back it up.
In the example of rent what is a consequence of implementing a price ceiling besides the surpluses?
It will cause further inefficiencies in the market. Since price is no longer the main driving factor producers can now pick their tenant based on non economical and personal characteristics.
When implementing rent controls what is the short and long term effect of the control regarding elasticity?
In the short term both supply and demand of housing will be highly inelastic because it takes time for any major behavior changes to happen.
In the long run however people are now able to move in or out, and suppliers are now able to reduce maintenance or sell their quantity. This leads both supply and demand to be highly elastic.
What will happen to the producer and consumer when a price floor is added.
The supply will increase and the demand will decrease. Causing a surplus in wheat, and reducing the consumer and producer surplus. There are many farmers that are willing to sell their wheat for less, but can’t due to the restrictions
When a product is taxed where does the burden of the tax fall on?
The burden is split between the producers and the consumers because the producers need to lower prices to meet the new market equilibrium, and the consumers need to pay more money as tax.
Is there a difference when taxing the consumer or supplier?
There is no difference, because eventually the producer and consumer will reach a market equilibrium whether you tax the supplier or the consumer.
What does a tax wedge illustrate and mean?
A tax wedge is a difference in what the consumers pay and what the suppliers receive. So it is the distance from the point of equilibrium where the tax wedge artificially creates an equilibrium.
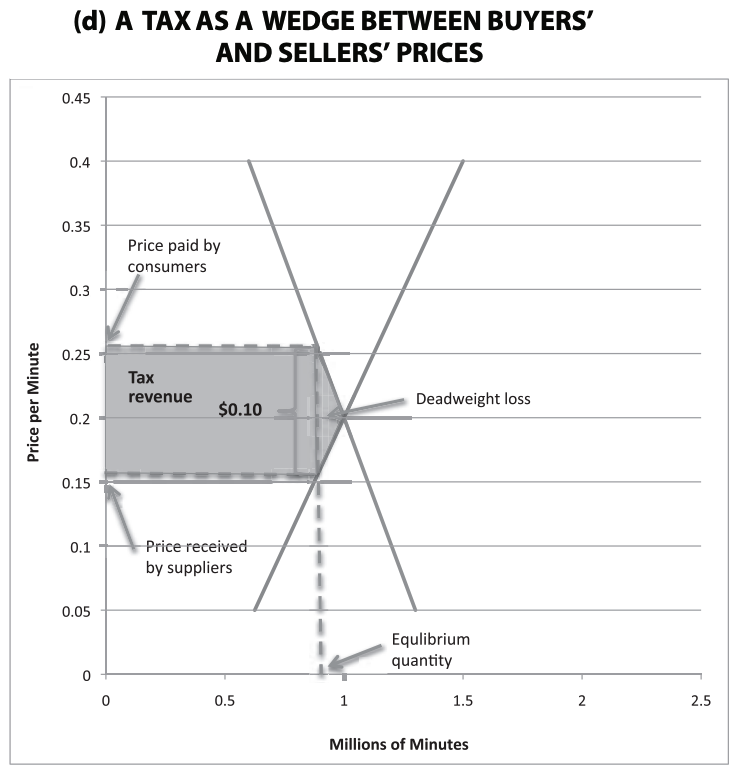
What is a dead weight loss?
It is a loss that is caused by the reduction of social welfare that is caused by taxes. I can be shown by the small triangle to the right of the new equilibrium and between the supply and demand curves
Is the revenue that the government receives equal, les then, or greater than the reduces experiences by the total surplus?
Equal
What does the distribution of the burden of tax depend on?
The relative price elasticities of supply and demand.
How do the price elasticities of supply and demand affect the distribution of the burden of taxes?
The less elastic the demand is the greater the share of the tax paid is from buyers, and vice versa
When there is a lower deadweight loss of tax what does that tell you about the elasticities of the supply and demand curve?
The lower deadweight loss of tax indicates the supply and demand curves are inelastic.
What is a production possibility frontier?
(PPF) is a oppurtunity cost graph.
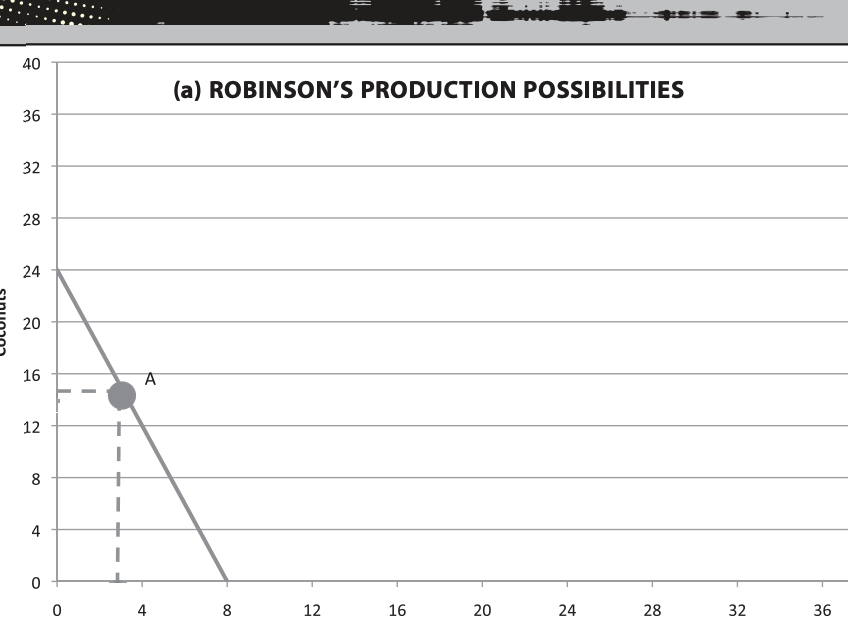
What do the intersection points on the PPF graph represent?
They represent the maximum amount og something that can be done. So if the line intersects the graph on the y axis at 24 that means in that timeframe there can only be 24 of that item.
What does the slope of a PPF graph represent?
The slope indicates the exchange value between those two items. For example 3 coconuts is equal to one fish, and will therefore have a slope of -3.
When can we say someone has an absolute advantage?
When their PPF graph is higher then their competitors at every single point.