
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
import demand curve
quantity of a good a country will import at different world prices, downward sloping
how to calculate import demand curve
quantity that Home consumers demand - quantity Home producers supply
As price increases the quantity of imports demanded
declines
As the price of the good increases, Home consumers demand _____, while Home producers supply more, so that the demand for imports _____
less, declines.
export supply curve
quantity of a good a country will export at different world prices, upward sloping
how to calculate export supply curve
quantity that Foreign producers supply minus the quantity that Foreign consumers demand, at each price
As price increases, the quantity of exports supplied .
rises
As the price of the good rises, Foreign producers supply _____ while Foreign consumers demand ____, so that the supply available for export _____.
more, less, rises
World Equilibrium
Home import demand (MD curve) equals Foreign export supply (XS curve).
Consumer surplus
amount consumers gain from purchases by computing the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay
Regarding consumer surplus, When price increases, the quantity demanded decreases as well as the ______.
consumer surplus
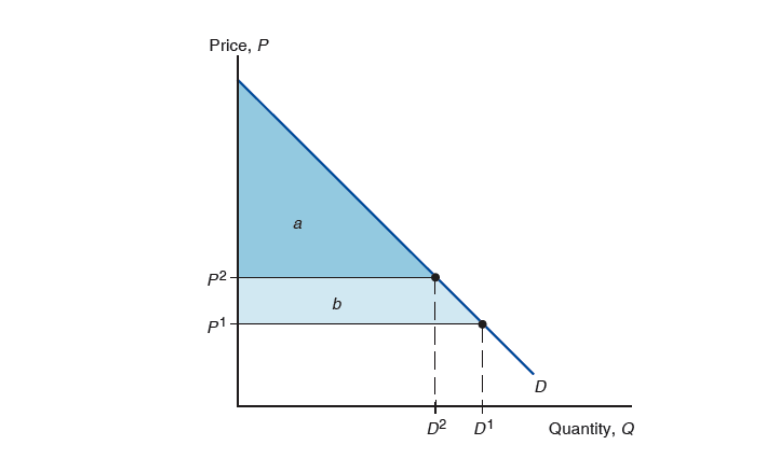
Consumer surplus is equal to the area _________
under the demand curve and above the price.
Producer surplus
difference between the amount a producer receives for a good and the minimum amount they would be willing to accept
In regards to producer surplus, when price increases, the quantity supplied _____ as well as the _______
increases, producer surplus
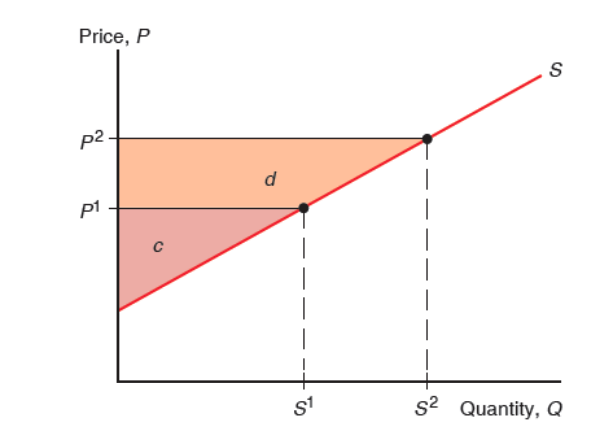
Producer surplus is equal to the area
above the supply curve and below the price.
Free trade is better than autarky, but domestic production ______ due to free trade
decreases
Why do countries impose tariffs: revenue effect
To raise government revenue
Why do countries impose tariffs: protective effect:
protect domestic firms by expanding domestic production and decreasing imports (this is the main reason!)
System of Tariffs: Most favored nation status
When a “General” rate of duty is applied to goods from countries to whom U.S. has granted “Most favored nation status”
System of Tariffs: “Special” rate of duty is applied to goods from
developing countries: generalized system of preferences: promote imports from developing countries, then let them buy from U.S.!
NAFTA: some special agreements
Tariffs Small Country Case: If we impose a tariff of t, the domestic market price of the product (increase/decreases)
increases to PW+t (free trade price + tarriff)
Tariffs Small Country Case: Domestic production
Increases & Producer Surplus Increases
Tariffs Small Country Case: Quantity consumed
decreases & consumer surplus decreases
Tariffs Small Country Case: tarriff revenues generated/not generated & welfare gain/loss
generated, tremendous loss
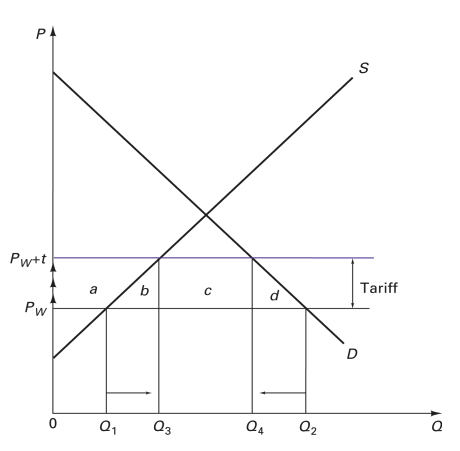
Small Country Changes from free trade to tariff
There is no change in Pw.
Domestic production increased from Q1 to Q3.
CS decreased by “a+b+c+d”
PS increased by “a”
Government revenue increased by “c” (the second objective)
DWL: “b+d”
welfare loss, primary objectives (increase in domestic production and in tariff revenue) are achieved
Tariffs Large Country Case: domestic/foreign market price change
domestic market price increases and the foreign market price decreases
Tariffs Large Country Case: welfare gain/loss
could be a welfare improvement if the country is a large and imports significant amount of the good (the optimal tariff)
Tariffs Large Country Case: If the domestic price rises, domestic demand ______ because the country is large. Therefore, world price ____
decreases, falls
Tariffs Large Country Case: Domestic price (new world price + t) is still ______ than original world price
higher
Consequences of Tariffs Large Country Case
Welfare under tariff can be greater than that under free trade
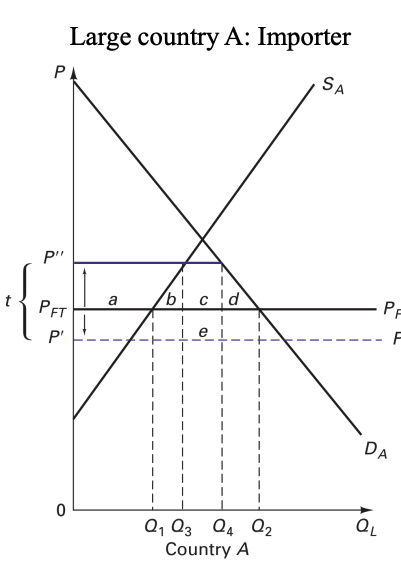
Changes from Free Trade to Tariff: Large Country Case
Country A (large country/importer)
CS decreases by “a+b+c+d”
PS increases by “a”
Government revenue increases by “c+e”
DWL: “b+d”
Total welfare: “e”- “b+d”
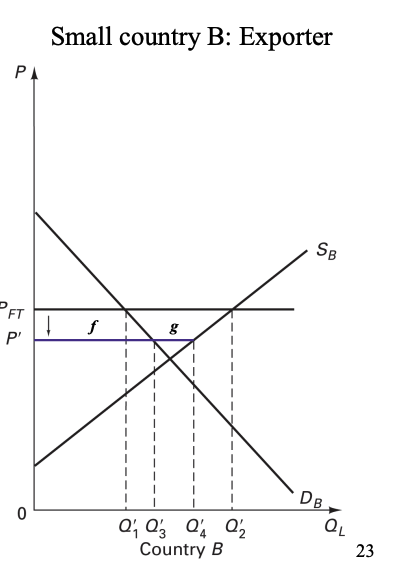
Country B (small country/exporter)
CS increases by “f”
PS decreases by “f+g”
Total welfare: “-g”
Country B (small country/exporter)
– CS increases by “f” – PS decreases by “f+g” – Total welfare: “-g”